[2025 CVPR] DEIM: DETR with Improved Matching for Fast Convergence
[Paper Review] 2D Object Detection
Paper Info.
https://github.com/Intellindust-AI-Lab/DEIM

Abstract
(제안)
- 우리는 Transformer-based architectures (DETR)에서 real-time object detection에서 convergence를 accelerate하기 위한
an innovative and efficient training framework, DEIM을 제안한다.
(문제 1 & 제안 1: 기존의 O2O matching은 sparse supervision으로 인해 convergence가 느림.
그래서 Dense O2O matching을 통해 더 많은 tragets을 추가하여 positive samples 수를 증가시켜 convergence를 가속화함.)
- DETR models에서 ont-to-one(O2O) matching이 갖는 the sparse supervision을 완화하기 위해,
- DEIM은 Dense O2O matching strategy를 제안한다.
이 strategy는 stand adata augmentation techniques을 활용하여 additional targets을 포함시킴으로써, image 당 postivie samples 수를 증가시킨다.
(문제 2 & 제안 2: 제안하는 Dense O2O matching은 많은 low-quality matches가 나옴. 이를 고려한 새로운 loss function 제안)
- Dense O2O matching은 convergence 속도를 향상시키지만, 많은 low-quality matches를 생성하여 성능 저하를 유발할 수 있다.
이를 해결하기 위해, 우리는 Matchability-Aware Loss (MAL)라는 a novel loss function을 제안한다.
MAL loss는 various quality levels에서의 matches를 optimize함으로써, Dense O2O matching의 효과를 더욱 향상시킨다.
(실험: convergence가 2배 정도 빠르고, SOTA 달성 가능)
- Extensive experiments on the COCO dataset validate the efficacy of DEIM. When integrated with RT-DETR and D-FINE,
it consistently boosts performance while reducing training time by 50%.
Notably, paired with RT-DETRv2, DEIM achieves 53.2% AP in a single day of training on an NVIDIA 4090 GPU.
1. Introduction
(background - O2M이란? O2M assignment strategy는 YOLO series에서 널리 활용되고 있다)
- One-to-many(O2M) assignment strategy는 YOLO series에서 널리 사용되어 왔으며, 이 방식에서는 각 target box가 multiple anchors에 할당된다.
O2M assignment는 dense supervision signals을 제공하여 convergence를 가속화하고 performance를 향상시키기 때문에, effective하다고 알려져 있다.
(background - O2M의 문제는? O2M assignment strategy의 문제점은 NMS와 같은 post-processing으로 인한 latency 증가)
- 하지만, O2M assignment는 object 마다 multiple overlapping bounding boxes를 생성하기 때문에,
redundancies를 제거하기 위해 a hand-crafted Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS)을 필요로 한다.
이는 latency and instability를 유발한다. [citations~~~]
(background - DETR의 O2O란? DETR paradigm은 NMS를 제거한 one-to-one(O2O) matching strategy를 사용하기 때문에 real-time object detection에서 a compelling alternative로 부상하고 있다.)
- Transformer-based detection (DETR) paradigm의 등장은
global context를 capture하기 위해 multi-head attention을 활용함으로써 localization and classification을 향상시키며, 많은 주목을 받아 왔다.
DETRs은 training 동안에 predicted boxes and the GT objects 간의 a unique correspondence를 만들어내기 위해 Hungarian algorithm을 사용한
a one-to-one(O2O) matching strategy를 적용한다.
O2O matching strategy를 통해 the need for NMS가 제거될 수 있다.
이러한 end-to-end framework는 a compelling alternative for real-time object detection을 제공한다.
(문제 제기: DETRS에서 O2O은 크게 두 가지 문제가 있다.)
- 하지만, DETRs의 primary limitations 중에 한 가지인 slow convergence 문제가 여전히 남아있다.
우리는 이 이유가 two-folds에 있다고 hypothesize한다.- Sparse supervision:
O2O matching mechanism은 only one positive sample per target을 할당하기 때문에, positive samples 수를 극히 제한한다.
반면, O2M은 More positive samples을 생성한다.
이러한 scarcity of positive samples는 dense supervision을 제한시키고, 이는 effective model learning을 방해한다.
dense supervision이 performance에 중요한 영향을 미치는 small objects의 경우는 특히 심하다.
(내 생각: 이 가설은 충분히 납득이 된다. 유사하게, yolov10에서도 O2O matching mechanism의 training signal을 풍부하게 만들기 위해 training 시에만 따로 O2M branch를 추가했다.) - Low-quality matches:
보통 8000개 이상의 dense anchors에 의존하는 traditional methods와는 다르게,
DETR은 a small number (100개 or 300개) of randomly initiazlied queries를 적용한다.
이러한 queries는 targets에 대한 spatial alignment가 부족하고, 이는 training 동안에 nemerous low-quality matches를 유발한다.
low-quality matches란 matched boxes가 targets에 대해 low IoU를 가지지만 high confidence scores를 가지는 것을 의미.
즉, 잘못된 위치에 높은 confidence를 가짐.
- Sparse supervision:
(1. sparse supervision에 대한 관련 연구들과 한계점)
- DETR에서의 supervision 부족 문제를 해결하기 위해,
최근 연구들은 O2O(one-to-one) matching의 제약을 완화하고 O2O training 중에 O2M assignments를 도입함으로써,
각 target에 대해 auxiliary positive samples을 추가하여 supervision을 증가시키는 방향을 취하고 있다.
Group DETR은 여러 개의 query groups을 사용하고 각 group마다 independent O2O matching을 수행함으로써 이를 달성하며,
Co-DETR은 Faster R-CNN과 FCOS와 같은 detectors에 O2M 방식을 통합한다.
이러한 approaches들은 the number of positive samples을 성공적으로 늘리는 데에는 성공적이지만,
(문제 1) additional decoders가 필요하다는 점에서 computational overhead가 증가하고,
(문제 2) traditional detectors에서와 유사하게 redundant high-quality predictions을 생성할 위험이 있다.
(제안 1: Dense O2O matching)- 반면에, 우리는 a novel yet straightforward approach named dense one-to-one (Dense O2O) matching을 제안한다.
우리의 key idea는 each training image에 대해서 the number of targets을 증가시켜, training 동안에 more positive samples을 생성시킨다.
이는 mosaic and mixup augmentations과 같이 classical techniques에 의해 쉽게 구현될 수 있다.
Dense O2O matching은 added complexity and overhead 없이, O2M approaches와 비교 가능한 수준의 supervisoin을 제공할 수 있다.
(2. low-quality matches에 대한 관련 연구들과 한계점)
- more effective query distributions around objects를 가능하게 하기 위해,
priors를 이용한 query initialization 시도들이 제안되어 왔다.
그러나 이러한 improved initialization methods들은 대개 encoder에서 추출된 limited feature information에 의존하기 때문에,
a few prominent(소수의 두드러진) objects 주변에 query가 집중되는 경향이 있다.
그 결과, non-salient(중요하지 않은) objects들은 nearby queries가 부족해져, low-quality matches가 발생하게 된다.
이 문제는 Dense O2O를 사용할 때 더욱 두드러진다.
target의 수가 증가할수록, prominent targets과 non-prominent targets 간의 disparity(격차)가 커지며,
전체 matching quantity가 증가함에도 불구하고 low-quality matches도 함께 증가하게 된다.
이때, loss function이 이러한 low-quality matches를 효과적으로 처리하지 못한다면, 이러한 disparity(격차)는 지속되어 model performance 향상을 방해하게 된다.- 기존 DETRs에서 사용되는 loss function, 예를 들어 Varifocal Loss (VFL)는 low-quality matches의 수가 상대적으로 적은 dense anchors 환경을 전제로 설계되었다.
이들은 주로 high IoU but low confidence인 high-quality matches에 penalize하고,
low-qualtiy matches는 discard한다.
(제안 2: Matchability-Aware Loss = MAL)- low-quality matches 해결하고 Dense O2O를 추가로 향상시키기 위해, Matchability-Aware Loss (MAL)을 제안한다.
MAL은 matched queries와 targets 간의 IoU와 classification confidence를 함께 고려하여 matchability에 따라 penalty의 크기를 조절한다.
MAL은 high-quality matchesDㅔ 대해서는 VFL과 유사하게 동작하지만,
low-quality matches에 대해서는 더 큰 비중을 두어, 학습 과정에서 제한적인 positive samples을 보다 효율적으로 활용할 수 있도록 한다.
또한 MAL은 VFL에 비해 a simple mathematical formulation을 제공한다.
- The main contributions of this work are summarized as follows:
- We introduce DEIM, a simple and flexible training framework for real-time object detection.
- DEIM accelerates the convergence by improving the quantity and quality of matching with Dense O2O and MAL, respectively.
- With our method, existing real-time DETRs achieve better performance while halving training costs.
Specifically, our method exceeds YOLOs and establishes a new SoTA in real-time object detection after being paired with efficient models in D-FINE.
2. Related Work
Object detection with transformer (DETR)
- DETR은 hand-crafted NMS as the post-processing을 없애고 end-to-end object detection을 가능하게 함.
하지만 slow convergence and dense computation으로부터 문제가 있음.
Increasing positive samples
-
O2O matching은 each target에 a single positive sample로 제한하므로,
O2M matching 보다 far less supervisoin을 제공함. -
O2O framework에서 supervision을 향상시키기 위해 여러 연구들이 진행되어 옴. (Group DETR, H-DETR, Co-DETR)
기존 연구들은 per target마다 #(positive samples)을 늘리는 것을 목표로 하지만,
우리는 per training image마다 #(targets)을 늘리는 것을 목표로 함.
또한, 이전 연구들과 다르게, 우리는 additional decoders or heads를 필요로 하지 않고 computation-free함.
Optimizing low-quality matches
-
sparse and randomly initialized queries는 targets에 대한 spatial alignment가 부족하기 때문에,
query initialization에 prior knowledge를 도입한 연구들(DAB-DETR, DN-DETR, and dense distinct queries)이 있었다. -
더 최근에는 DINO-DETR and RT-DETR과 같이 decoder queries를 refine하기 위해,
encoder's dense outputs으로부터 Top-ranked predictions을 도입하는 방식도 있었다.
이러한 방식들은 more effective query initialization closer to target regions을 가능하게 했지만,
여전히 Low-quality matches라는 문제가 남아있다. -
RT-DETR에서, Varifocal Loss(VFL)은 classification confidence와 box quality 사이의 uncertainty를 줄이기 위해 사용되었다.
하지만 VFL은 주로 traditional detectors에서 fewer low-quality matches and focuses on high-IoU optimization을 위해 설계되었기 때문에,
low-IoU matches들은 그들의 minimal and flat loss values로 인해 under-optimized되는 문제가 있다. -
그래서, 우리는 "a matchability-aware loss to better optimize matches across varying quality levels,
significantly enhancing the effectiveness of Dense O2O matching"을 제안한다.
Reducing computation cost
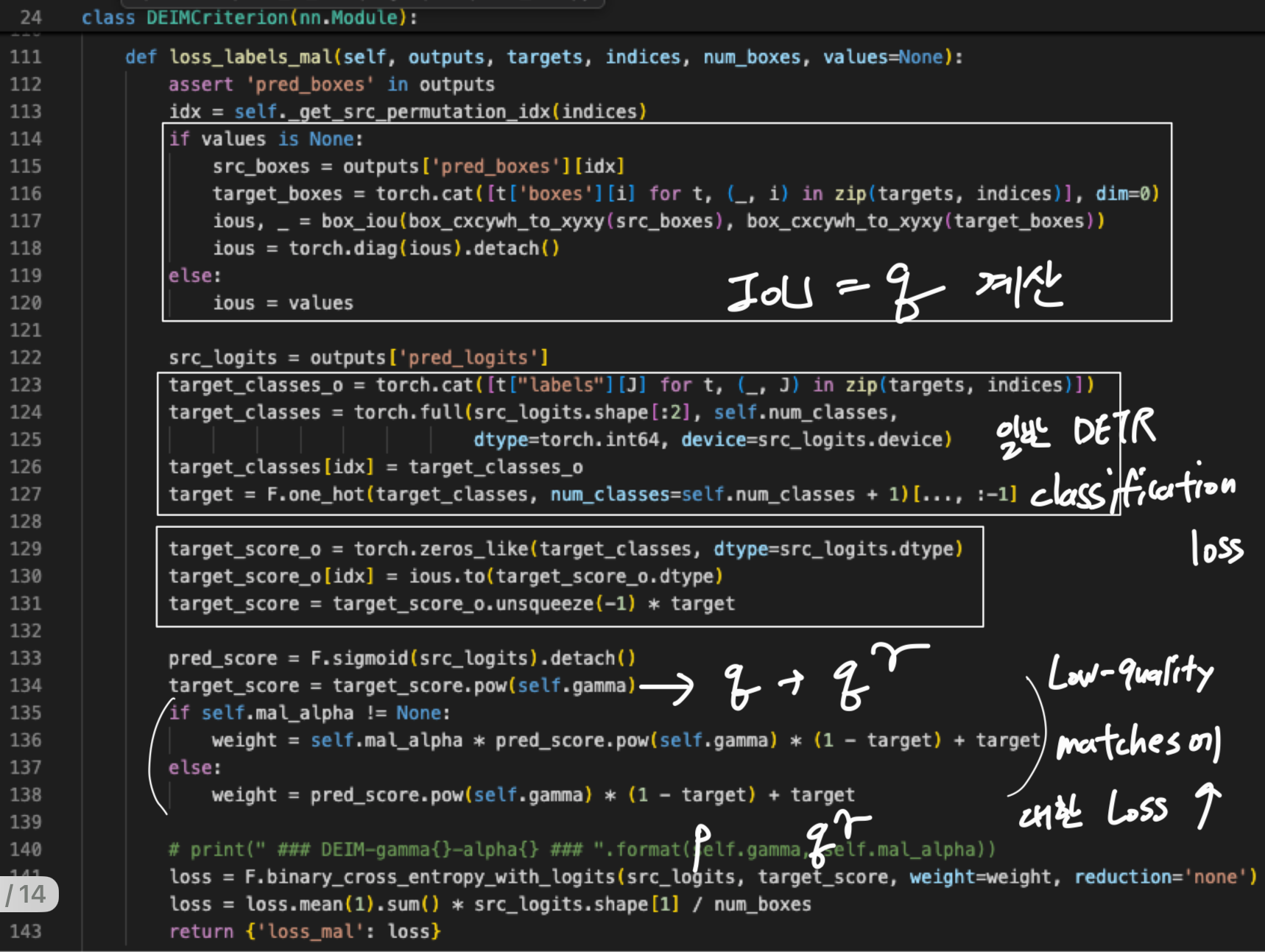
-
standard attention mechanism은 dense computation을 포함하므로 계산 비용이 크다.
efficiency를 개선하고 multi-scale features 간 interactions을 촉진하기 위해,
deformable attention [45], multi-scale deformable attention [42], dynamic attention [7], cascade window attention [37] 등과 같은 다양한 advacned attentions들이 제안되어 왔다. -
또한 최근 연구들은 more efficient encoders 설계에 초점을 맞추고 있다.
예를 들어 Lite DETR [17]는 high-level and low-level features 간의 interleaves updates하는 encoder block을 도입하였고,
RT-DETR은 encoder에서 CNN과 self-attention을 결합하였다.
두 design 모두 resource consumption을 크게 줄였다. -
이러한 hybrid encoder를 기반으로, D-FINE은 additional module을 도입하고 fixed coordinates를 predicting하는 대신 probability distributions을 iteratively updating하는 방식으로 regression process를 refine하여 RT-DETR을 더욱 optimize시켰다.
이와 같은 real-time DETRs의 발전을 바탕으로, 본 방법은 training costs를 줄이면서도 impressive performance를 달성하며,
real-time OD에서 YOLO models들을 substantial margin으로 outperforming한다.
3. Method
3.1. Preliminaries
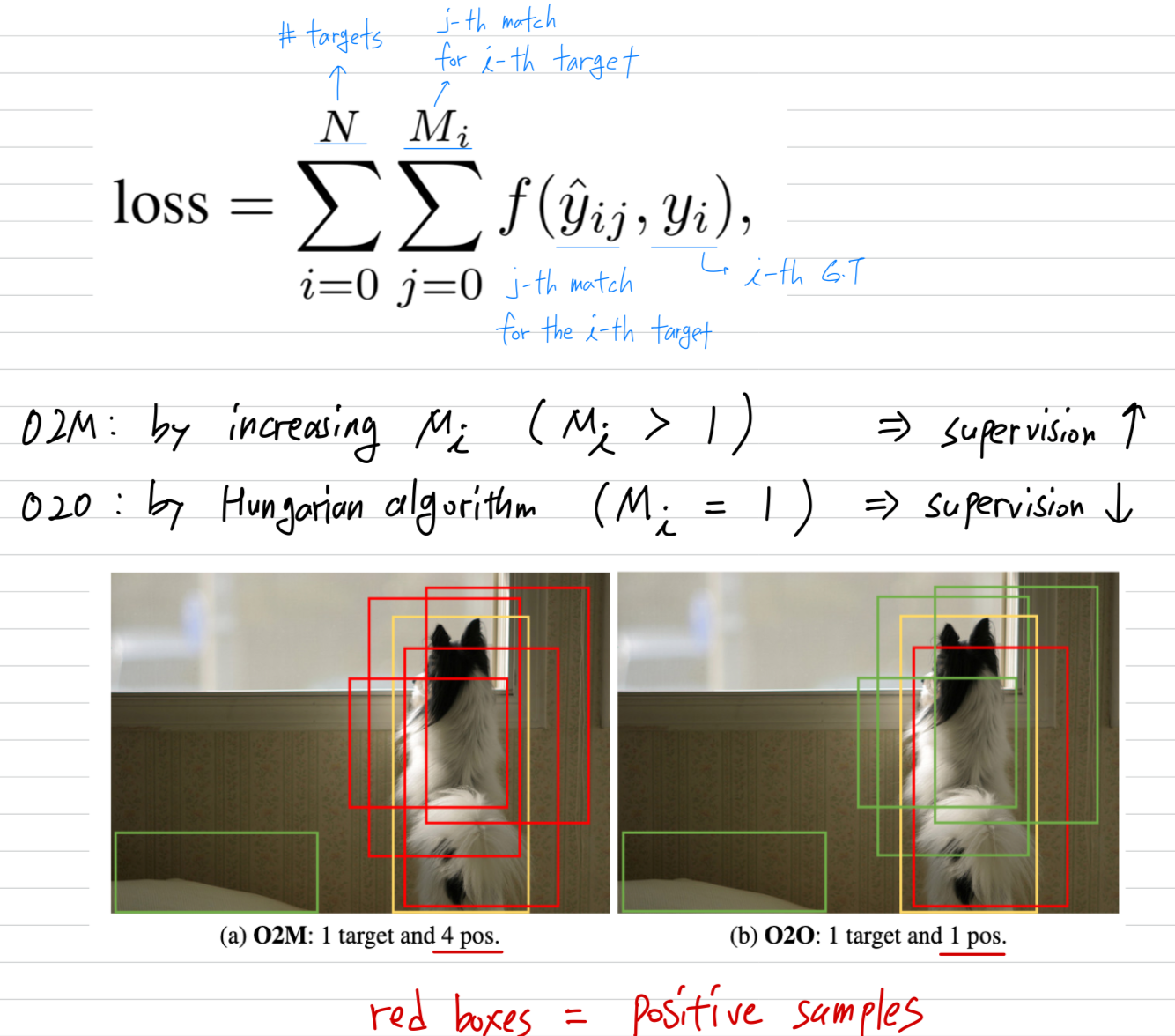
O2M vs. O2O
- O2M enchances supervision by increasing , ie.e., assigning multiple queries to each target and thus providing dense supervision.
In contrast, the O2O assignment only pairs each target with a single best prediction, determined via the Hungarian algorithm, which minimizes a cost function balancing classification and localization erros.
O2O can be considered a speical case of O2M where for all targets.
Focal loss
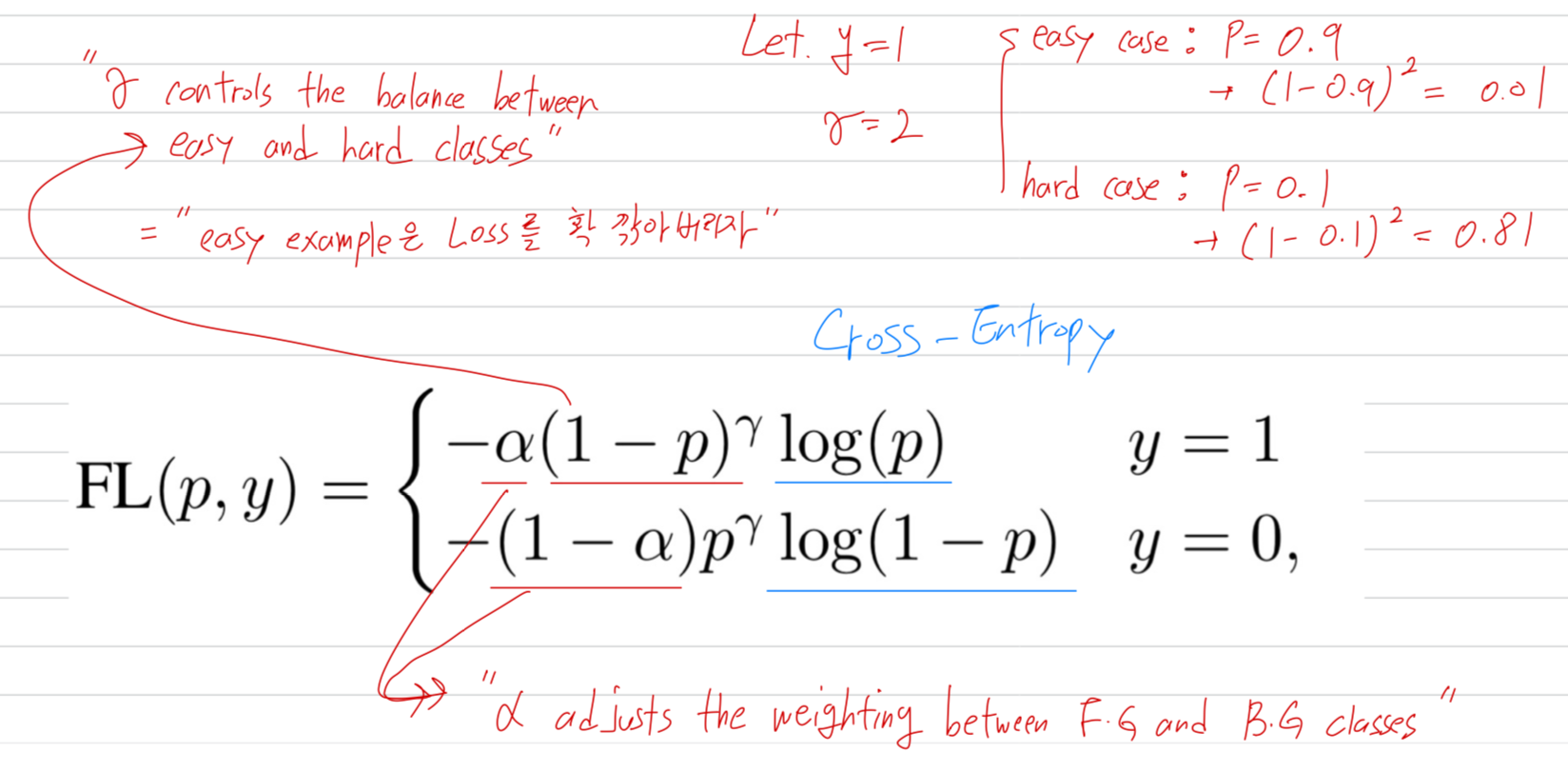
3.2. Improving matching efficiency: Dense O2O
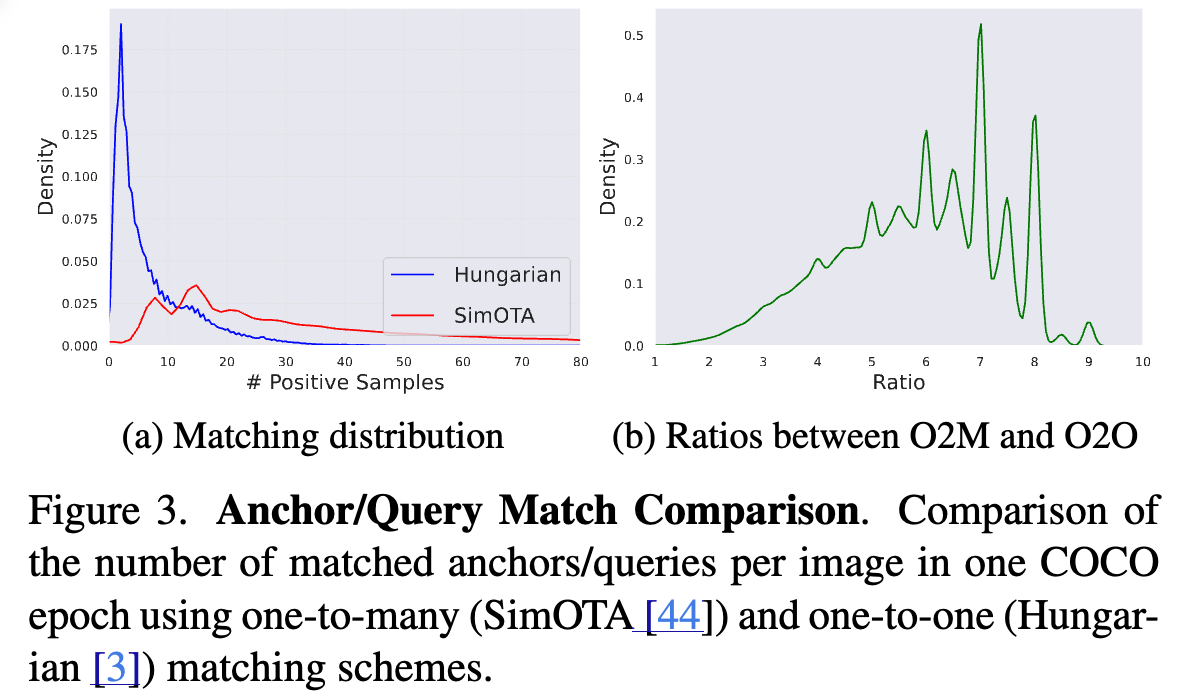
(가설과 분석)
- O2O의 key limitation은 SimOTA와 같은 traditional O2M methods와 비교했을 때, significantly fewer positive samples을 만든다는 것이다.
이 문제를 더 잘 이해하기 위해서, 우리는 RT-DETRv2 with a ResNet50을 학습했다.
우리는 the number of positive matches generated by both Hungarian (O2O) and SimOTA (O2M)을 비교했다.
Fig. 3a에 보이는 것처럼, O2O은 per image마다 under 10 positive matches에서 sharp peak를 만들어내는 반면,
O2M은 a broader distribution with many more positive matches를 만들어 낸다.
때로는 a single image에 대해서 80 positive samples를 넘기기도 한다.
Fig. 3b는 극단적인 경우에서 SimOTA가 O2O에 비해 약 10배 더 많은 matching을 생성함을 추가로 보여준다.
이는 O2O가 positive matches의 수가 상대적으로 적어, optimization이 느려질 가능성이 있음을 시사한다.
(제안)
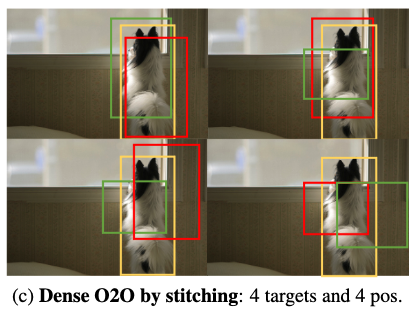
- 우리는 Dense O2O를 an efficient alternative로 제안한다.
이 방법은 O2O(with )의 구조를 유지하는데, image마다 the number of targets ()을 증가시키며, denser supervision을 달성한다.
예를 들어, Fig. 2c에 보이듯, original image를 four quadrants (네 개의 사분면)으로 replicate한 뒤
이를 a single composite image로 combine하면서도 original image dimension을 유지한다.
이 과정으로 target의 수는 1개에서 4개로 증가하여, matching structure를 변경하지 않고도 Eq. 1에서의 supervision level을 향상시킨다.
Dense O2O는 added complexity and computatoinal overhead 없이 O2M과 유사한 수준의 level of supervision을 달성한다.
- 어떻게 구현해야 하지?
3.3. Improving matching quality: MatchabilityAware Loss
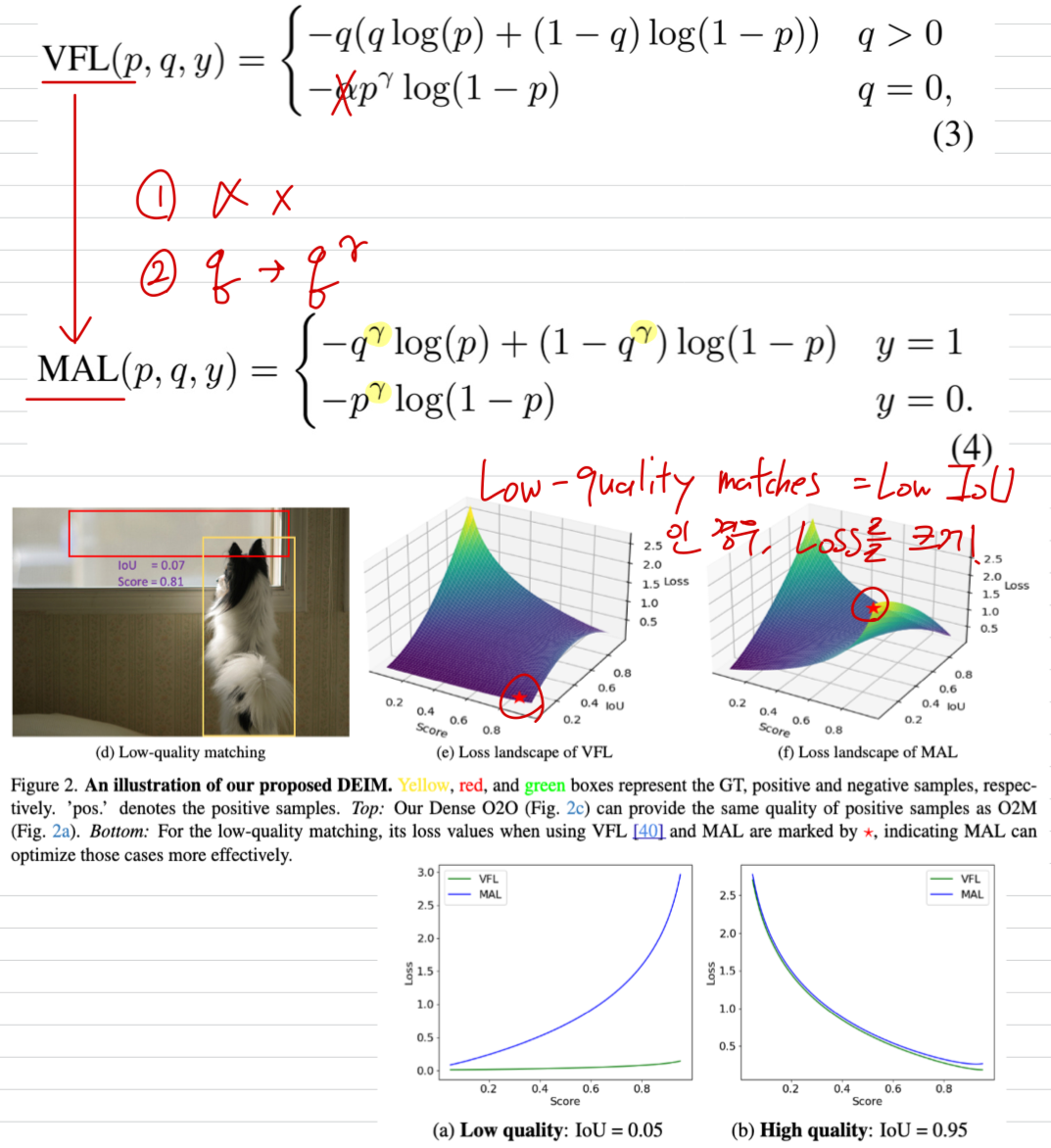
Limitations of VFL
-
VariFocal Loss (VFL)은 FL을 기반으로 만들어졌고, 특히 DETR models에서 object detection performance를 향상시키는 것으로 알려져 있따.
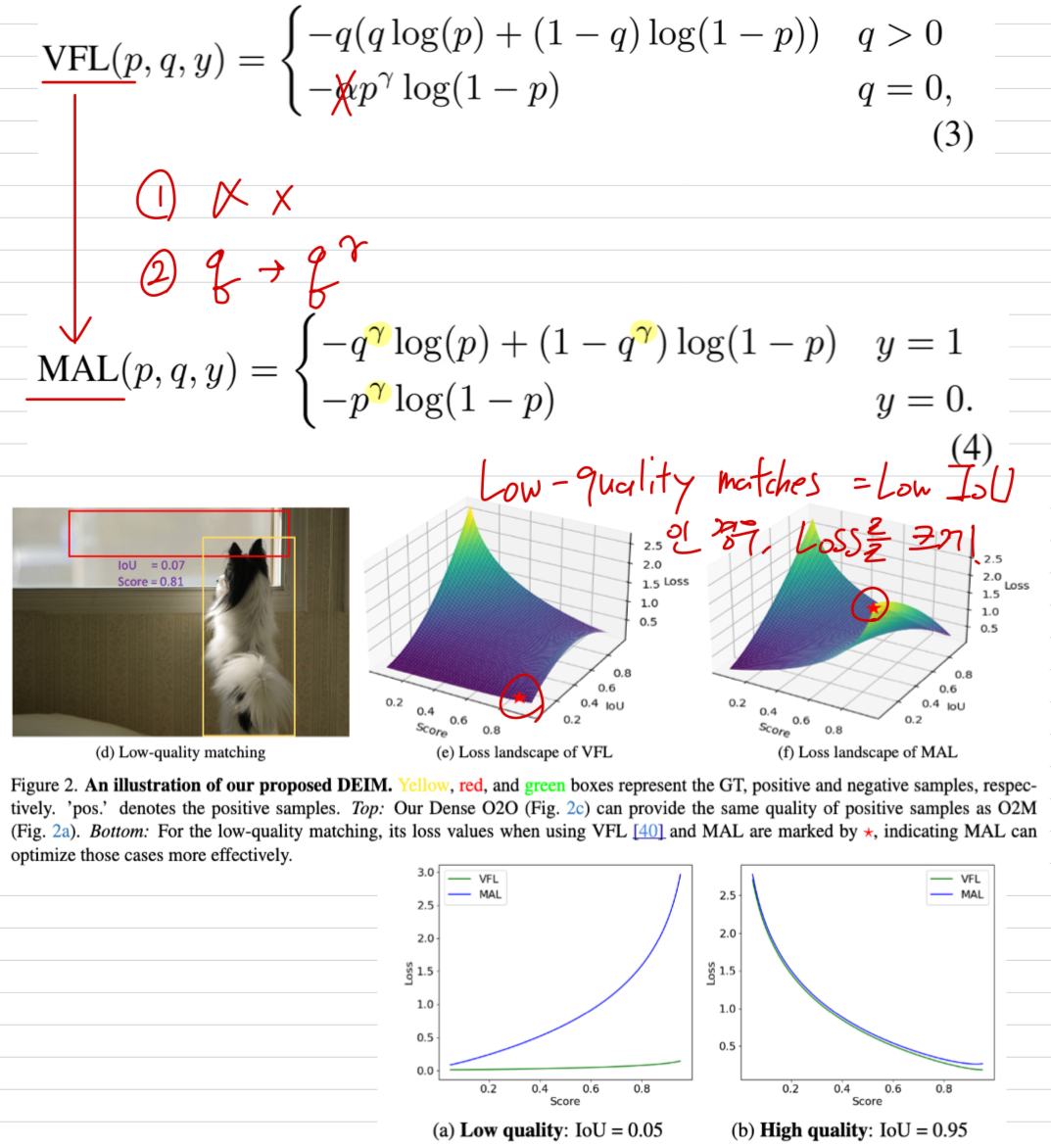
VFL loss는 다음과 같이 표현된다:
VFL은 IoU를 loss function에 통합함으로써 DETR에서의 the quality of queries을 개선한다.

-
하지만, VFL은 low-quality matches를 optimizing할 때 two key limitations이 있다:
-
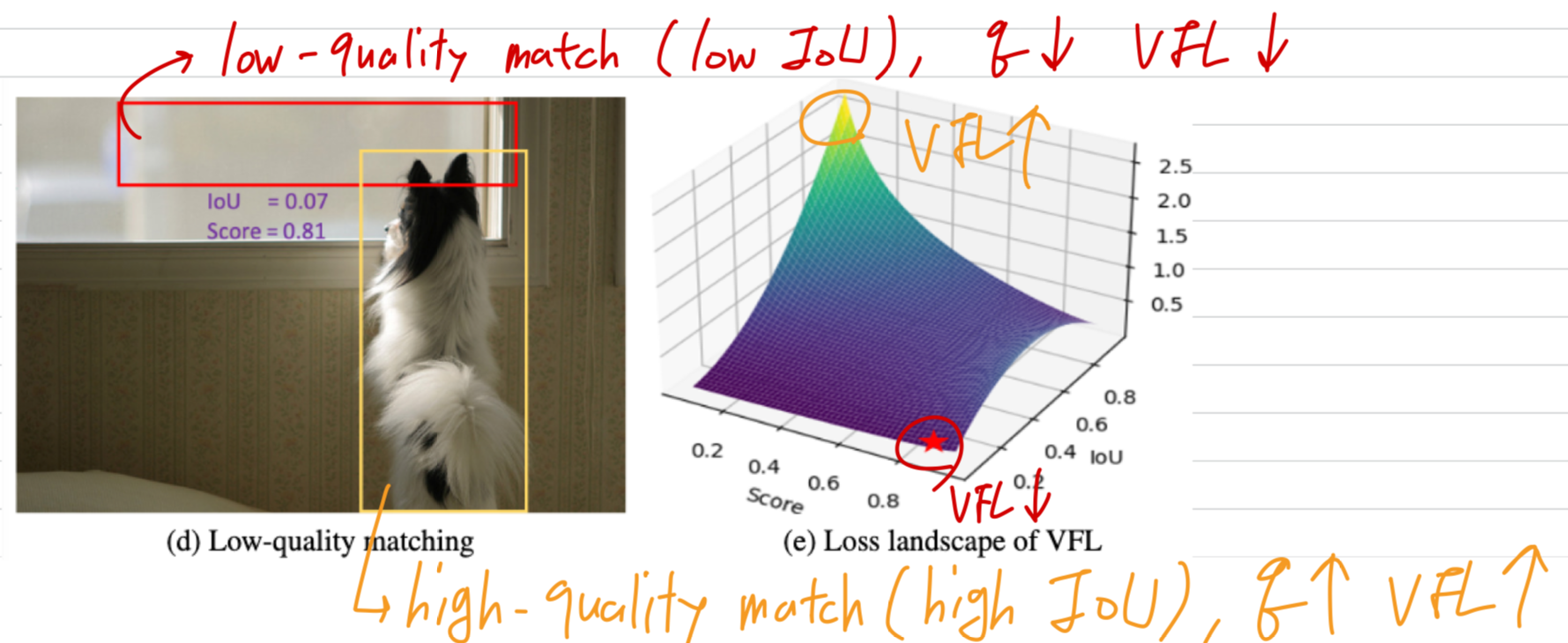
Low-Quality Matches
VFL은 주로 high-quality matches (high IoU)에 집중한다.
반면, low-quality matches (low IoU)의 경우 loss 값은 매우 작게 유지되며,
model이 low-quality boxes에 대한 prediction을 refining하는 것을 방해한다.
예를 들어, low-quatliy matching (with low IoU, Fig.2d)의 경우에도 loss는 여전히 minimal하며,
이는 Fig. 2e에서 확인할 수 있다.
-
Negative Samples
VFL은 no overlap된 matches를 negative samples로 취급하여,
the number of positive samples를 줄이고 effective training을 제한한다.이러한 문제는 dense anchors and O2M assignment strategies를 이용하는 traditional detectors에서는 덜 하지만,
queries are sparse and matching is more rigid한 DETR framework에서는 더 심각하게 나타난다.
-
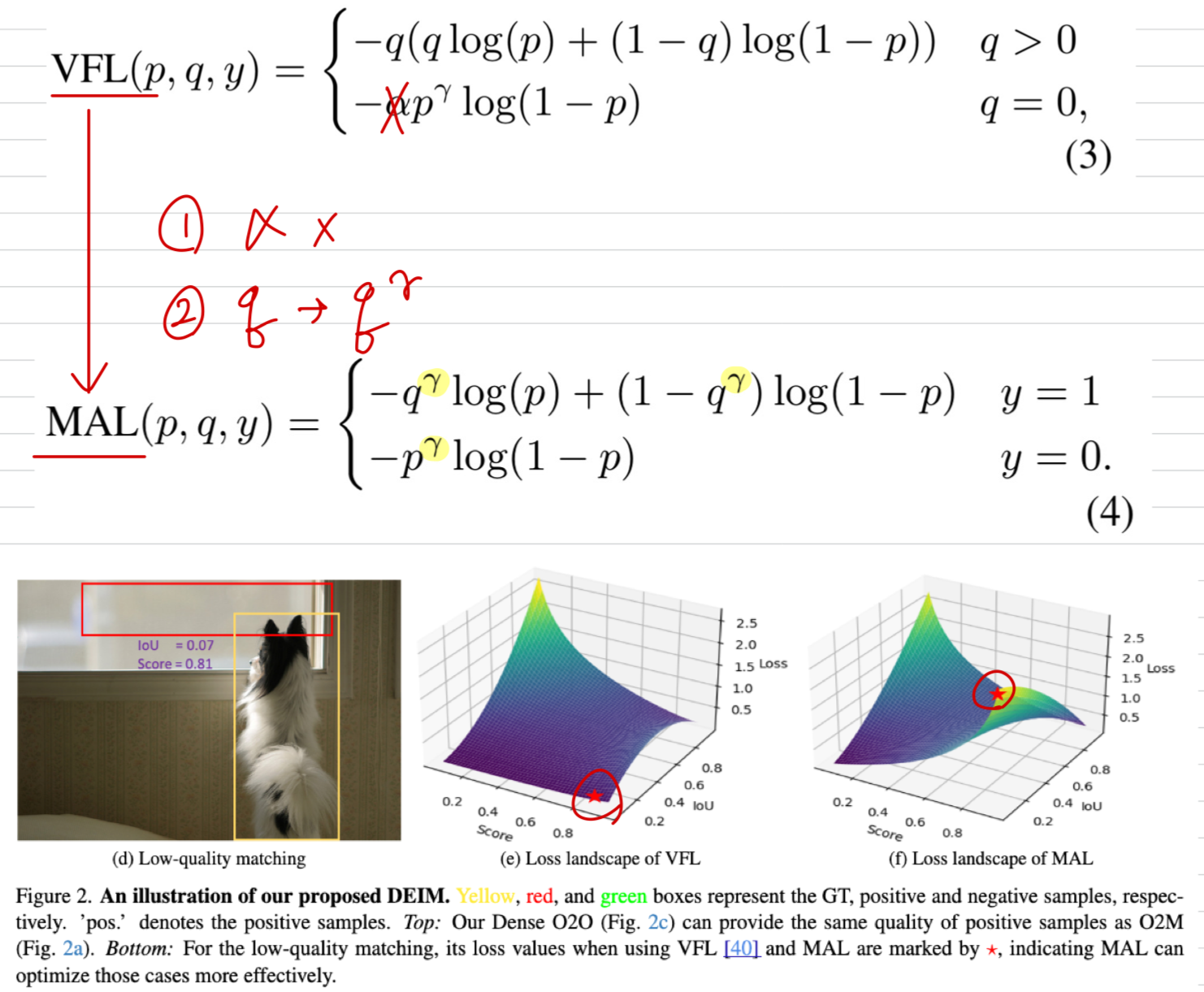
Matchability-Aware Loss.
- 위 문제를 해결하기 위해, 우리는 Matchability-Aware Loss (MAL)을 제안한다.
MAL은 VFL의 장점을 유지하면서 단점을 극복하며 확장한다.
MAL은 matching quality를 loss function에 directly 통합한다.
이는 low-quality matches에 대해 more sensitive하게 만든다.
VFL과 비교했을 때, 우리는 작지만 중요한 변화를 제안한다.
구체적으로, (1) the target label은 에서 로 수정하여,
the loss weights for positive and negative samples를 단순화하고,
(2) positive and negative samples를 balance하는 데 사용했던 hyperparameter 를 제거한다.
이 변화는 overemphasis on high-quality boxes를 피하고 the overall training process를 향상시키는 데 도움을 준다.
이는 VFL(Fig. 2e)과 MAL(Fig. 2f) 간의 loss lanscape로부터 쉽게 확인할 수 있다.
the impact of 는 Section 4.5.에서 다룬다.
Comparison with VFL.
- low-quality and high-quality matches를 둘 다 다룰 때, MAL과 VFL을 비교했다.
- the case of low-quality matches (IoU = 0.05, in Fig.4a)의 경우,
MAL은 predicted confidence가 증가함에 따라 loss가 a sharper increase하는 반면, VFL은 거의 변화가 없다. - the case of high-quality matches (IoU = 0.95, Fig. 4b)의 경우,
MAL과 VFL은 유사하게 동작하며, 이는 MAL이 high-quality matches에서의 성능을 저하시키지 않으면서도 training efficiency를 향상시킨다는 점을 확인해준다.
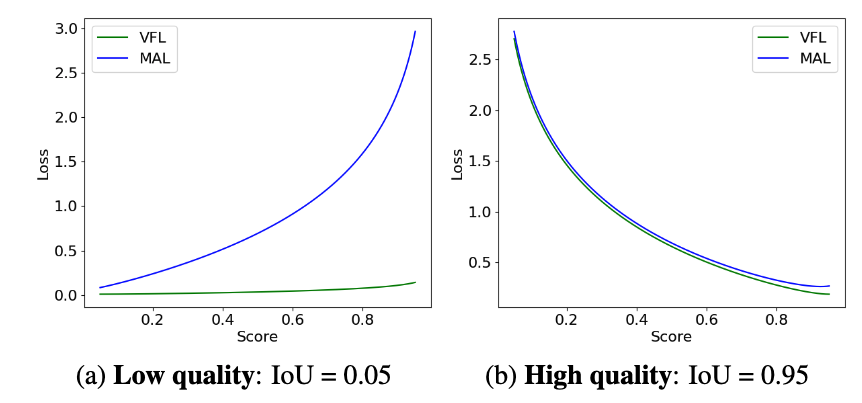
- the case of low-quality matches (IoU = 0.05, in Fig.4a)의 경우,
4. Experiments
4.1. Training details
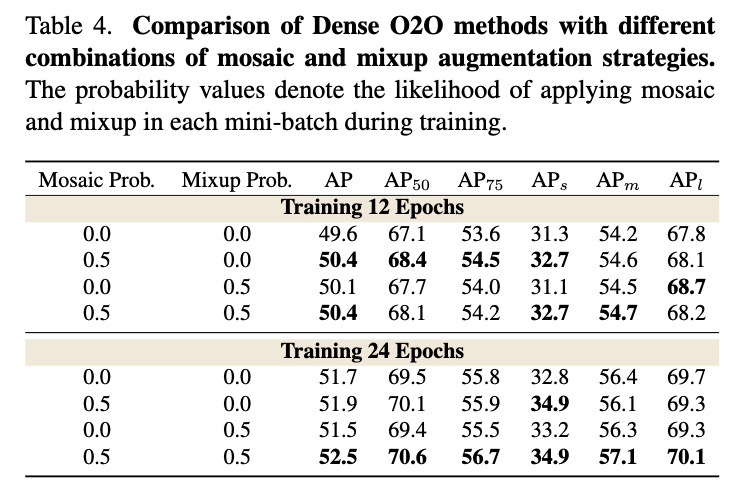
- For Dense O2O, we apply mosaic augmentation [1] and mixup augmentation [38]
to generate additional positive samples per image.
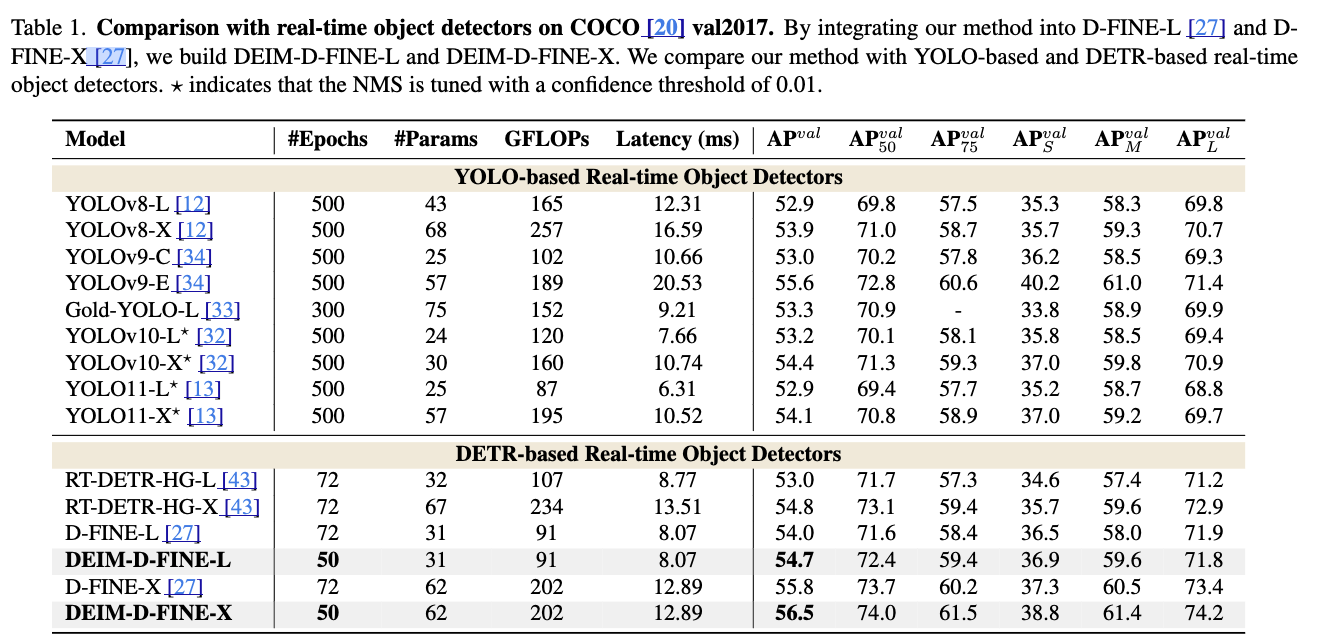
4.2. Comparisons with real-time detectors
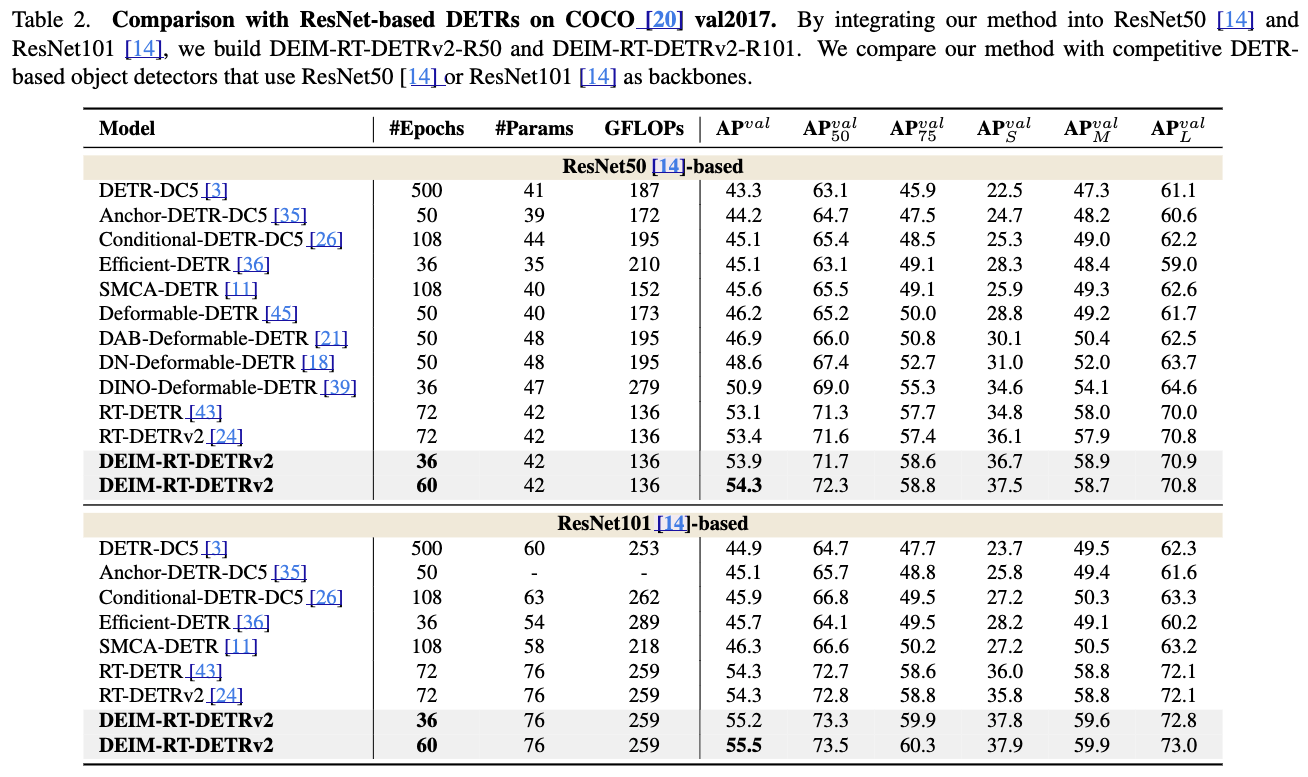
4.3. Comparisons with ResNet-based DETRs
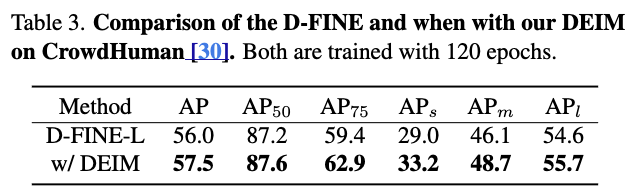
4.4. Comparisons on CrowdHuman
- CrowdHuman [30] is a benchmark dataset designed to evaluate object detectors in dense crowd scenarios.
4.5. Analysis
Methods for achieving Dense O2O.
- We explored two approaches to implement Dense O2O: mosaic [1] and mixup [38].
Mosaic is a data augmentation that combines four images into one,
while mixup overlays two images at a random ratio.
Both methods effectively increase the number of targets per image, enhancing supervision during training.
Impact of γ in MAL.

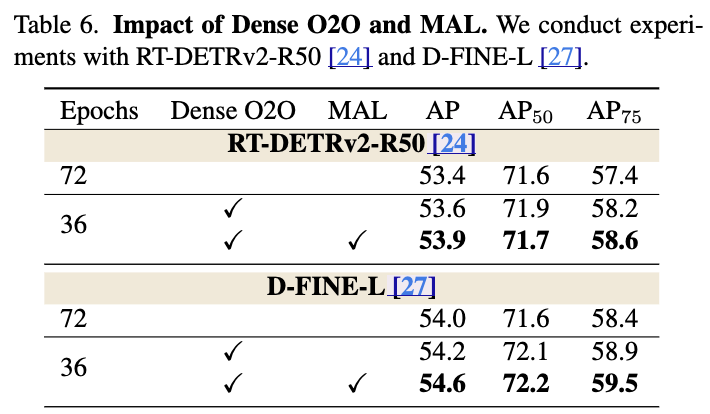
Effectiveness of Dense O2O and MAL
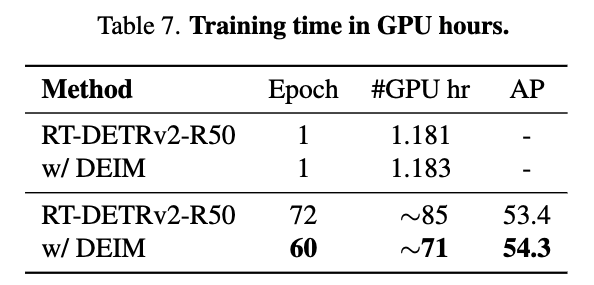
Training speed
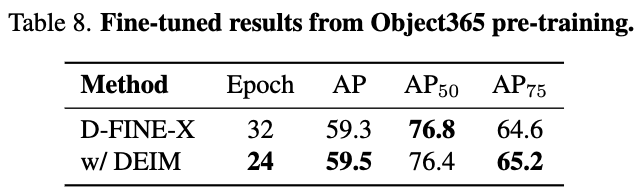
Finetuning from Object 365