1. Data Models, Schemas, and Instatnces
1-1. Data Models
- 데이터 추상화를 이루기 위해 필요한 의미들을 제공
- Represents a set of concepts to describe
- Structure(구조) of a database
- Operations(연산) for manipulating these structures
- Certain constraints(제약 조건) that the database should obey
- Structure는 data types, relationships, constraints를 표시한다.
- Operation
- DB의 구조를 retrieve(검색)하거나 update(갱신)하기 위해 사용.
- insert, delete, update와 같은 basic operation과, 사용자가 직접 정의하여 사용하는 user-defined operation이 있다.
Data Model Structure and Constraints
- Constucts are used to define the DB structure
- Construct typically include
- elements(and their data type) as well as groups of elements (entity, record)
- relationships among such groups
- Contraints valid한 data에 대해 몇 가지 제한사항을 명시
- 이러한 constraints는 항상 지켜져야 한다.
- 그렇지 않으면, data model에 따른다고 할 수 없다.
- 즉, data의 유효성을 위해 constraints는 항상 지켜져야 하고, constraints가 존재해야 data의 유효성 검증이 이루어진다.
- 이러한 constraints는 항상 지켜져야 한다.
1-2. Categories of Data Models
Conceptual (high-level, semantic) data models
- 중요한 개념 정의에 사용
- 데이터를 사용자가 인식하는 방식과 밀접한 개념으로 제공
- Entity, Attribute, Relationship 등과 같은 개념을 사용하여 데이터를 나타냄
- Called entity-based (E.g., the ER model) or object-based data models.
Physical (low-level, internal) data models
- 물리적 Data model이 Computer storage media(HDD or RAM/SSD)에 저장될 지에 대한 설명을 명시하는 Concepts를 제공
- 이 모델은 파일, 레코드 형식 (행 지향 또는 열 지향), 액세스 경로 (주/비주/클러스터링 인덱스) 등과 같은 개념을 포함
- 일반적으로 DBMS 설계 및 관리 매뉴얼을 통해 비정형 방식으로 지정
Implementation (representational, logical) data models
- High level과 Low level 사이에서 완충한 data model
- 많은 commercial DBMS에서 사용, relational data models or network/hierarchical models
Self-Describing data models
- 스스로를 식별하는 data model
- Combine the description of data with the data values
- E.g. XML, key-value stores, and some NoSQL systems (E.g., MongoDB/HBase)
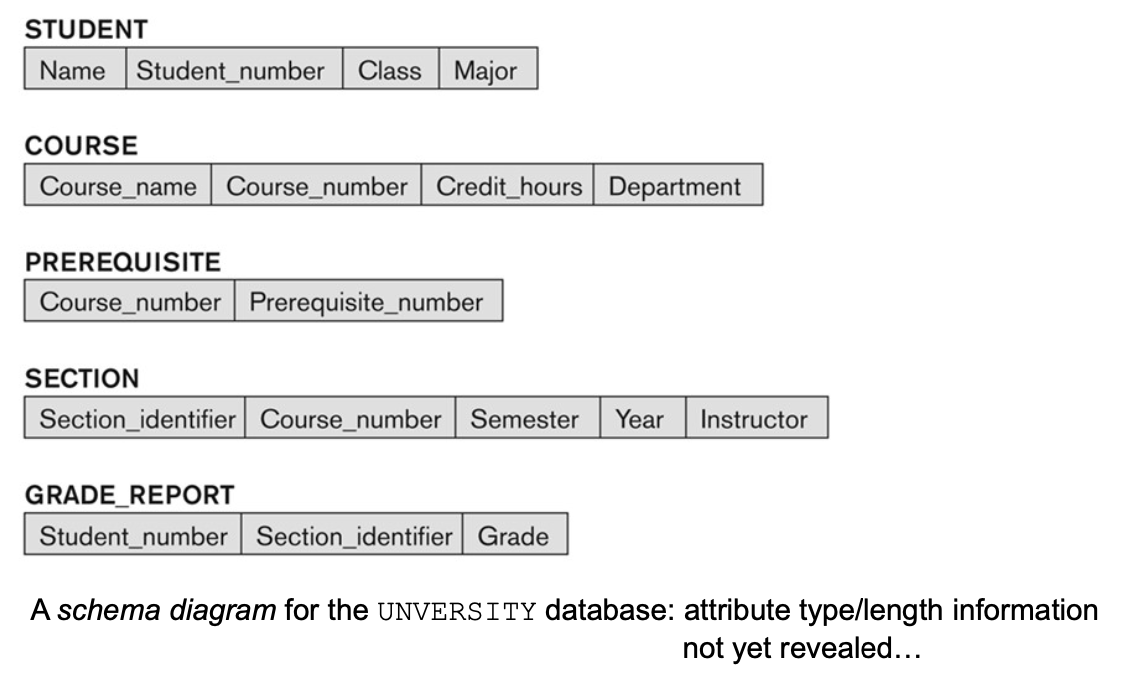
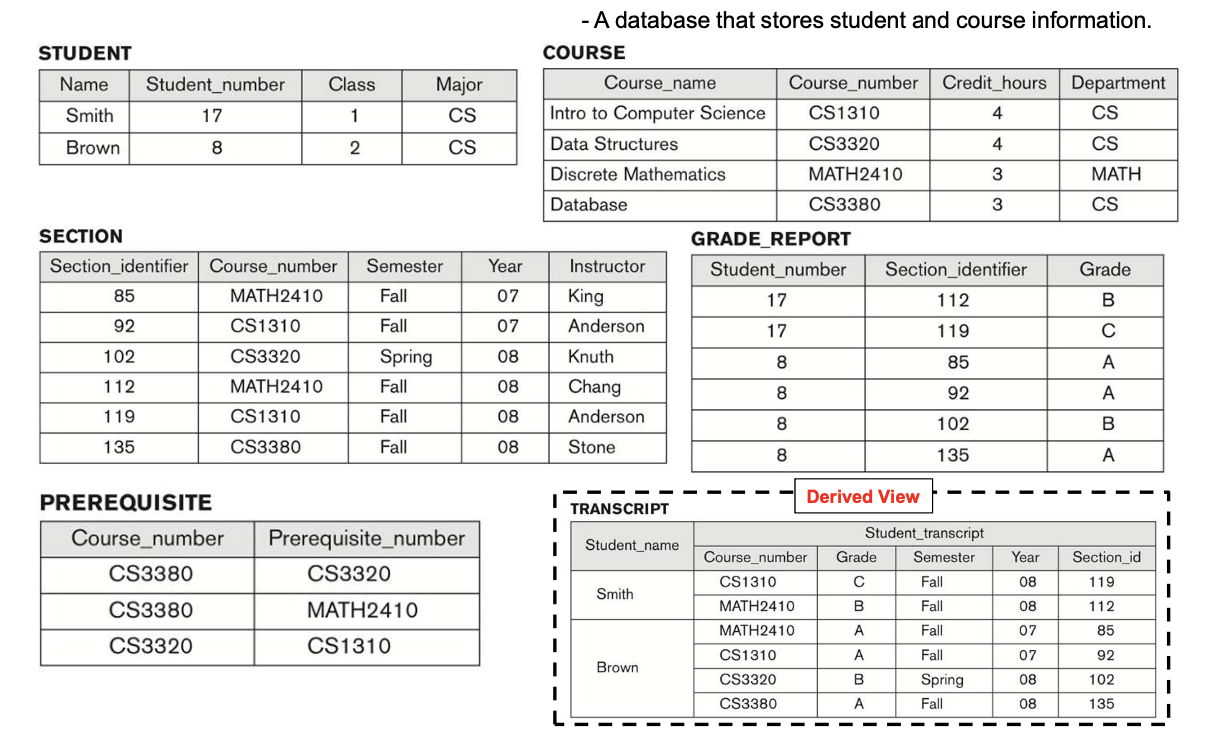
1-3. Recall the UNVERSITY Database
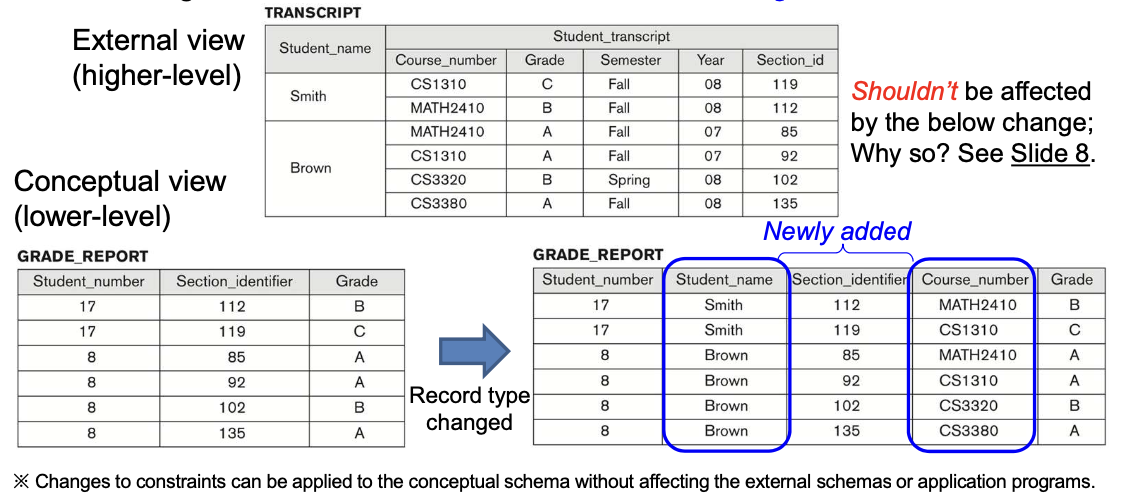
1-4. The “Database Schema” of UNVERSITY
Database Schema는 Structure만 설명하고 관계에 대한 표현은 포함되지 않는다.
1-5. Schemas vs. Instances
1-5-1. Database Schema (intension or meta-data)
- The description of a database : stored in the DBMS catalog
- DB 설계 중에 지정되며, 시간이 지나도 잘 변하지 않는다.
- 가끔, 특정한 경우에 schema evolution이 발생
- DB structure, data types, constraints의 설명을 포함한다.
- Schema construct : A component of the schema or an object within the schema
- E.g. STUDENT or COURSE
1-5-2. Database State (or extension)
- The actual data stored in a database at a particular moment in time.
- DB에 있는 모든 data의 collection을 포함
- Database instance(or occurrence or snapshot) 라고도 불린다.
- Instance는 개별적인 Database components에도 사용된다.
- record (an instance of an entity) instance, table instance, entity instance
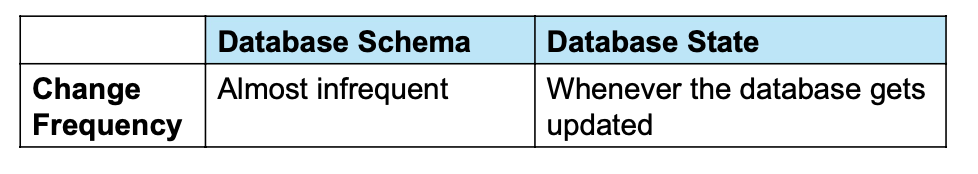
1-6. Database Schema vs. Database State
- Database State
- DB의 content를 특정 시간에 나타내는 것
- Initial Database State
- Database가 "DBMS에 처음으로 load되었을 때" or "초기 데이터로 채워진 상태"
- Valid State
- 데이터베이스의 Structure와 Constraints을 만족시키는 상태를 의미
- DBMS는 모든 database의 state가 valid 하도록 해야 한다.
2. THREE-SCHEMA ARCHITECTURE AND DATA INDEPENDENCE
2-1. Three-Schema Architecture
- Database approach([DB #01])의 4가지 특성 중 첫 3가지 특성을 지원하기 위해 제안됨
C1) Use of a catalog to store schema to make it self-describing
C2) Program-data or program-operation independence
C3) Support of multiple user views - Database system organization 설명시에 유용하다.
- Goal : User Applications를 physical database로부터 분리하기 위함
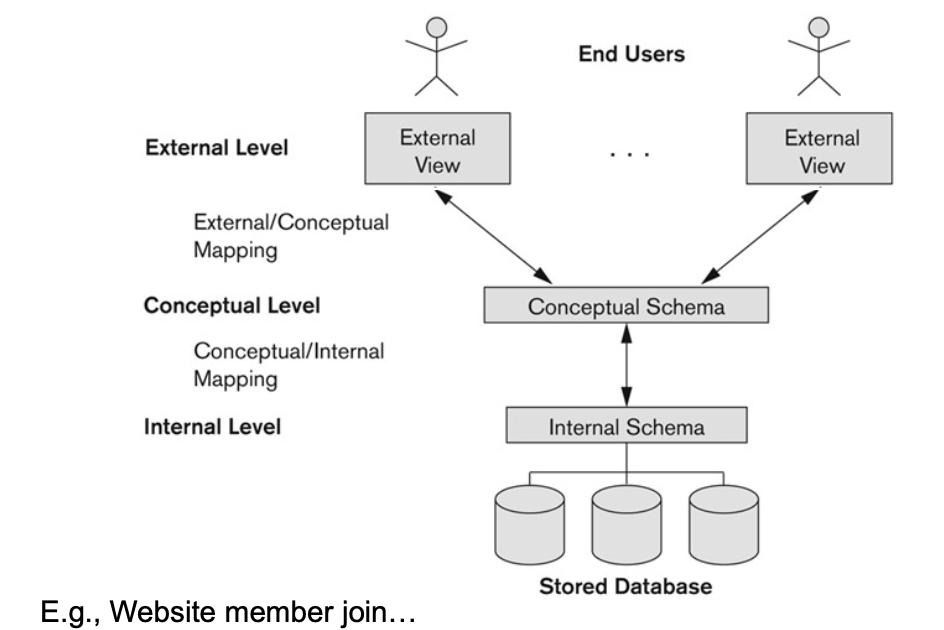
Level 간의 Mapping 정보 관리로 다른 level의 변화에 영향을 받지 않도록 한다.
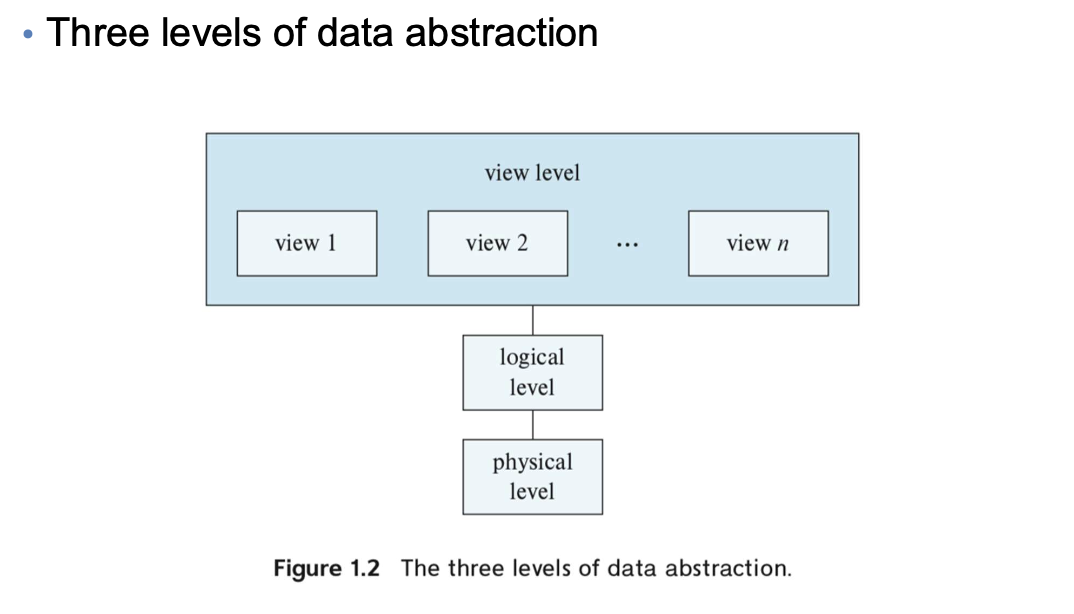
2-1-1. Defines DBMS schemas at three levels
-
Internal (= physical) schema (at the internal level)
- physical storage structures와 access paths에 대해 설명한다. (E.g. indices)
- 일반적으로 physical data model에서 사용한다.
-
Conceptual (= logical) schema (at the conceptual level)
- 사용자 community를 위한 체 database structure and constraints를 설명한다.
- physical storage structure의 details를 숨기고 사용자 그룹이 관심을 가지는 데이터베이스 구조를 설명하는 데에 집중한다.
- Uses a conceptual (e.g. ER) or an implementation (e.g. relational) data model.
-
External (= view level) schema (at the external level)
- 다양한 user view에 대해 설명한다.
- 일반적으로 conceptual schema와 같은 data model을 사용한다.
- 각 external schema는 특정 사용자 그룹이 관심을 가지는 데이터베이스의 "일부"를 설명하며, 해당 사용자 그룹에게 나머지 데이터베이스를 숨긴다.
- 다양한 user view에 대해 설명한다.
-
Mappings (on terms) among schema levels are needed to transform “requests” and “data”.
- 위의 Three schema는 데이터에 대한 설명뿐이다.
- 실제 data는 physical level에서 저장된다.
- 각 사용자 group은 그에 해당하는 고유의 external schema를 참조한다.
- 즉, 한 group는 다른 group의 external schema를 알 수 없다.
- External Schema에서 요청한 실제 data objects에 접권 권한을 갖기 위해 DBMS는 다음의 과정을 거친다.
- (i) External schema에서 주어진 request를 수행
- (ii) conceptual schema에 대한 request를 수행
- (iii) internal schema에 대한 request를 수행
- 이를 통해 stored database를 처리.
- Internal Level로부터 추출된 data는 external level에서의 original request와 일치하도록 'reformatted'된다.
- E.g. Web Page에서 보여주기 위해 SQL query의 결과를 Formatting
- 위의 Three schema는 데이터에 대한 설명뿐이다.
2-2. Data Independence
- 데이터 독립
- DB System에서 하나의 level에서 Schema를 변경하여도 다른 상위 level의 schema의 변경을 요구하지 않는 능력으로 정의
- Data의 논리적 구조와 물리적 구조를 분리함으로써 스키마 변경에 대한 영향을 최소화하고 데이터베이스 시스템의 유지 보수를 단순화한다.
Logical Data Independence
- 논리적 데이터 독립성은 Logical Schema Level에서의 스키마 변경에 대한 영향을 최소화한다.
- external schema와 associated application programs의 변경 없이 conceptual (or logical) schema를 변경할 수 있는 능력으로 정의
- 즉, 데이터베이스의 전체 구조를 변경하더라도 사용자 뷰와 응용 프로그램은 영향을 받지 않아야 한다.
Physical Data Independence
- 물리적 데이터 독립성은 Physical Schema Level에서의 스키마 변경에 대한 영향을 최소화한다.
- conceputal (or logical) schema의 변경 없이 internal (or physical) schema를 변경할 수 있는 능력
- 파일 구조의 재구성 또는 데이터베이스 성능을 향상시키기 위해 새로운 인덱스(primary index + secondary indexes)를 생성할 때 유용
[Example]Data Independence
하위 수준 스키마가 변경될 때, 데이터 독립성을 완전히 지원하는 DBMS에서는 오직 이 스키마와 상위 레벨 스키마 사이에 매핑만 변경된다. 즉, 상위 레벨의 스키마는 변경될 필요가 없다.
3. DATABASE LANGUAGES AND INTERFACES
3-1. Data Definition Language(DDL)
- DB의 conceptual/internal schema를 지정
- 두 스키마간의 매핑을 정의
- 현대의 많은 관계형 DMBS에서는 DDL이 엄격하게 분리되지 않고, DBA, DB 디자이너 모두가 사용
- 몇 DBMS는 명확하게 구분한다.
- Storage Definition Language for internal schemas: 현대의 DBMS에서는 더 이상 사용되지 않은 언어, DBA와 DB 디자이너에게 제공되는 DBMS 명령어를 통해서 구현
- View Definition Language for user views : SQL을 사용하면 미리 정의된 쿼리 결과를 저장하고 사용자 뷰를 만들 수 있다. -> 사용자는 필요한 데이터에 쉽게 access 가능
3-2. Data Manipulation Language(DML)
- DB에서 데이터 검색 및 업데이트시에 사용
- DML commands(called data sublanguage)는 범용적인 프로그래밍 언어(called host language)에 내장될 수 있다.
- Host language : C, C++ or Java ...
- 프로그래밍 언어로부터 DBMS에 access하기 위한 함수 라이브러리도 제공 될 수 있다.
- E.g. ODBC, JDBC ...
- Two types
- High Level or non-procedural languages(E.g., SQL) : declarative(선언적)
- why ?
- '검색할 방법'이 아닌 '무엇을 검색할 것'인지 명시한다.
- 독립 실행형 방식 (on SQL Plus, for instance): query language
- Programming language(C++/Jave)에서 내장 함수 Call로 사용
- Called set-at-a-time or set-oriented DML
- 한 번의 DML문으로 여러 record를 검색하고, 각 레코드를 처리할 수 있다.
- '검색할 방법'이 아닌 '무엇을 검색할 것'인지 명시한다.
- Low-level or procedural languages
- 프로그래밍 언어에 내장되어 있다.
- data를 한 번에 하나의 레코드를 검색하고 처리한다.
- 여러 record를 검색하려면 loop가 필요하다.
- Called record at-a-time DML
- 항상 row를 기반으로 하여 절차적으로 record 단위를 return하고 처리한다.
- 데이터를 개별적으로 처리하고 검색하기 때문에 프로그래머가 어떻게 데이터를 처리할 것인지를 상세하게 제어할 수 있다.
3-3. DBMS Interfaces
-
Stand-alone(독립 실행형) Query Interface
- E.g. SQL* PLUS
-
Programmer Interfaces for embedding DML in programming languages
-
User-friendly interfaces
- Menu-based, forms-based, graphics-based (e.g., SQLDeveloper), etc.
-
Mobile Interfaces
-
Interfaces allowing users to perform transactions using mobile (e.g., banking) apps
Programmer interfaces for embedding DML in a programming languages
- Embedded Approach:
- e.g. embedded SQL (for C, C++, etc.), SQLJ (for Java)
- Procedure Call Approach:
- e.g. JDBC for Java, ODBC (Open Databse Connectivity) for other programming languages as API’s (application programming interfaces)
- Database Programming Language Approach:
- e.g. ORACLE has PL/SQL, a programming language based on SQL; language incorporates SQL and its data types as integral components
- Scripting Languages:
- PHP (client-side scripting) and Python (server- side scripting) are used to write database programs.
4. THE DATABASE SYSTEM ENVIRONMENT
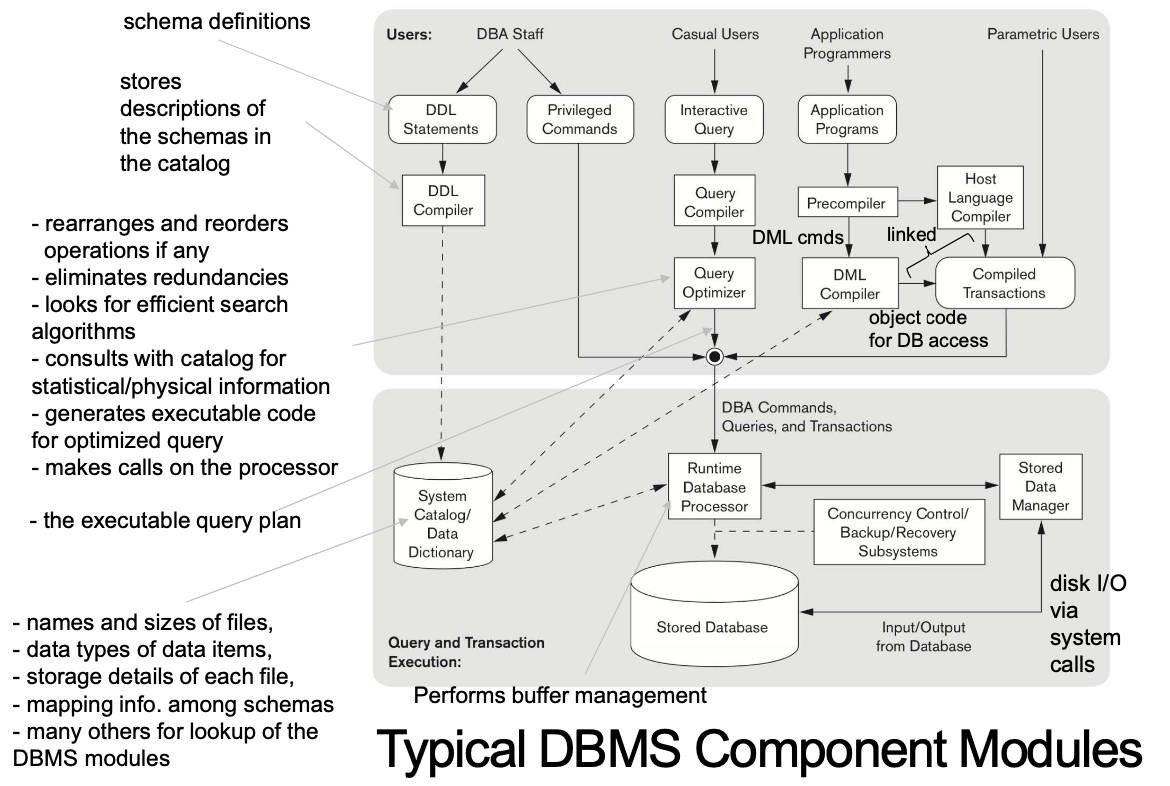
4-1. DBMS Component Modules
- Some things usually stored on disk
- The stored database
- The DBMS catalog
- Disk에 대한 접근 권한은 OS에서 관리하고, Disk read/write를 scheduling한다.
- 대부분의 DBMS는 disk read/write를 스케쥴 하기 위한 그들만의 buffer manager를 가진다.
- buffer manager를 통해 성능 향상에 상당한 영향을 미친다.
- OS의 kick off 정책에 반하여 자기만의 정책을 적용하여 disk-IO를 최소화하고 결과적으로 DB의 성능을 향상시킨다.
- DBMS의 high-level stored data manager(module)는 Disk에 저장된 DBMS 정보에 대한 접근을 제어한다.
- DB의 일부 or catalog 상관없이 제어
4-2. Typical DBMS Component Modules
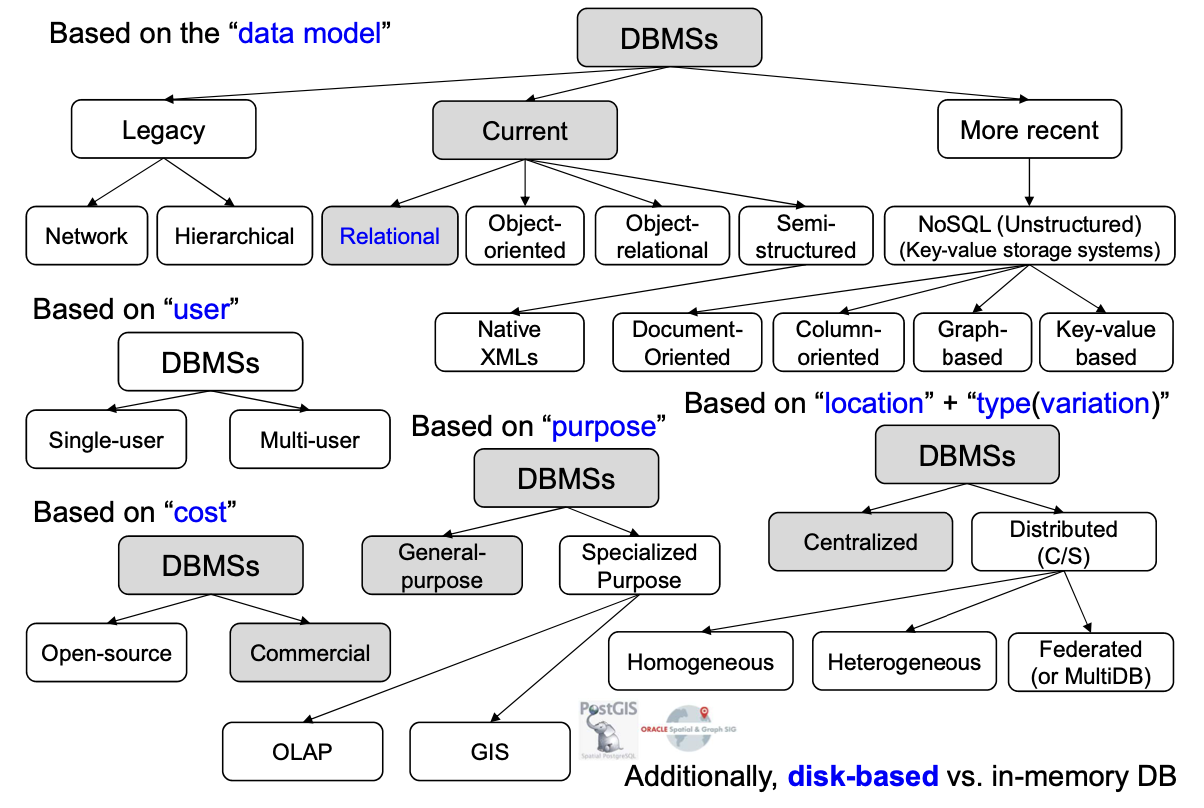
5.CLASSIFICATION OF DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
Reference
Database System Concepts | Abraham Silberschatz
데이터베이스 시스템 7th edition