[Paper Review] Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training (GPT-1)
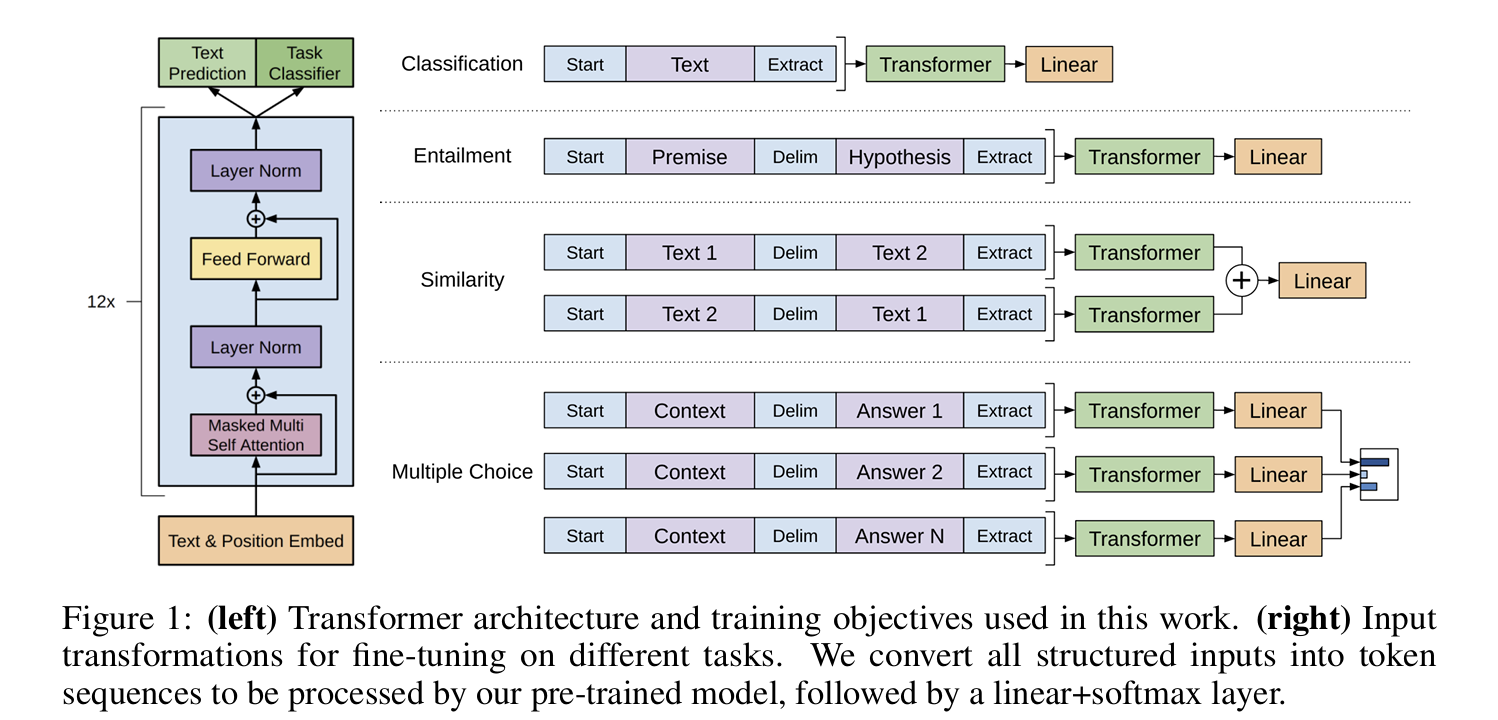
1. Overall Summary of the whole content
이 페이퍼는 Generative Pre-Training(GPT) 방식으로 자연어처리 성능을 개선하는 방법을 제안한다. (그 결과, 이전의 지도학습 기반 모델보다 더 적은 label data로 높은 성능을 달성.)
<제안된 방법론>
-
Generative Pre-Training: 대량의 비지도 데이터를 활용한 사전 학습 수행
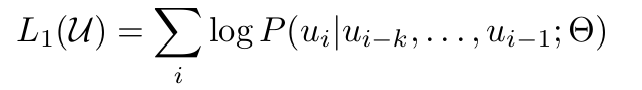
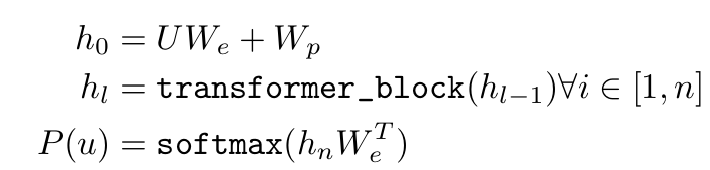
-
Fine-tuning(미세 조정): 사전 학습된 모델을 task별로 적은 label data로 조정
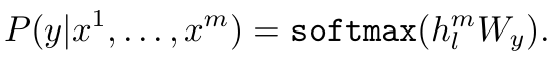
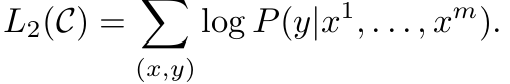
- 아키텍처: Transformer 구조를 기반으로, 기존의 RNN, LSTM보다 병렬화 및 성능에서 이점이 있음.
... we explore a semi-supervised approach for language understanding tasks using a combination of unsupervised pre-training and supervised fine-tuning.
... (생략) ...
For our model architecture, we use the Transformer, which has been shown to perform strongly on various tasks such as machine translation, document generation, and syntactic parsing. This model choice provides us with a more structured memory for handling long-term dependencies in text, compared to alternatives like recurrent networks, resulting in robust transfer performance across diverse tasks.
2. Details
(1) 사전 학습 기반 언어 모델의 필요성과 새로운 접근
-
기존의 NLP모델: task별로 훈련되었고, label data를 많이 필요로 함
-> task간의 일반화 어려움 + task별로 모델을 따로 학습이 필요하다는 비효율성 + 데이터 부족 문제 + 학습 비용 증가 -
논문에서 제안된 방법: 비지도(사전)학습을 통해 언어모델의 일반적 언어 이해 능력 학습, 이를 다양한 task에 적용가능하게 하여 학습 데이터 요구량 감소
(2) 제안된 방법의 한계와 향후 연구 방향
- 한계: task와 사전 학습 데이터 사이의 도메일 불일치가 있으면 성능이 저하되고, 모델 크기가 제한적이므로 대규모 데이터 활용에는 한계가 있다.
- 후속 연구: 다양한 task에서 성능 개선을 위한 사전 학습 방법 개선, 더 큰 규모의 모델과 데이터로 실험 확장(실제로도 GPT-2, GPT-3 등으로 연구가 이어짐).
(3) 연구에 대한 의문과 이에 대한 잠정적 답변
- 의문: 미세 조정 이전에 사전 학습 과정을 거치는 것이 어떠한 영향을 주는가?
- 잠정적 답변: Fine-tuning전에 사전 학습을 하지 않으면, 성능이 태스크 복잡도나 데이터의 양 등에 크게 의존하게 되므로, 미세 조정 이전 단계인 사전 학습이 초기 성능을 높이는 데 중요한 역할을 한다.
(4) 이론과 현실 간의 간극과 코드 구현 방법
- 이론과 현실의 괴리: 실제로는 메모리,GPU와 같은 하드웨어 자원과 모델 크기 등에 따라 제한을 받아 논문에서처럼 사전학습과 미세 조정을 모두 효율적으로 수행하기 어려워질 수 있다.
- 코드 구현: 딥러닝 프레임워크(pytorch, tensorflow 등)를 사용하여 Transformer구조를 구현할 수 있다.
(5) 아직 해결 못한 의문..
사전 학습 데이터가 특정 도메인에 대해 편향이 있으면 모델의 성능에 영향을 줄 것 같은데, 이후에 별다른 처리 없이 바로 미세 조정 단계로 넘어가도 특정 도메인에 대한 편중이 해결되는지, 아니면 그 영향이 미미해서 무시해도 되는건지 의문이 든다.
3. Conclusion
특정 task를 수행하기 위해 task별로 많은 레이블 데이터를 필요로 했던 기존의 NLP모델은 task간의 일반화를 잘 못했고, 데이터 수집 비용이 높았다. 하지만 언어 모델링 목표를 사용하여 신경망을 사전 학습한 후 감독을 통해 대상 작업에 맞게 미세 조정하는 방법을 통해 다양한 NLP task(natural language inference, text classification 등)에서 높은 성능을 달성하였다.
[Reviewed Paper]
https://cdn.openai.com/research-covers/language-unsupervised/language_understanding_paper.pdf
