In the last post, I discussed the modularity of SAP ERP. It offers a variety of functionalities, allowing companies to choose and implement only the modules they need. This can reduce the effort required to build an entire system and potentially lower costs, especially when compared to on-premise solutions using cloud infrastructure. But before diving deeper into each functionality, we need to better understand how the overall system works.
SAP operates through a range of products. Not only does* it offer S/4HANA, but there are also many other solutions like SuccessFactors and Ariba. These can be categorized by product type.
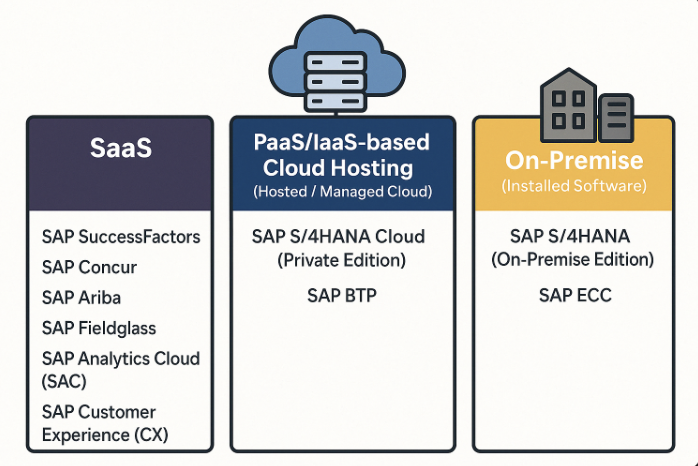
(1) SaaS (Software as a Service)
- SAP SuccessFactors (인사관리, HR management)
- SAP Concur (출장 및 경비관리, Travel and expense management)
- SAP Ariba (구매 및 조달관리, Procurement)
- SAP Fieldglass (외부 인력 관리, External workforce management)
- SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) (비즈니스 인텔리전스 분석, Business intelligence)
- SAP Customer Experience (CX) (고객 경험 관리, Customer experience management)
: These services can be used without the need to build or maintain infrastructure. By simply subscribing, users can access them through a web interface. SAP handles everything from updates and backups to security.
(2) PaaS/IaaS-based Cloud Hosting (Managed by SAP or Partners)
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud (Private Edition)
→ A dedicated S/4HANA environment deployed on cloud platforms like AWS or Azure - SAP BTP (Business Technology Platform)
→ A platform to develop or extend applications (PaaS)
: These systems are built on the cloud (with servers located outside the company) but can be customized to meet specific organizational needs. SAP or a certified partner builds and manages the infrastructure, and the company accesses it as a service.
(3) On-Premise (Installed Software)
- SAP S/4HANA (On-premise Edition)
- SAP ECC (legacy ERP system)
- Some industry-specific solutions and tools like SAP GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) are also available as on-premise options
: In this model, the organization is fully responsible for building, operating, and securing the system. It requires owning IT infrastructure and employing internal developers. This setup is especially preferred by large enterprises and public sector organizations.
And what I mentioned about modularity applies only to types (2) and (3). The products listed above are independent solutions, while modules exist within ERP systems like ECC or S/4HANA. The most representative ERP product is SAP S/4HANA. Understanding the difference between modules and products is key to grasping how SAP systems are structured.
✔️ Not only로 문장이 시작할 때는 앞문자에 도치가 이뤄져야 한다.
✔️ Next post preview
- SaaS, PaaS, IaaS에 대한 깊은 설명
- SAP의 여러 제품군 소개
