Machine_Learning 8. 이미지 처리
-목 차
1. 딥러닝
2. 이미지 분류
3. CNN을 활용한 이미지 분류
1. 딥러닝
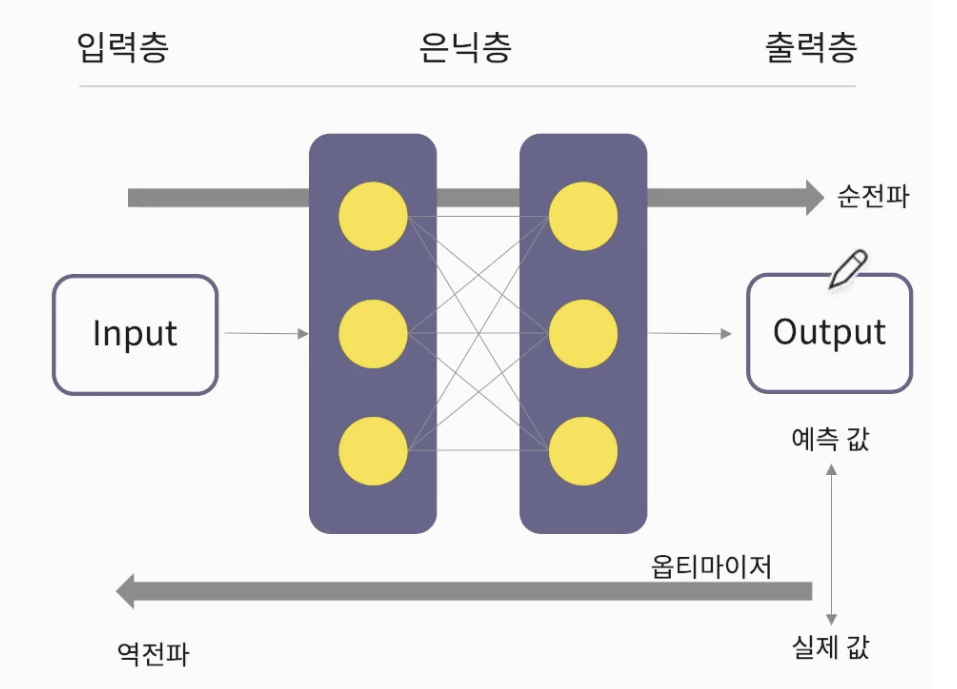
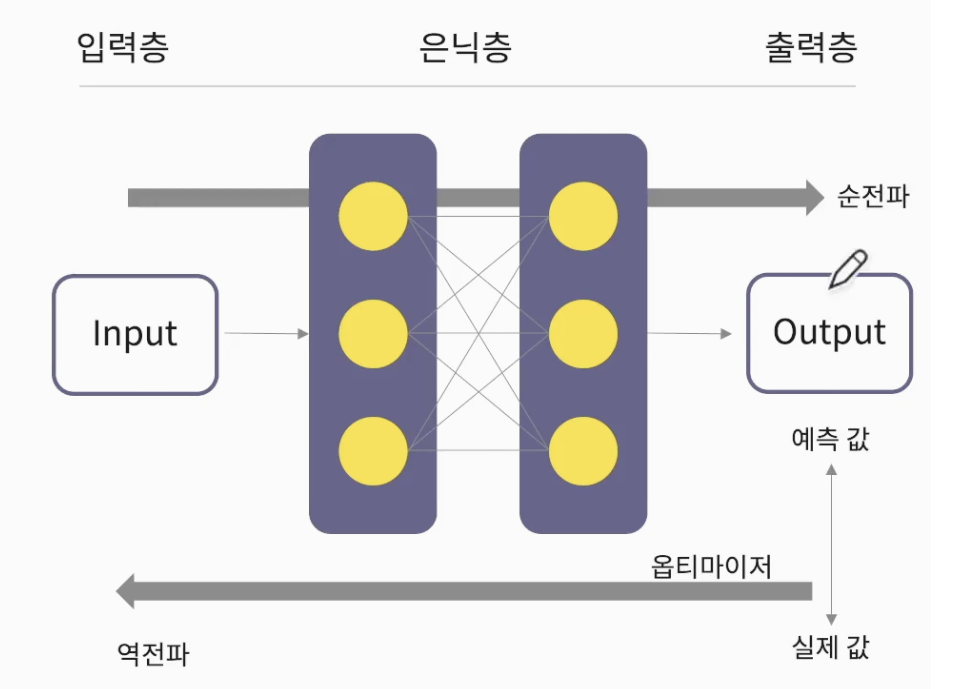
- 뇌의 뉴런과 유사한 머신러닝 알고리즘
- 심층 신경망 (DNN, Deep Neural Network)
- 입력층(Input Layer) - 은닉층(Hidden Layer) - 출력층(Output Layer)이 있음
(출력층 : 이진/다중 분류에 따라 출력의 개수가 달라진다)
[딥러닝의 학습 과정]
-
순전파 : 예측값(pred) 계산
-
손실함수 : 오차(error) 측정
-
Optimizer(최적화, 옵티마이저) : 경사 하강법
-
역전파: 가중치(W:weght) 조절
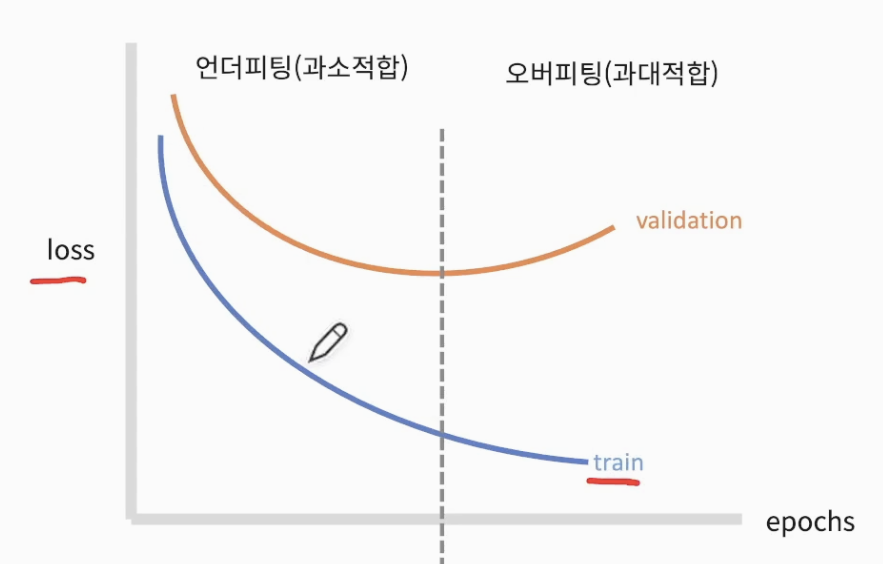
-
딥러닝은 오버피팅(과대적합)이 많이 발생한다
-
Validation 에서 loss 값이 올라가는 부분부터 오버피팅 지점
(잘 찾는 것이 관건) -
x축 epochs : 데이터셋 학습을 모두 끝낸 수 (N번 루프)
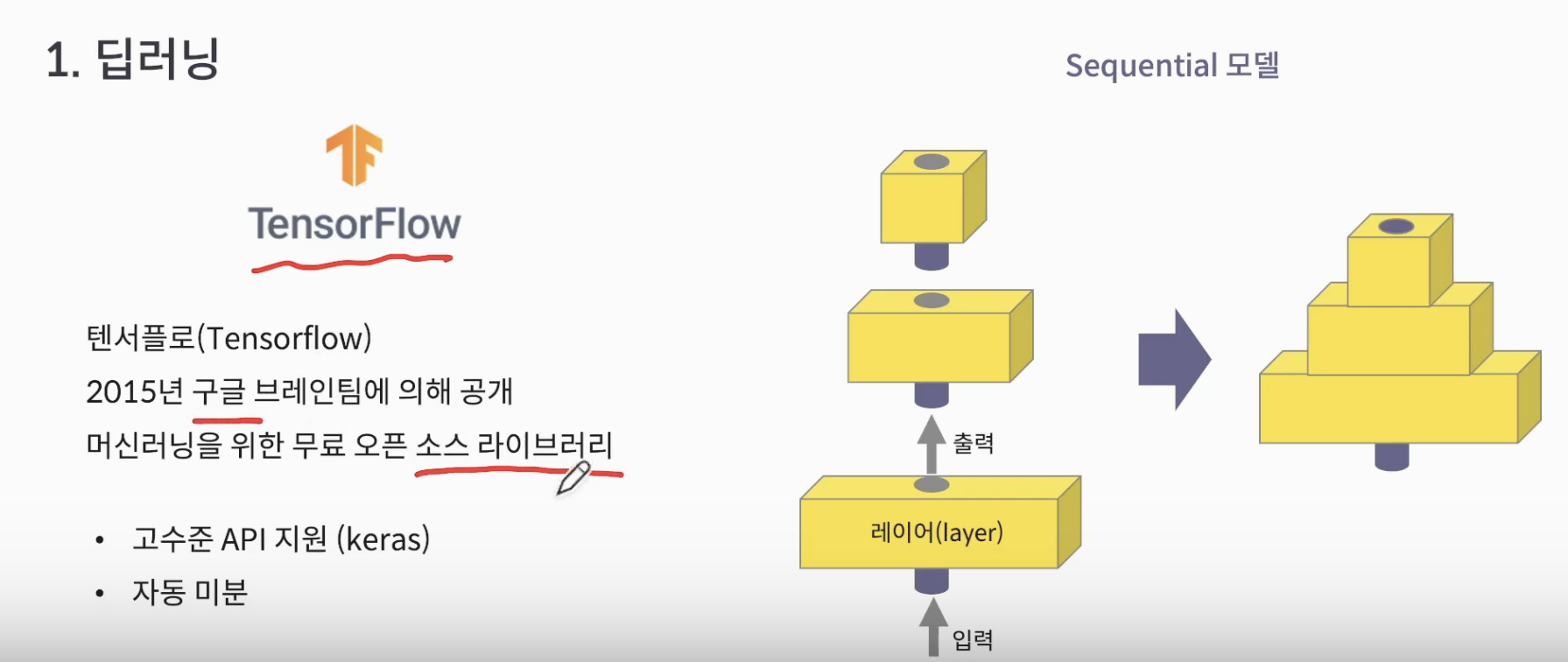
- 딥러닝을 쉽게 활용하기 위해 Tensorflow library 활용
- Sequential model : 원하는 Layer들을 만들어 쌓아서 만드는 모델
2. 이미지 분류
- 2가지 데이터 셋 활용할 예정
1) Mnist 손글씨 데이터
- Mnist : 손글씨 데이터, 흑백, 28x28 픽셀의 이미지
- 데이터셋이 0~9 까지 모양별로 구분 되어 있다 (class = 10개, 10개를 분류하는 모델)
# Sequential 모델 만들어보기
model = Sequential([
# Flatten Layer : 28x28 행렬을 1행으로 풀어준다
Flatten(input_shape(28,28),
# Dense Layer : 완전 연결 Layer, 뉴런의 수 128개, 활성화함수 relu 사용
# relu : 가장 흔히 사용, x값 0부터 값을 출력, 0 이전은 0 출력
Dense(units=128, activation='relu'),
# Dense Layer2(출력) : class 10개로 출력, 활성화 함수 softmax 활용
# softmax : class 마다 확률값 출력해서 그 중 가장 높은 확률 출력
Dense(units=10, activation='softmax')
])# 2번째 모델 compile(엮다) 진행
model.compile(
# 최적화 모델 'adam' 사용
optimizer='adam'
# loss 함수는 sparse_categorical_crossentropy(다중분류) 활용
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
# 행렬(차원) accuracy 활용
metrics=['accuracy']# epochs
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)# 이미지 분류 실습
# 라이브러리 호출
import tensorflow as tf
# 시각화를 위한 라이브러리 plt 호출
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# version 확인 (error가 생각보다 많이 나니 확인 하자!)
tf.__version__
# 데이터셋 호출
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 데이터 EDA(분석) 시작
# 데이터셋 크기 확인 (이 데이터셋은 train, test 데이터가 분리 되어 있다.
x_train.shape, y_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_test.shape
# 6만개 데이터(2차원 28x28), 6만개 데이터, 1만개 데이터(2차원 28x28), 1만개 데이터
>> (60000,28,28), (60000,), (10000, 28,28), (10000,)
# 데이터 확인
# 깔끔하게 출력 해보기 위해 np 호출, printoption 설정
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(linewidth=120)
print(x_train[0])
# 이미지로 확인
plt.imshow(x_train[0])
# label 확인
y_train[0]
# 전처리는 따로 필요없다(이미 깔끔하게 되어 있는 데이터셋)
# 모델 만들기
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Flatten, Dense
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
model = Sequential([
Flatten(input_shape=(28,28),
Dense(256, activation='relu'),
Dense(10, activation='softmax'
])
# 모델 요약
model.summary()
# compile
model.compile(
optimizer='adam',
loss = 'sparse_categorical_acrossentropy',
metics = ['accuracy']
# 학습 (딥러닝은 batch 활용, 디폴트 32, 데이터 학습 6만/32 = 1875개 학습)
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)
# 학습 정확도 (epochs에 따른 accuracy 변화)
# accuracy 확인, 그래프 표기는 acc
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='acc')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.legend()
2) Fashion-Mnist : 10개 클래스(이미지 종류), 그레이, 28x28 픽셀
# 이미지 분류 실습
# 라이브러리 호출
import tensorflow as tf
# 시각화를 위한 라이브러리 plt 호출
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# version 확인 (error가 생각보다 많이 나니 확인 하자!)
tf.__version__
# 데이터셋 호출
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 데이터 정규화 (0~1 사이)
# 픽셀 이미지는 채널값이 기본 255까지의 픽셀로 표현 되어 있기 때문에 255로 나눠준다(0~1 사이의 값으로 만들기 위함)
# 채널은 이미지에서 (높이, 너비, 채널(색상))
x_train, x_test = x_train/255.0. x_test/255.0
# 데이터 EDA(분석) 시작
# 데이터셋 크기 확인 (이 데이터셋은 train, test 데이터가 분리 되어 있다.
x_train.shape, y_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_test.shape
# 6만개 데이터(2차원 28x28), 6만개 데이터, 1만개 데이터(2차원 28x28), 1만개 데이터
>> (60000,28,28), (60000,), (10000, 28,28), (10000,)
# 데이터 확인(이미지)
plt.imshow(x_train[0])
# label 확인
# 위 x_train[0] 데이터가 뭔지 모르니 classes 리스트 생성
# 데이터셋에 있는 컬럼명
classes = [
'T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat',
'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot'
]
# print(classes[y_train[0]])
>> Ankle boot
# 전처리는 따로 필요없다(이미 깔끔하게 되어 있는 데이터셋)
# 모델 만들기
# Dropout Layer 추가 : Dense 같은 완전 연결이 아닌 랜덤하게 뉴런을 고르는 Layer
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
model = Sequential([
Flatten(input_shape=(28,28),
Dense(256, activation='relu'),
# 오버피팅 방지를 위한 20%만 드롭 아웃 시키자
Dropout(0.2),
Dense(10, activation='softmax'
])
# 모델 요약
model.summary()
# compile
model.compile(
optimizer='adam',
# 원핫 인코딩 진행한 데이터셋은 sparse 생략
loss = 'sparse_categorical_acrossentropy',
metics = ['accuracy']
# 학습 (딥러닝은 batch 활용, 디폴트 32)
# history 변수에 학습 과정 저장
# train 데이터도 학습, test(검증) 데이터도 학습
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
validation_data=(x_test,y_test), epochs=5)
# 학습 정확도 (epochs에 따른 accuracy 변화)
# accuracy 확인, Validation 데이터도 같이 확인
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='train')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='val')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.legend()
# loss 확인 (시각화)
plt.plot(history.history['loss'], label='train')
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label='val')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.legend()
# 예측
pred = model.predict(x_test)
pred[1]
# 가장 높은 값 찾기
np.argmax(pred[1])
# 예측한 label
classes[np.argmax(pred[1])]
# 실제 label
classes(y_test[1])
# 이미지 확인
plt.imshow(x_test[1])
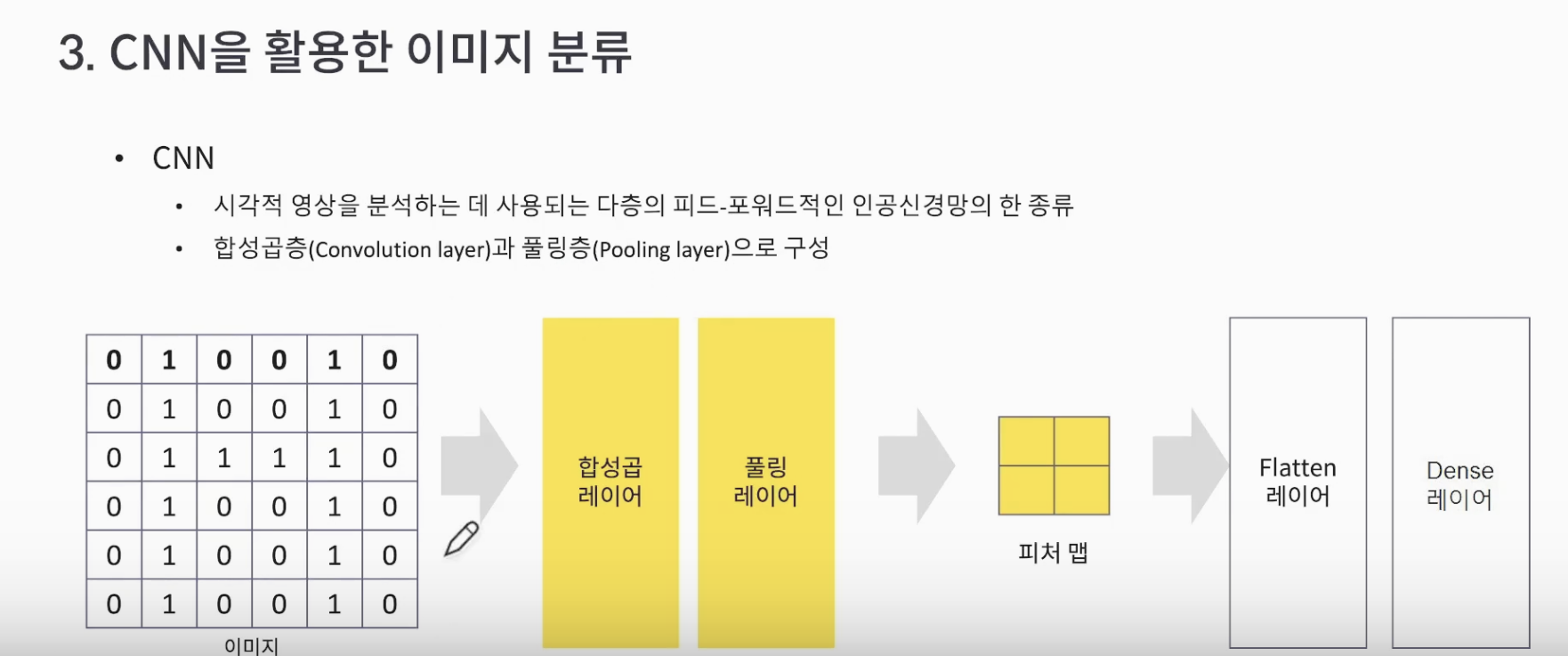
3. CNN을 활용한 이미지 분류
- 모델의 성능을 향상 시키기 위해 CNN (인공 신경망의 한 종류) 활용
- 시각적 영상을 다층의 피드-포워드적으로 분석
- 합성곱층(Convelution layer)와 풀링층(Pooling layer)로 구성
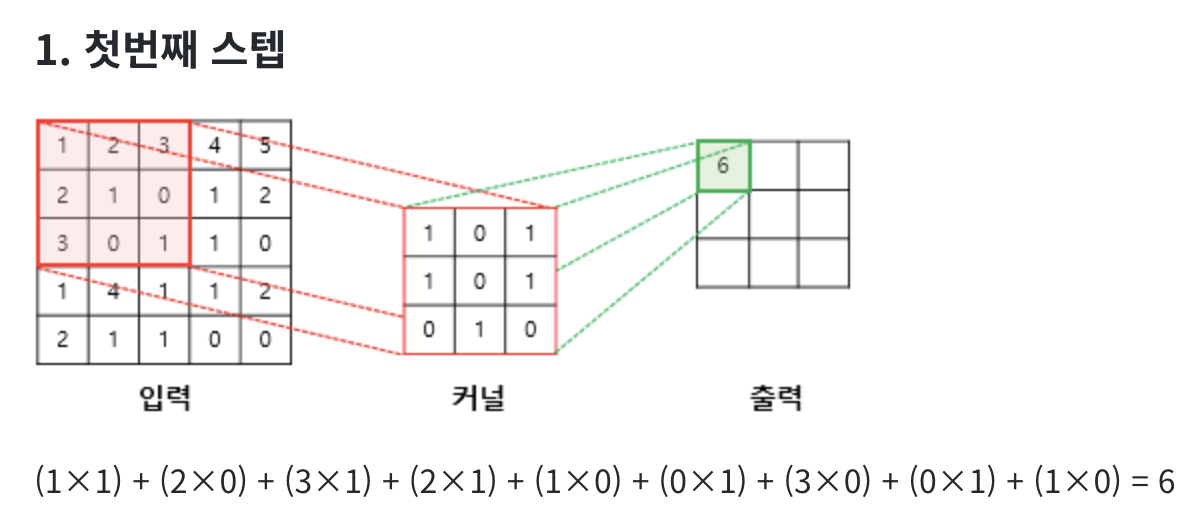
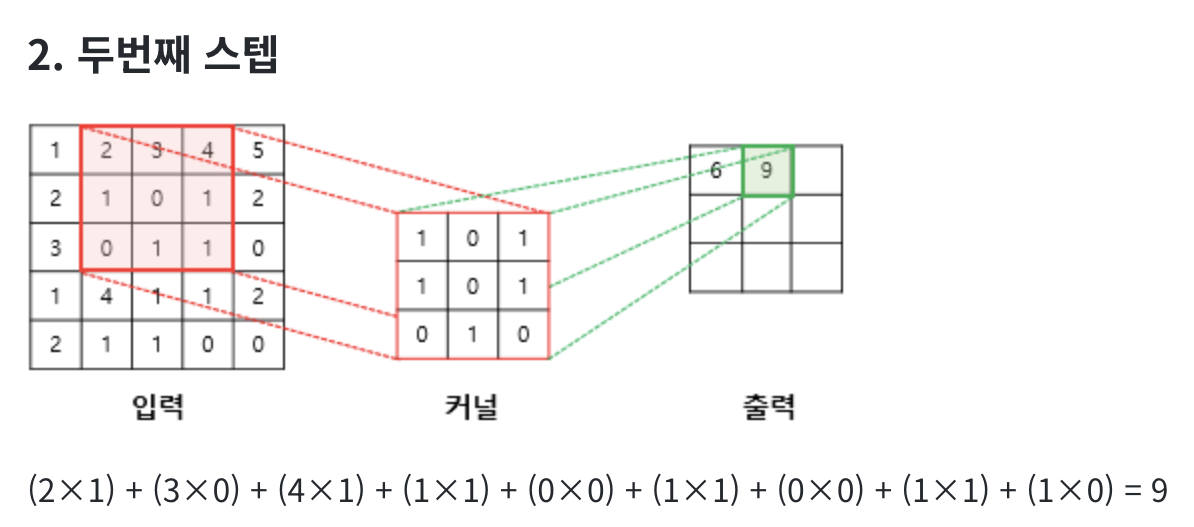
합성 곱 연산(Convolution operation)
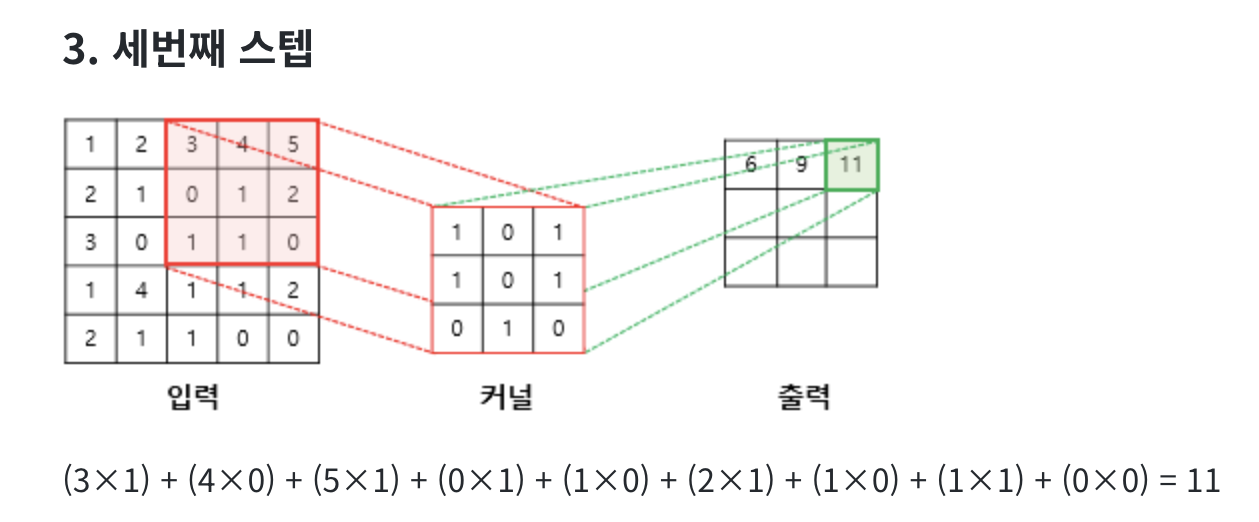
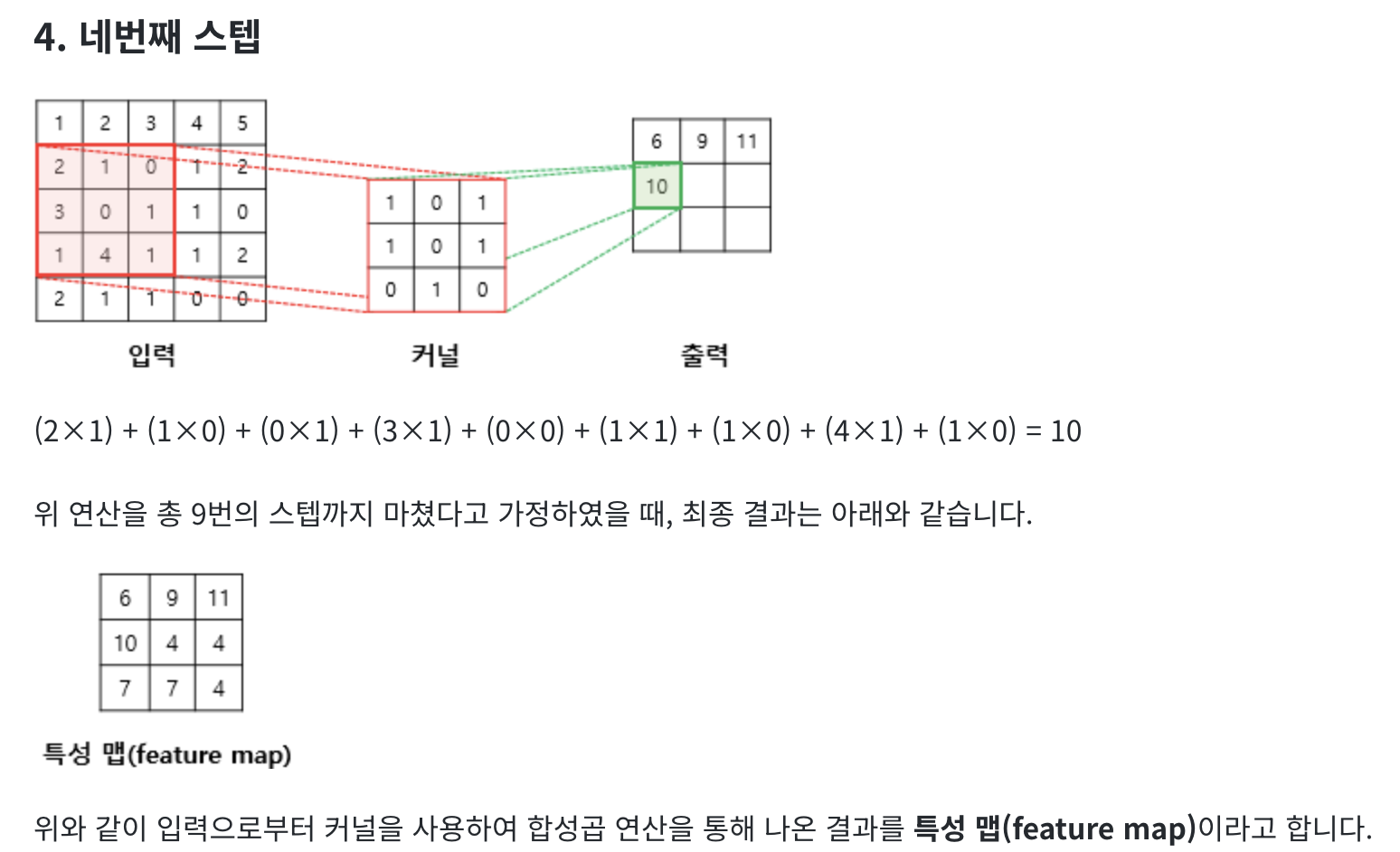
합성곱층은 합성곱 연산을 통해서 이미지의 특징을 추출하는 역할을 합니다. 합성곱은 커널(kernel) 또는 필터(filter) 라는 nxm 크기의 행렬로 높이x너비x크기의 이미지를 처음부터 끝까지 겹치며 훑으면서 nxm 크기의 겹쳐지는 부분의 각 이미지와 커널의 원소의 값을 곱해서 모두 더한 값을 출력으로 하는 것을 말합니다. 이때, 이미지의 가장 왼쪽 위부터 가장 오른쪽까지 순차적으로 훑습니다.
커널(kernel)은 일반적으로 3 × 3 또는 5 × 5를 사용합니다.
풀링(Pooling)
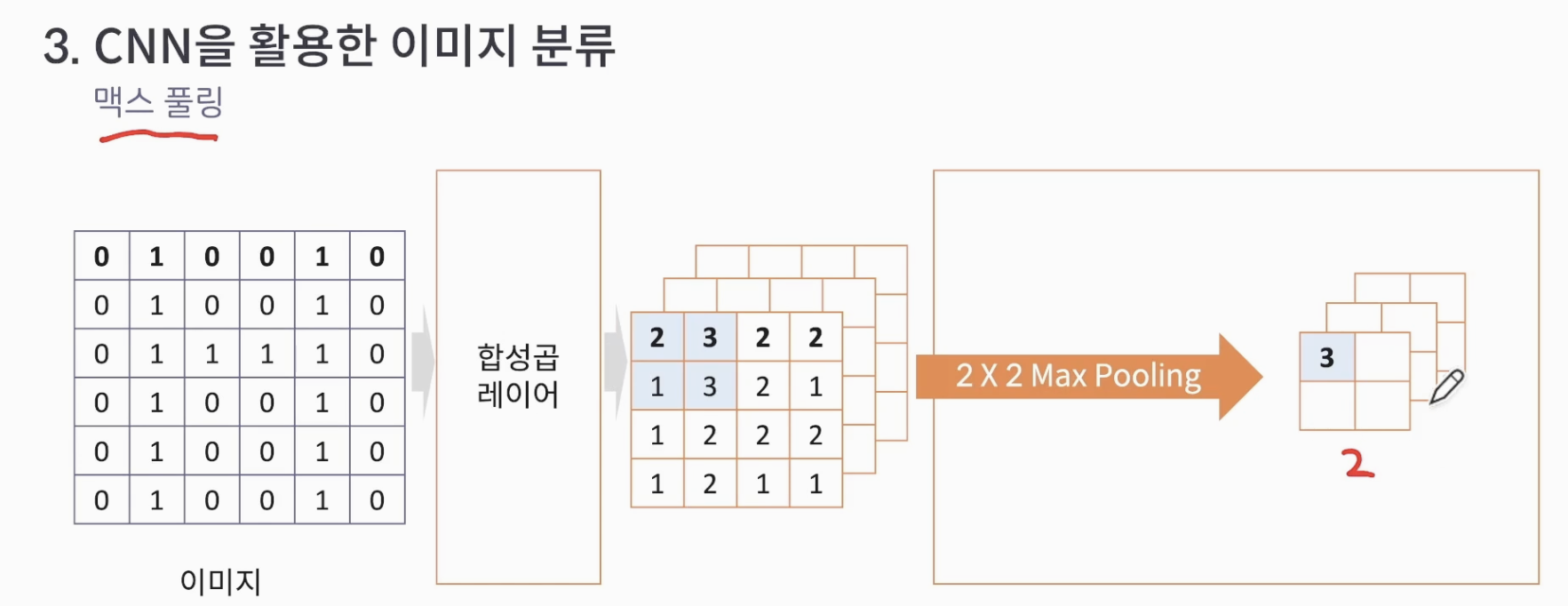
위 특성 맵을 Layer를 통해 결과를 출력합니다
- CNN 활용 코드
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, conv2D, MaxPooling2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
# 데이터 불러오기
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(x_train, y_train),(x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# shape 변경
# 채널 1 학습을 위해 추가, 흑백으로 바꾼 건가??
x_train = x_train.reshape((60000,28,28,1))
x_test = x_test.reshape((10000,28,28,1))
# 정규화
x_train, x_test = x_train/255.0, x_test/255.0
# 모델
model = Sequential([
# 합성곱, 커널 수 32개, 28x28을 커널 3 by 3 합성곱 하면 26x26이 된다 (3x3은 보통 -2)
Conv2D(32, (3,3), activation='relu', input_shape(28,28,1)),
# 합성곱에서 2x2로 나온 값 중 가장 큰 값 구하기 (절반으로 차원 감소)
MaxPooling2D((2,2)),
Con2D(64, (3,3), activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D((2,2)),
Flatten(input_shape=(28,28),
Dense(256, activation='relu'),
# 오버피팅 방지를 위한 20%만 드롭 아웃 시키자
Dropout(0.2),
Dense(10, activation='softmax'
])4. 과정 총 정리
이미지 분류
- 딥러닝
- 데이터 > 모델 > 컴파일
- 모델(keras Sequential) : 이미지 분류는 CNN(Conv,Pooling) 을 활용하여 성능 향상
- 컴파일(Optimizer, Loss, Metrics)하고 학습(fit, epochs)
- 검증(Val) 및 테스트(test) 시각화(plt) 검사