Socket
Socket이 왜 나왔는가?:
Unix 계열의 system들에서 process들은 각각 독립적이다.
process 간의 data를 주고 받는 것이 쉽지 않다.
따라서 process 간의 communication을 하기 위해서는 OS의 service(system call)을 받아야 한다.
그렇다고 하더라도 process 간의 communication을 하기 위해서는
shared memory, pipeline, mutex, semaphore, critical section 보호 등을 해야 하기 때문에 복잡함.
그래서 나온게socket이다.
원래 socket은 보다 효율적인 process 간의 communication을 위해 burkley 대학에서 개발되었다.
그런데 network가 개발되면서,
network 측면에서도 내 안에 있는 process와 다른 host의 process끼리 communication을 하는 것은 똑같이 process 간의 communication이기 때문에
socket이라는 interface를 network에도 적용해서 application에서 TCP/IP stack을 이용하면서도 다른 process와 통신할 수 있게 되었다.
그래서 이제 network programming을 하기 위해서는 socket이 필수적임.
high level language (node.js, etc)를 쓰더라도 내부는 모두 socket으로 되어 있음.
그 socket을 어떤 식으로 열고? 쓰고? 관리하는가?
Socket Creation in C : socket(2)
-
int s = socket(domain, type, protocol):
file을 open하는 것처럼, socket도 open해야 함.s = sockid: socket descriptor. (열리는 socket은 모두 고유한 socket identifier를 갖는다.)domain: communication domain(PF_INEF = IPv4 protocol -> typically used)type:
Two essential types of sockets.
server에서 사용하고 있는 type을 맞춰야 한다 (server가 TCP를 쓰고 있으면, 나도 TCP를 써야 함)SOCK_STREAM: socket을 TCP로 만들 것이다.SOCK_DGRAM: socket을 UDP로 만들 것이다.
protocol: specifies protocol (usually set to 0)
-
socket(2)으로 socket을 열면, 열릴 수도 있고 안열릴 수도 있다.
Ports
- socket을 열기 위해서는
port number도 필요하다.
그런데 port number는 특정 application에서 사용하는 specific port number가 있는데,
걔네를 피해서 설정해야 함. (60,000 이후의 port number를 이용해야 함)
bind(2)
int status = bind(sockid, &addrport, size):
socket을 열 때, 열기만 했지 나의 network에 대한 정보가 없었음.
그래서 connection setup할 때,
지금 나의 system의 network interface(Ethernet, 무선랜 등)와 나의 socket을 연결하기 위해 사용한다.
각각의 socket마다 다른 bind를 할 수 있다.
SOCK_DGRAM(UDP)방식에서, 내가 보내기만 할 때는 bind()할 필요가 없다.
보낼 때, 상대방의 port number만 적어서 보내면 된다.
그런데 bind(2)는 overhead가 없기 때문에 connection setup과정에서 bind(2)를 하는게 좋다...sockid: sock(2) system call에 대한 반환값. socket descriptor.addrport:- struct sockaddr(나중에 이 구조체에 대해 자세히 다룸),
- 내 IP address(직접 쓰지 않아도 자동으로 내 IP가 입력됨) and 나의 port 번호
size: the size(bytes) of the addrport structure.
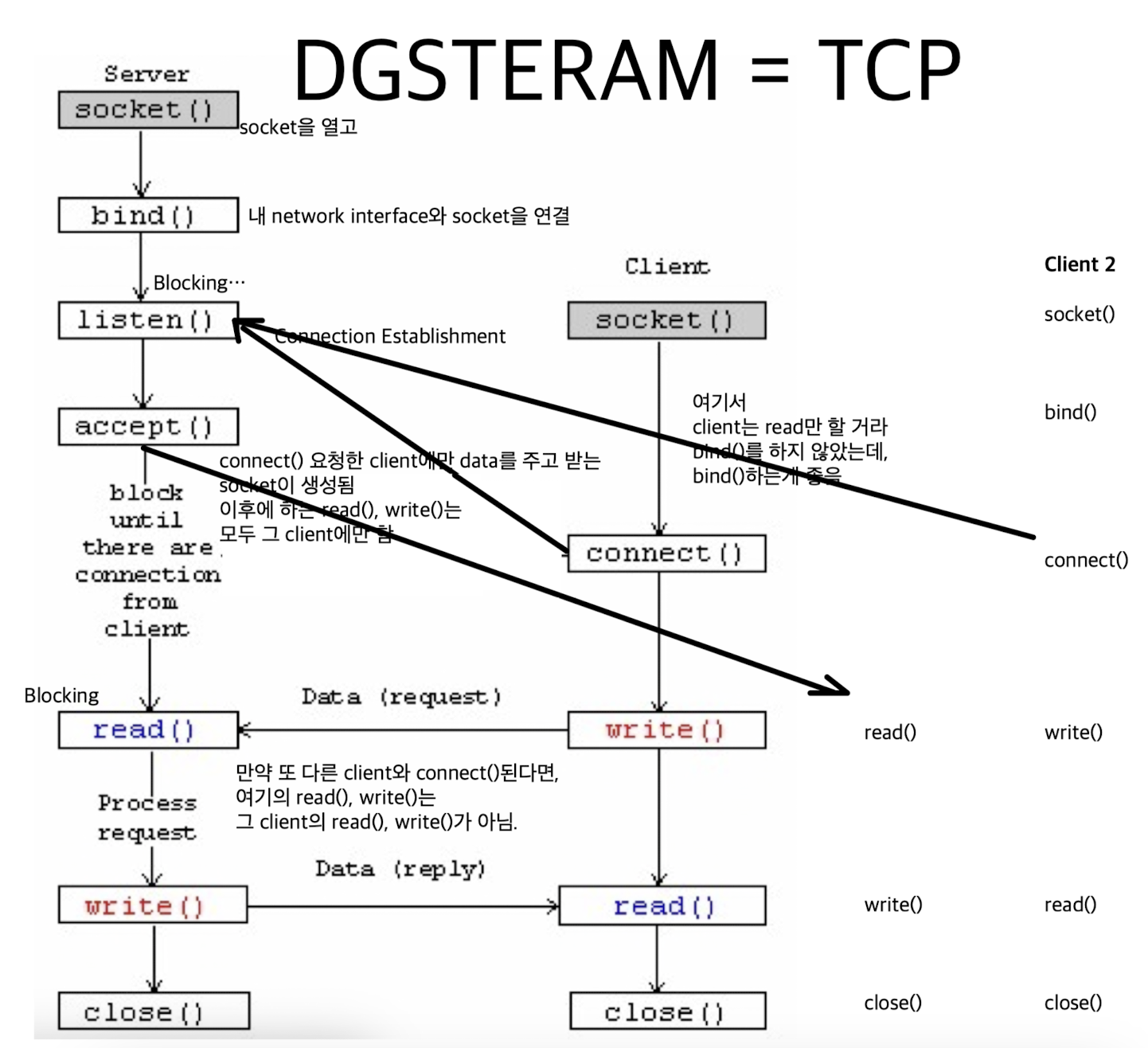
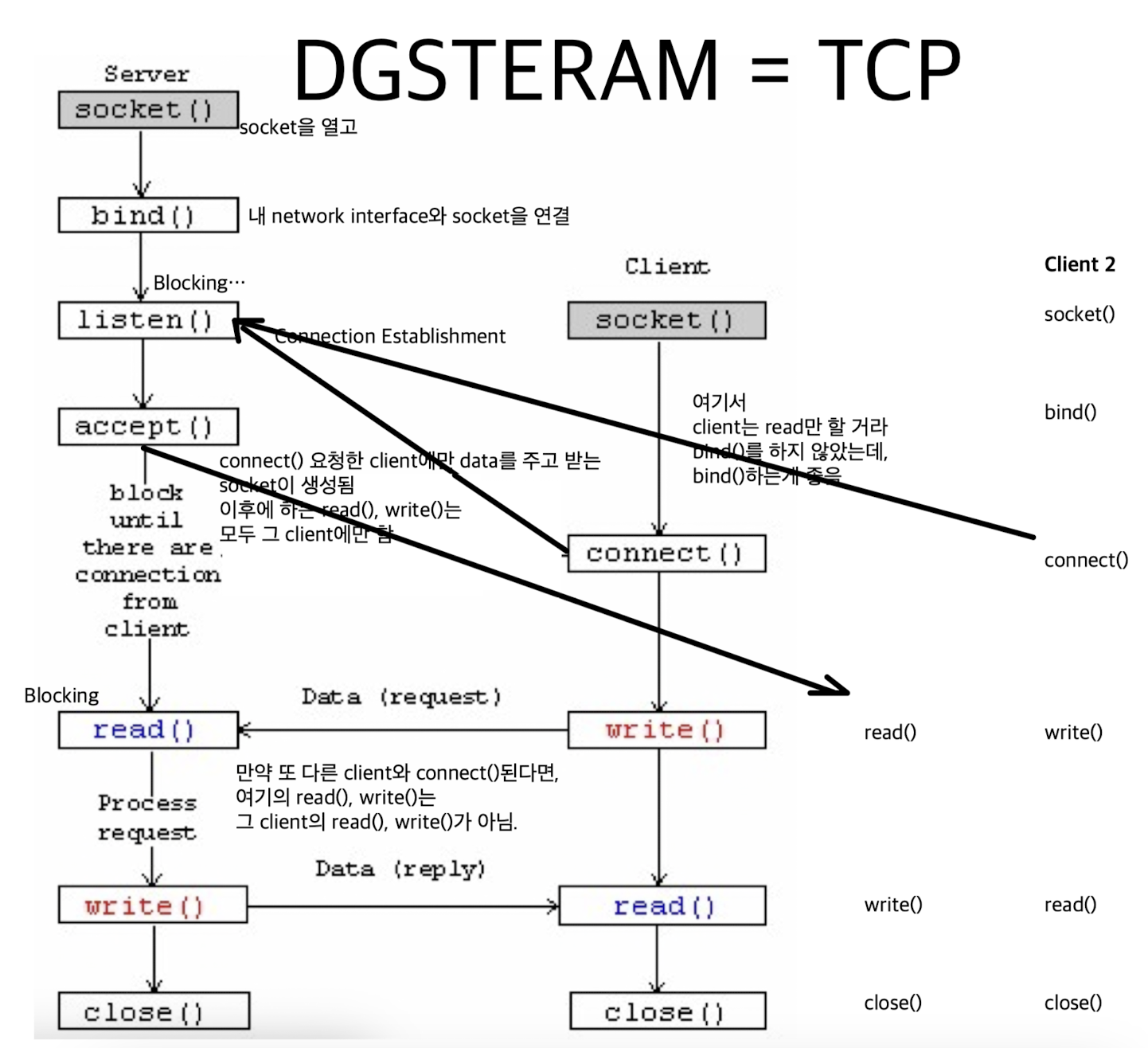
Connection Setup (SOCK_STREAM)
- Server는 Client의 요청을 기다리고 있으니, client에서 먼저 connection을 요청.
- passive participant : server
- active participant : client
Passive participant & Active participant Connection Setup Flow:
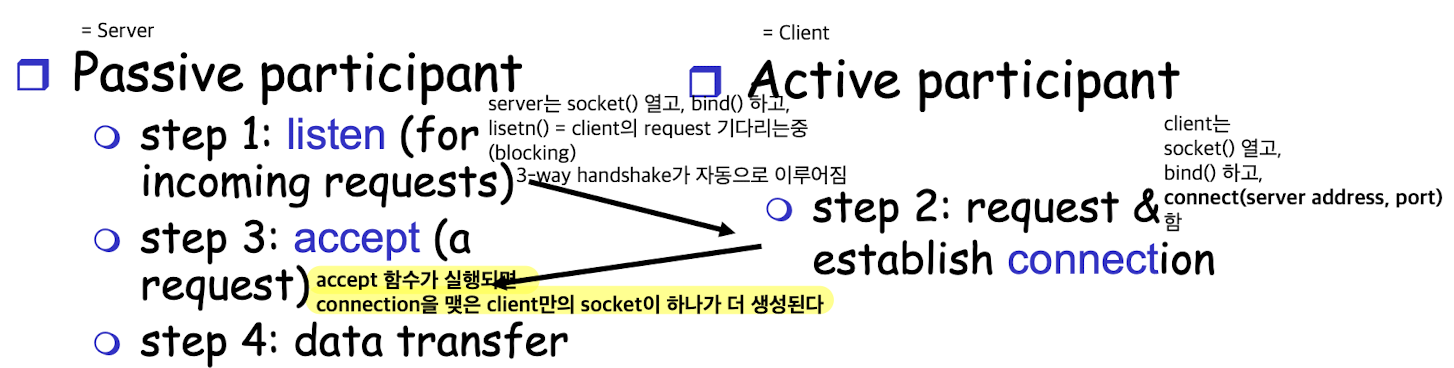
listen(2) & accept(2)
int status = listen(sock, queuelen):
called by passive participant(server)status: 0 if listening, -1 if errorsock: socket descriptorqueuelen: client의 request를 몇 개까지 기다릴 것인가?
많은 client를 기다린다고 좋은 것도 아니고, 적은 client를 기다린다고 나쁜 것도 아니기 때문에
들어오면 들어온 대로 실행해준다.
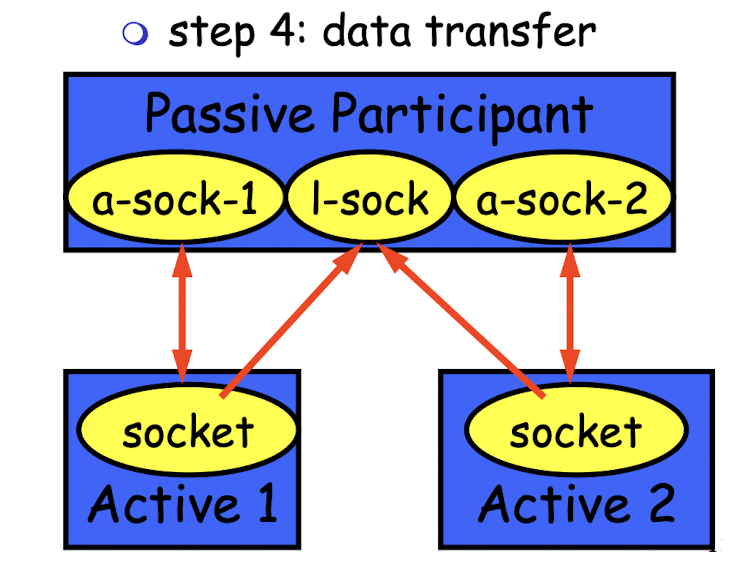
int s = accept(sock, &name, &namelen):
called by passive participant(server)s: connection을 request한 client랑만 통신하기 위해 server에 생성되는 new socket's descriptor. (accept socket)sock: 기존 server에서 client들의 request를 listen()하기 위한 socket. 또 다른 client와의 연결을 위해 계속 listen. (Listen socket)&name: sockaddr형 구조체를 넣음. (해당하는 client의 ip address와 port number에 대한 정보가 들어가 있음.)&namelen: sizeof(name)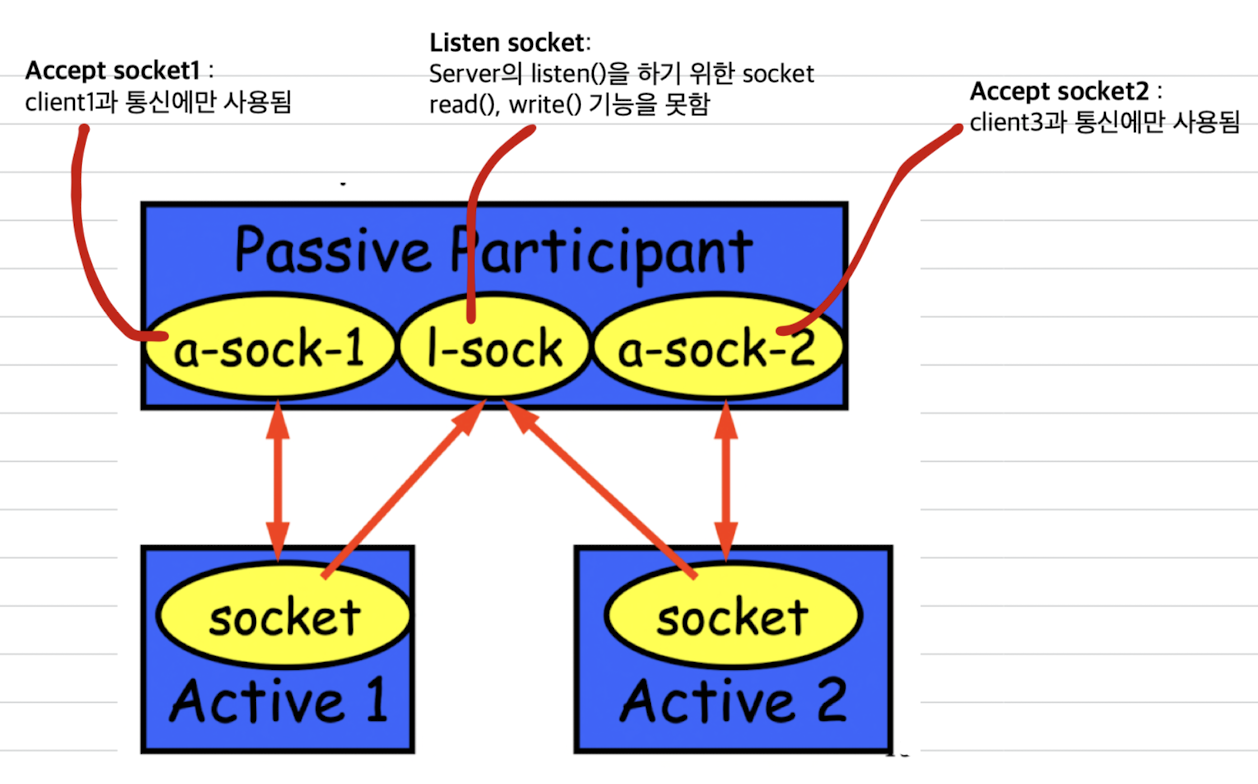
connect(2)
int status = connect(sock, &name, namelen):
called by active participant(client)status: 0 if successful connect, -1 otherwisesock: client's socket descriptor&name: sockaddr 구조체에다가 값을 직접 써야 함. (server의 IP address & port)namelen: sizeof(name)
send(2) / recv(2)
-
SOCK_STREAM: With a connection-
int count = send(sock, &buf, len, flags):count: #bytes transmitted (-1 if error)sock: client의 request에 의해 생성된 server의 accept socket descriptor&buf: char[], bffer to be transmittedlen: length of buffer to transmitflags: special options
-
int count = recv(sock, &buf, len, flags):count: # bytes received (-1 if errors)sock: client의 socket? server의 accept socket?buf: void[]->(type casting), stores received byteslen: #bytes receivedflags: speical options
-
recv(2)는 blocking io이다.
blocking io는 그 함수를 실행했을 때, 어떤 조건을 만족하지 않으면 그 함수에서 계속 blocking이 되어 있음. (ex: scanf(3))
나중에 이 blcoking io가 발목을 잡음...
-
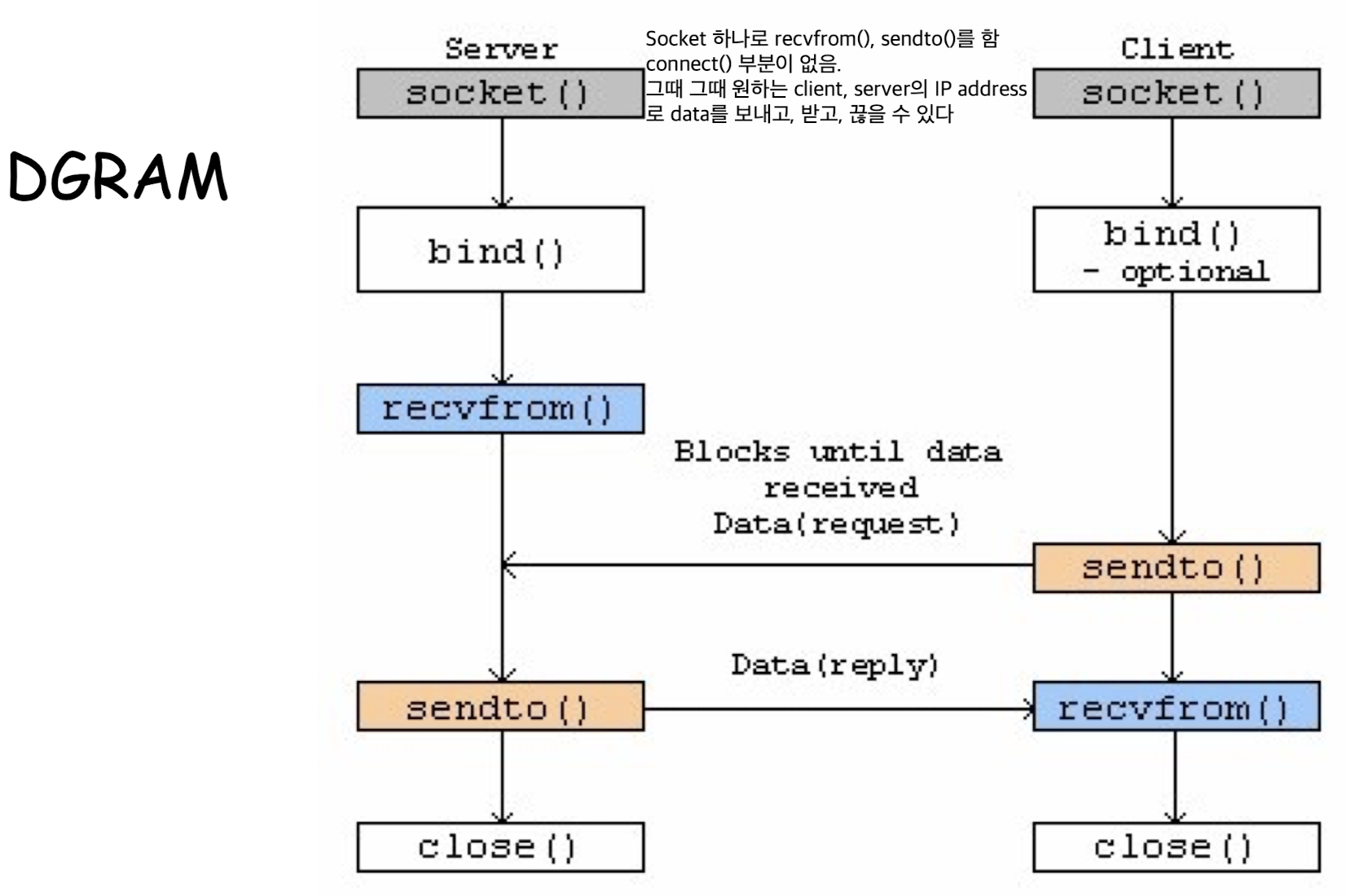
SOCK_DGRAM: Without a connection
connection이 없기 때문에
socket 열고, bind하고, 바로 sendto() 또는 recvto()를 실행하면 된다.
TCP에서는 accept될 때마다 dedicated socket이 만들어져서 socket descriptor만 있기 때문에
따로 address를 쓸 필요가 없었다.
SOCK_DGRAM은 server에서 socket 1개로만 여러 client들과 data를 주고 받을 수 있기 때문에
그 server의 IP address를 명시해줘야 한다.int count = sendto(sock, &buf, len, flags, &addr, addrlen)sock: server에 있는 1개의 socket&addr: struct sockaddr (server의 IP address)
int count = recvto(sock, &buf, len, flags, &addr, &addrlen)
정리)
SOCK_STREAM(TCP)에서는 Client A가 accept socketA에만 send, receive를 할 수 있다.
SOCK_DGRAM(UDP)는 하나의 socket을 Client A, Client B 등이 send, receive를 할 수 있다.
close(2)
status = close(s):
socket을 termination하여 해당하는 descriptor를 종료할 수 있어.
Server의 경우, 열려진 socket이 많기 때문에 그 열려진 socket들을 하나하나 모두 close()해줘야 한다.
만약 close()해주지 않는다면, resource가 제한된 system의 경우에서는 낭비가 될 수 있다.
close()할 때 4-way handshake가 이루어진다.
DGSTREAM(TCP) Flow
이 flow는 모든 platform, 모든 language에서 동일함
TCP Flow:
DGRAM(UDP) Flow
UDP Flow:
struct sockaddr
structure sockaddr의 구조:

sin_family: AF_INET(IPv4)sin_port: port # (0 - 65535)sin_addr: IP addresssin_zero: unused
sin_port,sin_addr만 써도 된다.
address and port byte-ordering
-
최근에는 내부적으로 Byte-ordering을 하기 위해서 host byte order라는 program이 실행되고 있어서 크게 상관하지 않는다.
-
Big-Endian machine:
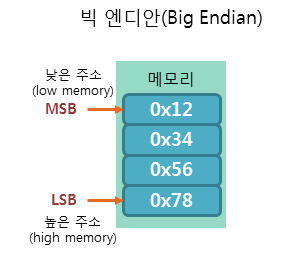
-
Little-Endian machine:
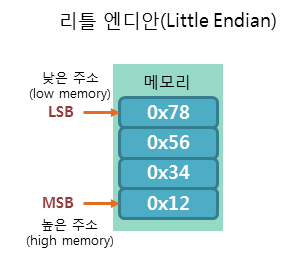
Dealing with blocking calls
-
Blocking I/O:
Blocking I/O 밑에 아무리 중요한 code를 작성했더라도
blocking되어 있으면, 밑의 code는 실행되지 않음.
ex : accept(), connect(), recv(), recvfrom(), send(), sendto() -
program을 작성할 때, Blocking I/O를 사용하면 편리하긴 하다.
Reliable data transfer할 때, Stop and Wait로 예시를 들면
data 하나 보내고 그게 완전히 처리될 때까지 기다렸다가 다음 data 보내고... 하면 되니까 생각할게 없었음.
하지만 blocking이 풀린 pipeline 방식으로 바뀌면서 복잡해졌다.
➡️ 이처럼 Blocking I/O를 사용하면 program 작성이 편리하긴 하지만, 복잡한 system에서는 문제가 발생한다.multiple conection일 때
server에서 accept()하는 중에 client A가 connect()를 하면 blocking이 풀림.
풀리면서 read()에서도 blocking되어 있음.
그런데 만약 채팅 program이라면?
다른 clientB가 connect()를 하면 server는 read()에서 blocking중이므로
clientB의 connect()를 server에서 accept()할 수 없는 상황이 발생함simultaneous sends and receives가 안 된다
예를 들어 채팅 program에서
client와 server가 번갈아 가면서 data를 주고 받으면 문제가 없다.
예를 들어,
➡️ Client A에서 data를 send()하고 나서 recv()에서 blocking중...
➡️ Server는 data recv()에서 blocking 해제, send()에서 blocking중...
➡️ Server에서 data를 send()하고 나서 recv()에서 blocking중...
➡️ Client A는 data recv()에서 blocking 해제, send()에서 blocking중...
(문제 없음)
하지만 client A에서 data를 계속해서 send() 한다면?
➡️ Client A에서 data를 send()하고 나서 recv()에서 blocking중...
➡️ Server는 data recv()에서 blocking 해제, send()에서 blocking중...
➡️ Client A에서 data를 계속해서 send()
➡️ Server는 send()에서 blocking 중이므로 recv()를 할 수가 없음non-networking processing
scanf(), gets() 와 같은 다른 blocking I/O와 같이 사용하면
1., 2.처럼 더 꼬이게 된다.
Solution : select(2)
int status = select(nfds, &readfds, &writefds, &exceptfds, &timeout):
select(2)를 사용하여 permanent blocking, time-limited blocking, non-blocking을 구현할 수 있다.status: # of ready objects, -1 if errornfds: 1 + largest file descriptor to check&readfds: list of descriptors to check if read-ready&writefds: list of descriptors to check if write-readyexceptfds: list of descriptors to check if an exception is registeredtimeout: time after which select returns, even if nothing ready - can be 0 or
select server
- main thread는 accept()에서 client가 connect()할 때까지 blocking하고 있고,
생성된 thread는 select()를 이용하여 비동기적으로 data를 read(), write()한다.
