0. 개요 및 복습
주제 : 딥러닝
목표 : 머신러닝에서 나아가 딥러닝에 대해 배워 보자!
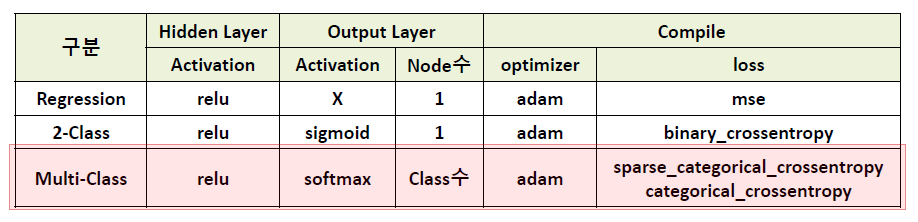
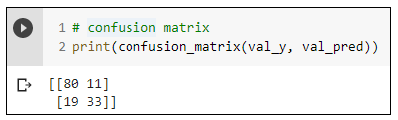
1) 분류문제 평가 : Confusion Matrix
2) 분류문제 평가 : Classification report
3) 전체 코드 정리(이진분류)
# 데이터 준비
target = 'Survived'
x = data.drop(target, axis = 1)
y = data.loc[:, target]
# 가변수화
cat_cols = ['Pclass','Sex', 'Embarked']
x = pd.get_dummies(x, columns = cat_cols, drop_first = True)
# 데이터분할
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=.3, random_state = 20)
# 스케일링
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_val = scaler.transform(x_val)
# 모델링
n = x_train.shape[1]
n
# 메모리 정리
clear_session()
# Sequential 모델
model3 = Sequential([ Dense( 4, input_shape = (n ,), activation = 'relu'),
Dense( 1, activation = 'sigmoid')])
# 모델요약
model3.summary()
# compile + 학습
model3.compile( optimizer=Adam(learning_rate= 0.01), loss ='binary_crossentropy')
hist = model3.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs = 50, validation_split=.2 ).history
# 예측 및 검증
pred3 = model3.predict(x_val)
pred3 = np.where(pred3 >= 0.5, 1, 0)
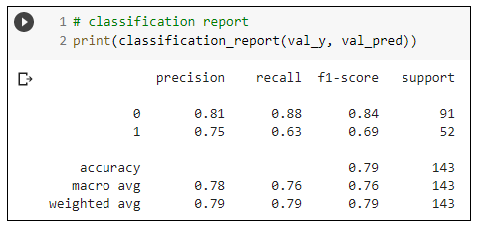
print(classification_report(y_val, pred3))4) 전체 코드 정리(다중 분류)
# y 값을 0,1,2로 변환하기
# (sparse_categorical_crossentropy 사용을 위해)
data['Species'] = data['Species'].map({'setosa':0, 'versicolor':1, 'virginica':2})
data.head()
# 데이터 준비
target = 'Species'
x = data.drop(target, axis = 1)
y = data.loc[:, target]
# 데이터 분할
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = .3, random_state = 20)
# 스케일링
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_val = scaler.transform(x_val)
# 모델링
nfeatures = x_train.shape[1] #num of columns
nfeatures
# 메모리 정리
clear_session()
# Sequential 타입 모델 선언
model = Sequential([Dense(8 , input_shape = (nfeatures,), activation = 'relu'),
Dense(3 , activation = 'softmax')
])
# 모델요약
model.summary()
# 컴파일 + 학습
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.1), loss= 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy')
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs = 50,
validation_split=0.2).history
# 예측 및 검증
pred = model.predict(x_val)
pred_1 = pred.argmax(axis=1)
# 평가
print(confusion_matrix(y_val, pred_1))
print(classification_report(y_val, pred_1))
1. 이진 분류
1) 딥러닝 구조 - 이진분류
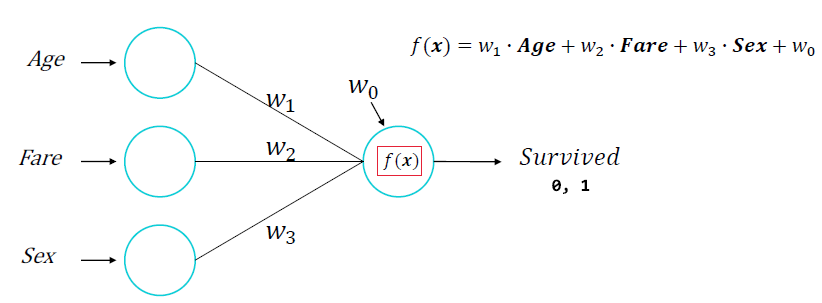
- 위 구조에서 Sruvived 0,1로 예측결과를 만들고 싶습니다.
- Node의 결과를 변환해주는 활성 함수가 필요합니다!
2) 딥러닝 구조 - Loss Function : binary_crossentropy
우리는 실제 값과 예측 값을 하나의 숫자(오차)로 평가해야 합니다.
이 오차들의 평균 = binary_crossentropy(log loss)
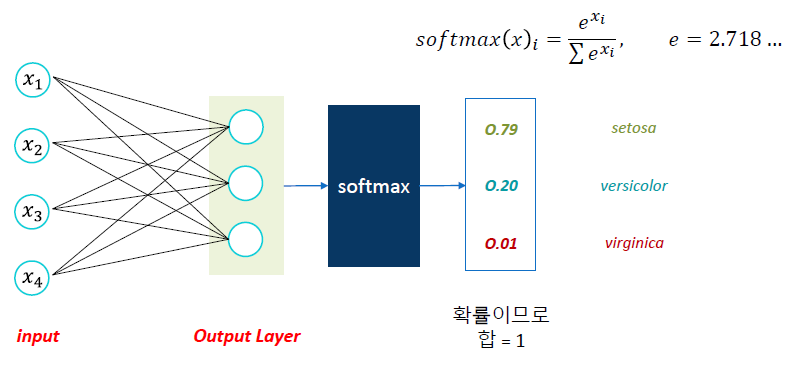
2. 다중 분류
1) 딥러닝 구조 - Output Layer
Node수
- 다중분류 모델에서 Output Layer의 node 수는 y의 범주 수와 같습니다.
Softmax
- 각 Class별로 예측한 값을 ,하나의 확률 값으로 변환
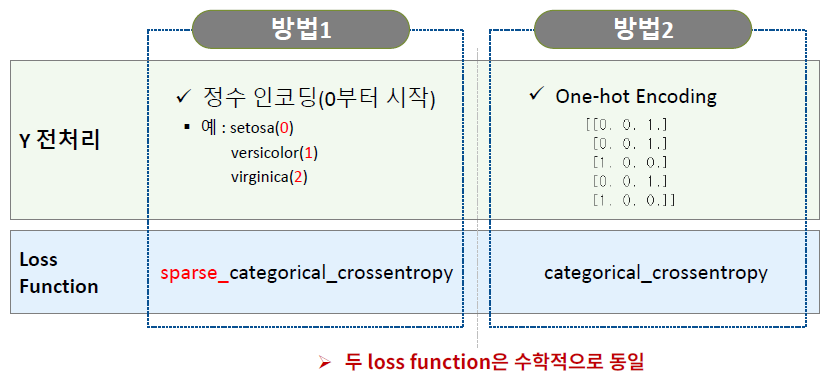
2) 다중 분류 모델링을 위한 전처리
다중 분류 : Y가 범주이고, 범주가 3개 이상
[방법1] 정수 인코딩 + sparse_categorical_crossentorpy
- Target의 class들을 0부터 시작하여 순차 증가하는 정수로 인코딩
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
int_encoder = LabelEncoder()
data['Species_encoded'] = int_encoder.fit_transform(data['Species'])
data.head()
- 인코딩 된 범주 조회
- int_encoder.classes__ -> 배열의 인덱스가 인코딩 된 정수
[방법2] 원핫 인코딩 + categorical_crossentropy
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
oh_encoder = OneHotEncoder()
encoded_y1 = oh_encoder.fit_transform(data[['Species']])
pritn(encoded_y1.toarray())
요약