useRoutes 훅을 사용한 라우팅 구성
참고사이트: https://reactrouter.com/docs/en/v6/api#useroutes
원래 라우터로 구성한 코드를 다음과 같이 useRoutes를 통한 코드로 변경
App.js
import { useRoutes, Navigate } from 'react-router-dom';
import { Layout, Home, SignIn, SignUp, PageNotFound } from 'pages';
export default function App() {
const routesElement = useRoutes([
{
element: <Layout offset={120} />,
children: [
{ path: '/', element: <Home /> },
{ path: 'signin', element: <SignIn id='signin' /> },
{ path: 'signup', element: <SignUp id='signup' /> },
{ path: 'page-not-found', element: <PageNotFound /> },
{ path: '*', element: <Navigate to='page-not-found' replace /> },
],
},
]);
return routesElement;
}useLayoutEffect 훅을 사용한 라우팅 구성
헤더를 구성할 때, 헤더 자체가 fixed 설정이 되어있기 때문에 화면의 normal flow에서 떠버린다. 이를 위해 화면이 렌더링 될 때 useLayoutEffect를 사용하여 헤더의 높이를 계산해주는 작업이 필요하다.
useLayoutEffect는 클래스 컴포넌트의 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()와 비슷한 시기 (업데이트 되기 전)에 실행된다.
Layout.js
...
export default function Layout({ offset }) {
const headerRef = useRef(null);
let [headerHeight, setHeaderHeight] = useState(0);
useLayoutEffect(() => {
let { height } = headerRef.current.getBoundingClientRect();
setHeaderHeight(`${height + offset}px`);
}, [offset]);
return (
<Container>
<Header ref={headerRef} blur />
<Wrapper
as="main"
css={`
min-height: 100vh;
padding-top: ${headerHeight};
`}
>
<Outlet />
</Wrapper>
</Container>
);
}
...react-loading-icons 활용
참고사이트: https://www.npmjs.com/package/react-loading-icons
Form 컴포넌트 컴파운드 컴포넌트 패턴 활용
import 'styled-components/macro';
import { forwardRef, memo } from 'react';
import { string, bool, object, oneOf } from 'prop-types';
import { A11yHidden } from 'components';
import {
Form as StyledForm,
Container,
Headline,
Control,
Label,
Input,
IconSuccess,
IconError,
ErrorMessage,
Button,
Info,
} from './Form.styled';
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Form */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
export const Form = memo(
forwardRef(function Form({ css, ...resetProps }, ref) {
return <StyledForm ref={ref} css={css} {...resetProps} />;
})
);
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* FormContainer */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
Form.Container = memo(function FormContainer(props) {
return <Container {...props} />;
});
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* FormHeadline */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
Form.Headline = memo(function FormHeadline(props) {
return <Headline {...props} />;
});
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* FormInput */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
Form.Input = memo(
forwardRef(function FormInput(
{
id,
label,
type,
invisibleLabel,
error,
success,
children,
controlProps,
...restProps
},
ref
) {
let descId = `${id}__desc`;
return (
<Control {...controlProps}>
{invisibleLabel ? (
<A11yHidden as="label" htmlFor={id}>
{label}
</A11yHidden>
) : (
<Label htmlFor={id}>{label}</Label>
)}
<Input
ref={ref}
id={id}
type={type}
placeholder={children}
error={error}
success={success}
aria-describedby={descId}
{...restProps}
/>
{success && <IconSuccess />}
{error && <IconError />}
<ErrorMessage id={descId} role="alert" aria-live="assertive">
{error}
</ErrorMessage>
</Control>
);
})
);
Form.Input.defaultProps = {
type: 'text',
invisibleLabel: false,
error: '',
success: false,
};
Form.Input.propTypes = {
id: string.isRequired,
label: string.isRequired,
type: oneOf(['text', 'email', 'password']),
invisibleLabel: bool,
error: string,
success: bool,
children: string,
controlProps: object,
};
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* FormButton */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
Form.Button = memo(
forwardRef(function FormButton({ submit, reset, css, ...restProps }, ref) {
let buttonType = 'button';
if (submit) buttonType = 'submit';
if (reset) buttonType = 'reset';
return <Button ref={ref} type={buttonType} css={css} {...restProps} />;
})
);
Form.Button.defaultProps = {
submit: false,
reset: false,
css: null,
};
Form.Button.propTypes = {
submit: bool,
reset: bool,
css: string,
};
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* FormInfo */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
Form.Info = memo(
forwardRef(function FormInfo(props, ref) {
return <Info ref={ref} {...props} />;
})
);
memo와forwardRef두 가지의 고차컴포넌트를 사용하여 컴포넌트 컴파운드 패턴 구성
useMemo 대신 memo를 사용하여 컴포넌트 구성
페이지 별 코드 스플리팅
참고 사이트: https://reactjs.org/docs/code-splitting.html#code-splitting
React.lazy를 Suspense와 사용
lazy => 비동기 방식
Suspense는 무조건 fallback을 써주어야 함
import { lazy, Suspense } from 'react';
import { useRoutes, Navigate } from 'react-router-dom';
import { Loading } from 'components';
// Sync. Loaded Components
// import { Layout, Home, SignIn, SignUp, PageNotFound } from 'pages';
// Lazy Loaded Components (Async.)
const Layout = lazy(() => import('./pages/Layout/Layout'));
const Home = lazy(() => import('./pages/Home/Home'));
const SignIn = lazy(() => import('./pages/SignIn/SignIn'));
const SignUp = lazy(() => import('./pages/SignUp/SignUp'));
const PageNotFound = lazy(() => import('./pages/PageNotFound/PageNotFound'));
// App
export default function App() {
const routesElement = useRoutes([
{
element: <Layout offset={120} />,
children: [
{ path: '/', element: <Home /> },
{ path: 'signin', element: <SignIn id='signin' /> },
{ path: 'signup', element: <SignUp id='signup' /> },
{ path: 'page-not-found', element: <PageNotFound /> },
{ path: '*', element: <Navigate to='page-not-found' replace /> },
],
},
]);
return (
<Suspense fallback={<Loading message='페이지가 로딩 중입니다...' />}>{routesElement}</Suspense>
);
}모든 페이지를 하나로 번들링 하는 것이 아닌 필요할 때마다 페이지에 대한 js를 불러온다는 것을 알 수 있음(Network 탭에서)
react router의 lazy loading
현재 리액트 lazy는 무조건 페이지를 default로 내보내야만 작동이 가능함. 따라서 스플리팅을 하기 위해서는 이를 고려해서 코드를 작성해야한다.
참고 사이트: https://reactrouter.com/docs/en/v6/examples/lazy-loading
폼 유효성 검사
validator.js
/* eslint-disable no-useless-escape */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 아이디 체크 유틸리티
// ▸ 5 ~ 20자 — 영문, 숫자 조합
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
export const isId = (value, { min = 4, max = 19 } = {}) => {
const regExp = new RegExp(`^[a-z]+[a-z0-9]{${min},${max}}$`, 'g');
return regExp.test(value);
};
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 이메일 체크 유틸리티
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
export const isEmail = value => {
const regExp =
/^[0-9a-zA-Z]([-_\.]?[0-9a-zA-Z])*@[0-9a-zA-Z]([-_\.]?[0-9a-zA-Z])*\.[a-zA-Z]{2,3}$/i;
return regExp.test(value);
};
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 패스워드 체크 유틸리티
// ▸ [normal 모드] 6 ~ 16자 — 영문, 숫자 조합
// ▸ [strong 모드] 6 ~ 16자 — 영문, 숫자, 특수문자 최소 한가지 조합
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
export const isPassword = (value, { min = 6, max = 16, isStrong = false } = {}) => {
let regExp = null;
if (!isStrong) {
regExp = new RegExp(`^(?=.*\\d)(?=.*[a-zA-Z])[0-9a-zA-Z]{${min},${max}}$`);
} else {
regExp = new RegExp(
`^(?=.*[a-zA-z])(?=.*[0-9])(?=.*[$\`~!@$!%*#^?&\\(\\)\-_=+]).{${min},${max}}$`
);
}
return regExp.test(value);
};
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 폰 넘버 체크 유틸리티
// ▸ [normal 모드] 010-9814-1461
// ▸ [withoutHyphen 활성화] 010-9814-1461 or 01098141461
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
export const isPhoneNumber = (value, withoutHyphen = false) => {
value = value.toString();
if (withoutHyphen && value.length < 12) {
value = value.split('');
let firstNumber = value.splice(0, 3).join('');
let lastNumber = value.splice(value.length - 4).join('');
let middleNumber = value.join('');
value = `${firstNumber}-${middleNumber}-${lastNumber}`;
}
const regExp = /^01(?:0|1|[6-9])-(?:\d{3}|\d{4})-\d{4}$/;
return regExp.test(value);
};
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 체크 유틸리티
// ▸ 한글, 영문, 대문자, 소문자, 숫자, 공백, 특수문자 (_-/,.)
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
export const isCheck = (value, checkType = isCheck.types[0]) => {
const { types } = isCheck;
let regExp = null;
switch (checkType) {
// '영,대소문자,문자사이공백'
default:
case types[0]:
regExp = /^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z ]*$/;
break;
// '영,대소문자,숫자,문자사이공백,특수문자(-_/,.)'
case types[1]:
regExp = /^[a-zA-Z0-9-_/,.][a-zA-Z0-9-_/,.]*$/;
break;
// '한영'
case types[2]:
regExp = /^[a-zA-Zㄱ-힣][a-zA-Zㄱ-힣]*$/;
break;
// '한'
case types[3]:
regExp = /[ㄱ-힣]/;
}
return regExp.test(value);
};
isCheck.types = [
'영,대소문자,문자사이공백',
'영,대소문자,숫자,문자사이공백,특수문자(-_/,.)',
'한영',
'한',
];
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// validator
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
const validator = {
isId,
isEmail,
isPassword,
isPhoneNumber,
isCheck,
};
export default validator;SignUp.js
import 'styled-components/macro';
import { useRef, useState, useCallback } from 'react';
import { Helmet } from 'react-helmet-async';
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';
import { string } from 'prop-types';
import { isInputed, setDocumentTitle, isCheck, isEmail, isPassword } from 'utils';
import { Form } from 'components';
import { signUp } from 'services';
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* SignUp */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
import 'styled-components/macro';
import { useRef, useState, useCallback } from 'react';
import { Helmet } from 'react-helmet-async';
import { Link, useNavigate } from 'react-router-dom';
import { string } from 'prop-types';
import { isInputed, setDocumentTitle, isCheck, isEmail, isPassword } from 'utils';
import { Form } from 'components';
import { signUp } from 'services';
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* SignUp */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
export default function SignUp({ id, ...restProps }) {
const formRef = useRef(null);
const navigate = useNavigate();
const [name, setName] = useState('');
const [nameError, setNameError] = useState('');
const [nameSuccess, setNameSuccess] = useState(false);
const [email, setEmail] = useState('');
const [emailError, setEmailError] = useState('');
const [emailSuccess, setEmailSuccess] = useState(false);
const [password, setPassword] = useState('');
const [passwordError, setPassWordError] = useState('');
const [passwordSuccess, setPassWordSuccess] = useState(false);
const [passwordConfirm, setPasswordConfirm] = useState('');
const [passwordConfirmError, setPasswordConfirmError] = useState('');
const [passwordConfirmSuccess, setPasswordConfirmSuccess] = useState(false);
const handleChange = useCallback(
e => {
const { name, value } = e.target;
switch (name) {
case 'name':
// 조건: 사용자 입력 값이 한글인가요?
// 입력 값의 갯수는 2개 이상인가요?
let isValidName = isCheck(value, isCheck.types[3]);
let isValidLength = value.length > 1;
if (!isValidName) {
setNameError('이름은 한글만 입력이 가능');
setNameSuccess(false);
} else {
setNameError('');
setNameSuccess(true);
}
if (!isValidLength) {
setNameError('2글자 이상 입력해야 한다.');
setNameSuccess(false);
}
setName(value);
break;
case 'email':
if (isEmail(value)) {
setEmailError('');
setEmailSuccess(true);
} else {
setEmailError('이메일 형식으로 입력하세요.');
setEmailSuccess(false);
}
setEmail(value);
break;
case 'password':
if (isPassword(value, { min: 8 })) {
setPassWordError('');
setPassWordSuccess(true);
} else {
setPassWordError('비밀번호는 영문, 숫자 조합 8자리 이상 입력해야 합니다.');
setPassWordSuccess(false);
}
setPassword(value);
break;
case 'passwordConfirm':
if (password === value) {
setPasswordConfirmError('');
setPasswordConfirmSuccess(true);
} else {
setPasswordConfirmError('입력한 비밀번호와 동일하지 않습니다.');
setPasswordConfirmSuccess(false);
}
setPasswordConfirm(value);
break;
default:
}
},
[password]
);
const handleSubmit = useCallback(
e => {
e.preventDefault();
console.log(formRef.current); // <form />
// DOM form 요소 <- FormData()
const formData = new FormData(formRef.current);
// 서버에 전송할 객체
const requestData = {};
// 폼의 각 컨트롤이 사용자로부터 입력 받은 값을 순환해서 수집
for (const [key, value] of formData.entries()) {
if (key !== 'passwordConfirm') {
requestData[key] = value;
}
}
console.log(requestData);
// [서비스] 서비스를 통해 서버에 로그인 요청, 응답
signUp(requestData)
.then(response => {
navigate('/');
// [라우팅] 홈페이지로 이동 또는 로그인 한 사용자 페이지로 이동
// 프로그래밍 방식의 내비게이팅
})
.catch(({ message }) => console.error(message));
},
[navigate]
);
const handleReset = useCallback(e => {
setName('');
setEmail('');
setPassword('');
setPasswordConfirm('');
}, []);
let isAllInputed =
isInputed(name) && isInputed(email) && isInputed(password) && password === passwordConfirm;
return (
<>
<Helmet>
<title>{setDocumentTitle('회원가입')}</title>
</Helmet>
<Form.Container>
<Form.Headline id={id}>회원가입 폼</Form.Headline>
<Form ref={formRef} aria-labelledby={id} onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<Form.Input
id='userName'
label='이름'
autoComplete='user-name'
name='name'
value={name}
onChange={handleChange}
error={nameError}
success={nameSuccess}
>
이름을 작성합니다. (영문, 숫자 조합 6자리 이상)
</Form.Input>
<Form.Input
type='email'
id='userMail'
label='이메일'
autoComplete='user-email'
name='email'
value={email}
onChange={handleChange}
error={emailError}
success={emailSuccess}
>
이메일 주소를 올바르게 입력하세요.
</Form.Input>
<Form.Input
type='password'
id='userPass'
label='패스워드'
autoComplete='current-password'
name='password'
value={password}
onChange={handleChange}
error={passwordError}
success={passwordSuccess}
>
비밀번호를 입력하세요. (영문, 숫자 조합 8자리 이상)
</Form.Input>
<Form.Input
type='password'
id='userPassConfirm'
label='패스워드 확인'
autoComplete='current-confirm-password'
name='passwordConfirm'
value={passwordConfirm}
onChange={handleChange}
error={passwordConfirmError}
success={passwordConfirmSuccess}
>
입력한 비밀번호와 동일한 번호를 다시 입력하세요.
</Form.Input>
<Form.Button callToAction type='submit' disabled={!isAllInputed}>
회원가입
</Form.Button>
<Form.Button type='reset' onClick={handleReset}>
초기화
</Form.Button>
</Form>
<Form.Info>
이미 회원가입 했다면? <Link to='/signin'>로그인</Link> 페이지로 이동해 로그인하세요.
</Form.Info>
</Form.Container>
</>
);
}
SignUp.propTypes = {
id: string.isRequired,
};useState를 사용하여 상태관리를 하고 최종적으로 react router의
useNavigate를 통해 회원가입이 되면 페이지를 이동시켜줌.
validator라는 util을 따로 만들어서 사용하지 않고도 라이브러리를 사용하는 방법이 있다.
⬇️
참고 사이트: https://www.npmjs.com/package/validator
Context API
React 애플리케이션에서 Context API를 사용해 상태를 관리하는 방법을 학습한다.
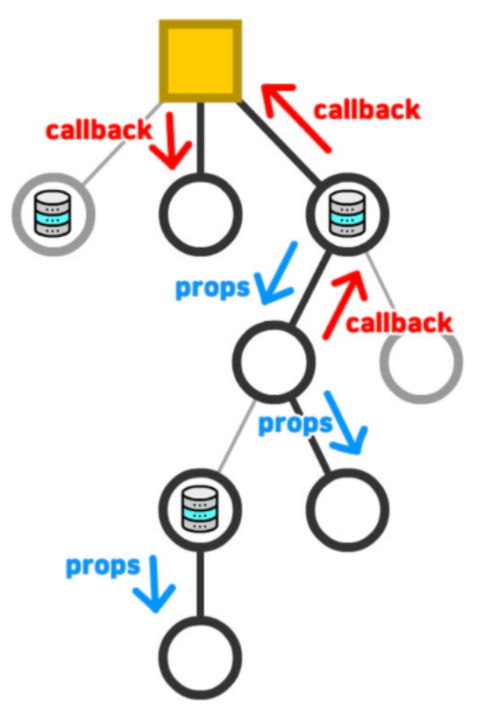
불행히 props, callback을 활용한 컴포넌트 상태 공유방법은 간단한 시나리오를 벗어나면 현실적이지 않다. 애플리케이션은 많은 컴포넌트가 상태를 가지고 있거나, 다른 컴포넌트와 공유(동기화)해 상호 작용 되어야 한다.
하지만 애플리케이션의 상태를 컴포넌트가 개별적으로 소유하다 보니 관리의 어려움이 생긴다. 자신의 상태를 하위 컴포넌트에 전송 → 전송 → 전송, 하위 컴포넌트에서 상위 컴포넌트로 콜백 ← 콜백 ← 콜백해 복잡하고 어려워진다.
컴포넌트 간 관계가 복잡해지면 props, callback은 관리가 어려워 지는 문제가 생긴다.
상태 공유 문제 해결방법
- 컨텍스트 활용

React는 중첩된 컴포넌트의 데이터 공유 문제를 해결하기 위한 방법으로 컨텍스트를 제공한다.
단, Context는 컴포넌트를 재사용하기 어렵게 만드므로 꼭 필요한 경우만 사용하는 것이 좋다.
- 상태 관리 라이브러리 활용
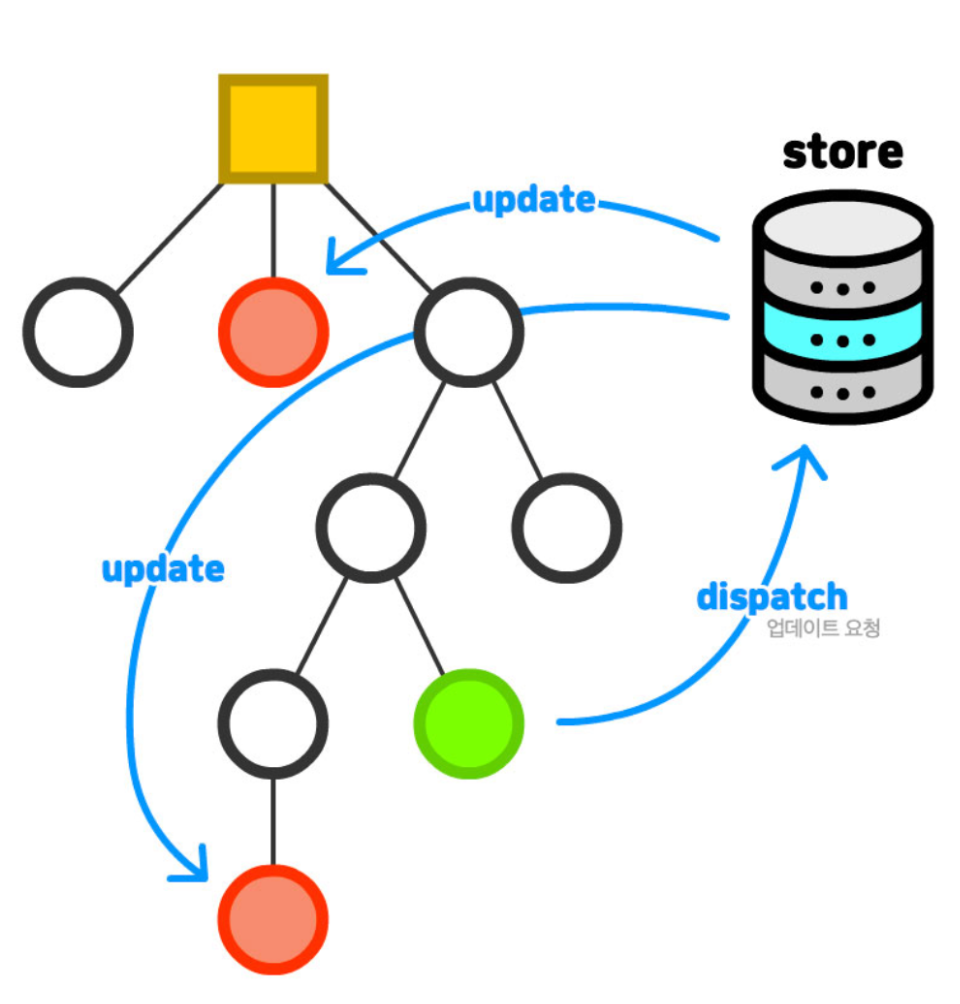
상태 관리 시스템은 상태 관리의 복잡한 문제를 해결하기 위해 고안되었다. 상태를 각 컴포넌트가 소유하는 데서 기인된 문제 해결 방안으로 모든 상태를 하나의 저장소에서 관리하도록 만든다.
이러한 접근 방법은 여러가지 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다. 복잡한 컴포넌트 계층을 위/아래로 탐색하지 않고도 상태를 공유할 수 있기 때문입니다. 대표적인 상태 관리 라이브러리로 Redux, Mobx, Vuex, XState 등이 있다.
인증을 위한 contexts 만들기
contexts/auth.js
import { createContext, Component, useState, useMemo, useContext } from 'react';
import { Navigate } from 'react-router-dom';
// 1. 컨텍스트 객체 생성
const AuthContext = createContext();
// console.log(AuthContext);
// 2. 컨텍스트 공급자를 사용해 value를 children(컴포넌트 트리)에 공급
export const AuthProvider = props => {
const [authUser, setAuthUser] = useState(null);
// 상태가 변할 때만 렌더링(불필요한 렌더링 방지)
const contextValue = useMemo(
() => ({
authUser,
setAuthUser,
}),
[authUser]
);
return <AuthContext.Provider value={contextValue} {...props} />;
};
// 3.0 Context.Consumer - render props 패턴
// 3.1 Class 컴포넌트 contextType 클래스 멤버 - 고차 컴포넌트(HOC) 활용
// 고차함수(함수컴포넌트) -> 향상된 클래스 컴포넌트
// React.forwardRef((props, ref) => {})
// React.memo(() => {})
// export const withAuth = FuncComp => {
// // 함수 컴포넌트 -> 클래스 컴포넌트(리턴, contextType 설정)
// class AuthHOC extends Component {
// static contextType = AuthContext;
// redner() {
// return <FuncComp context={this.context} {...this.props} />;
// }
// }
// };
// 위 방법을 사용하는 대신, 커스텀 훅 사용
// 3.2 컨텍스트 value를 반환하는 커스텀 훅(함수)을 작성
export const useAuth = () => {
// 빌트인 훅을 사용하는 특별한 함수 => 커스텀 훅(함수)
// 함수 컴포넌트 또는 다른 빌트인/커스텀 훅 안에서만 사용 가능
const contextValue = useContext(AuthContext);
if (!contextValue) {
throw new Error('useAuth 훅은 Auth Context 내에서만 호출되어야 합니다.');
}
return contextValue;
};
export const useAuthUser = () => useAuth().authUser;
export const useSetAuthUser = () => useAuth().setAuthUser;
// 4. 인증 라우팅을 보호하는 래퍼 컴포넌트
export const RequireAuth = ({ children }) => {
// 인증 사용자입니까?
const authUser = useAuthUser();
if (!authUser) {
// 아니오
// 로그인 페이지로 이동
return <Navigate to='/signin' replace />;
} else {
return children;
}
};
// ⬇️
// 5. constate 라이브러리 (context + state, 불필요한 렌더링 관리)index.js
import './reportWebVitals';
import { StrictMode } from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
import { HelmetProvider } from 'react-helmet-async';
import { GlobalStyle } from 'styles/global.styled';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { AuthProvider } from 'contexts';
import App from 'App';
render(
<StrictMode>
<GlobalStyle />
<BrowserRouter>
<HelmetProvider>
<AuthProvider>
<App />
</AuthProvider>
</HelmetProvider>
</BrowserRouter>
</StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);index부분에 auth관련 Context를 받을 컴포넌트 트리에
<AuthProvider>로 감싸주어 contextAPI를 사용한다.
