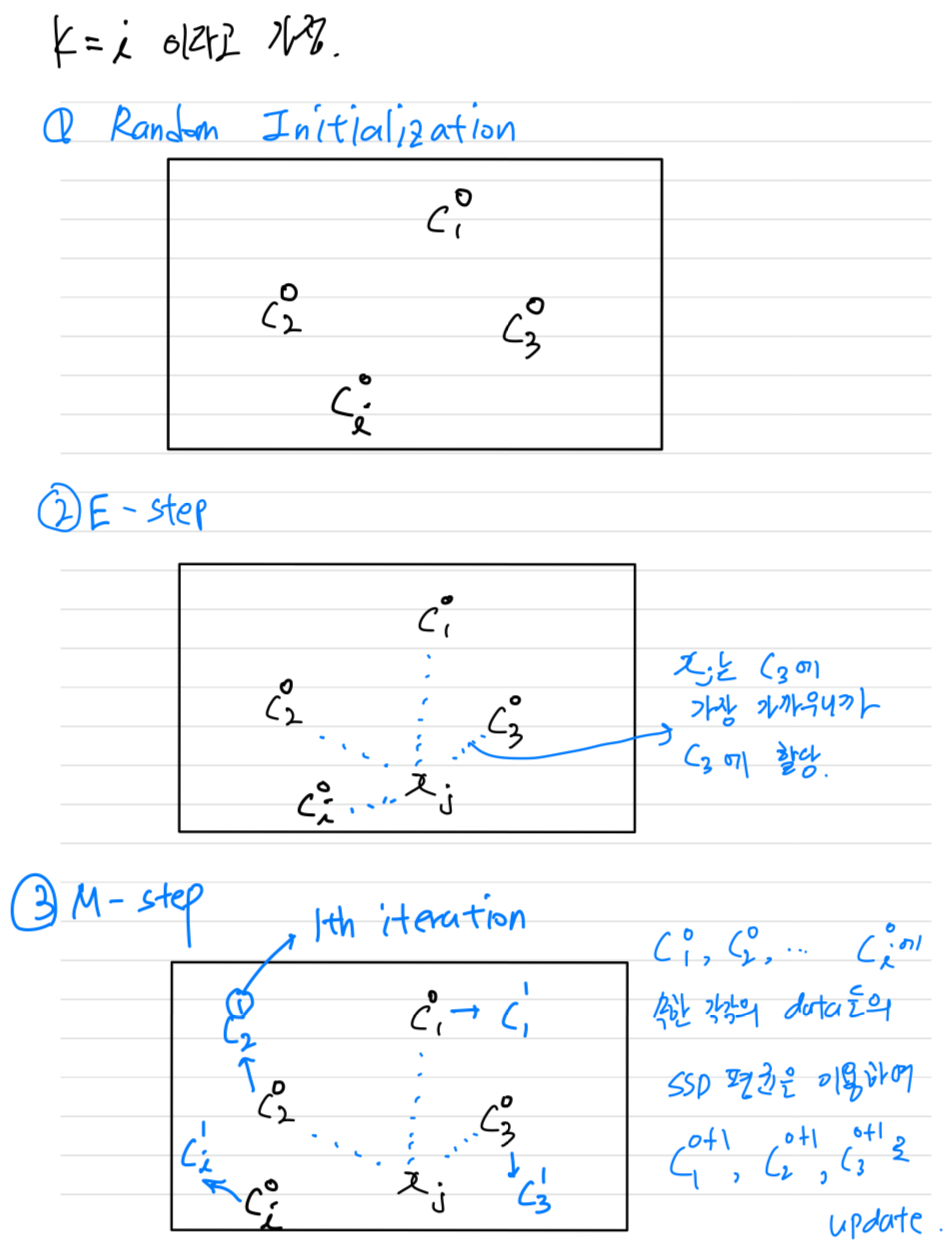
Introduction to Segmentation and Clustering
-
Segmentation:- identify groups of pixels that go together
- separate image into coherent(동등한) "objects"
-
Major process for segmentation:
token = segmentation을 수행하기 위한 작은 unit.- bottom-up :
고전적인 algorithm.
group tokens with similar features - top-down :
최근 Deep Learning의 기반한 방식들.
커다란 part를 조각난 part들로.
- bottom-up :
-
clustering:- 어떠한 유사성에 의해서 data를 묶어나가는 작업.
- unsupervised learning method이다.
- 어려운 점 : 어떤 point들이 유사한가? 몇 개의 group으로 묶을 것인가?
How do we cluster?
agglomerative clustering:
tree형식으로 각각의 cluster가 자기 자신의 cluster를 찾아나감k-means:
가장 보편적으로 사용되는 clustering 방법.
k = #clustersmean-shift clustering:
평균을 이동시켜서 clustering
1. Agglomerative Clustering
-
Agglomerative Clustering=bottom-up hierarchical clustering -
Algorithm:initialization:
각각의 point들을 own cluster로 생성.repeat:
N개의 쌍이 있다면, N개의 쌍 각각의 거리를 계산
그 중에서 가장 유사한 pair를 찾으며 묶어나감.until:
그 작업을 우리가 원하는 cluster수에 도달할 때까지 수행.
또는
only one cluster가 될 때까지 수행.
-
clustering의 결과를 Dendrogram(tree)으로 나타낼 수 있다.
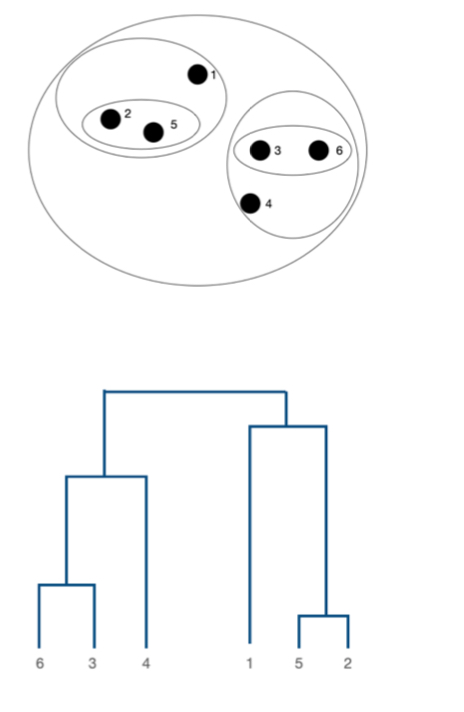
-
Agglomerative Clustering에서 heuristic하게 적용되는 method:
How to define cluster similarity?
정답은 없고, 해봐야 안다.- minimum distance
- maximum distance
- average distance between points
-
장점:- 간단하다
- adaptive shapes (shape이 갑자기 확 생기지 않음)
-
단점:- imbalanced cluster
- time complexity
2. K-means Clustering
-
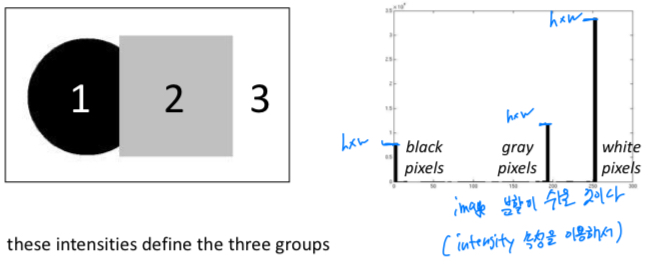
간단한 image가 있을 때, 우리는 pixel의 intensity로 clustering을 쉽게 수행할 수 있을 것이다.
 하지만 Gaussian noise가 있다면? 다음과 같을 것인데,
하지만 Gaussian noise가 있다면? 다음과 같을 것인데,
intensity가 겹치는 부분에 대해서 어떻게 clustering을 할 것인지? 애매한 점이 있다.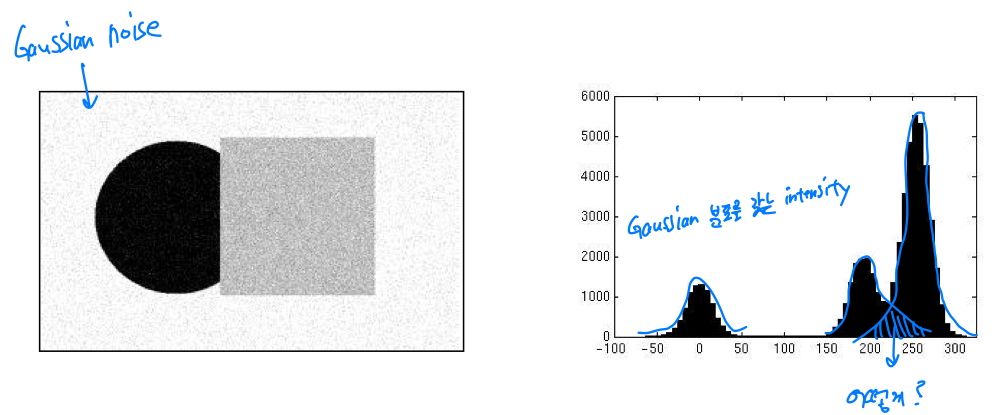
-
그래서 우리가 가지고 있던 intensity feature를 1차원으로 mapping시키면 다음과 같은데,
가운데에 애매하게 위치하여 있는 feature들을 어느 center(C)로 줄 것인지를 결정해야 한다.
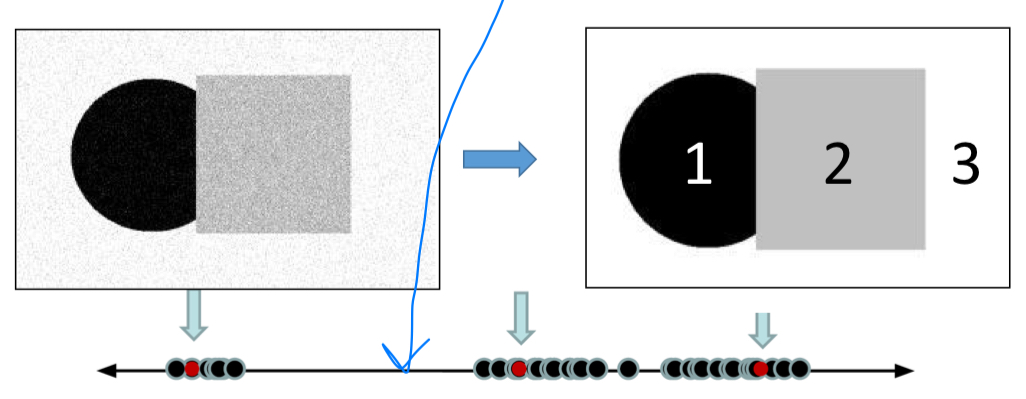 각각의 cluster에 대해서는 center(C)가 존재하고,
각각의 cluster에 대해서는 center(C)가 존재하고,
data들과의 거리 SSD(sum of square distance)를 계산하여,
Center와 data들 간의 SSD가 가장 작은 곳을 Center로 정한다.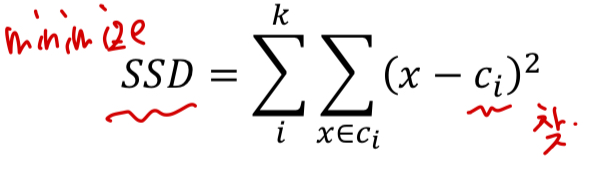 이러한 원리가 K-means에 그대로 적용된다.
이러한 원리가 K-means에 그대로 적용된다. -
goal,object function:
개의 주어진 data가 있을 때, 개의 cluster로 할당시켜야 한다.
그래서 center와 data 사이의 거리(=SSD)를 minimization하는 방향으로 학습하여
center(C)와 를 찾는 것이 목적.
( : 와 를 이을 것인지 판단하는 binary value. = mask)
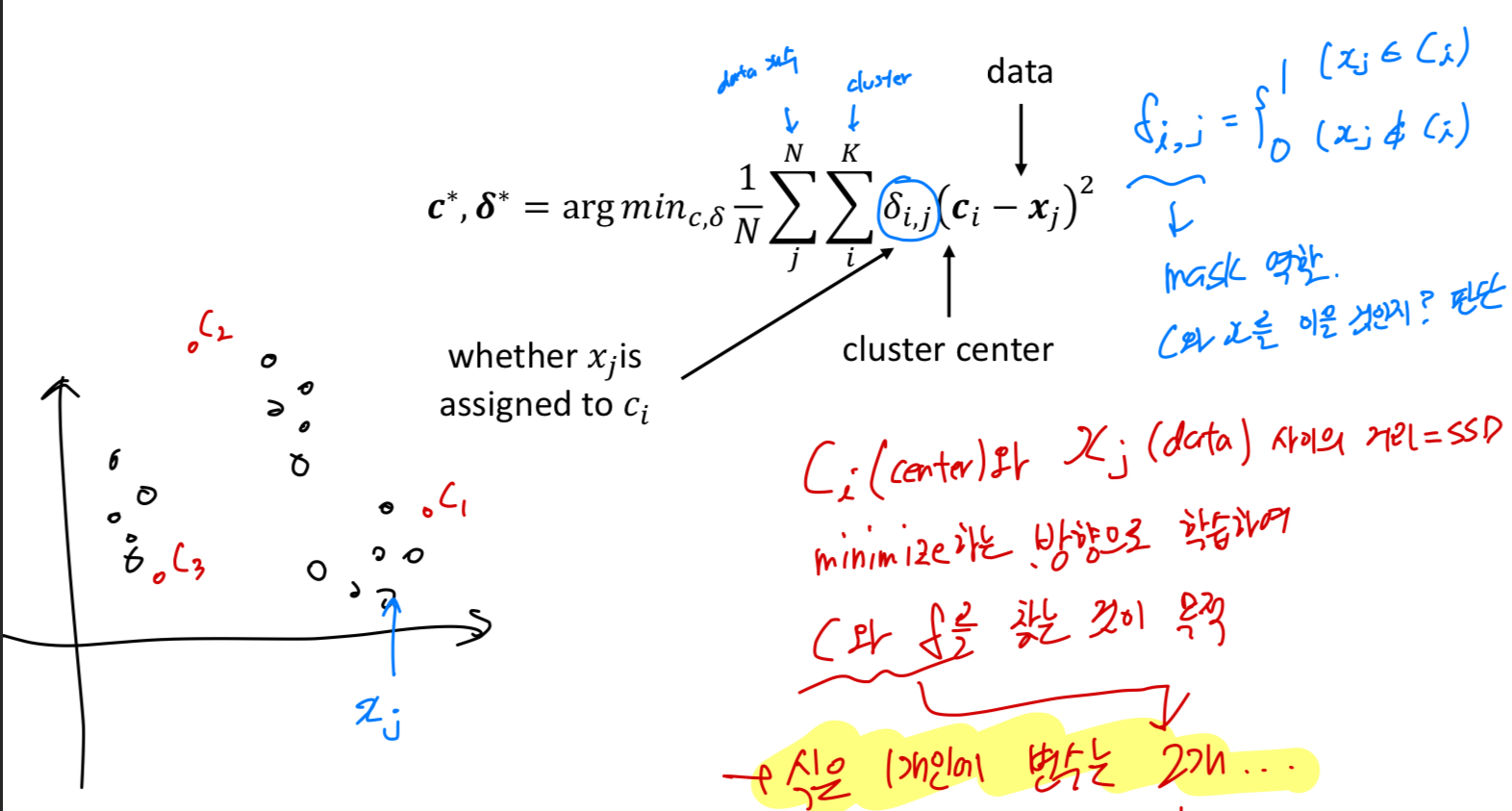 우리의 목적을 만족시키는 식은 1개이지만, 찾아야 하는 변수는 2개이다.
우리의 목적을 만족시키는 식은 1개이지만, 찾아야 하는 변수는 2개이다.
따라서 iterative하게 optimum을 찾아야 한다.
K-means clustering algorithm
-
initialization:
우선 개의 center 를 random하게 initialization
-
E-step (assignment step):
각 cluster의 center(c)와 data의 SSD를 비교하여, 가장 가까운 cluster의 center(c)에 할당해주는 과정 = data에 label을 할당해주는 과정

-
M-step (update step):
각 cluster의 center(c)와 그 cluster에 속하는 data들의 SSD 평균을 사용하여 center(c)를 update.
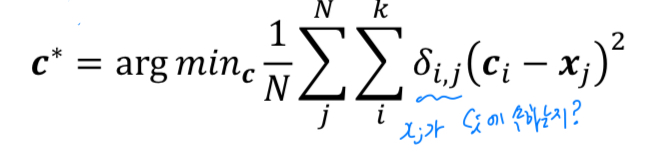
-
termination: E, M step을 반복적으로 수행.- iteration이 정해진 maximum number에 도달하거나,
- 더 이상 assignment가 변하지 않을 때까지
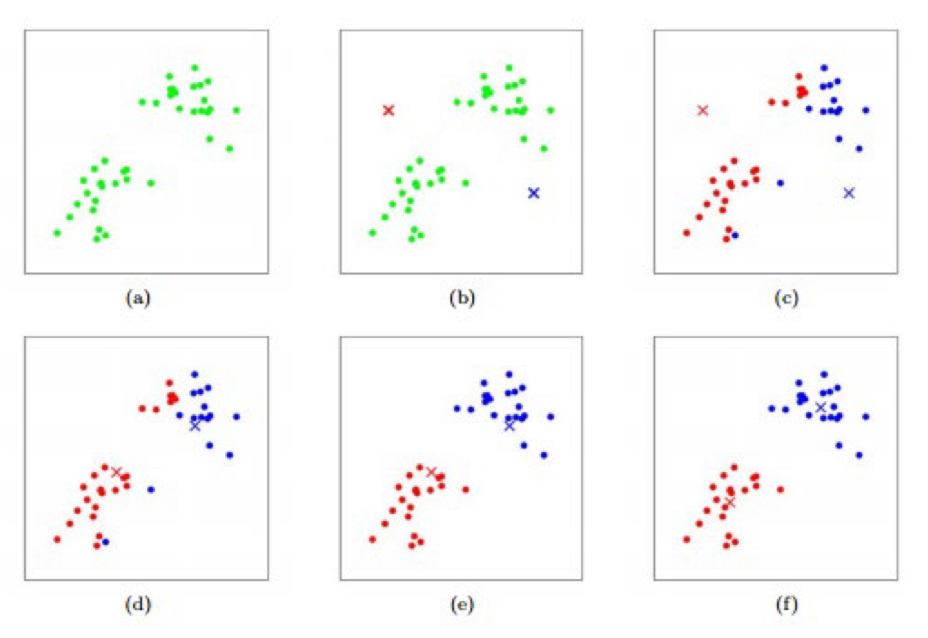
k-means는 Local optimum을 찾는 것이다.
global optimum을 찾을 수 있겠지만 조건이 매우 까다롭다.
(초기화에 따른 영향이 많이 있다. extremely sensitive.)
how to initialize?
- 초기화는 일반적으로 random하게 초기화한다.
- k-means++에서는 center들을 최대한 넓게 퍼져있도록("spread-out") 초기화
how to choose K?
-
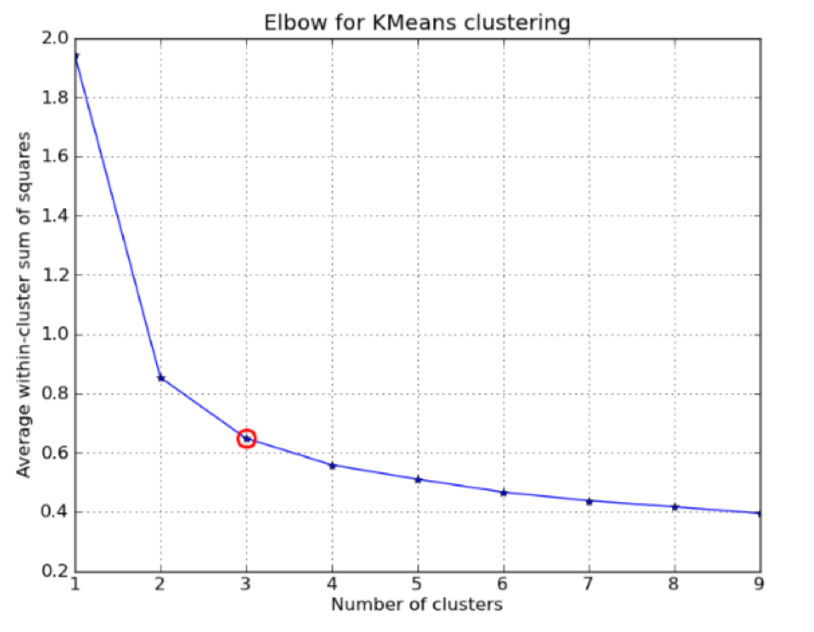
elbow point:
몇 개의 cluster가 최적인지 알 수 없다.
따라서 최적의 K를 결정하기 위해서는 모든 K를 해볼 수 밖에 없다.
각 K 별로 SSD를 계산하여 graph로 시각화해보면,
'elbow point'가 나타난다.
여기서는 cluster가 3인 부분에서 어느정도 SSD가 saturation된다.
너무 많은 cluster로 나누면, 똑같은 class를 너무 세분화하여 나눠질 수 있기 떄문에 좋지 않다.
-
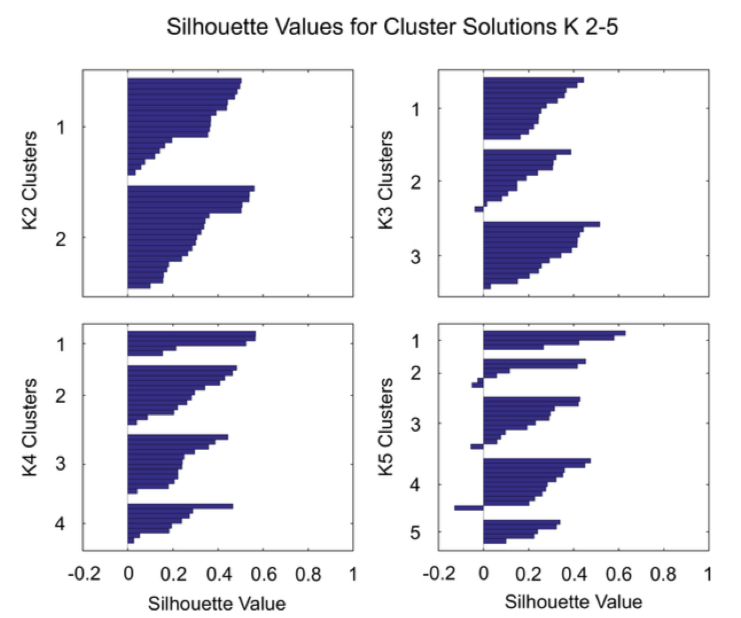
silhouette value (실루엣):
center쪽으로 data들이 뭉치는 속성과
cluster들끼 서로 멀어야 하는 속성이 있어야 좋은 cluster이다.
이러한 속성을 나타내는 지표.
graph가 빵빵하게 많이 차있는 것을 좋은 것으로 봄.
-
validation set
distance measure & termination
distance measure:- Euclidean (commonly used)
- Cosine
- non-linear (kernel method)
termination:- 미리 정해놓은 maximum number iteration에 도달했을 때, 종료
- assignment step에서 변화가 없을 때, 종료
Segmentation as clustering
-
단순히
intensity만으로 clustering할 수도 있고,
color similiarity로 clustering할 수도 있다. -
하지만 color로만 RGB image를 의미 있는 class로 segmentation할 수 없다.
-
이를 막기 위해
texture similarity를 고려한 clustering을 고려할 수도 있다. -
또한
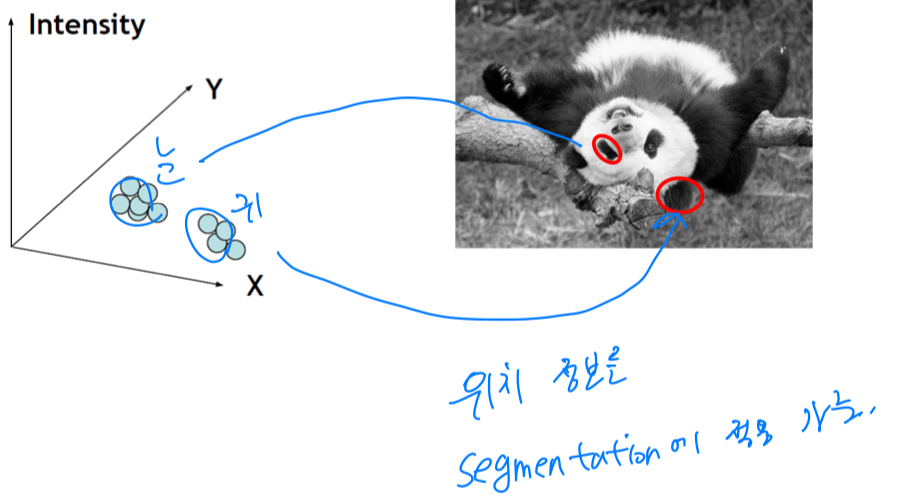
intensity + position similarity도 고려하여 clustering할 수 있다.
눈과 귀를 분류하기 어려운데, position 정보가 있다면 분류할 수 있다.
k-means limitations
-
hard assignment:
1 or 0으로 극단적인 cluster 선택. -
outlier example에 취약하다. -
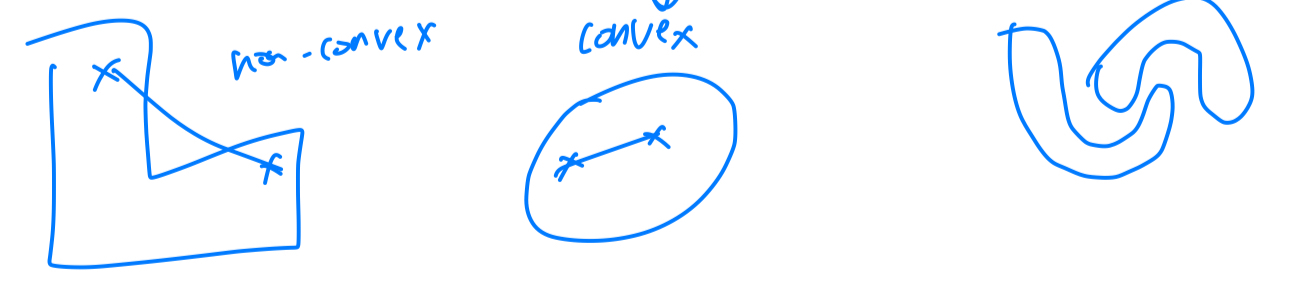
round shape에 대해서는 잘 작동하지만,
non-convex shape에 대해서는 잘 동작하지 않는다.
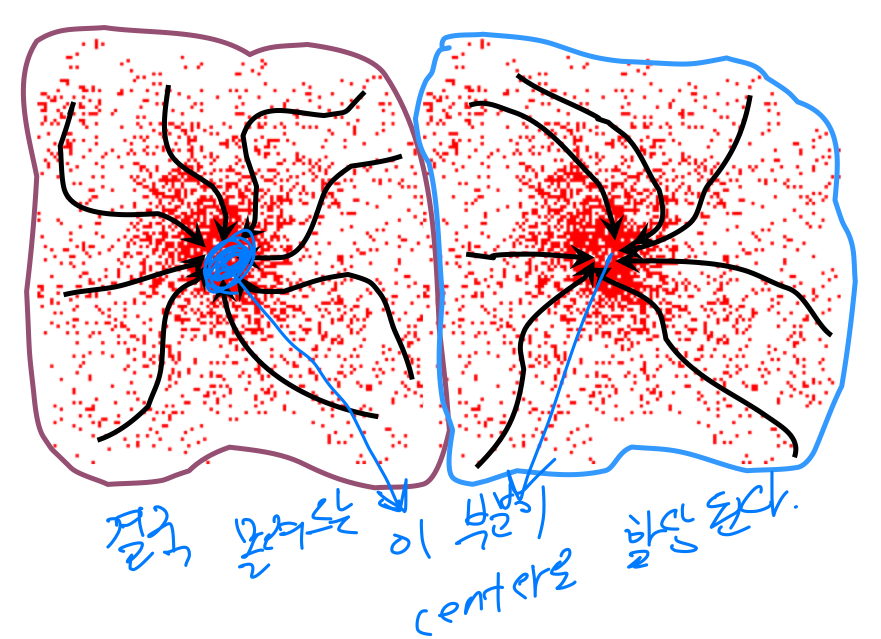
3. Mean-shift Clustering
-
assumption:
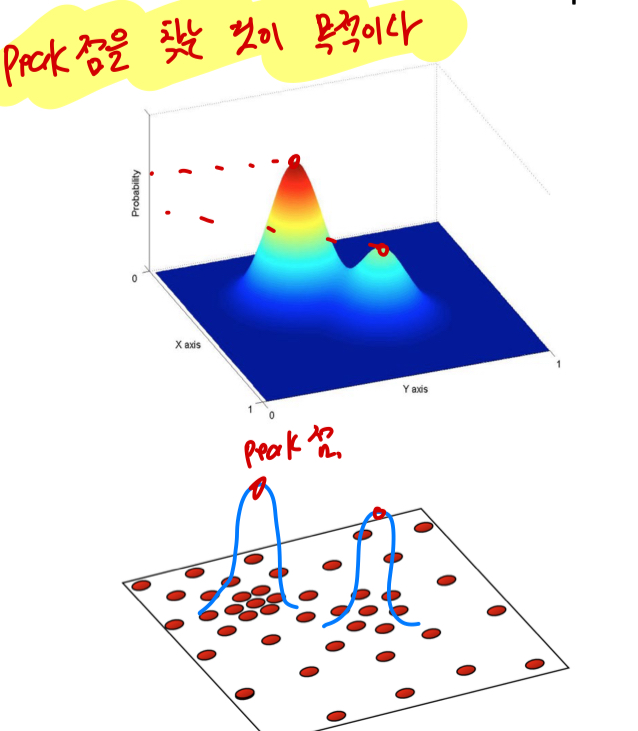
주어진 data들이 확률 밀도 함수(probability density function, pdf)에 존재한다는 가정.
data들을 확률 밀도 함수로 나타내었을 때, peak점을 찾는 것이 목적이다.
-
Mean-shift:Region of Interest(RoI)을 random하게 설정
관심영역(RoI)의 중심과 이 안에 속하는 data들의 무게중심(Center of mass)이 일치하지 않을 것이다.Center of mass 계산RoI를 center of mass로 옮김. 이떄, vector를 mean-shift vector라고 함
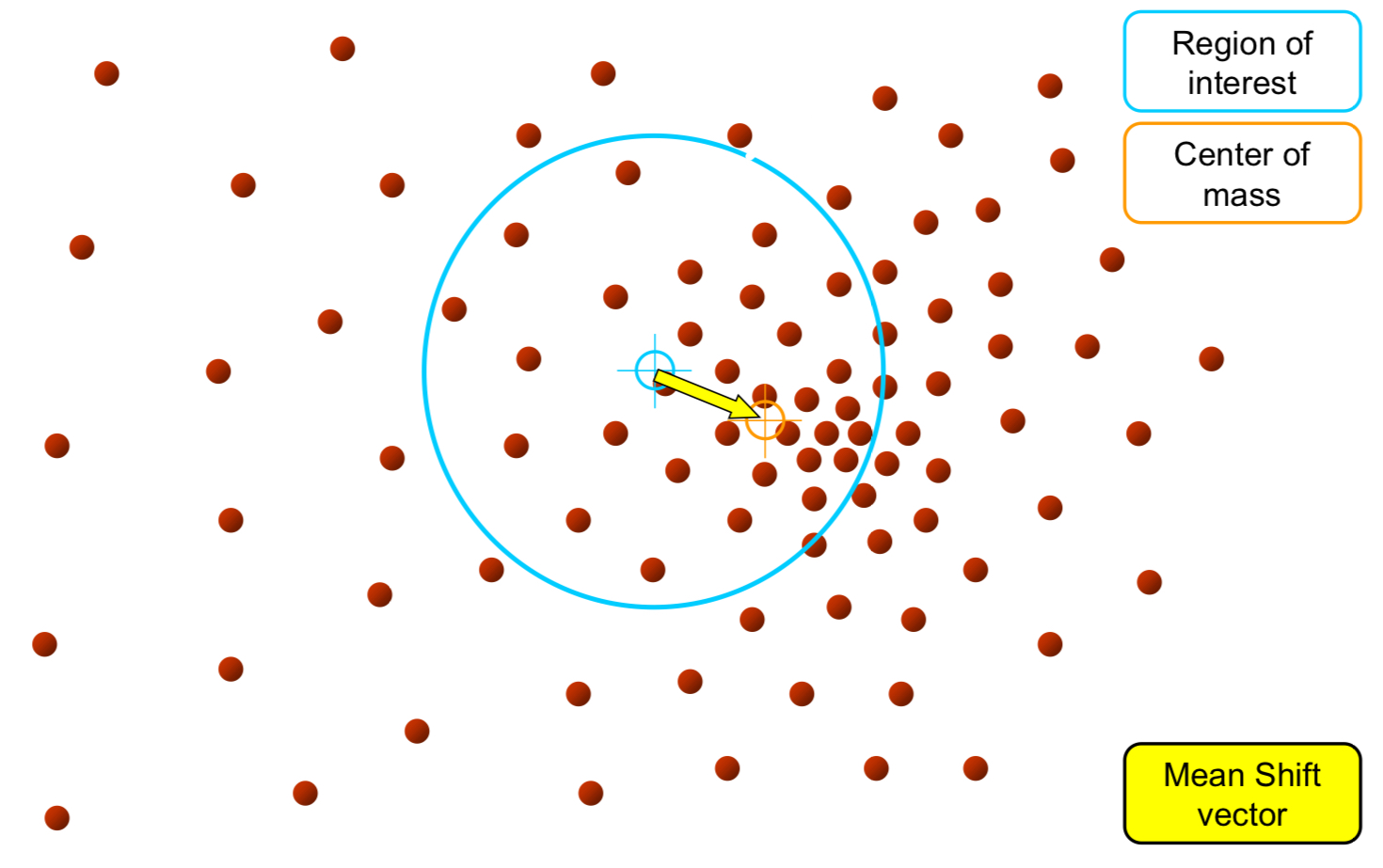
이렇게 점차점차 data의 밀도가 높은 곳으로 옮겨짐.
mean-shift vector가 0이 될 때까지 반복하여 수행.
-
Mean-shift algorithm은 cluster의 개수를 설정 안해도 된다.
attraction basin
- data들이 몰려드는 이 부분이 center로 할당 되는데, 그 부분을
attraction basin(분지)라고 함.