Multicore Processor
하나의 computing component는 2개 또는 그 이상의 독립적인 core로 이루어져 있음
- Core (CPU)
- program instruction을 읽고 실행하는 computing 단위
- dual-core, quad-core, hexa-core, octa-core, ...
- share cache / not share cache
- symmetric or asymmetric
Core (CPU)
- Arithmetic operations
- add, sub, mul, div...
- Memory access
- read, write
- Control
- jump, test, branch
- Arithmetic operations
Intel Multicore CPU (Recent)
Intel Multicore CPU에는 Performace Core와 Efficiency Core가 있음

위 그림을 보면 8+16코어 부분이 적혀 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
이때, 8은 performace core, 16은 efficiency core를 나타낸다.
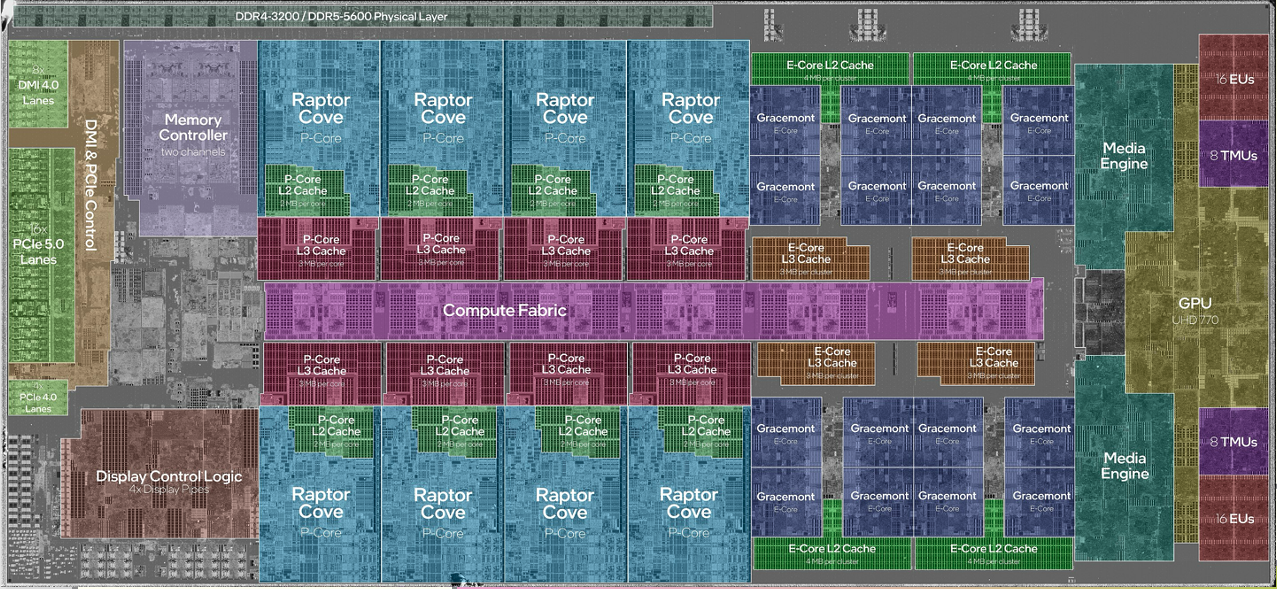
위 그림에서 Raptor Cove는 performance core, Gracemont는 efficiency core를 나타낸다. 이때 performance core가 큰 것을 확인할 수 있는데 이는 에너지를 절약하기 위해 efficiency core를 더 작게 만든다.
P-Core vs. E-Core
| 기능 | Performance Core | Efficiency Core |
|---|---|---|
| Role | high-performance task를 다룸 | power-efficient multitasking 관리할 때 이용 |
| Clock Speed | Higher (빠른 연산에 최적화) | Lower (power saving에 최적화) |
| Power Consumption | Higher (workload를 요구) | Lower (battery life를 향상) |
| Tread Support | Hyper-Threading 지원 1 core = 2 threads | No Hyper-Threading 지원 1 core = 1 thread |
| Workload Type | 하나의 thread 성능이 최고일 때 사용 | multi-thread나 background 작업 시 사용 |
| Ex. | Gaming, video editing, 3D rendering | Web browsing, document processing, background apps |
- Performance Cores
- 높은 performance 작업시 사용
- 높은 clock speed와 강한 processing power
- 높은 sing-core performance가 필요 시 사용
- Efficiency Cores
- low-power task를 위해 설계
- background program, multitasking, system maintenancedp tkdyd
- multi-core을 효율적으로 사용할 때 사용
Apple CPUs: M1 (2021), M3 (2023)
Apple은 이전에 Intel Processor를 사용했지만 최근 들어 자체적으로 CPU를 생산한다.
이때, GPU와 NPU가 있는데 GPU는 6000~8000의 computing 단위가 들어가 있고, NPU는 AI processor에 특화되어 있어 연산에 최적화가 되어 있다.
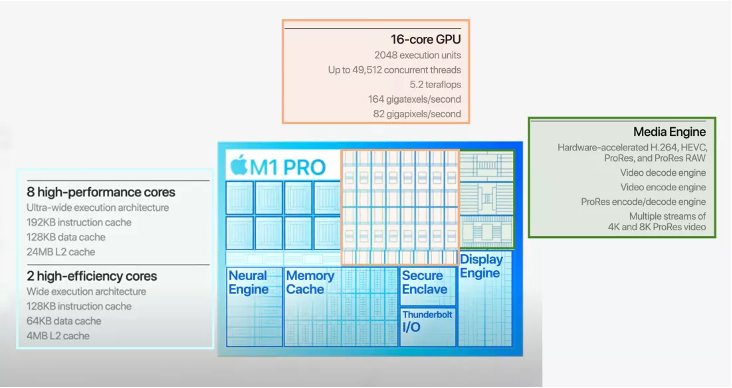
Apple Unified Memory
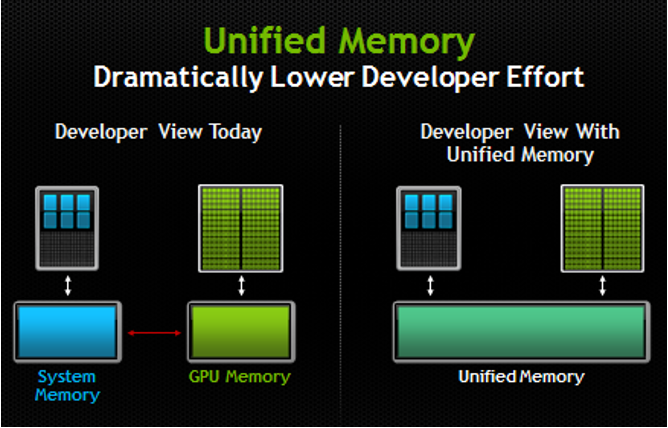 기존 memory는 data를 주고받는 과정이 필요하다. (왼쪽) 하지만 Apple은 자체 CPU를 사용하므로 CPU, GPU 둘다 memory에 접근이 가능하다.(오른쪽) 즉, CPU, GPU, NPU는 하나의 chip에서 memory를 공유하게 된다.
기존 memory는 data를 주고받는 과정이 필요하다. (왼쪽) 하지만 Apple은 자체 CPU를 사용하므로 CPU, GPU 둘다 memory에 접근이 가능하다.(오른쪽) 즉, CPU, GPU, NPU는 하나의 chip에서 memory를 공유하게 된다.
- 장점
- 효율적
- 단점
- 생산 이후, 수정할 수 없다.
- 이는 CPU, GPU, NPU가 다 연결되어 있으므로 변경이 힘들게 된다.
Multicore Processor
- Multiple core는 동시에 multiple instruction을 연산할 수 있다. (Concurrently)
- program의 전반적인 속도가 상승한다. (Performance)
- Software algorithm이나 구현에 대해 강하게 의존적이다.
- 이는 multicore processor를 동시에 사용하기 위해서는 코드를 짜야 실행이 가능하다.
- ex. Desktop PCs, mobile devices, servers
Manycore Processor (GPU)
multi-core architecture는 높은 수의 core를 가지고 있다. (주로 2000 cores)
(RTX 3080 Ti는 1024개의 processor를 가지고 있음)
- CUDA
- NVIDIA에서 제조
- GPGPU (General Purpose Graphics Processing Unit)
- OpenCL
- 표준 parallel programming platform
Parallel Applications
- Image and video processing
- 주로 image나 video는 여러 pixel로 구성되어 있다. 이를 짧은 시간 내에 생성하기 위해서는 동시에 pixel에 작성하는 과정이 필요하다.
- 3D graphics
- rendering, animation
- 각각 triangle mesh로 3D를 표현하게 되는데 이때 각 triangle을 독립적으로 처리
- 3D gaming
- Simulation
- protein folding, climate modeling
- Machine learning, deep learning
Thread/Process
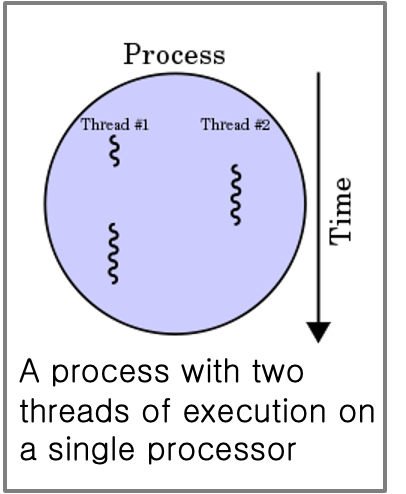
| Thread | Process | |
|---|---|---|
| 공동점 | 실행하기 위한 독립적인 sequence | |
| 차이점 | - 하나의 process 안에서 shared memory가 실행된다. - 하나의 process에는 multiple thread가 존재한다. | 독립적인 memory 공간에서 실행됨 |
- Multithreaded Program
- Program이 다중의 thread를 이용해 동시에 실행된다.
What is Parallel Computing?
- Parallel computing
- 여러 process를 병렬로 사용해 problem을 해결
- ex
- cluster computer
다양한 PC들을 결합해 높은 성능을 냄. physical로는multiple computer이지만 logical로는one computer - shared memory multiprocessor
하나의 memory system에 다양한 processor들이 연결되어 있음
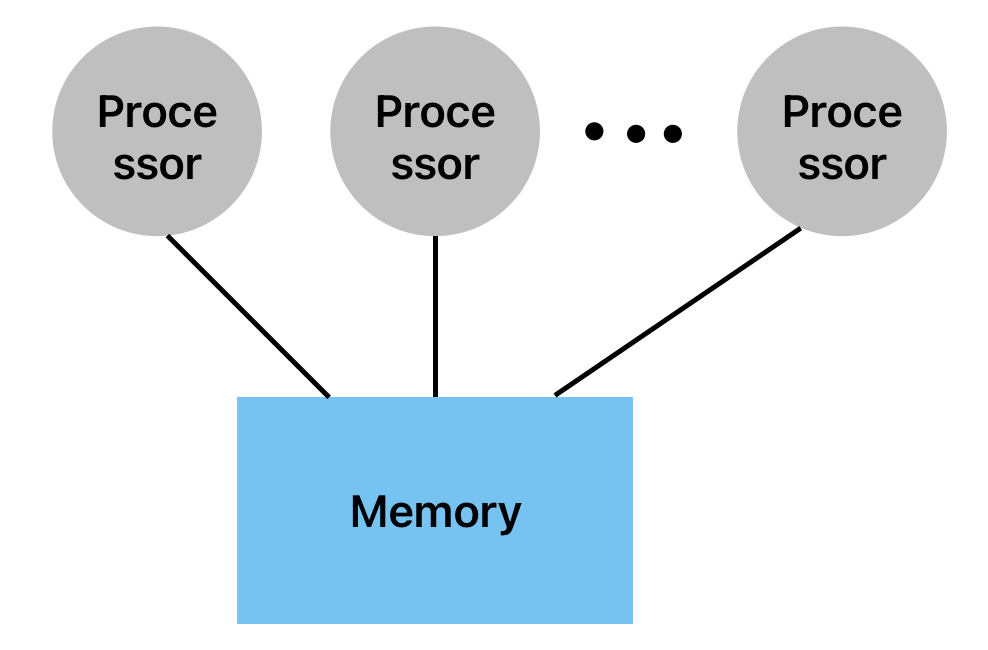
- Chip Multi-Processor (CMP)
하나의 chip 안에 여러개의 processor(cores)가 있음
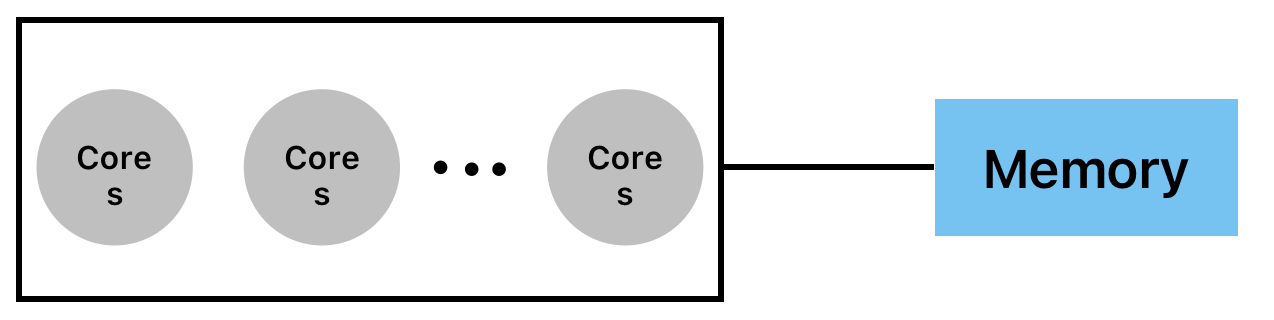
- cluster computer
Parallelism vs Concurrency
Parallel Programming
- 추가적인 computational resource들 필요
- 추가적인 자원을 효율적으로 어떻게 사용할까?
- ex. 다양한 n개의 processor들로 array의 숫자를 합함
- 기술
- Shared Memory
- OpenMP, pthreads
- 하나의 memory에 여러개의 process가 있음

- Distributed Memory
- 각 process별 memory가 하나씩 있음
- MPI
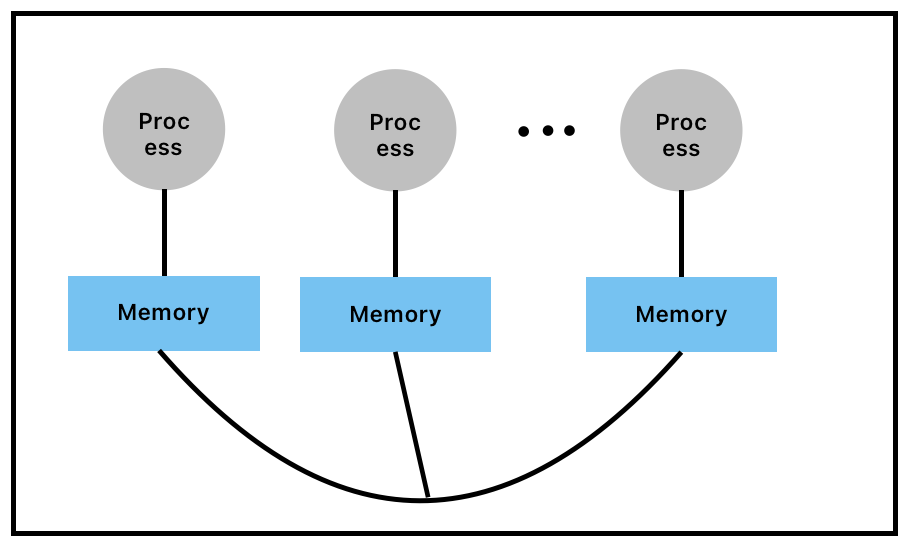
- Distributed/Shared Memory
- Hybrid (MPI + OpenMP)
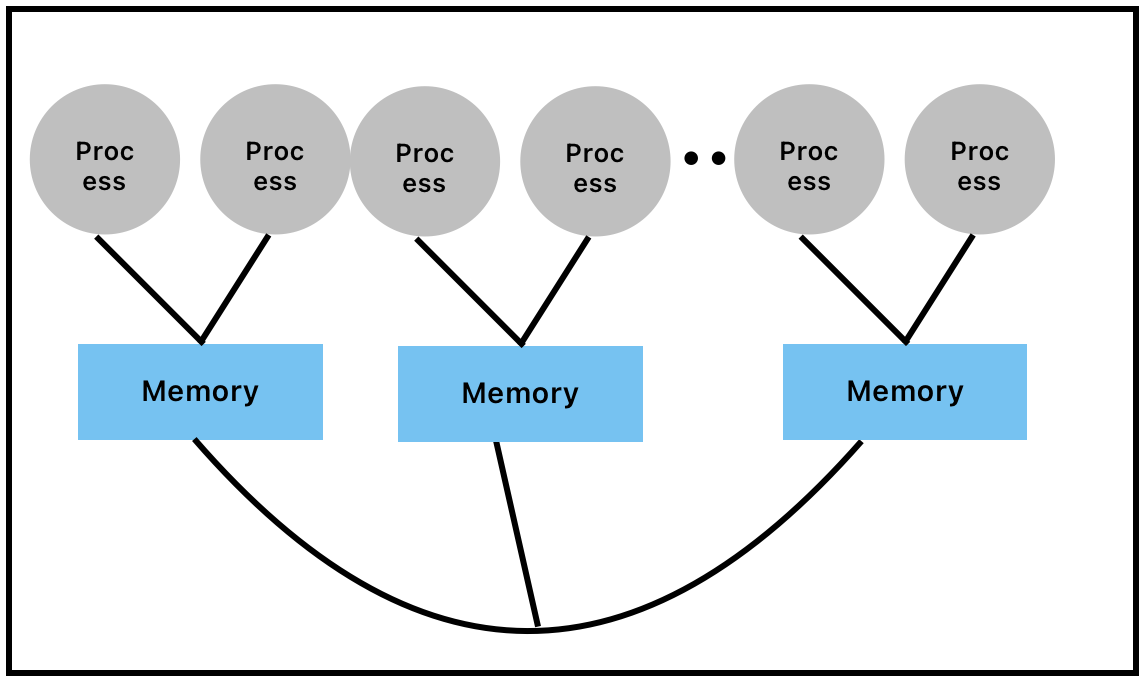
- Hybrid (MPI + OpenMP)
- GPU Parallel Programming
- CUDA programming (NVIDIA)
- OpenCL
- Shared Memory
Concurrent Programming
- 공유 자원을 다양한 thread들로 접근해 correctly하고 efficiently하게 control
- 서로 다른 thread에서 발생하는 연산의 잘못된 interleaving 문제를 예방
- interleaving : 연속적인 데이터를 섞어주거나 끼워 넣는 기법
- 주로 data를 access할 때 많이 쓰임
- ex
- hashtable인 dictionary 구성
- insert, update, lookup, delete가 동시에 일어남 (concurrently)
- 다양한 thread들로 같은 hashtable에 접근
- Web Visit Counter
- hashtable인 dictionary 구성
종종 Parallel과 Concurrent는 같은 의미로 사용됨
차이점
| 항목 | Parallel Programming | Concurrent Programming |
|---|---|---|
| 목표 | 작업을 동시에 수행 | 여러 작업을 동시에 다룸 |
| 예시 | 큰 배열을 여러 CPU 코어로 나누어 동시에 계산 | 사용자 입력을 기다리면서 백그라운드에서 파일 다운로드 수행 |
| 하드웨어 활용 | 여러 CPU 코어나 GPU 등 물리적 병렬성을 활용 | 한 개 또는 여러 개의 코어에서 논리적 병행성 표현 |
Parallel Computing vs. Distributed Computing
- Parallel Computing
- 모든 process들은 process 간 정보를 교환하기 위해 shared memory에 접근은 함
- Multi-threading과 긴밀하게 결합됨

- Distributed Computing
- multiple computer들이 network를 통해 통신함
- 각각의 processor는 개인 private memory를 가지고 있음
- 서로 다른 machine에서 sub-task들을 실행하고 결과를 통합

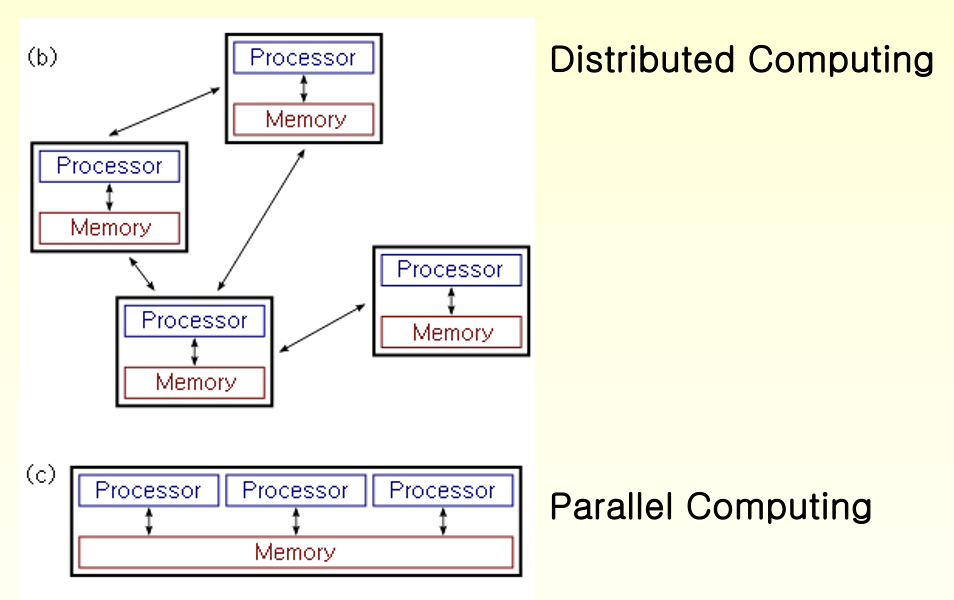
Distributed System
- Client/Server System
- Client : 요청을 보내는 것
- Server : 요청의 결과를 보내는 것
- 데이터 저장, 처리, ..등을 위해 중앙 서버와 상호작용하는 다수의 네트워크에 연결된 컴퓨터가 포함
- Peer-to-Peer System
- 중앙 기관에 의존하지 않고 peer들이 네트웨크 리소스, 연산 능력, data storage를 공유할 수 있는 컴퓨터 네트워크로, client와 server의 기능 모두 수행
- Middleware
- RPC (Remote Procedure Call)
- Three-tier
- N-tier
Distributed System의 특징
- Resource Sharing
- System 내에서 모든 Hardware, software, data를 사용할 수 있는 기능
- Openness (변화에 대한 개방)
- 시스템의 확장 및 개선 등 소프트웨어가 얼마나 공개적으로 개발되고 다른 사람과 공유가 되는지
- Concurrency
- remote location에 있는 별도의 사용자가 동일한 활동이나 기능을 수행
- 모든 local system에는 독립적인 운영체제 및 리소스가 있음
- Scalability (확장성)
- 시스템의 응답성을 개선하기 위해 다수의 processor가 더 많은 사용자와 통신할 수 있도록 수용하여 system 규모를 늘림
- resource가 늘어날수록 performance로 맞춰 늘어나는 것
- Fault tolerance (결함 내성)
- hardware나 software에 장애가 발생했을 때 시스템의 성능 저하 없이 계속 정상적으로 작동할 수 있도록 함
- ex. 수술에 정전이 일어나면 안됨
- Transparency
- Distributed system의 복잡성을 사용자 및 application에 숨김
- 투명성 : 내부 작동이 안보임 (internel complexity is invisible)
- Heterogeneity
- 네트워크, 컴퓨터 하드웨어, 운영체제, 프로그래밍 언어, 개발자 구현은 다양하고 분산된 시스템 구성마다 다를 수 있음
Challenges of Distributed System
- Network latency
- Distributed system의 통신 네트워크는 지연 시간을 유발해 시스템 성능에 영향을 줄 수 ㅣㅇㅆ음
- Design, algorithm에 의존
- Distributed coordination
- Distributed System은 node간의 조정이 필요한데 이는 시스템의 분산된 특성으로 힘들 수도 있음
- Deadlock...
- Data consistency
- Distributed System의 여러 node에서 data의 일관성을 유지하는 것은 어려울 수 있다.
- information update 비율 ⬆️
- 하나의 정보를 modify하면 다른 곳도 modifiy -> expensive
Cluster Computing vs. Grid Computing
둘 다 여러개의 computer를 연결해 대규모 연산을 수행한다는 공통점이 있음
Cluster Computing
- computer들이 loosely connected (computer가 network로 연결되어 있음) 되어 있어 single system으로 보임
- 서로 가까운 위치에 있는 컴퓨터들을 하나의 system처럼 동작하도록 구성
- 고속 네트워크 (LAN)으로 연결
- 한 작업을 여러 노드에 나눔
- 노드 간 긴밀한 협업
- price, performance가 좋음
- memory를 share하지 않음
Grid Computing
- 대규모 distributed system에 도달하기 위해 여러 위치의 computer resource들을 통합
- cluster computing보다 더 loosely coupled되어 있고, 지역적으로 떨어져 있음
- 전 세계에 분산된 컴퓨터를 네트워크를 통해 연결하여 연산을 분해
- 각 computer가 독립적인 system -> 대규모 분산 컴퓨팅
- 인터넷을 통한 네트워크 연결
- 각 컴퓨터가 독립적, 필요할 때 연산 참여
- 분산 환경에서 대규모 연산 수행
- 엄청난 연산 능력을 저비용으로 달성
- 각 computer가 독립적인 system -> 대규모 분산 컴퓨팅
Cloud Computing
(ubiquatous computing이라고도 함)
- application을 처리하기 위해 local server나 개인 기기를 사용하는 대신 network computing resource를 사용함
Good Parallel Program
- Correct (Result)
- 두 process 간 충돌이 일어날 수 있어서..
- 데이터 동기화, 경쟁, deadlock 등의 문제를 방지 -> 정확한 결과를 보장해야 함
- Good Performance
- 성능이 직렬보다 실제로 더 빨라야 함
- 즉, overhead를 줄여야 함
- Scalability
- CPU core 수 증가, cluster node 추가시 성능이 선형적으로 증가
- Load Balance
- Load Balance가 좋지 않으면 Scalability는 좋은 성능을 내지 않을 것
- 즉, 모든 core가 균등한 작업을 수행하도록 해야 함
- Portability
- 특정 hardware에 종속 X -> 다양한 platform에서 실행 가능
- Hardware Specific Utilization
- 하드웨어 특성 최대한 활용
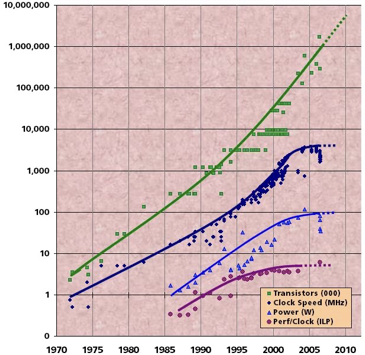
Moore's Law
- integrated circuits의 transistor의 수는 약 2년마다 2배로 증가한다.
- microprocessor는 더 작고, 더 밀집되고, 더 강력해진다.
Computer Hadware Trend
- Chip density는 2년마다 2배씩 증가하지만 clock speed는 그렇제 않다.
- 높은 clock speed에서는 power consumption과 Heat generation이 너무 높아 견딜 수 없다.
- core의 수는 2배가 될 수도 있다.
- Transistor의 수는 지속적으로 증가
- Clock speed는 평준화 됨
Example of Parallel Computer
- Chip MultiProcessor (CMP)
- Intel Core Duo
- AMD Dual Core
- Symmetric Multiprocessor (SMP)
- Sun Fire E25K
- Heterogeneous Chips
- Cell Processor
- Clusters
- Supercomputers
Chip MultiProcessor (CMP)
Intel Core Duo
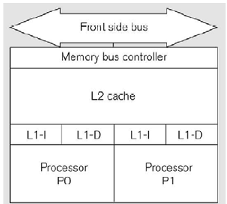
- 2개의 32 bit pentium processor를 가지고 있음
- processor 각각은 32K L1 cache를 가지고 있음
- 2MB나 4MB인 L2 cache를 가지고 있음
- L2 cache를 공유함으로써 빠른 통신 속도를 가짐
- shared memory를 가지고 있음
AMD Dual Core
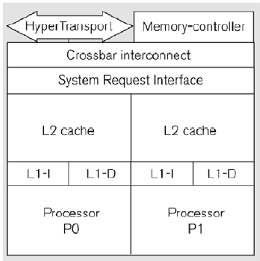
- processor 각각 64K L1 cache와 1MB L2 cache를 가지고 있음
- shared memory를 가지고 있음
Symmetric Multiprocessor (SMP)
Generic SMP
- Systemmetric MultiProcessor (SMP) System
- multiprocessor hardware architecture를 가짐
- 하나의 shared memory에 여러 processor가 연결되어 있음
- OS가 다룸
- 하나의 logical memory image를 가짐
- shared bus는 bottleneck를 가짐
GPGPU : NVIDIA GPU
- Tesla K20
- GTX 680
Hybrid Programming Model
- Main CPU가 병렬화 하기 어려운 부분을 수행
- 연결된 processor (GPU)는 intensive한 부분을 수행
Parallel Computing의 원리
- Finding enough parallelism (AmdahI's Law)
- granularity
- Locality
- Load balance
- Coordination and synchronization
➡️ 위 모든 것이 parallel programming을 sequential programming보다 어렵게 만든다.
Finding Enough Parallelism
- application의 일부만 parallel로 표시된다고 가정
P = processor의 개수
s는 sequentially 함수, (1-s)는 parallelizable 함수
Parallel 부분이 빨라져도 sequential 부분이 느려진다.
Overhead of Parallelism
- enough parallel 작업을 위해 큰 장벽이 존재함.
- thread 또는 process의 시작 비용
- shared data의 통신 비용
- synchronizing 비용
- 추가적인 (중복적인) 계산
- Tradoff 관계에 있음
- algorithm이 병렬로 빠르게 실행되려면 큰 작업 단위가 필요함
Load Imbalance
- Load imbalance는 불충분한 parallelism과 동일하지 않은 task의 size로 인한 processor가 idle을 가지게 되는 시간
- 즉, algorithm은 balance load가 필요함
- hyper-threading
- performance ⬆️ (best 20%, 30%..)
- CPU 내부에는 여러 unit이 있지만 100% 활용 X
- hyper-threading은 idle 자원을 활용해 다른 thread들도 함께 실행

