1. ER MODEL
1-1. Overview of Database Design Process
Database application
- 특정 데이터베이스와 관련된 Query와 Update를 구현하는 프로그램
- E.g. A BANK database application
- Includes two main activities: applications design & database design
Application desing
- DB에 접근하는 Program과 Interface에 Focus
- Generally considered part of software engineering
Database design
- Conceptual -> DB Application의 the conceptual schema를 design 하기 위함 (External)
- Logical (Representational; DBMS-Specific)
- Physical (Internal)
1-2. A Simplified Overview of Database Design Process
- Step 1: Requirements collection and analysis (DB 설계)
- Functional/Data requirements
- Step 2: Conceptual design
- Conceptual schema
- Step 3: Logical design(or data model mapping)
- Logical schema
- DBMS마다의 DDL을 사용하기에 DBMS마다 다르다
- Step 4: Physical design
- Internal schema: internal storage structures, file organizations, indexes, access paths, and parameters for database files
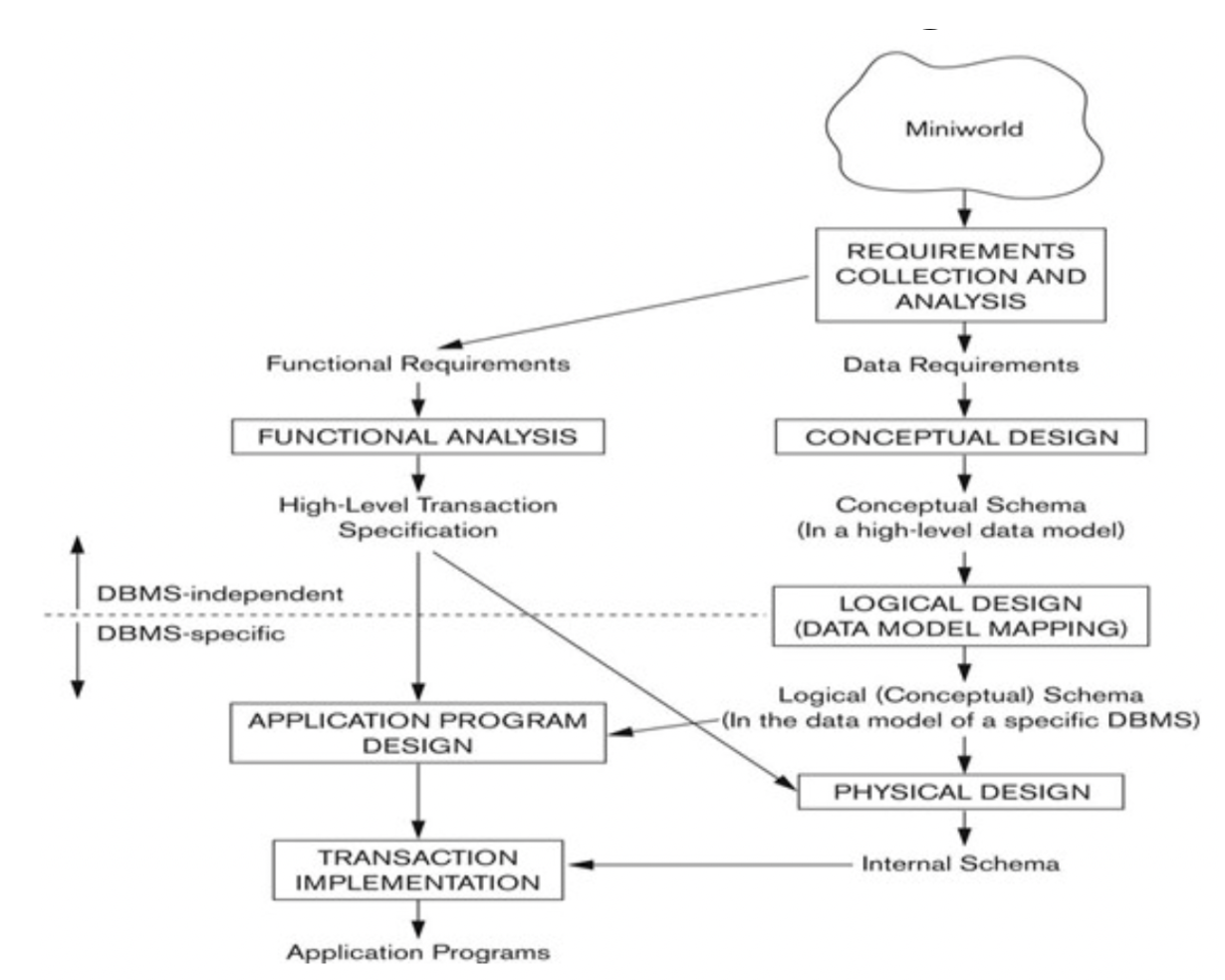
- Internal schema: internal storage structures, file organizations, indexes, access paths, and parameters for database files
2. ENTITY TYPES, ENTITY SETS, ATTRIBUTES, AND KEYS
2-1. Concepts : Entities & Attributes
- The Entity-Relationship (ER) model에서는 data를 다음으로 표현한다.
- Entities, relationships, and attributes
- Entities, relationships, and attributes
Entity(s)
- ER model의 기본 concept
- DB에 표현되는 things or objects를 특정한다.
Attribute(s)
- Entity를 기술하는 특성
- Entity는 자신의 attribute의 특정 값을 가진다.
- 각 attribute는 value set(or data type)을 가진다.
- E.g. integer, string, date, enumerated type...
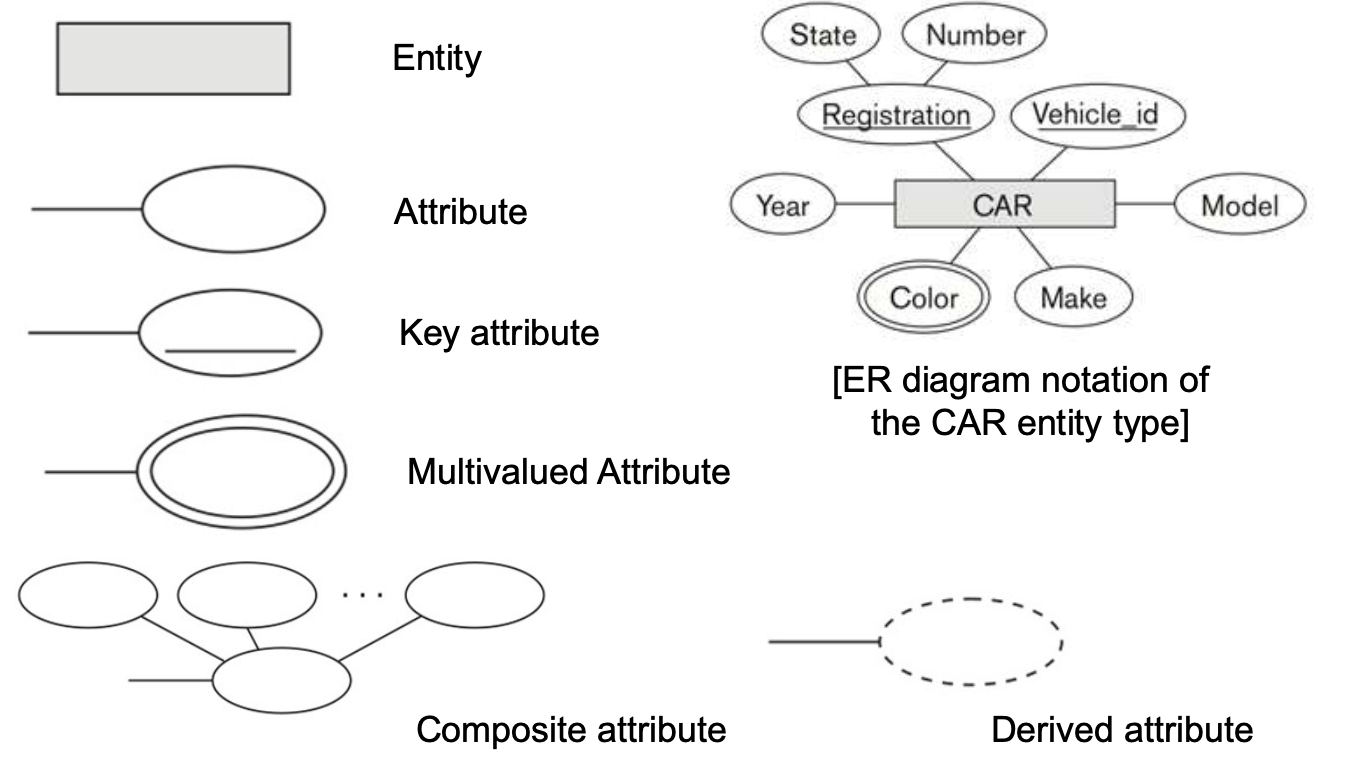
2-2. Types of Attributes
- Simple (atomic)
- 각 Entity는 attribute에 대한 single atomic value(원자값)을 가진다.
- E.g. SSN, Sex
- E.g. SSN, Sex
- 각 Entity는 attribute에 대한 single atomic value(원자값)을 가진다.
- Composite (합성)
- Attribute는 여러 Component로 구성될 수 있다.
- E.g.
- Address (Apt#, Room#, Street, City, State, Zip Code, Country)
- Name (FirstName, LastName)
- Composition은 몇 개의 "composite"한 componenets와 계층 구조를 가질 수 잇다.
- Multi-valued (다중 값)
- Entity는 특정 attribute에 여러 값을 가질 수 있다.
- E.g.
- “Color” of a CAR entity -> 차가 여러 색을 가질 수 있다
- “PreviousDegrees: of a STUDENT entity. -> 이전 학위는 석사, 학사일 수 있다.
- Denoted by “{”, “}”;
- e.g., {Color}, {PreviousDegrees} in ER
- Composite와 multi-valued attribute는 매우 드물지만 임의의 수준으로 중첩될 수 있다.
- E.g.
- PreviousDegrees of a STUDENT : a composite multi-valued
- {PreviousDegrees(College, Year, Degree, Field)}
- {} : Multi-valued, () : Composite
- E.g.
임의의 수준
중첩된 구조나 계층적인 구조가 어떤 제한 없이 여러 수준으로 반복될 수 있다.
즉, 어떤 구조나 개념이 다른 구조나 개념 안에 중첩되어 계층적인 구조를 형성하며, 이 중첩된 구조가 무한히 반복될 수 있다는 의미입니다.
- Stored attributes vs Derived attributes
- Stored attribute
- Value가 이미 저장된 attribute
- 변하지 않는 것, 홍길동의 생일은 1월 1일
- Derived attribute
- 이미 저장된 attribute로부터 값을 계산할 수 있는 attribute
- 추측 가능한 것, 홍길동의 나이는 XX살
- Fact를 기반으로 계산, 추출
- Stored attribute
- Complex attributes
- Mixed attributes of composite attributes and multi-valued attributes
- E.g.
- {Address_phone({Phone(Area_code, Phone_number)}, Address(Street_address(Number, Street, Apartment_number), City, State, Zip))}
- Q: How many composite attributes in the above complex attribute, Address_phone?
- 3, Phone, Address, Street_address
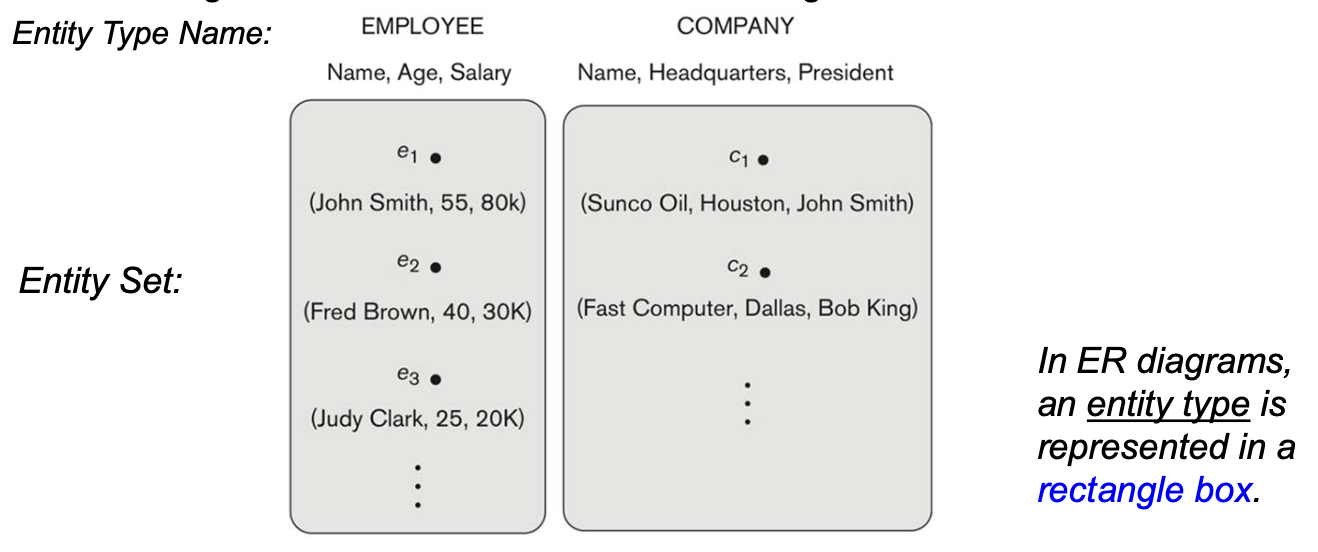
2-3. Entity Types and Entity Sets
- Entity Type(Intension)
- 동일한 기본 속성을 가지는 개체의 유형 또는 그룹 (Like schema)
- E.g. EMPLOYEE, COMPANY
- Entity set(Extension)
- DB에 특정 Entity type의 특정 시점에서의 collection (Like state)
- E.g. EMPLOYEEL: e1, e2, ...
2-4. Key Attributes of an Entity Type
- Key attribute(키 속성)
- 각 Entity Type은 고유한 값을 가져야하고 그 값을 통해 고유하게 식별할 수 있는 속성을 Key attribute라고 한다.
- 하나 또는 복수 개의 key가 존재할 수 있다.
- E.g.
- SSN of EMPLOYEE, Student_number of STUDENT
2-5. Value Sets(Domains) of Attributes
- 각 simple attribute는 value set(or domain of values)과 관련이 있다.
- Date는 MM-DD-YYYY, 각 letter는 Integer형으로 저장되어야 한다.
- Age는 16 ~ 70 사이 값, lastname은 15bytes 제한 등 ....
- Value set은 attribute가 가지는 Valid한 값의 범위를 정의한다.
- Domain이 다르면 해당 attribute로 저장되지 않는다.
- Domain이 다르면 해당 attribute로 저장되지 않는다.
- Value sets는 대부분의 programming languages에서 이용가능한 data types과 비슷하다.
- E.g. Integer, String, double ...
2-6. Notation and Example for Entity & Attribute in Entity-Relationship (ER) Diagrams
3. INITIAL CONCEPTUAL DESIGN OF A DATABASE
3-1. Requirements
-
COMPANY는 DEPARTMENT로 구성되어 있다.
- 각 DEPARTMENT는 unique name, unique number, DEPARTMENT를 관리하는 특정 EMPLOYEE도 가진다.
- EMPLOYEE가 일을 시작한 날(start date) 또한 가진다.
- Department는 여러 장소에 있을 수 있다.
-
DEPARTMENT는 PROJECTs를 관리한다.
- 각 PROJECTs는 unique name, unique number, single location 정보를 가진다.
-
각 EMPLOYEE는 아래의 attributes를 가진다:
- name, Social Security Number(SSN: 주민번호), address, salary, sex, and birth date
- 각 employee는 한 개의 department에 works for하지만, 몇 개의 projects에 works on할 수도 있다.
- 각 employee는 각 프로젝트에 일한 시간과 직속 상사를 가진다.
-
각 employee는 여러 명의 DEPENDENTs(부양가족)을 가질 수 있다.
- 각 dependent는 first name, sex, birth date, and employee에 대한 relationship 정보를 가진다.

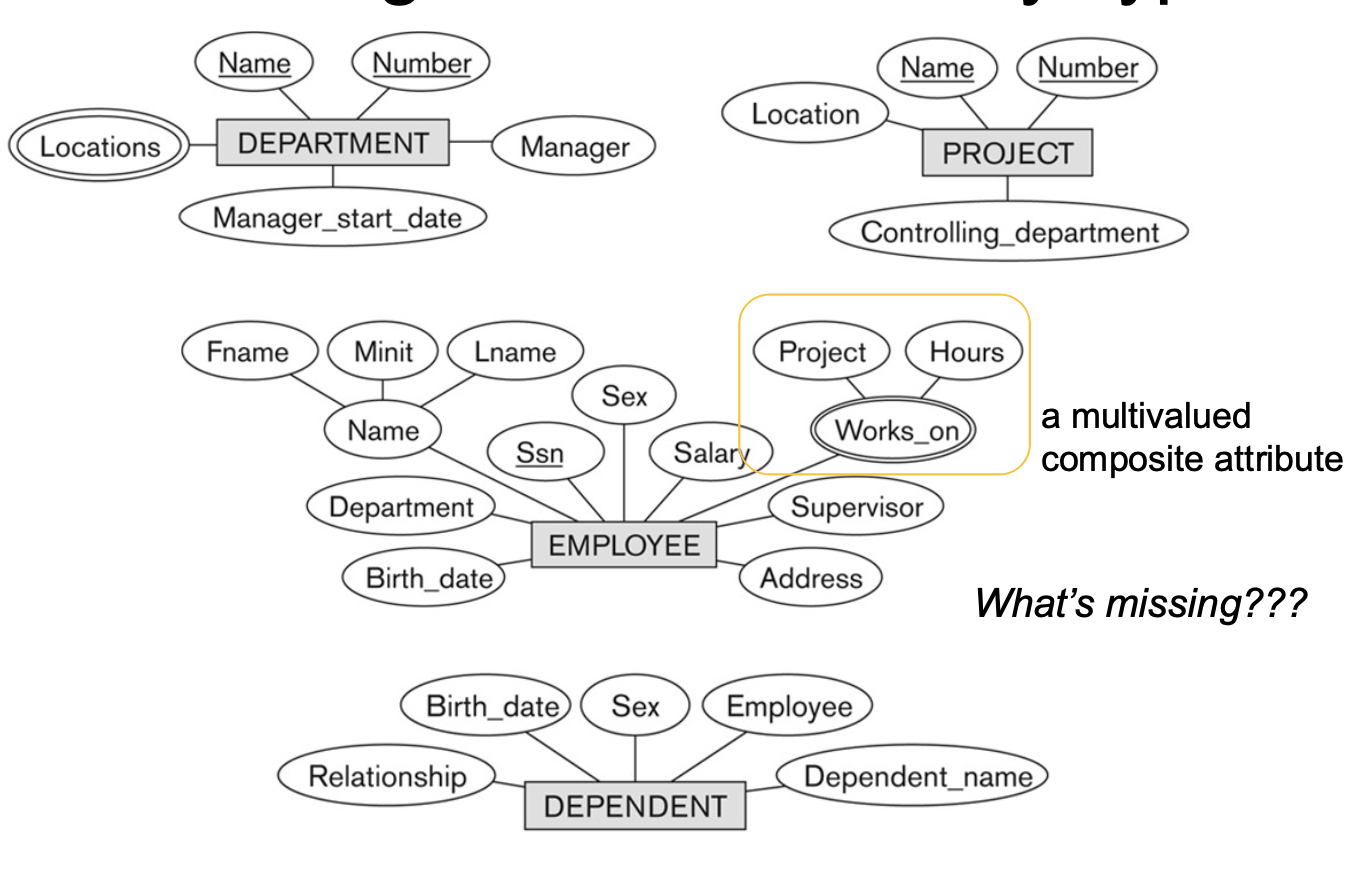
- 각 dependent는 first name, sex, birth date, and employee에 대한 relationship 정보를 가진다.
4. RELATIONSHIP TYPES, RELATIONSHIP SETS, ROLES, AND STRUCTURAL CONSTRAINTS
4-1. RELATIONSHIP TYPES, RELATIONSHIP SETS, ROLES, AND STRUCTURAL CONSTRAINTS
- A relationship
- 구체적인 의미를 가진 두 개 또는 그 이상의 밀접한 엔티티가 관련되어 있다.
- Ex1) EMPLOYEE 홍길동 works on the GPT-5 PROJECT.
- Ex2) EMPLOYEE 안철수 works for the R&D DEPARTEMENT.
- 구체적인 의미를 가진 두 개 또는 그 이상의 밀접한 엔티티가 관련되어 있다.
- A relationship type R (관계 유형)
- 동일한 N entity types 사이에 있는 관계
- "WORKS_ON" 과 "WORKS_FOR" 관계형은 "EMPLOYEE"와 "PROJECT"사이에 관계이다.
- Degree of Relationship Type
- 관계에 참여하는 (distinct) entity types의 수
- WORKS_ON과 WORKS_FOR의 DEGREE는 몇인가 ?
- Unary : 1 (for self), Binary : 2 (involving two), Tertiary (about three)
- 동일한 N entity types 사이에 있는 관계
- A relationship set R (관계 집합) among n entity types E1, E2, ... En
- A set or relationship instances ri
- 각 ri는 n개의 개별 entities(e1,e2,....,en)에 연관된다.
- ri에 있는 각 entity ej는 Ej set의 멤버이다.
- A set or relationship instances ri
4-2. Degree of a Relationship Type
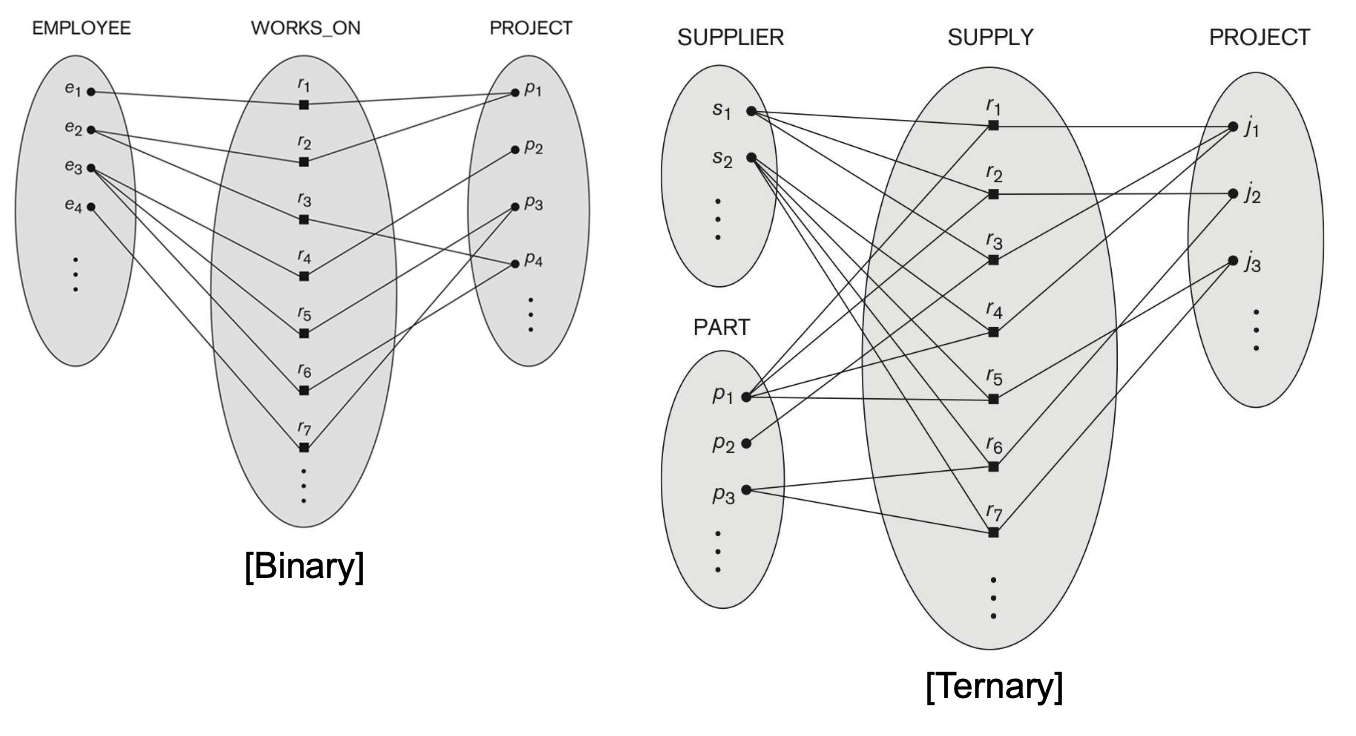
4-3. Relationship Type vs Relationship set
4-4. Role Name
- Relationship에 참여하는 Entity에게 부여된다.
- 각 엔티티 유형이 관계 Instance에서 어떤 역할을 하는 지를 나타낸다.
- For the WORKS_FOR relationship
- EMPLOYEE's role : EMPLOYEE or WORKER
- DEPARTMENT's role : DEPARTMENT or EMPLOYER
- For the WORKS_FOR relationship
- 관계 집합에 참여하는 엔티티 유형들이 충분히 구별되고 서로 다른 역할을 수행한다면, Entity type name자체가 역할의 이름으로 사용될 수 있기 때문에 역할을 명시적으로 작성할 필요가 없다.
- 하지만 만약, 하나의 Entity type이 하나 이상의 Relationship에 다른 역할로 참여하는 경우에는 Role name을 명시해야 한다.
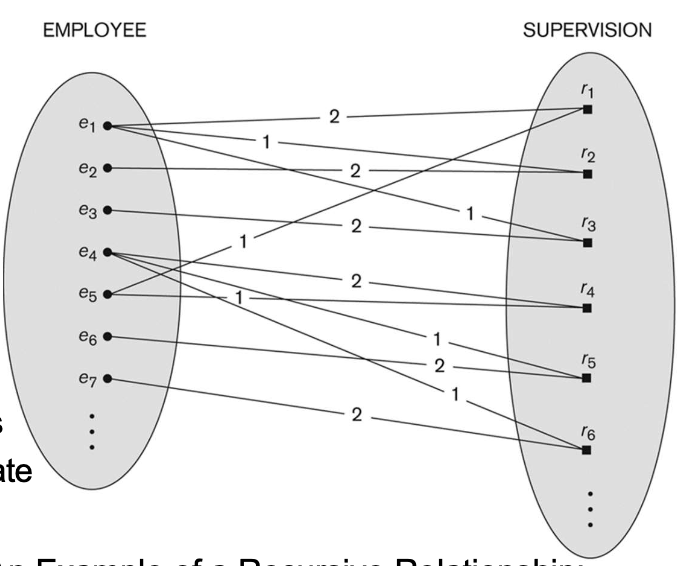
4-5. Recursive Relationship (or Self-Referencing Relationships)
- 관계에 참여하는 두 개의 Entity가 동일한 Entity type을 가진 관계
- SUPERVISION은 EMPLOYEE와 EMPLOYEE간의 relationship이다.
- in role of supervisor or boss
- in role of worker or subordinate
Role name 1은 supervisor role
Role name 2는 worker
4-6. Structural Constraints on Binary Relationship Types
- 이진 관계 유형의 구조적 제약 조건
Scenarios - "모든 EMPLOYEE는 정확하게 한 개의 DEPARTMENT에서 work for해야 한다."
- "몇 명의 EMPLOYEE은 그들의 DEPARTMENT를 manage해야 한다."
4-6-1. Cardinality ratio (of a binary relationship)
- Entity가 참여하는 relationship instances의 최대 숫자를 명시
- E.g. 1:1, 1:N, N:1, M:N
- Shown by placing appropriate numbers on relationship edges in ER diagrams
[EXAMPLE]
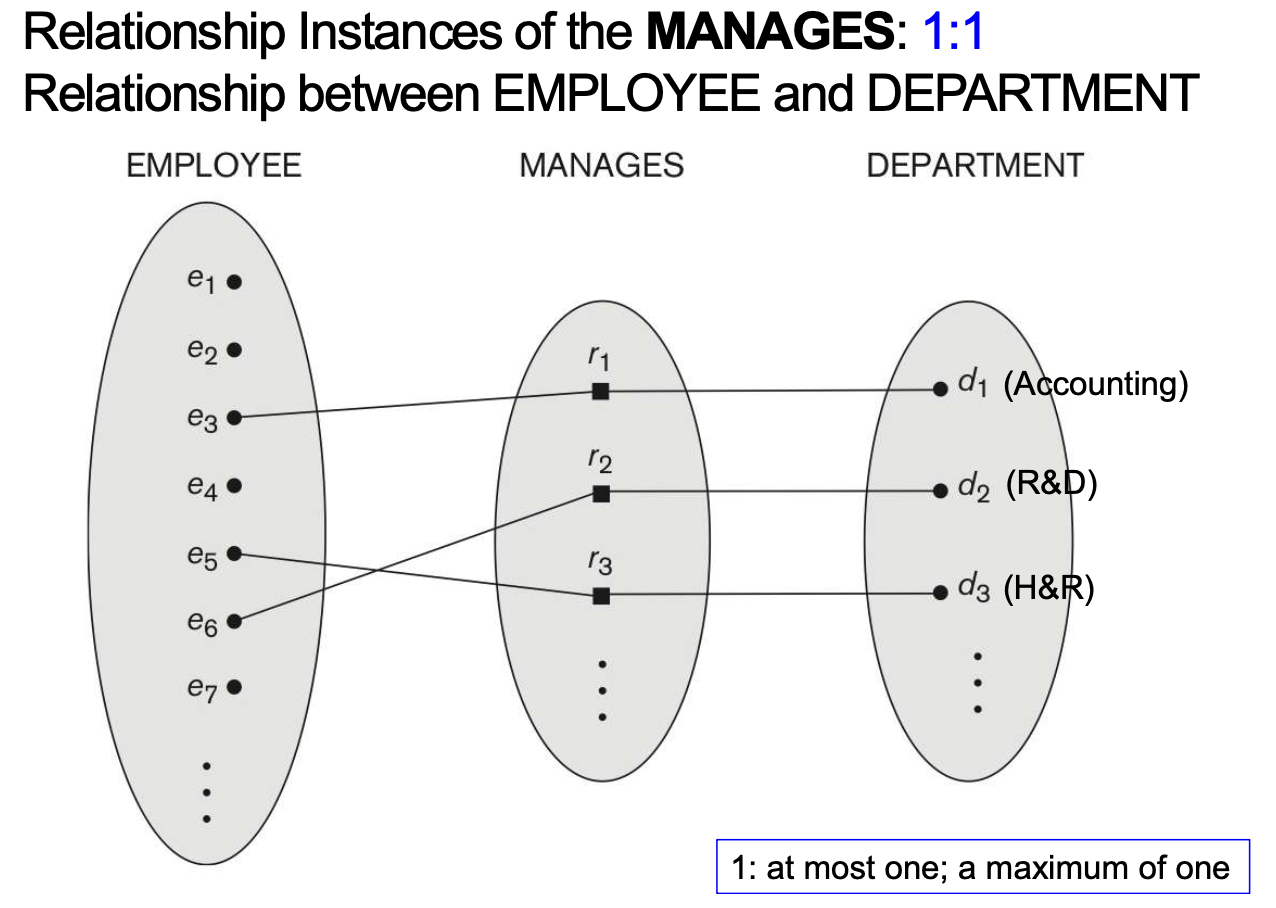
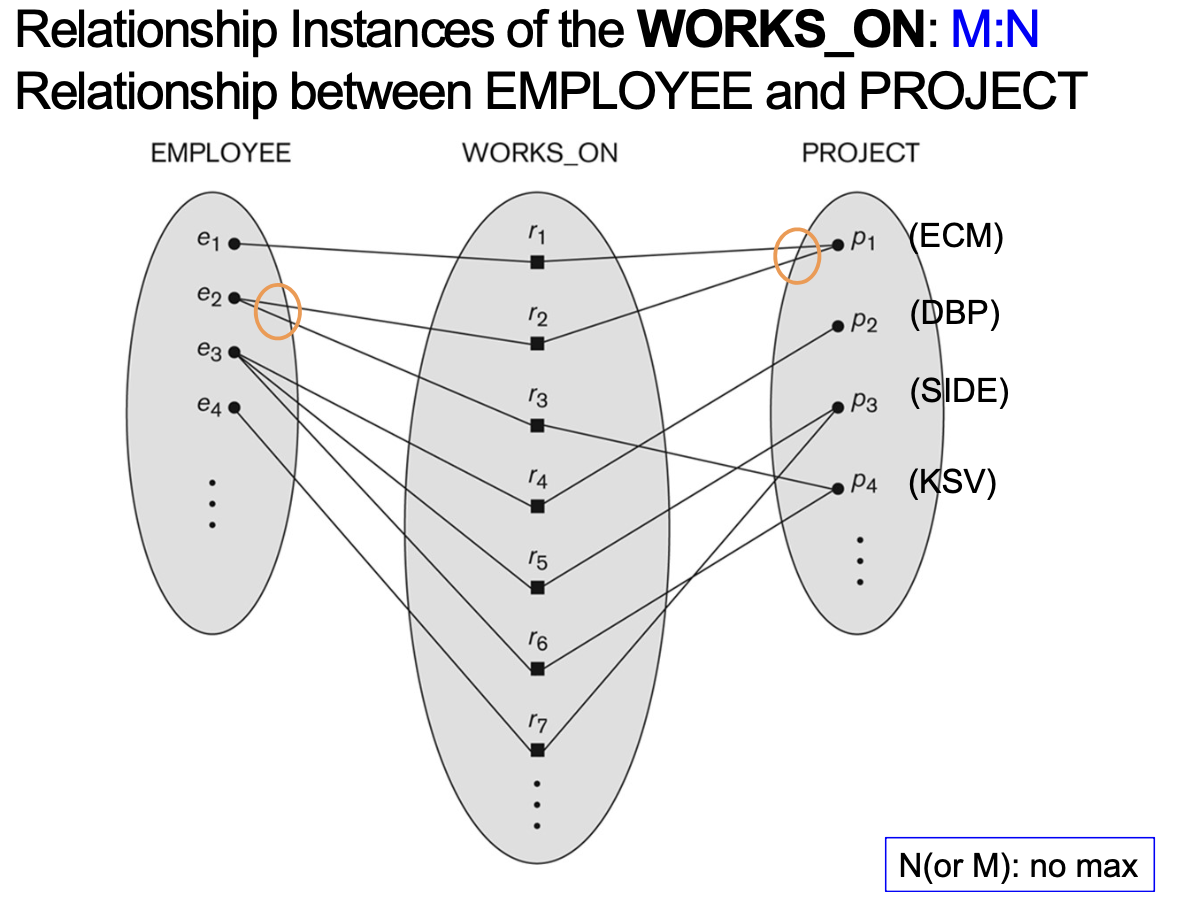
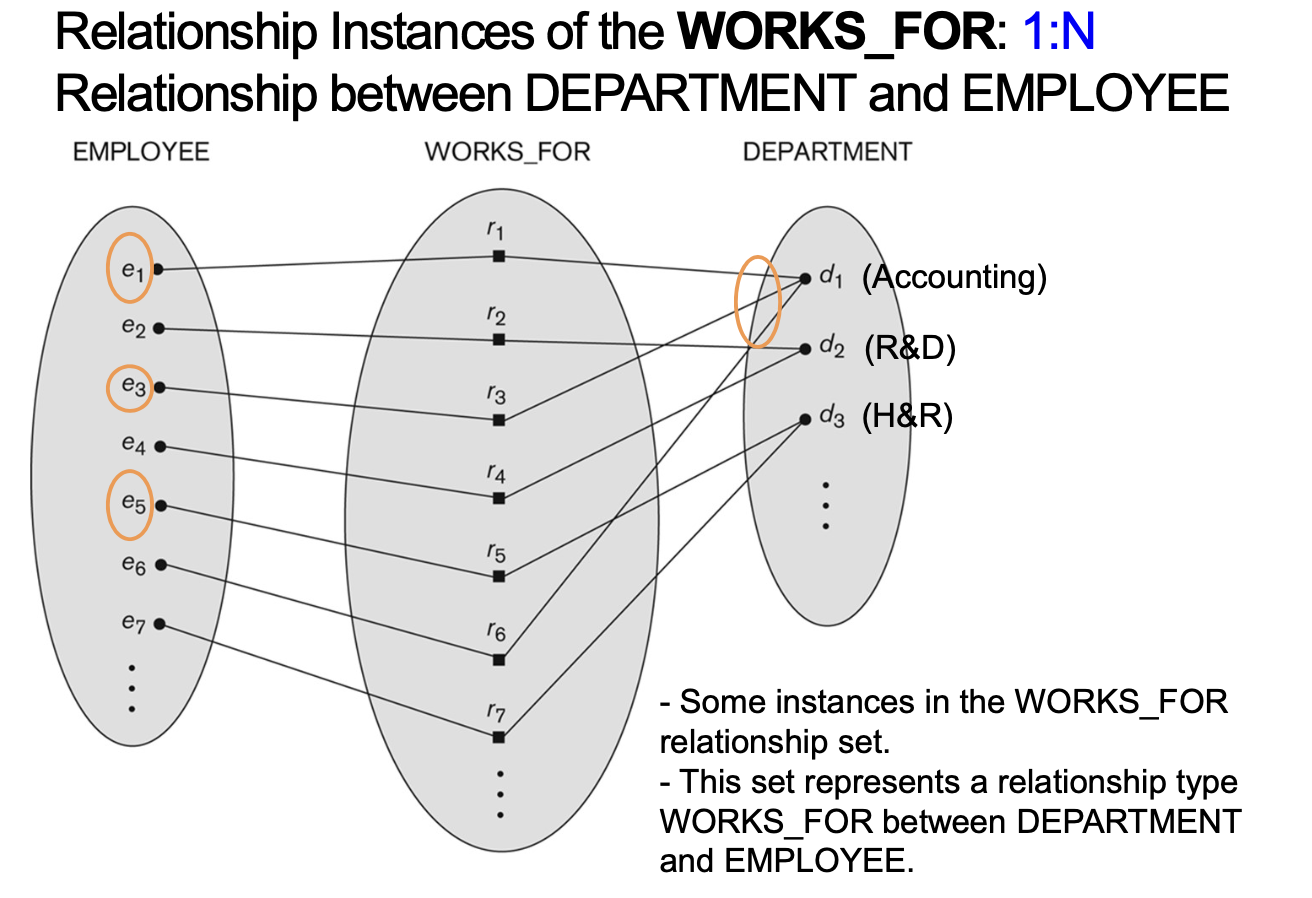
4-6-2. Participation constraint
- 어떤 relationship type에 대해 어떤 entity가 존재하기 위해서는, 또 다른 entity와 전체적으로/부분적으로 관계되어야 한다.
- relationship instance에 참여할 수 있는 최소한의 숫자 (cardinality ratio는 최대 숫자)
- "모든 EMPLOYEE는 DEPARTMENT에서 일해야 한다." -> 전체 참여
- EMPLOYEE ENTITIES의 total set은 WORKS_FOR에 의해 DEPARTMENT와 관계되어야한다.
- "모든 EMPLOYEE가 반드시 DEPARTMENT를 관리할 필요는 없다." -> 부분 참여
-> EMPLOYEE ENTITIES 중 몇 개의 ENTITY만 MANAGE를 통해 몇 개의 DEPARTMENT와 관계된다.
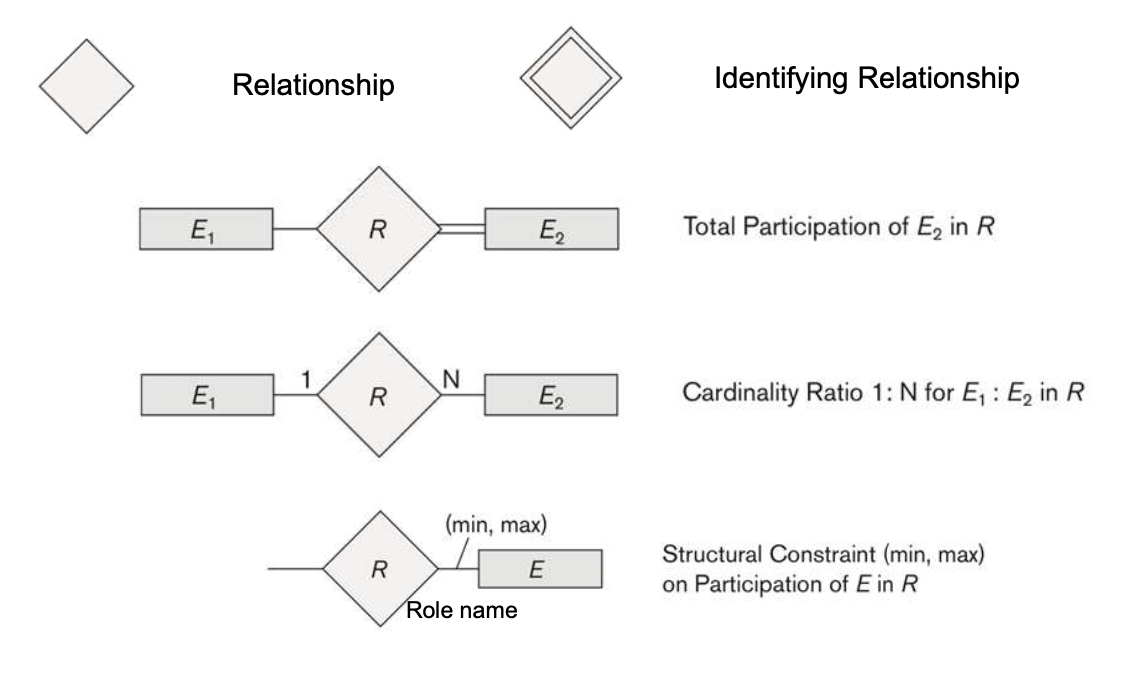
Total participation (Called existence dependecy)
Shown by a double line in ER diagrams
Partial participation (by default)
Shown by a single line in ER diagrams
4-7. Attributes of Relationship Types
- Relation types 또한 Entity types과 비슷하게 relationship attributes를 가질 수 있다.
- “How many hours per week (HoursPerWeek) Rachel work on the ECM project?”
- “When (Start_date) did Chandler start managing his department?
- 대부분의 relationship attributes는 M:N 관계에서 사용된다.
- E.g.
- HoursPerWeek와 같은 속성 값을 가졌다고 가정해보자.
- HoursPerWeek는 EMPLOYEE와 PROJECT의 관계의 Attribute
- (이석환,CSE)와 (레이첼,ECM)는 조합이 다르기 때문에 HoursPerWeek가 다르다.
- E.g.
- 1:N relationship에서 relationship attribute는 N쪽에 있는 Entity의 Attribute로 이동할 수 있다.
- E.g.
- WORKS_FOR 관계에서, Emp_start_date는 N_side로 이동이 가능하다.
- E.g.
- What about 1:1 ?
어느 쪽이라도 가능하다.
5. WEAK ENTITY TYPES
다른 Entity가 존재해야 존재할 수 있는 Entity type
5-1. Concept
- Weak Entity type : 자기 자신을 위한 Key attribute를 갖지 않는 Entity type
- Also called the cild (or subordinate) entity type
- C.f. regular (or strong) entity types
- Also called the cild (or subordinate) entity type
- Weak entity type entities (자기 자체로 존재 불가)
- 또 다른 entity type or parent(dominant, identifyingm or owner) entity type의 특정 entity와 연관되어지는 것으로 식별된다.
- Identifying relationship (of the weak entity type) : 식별되는 관계
- E.g. class - instance (in Java), EMPLOYEE - DEPENDENT
- Weak Entity type은 해당 Entity type을 식별하는 relationship에 대해서 partial VS total 어떤 participation을 가지는가 ?
- Total participation
- WHY ?
- weak Entity는 Owner Entity로 인해 존재하고 식별될 수 있기 때문
5-2. Concept and Notation in ER
- Weak Entity type entities
- Identified by the combination of (= Weak Key + Strong key)
- A partial key of the weak entity type
- 같은 Owner Entity에 관계되어 있는 weak entity를 Unique하게 식별할 수 있는 attribute를 사용한다.
- E.g.
- Dependent_ID (or in the worst case, 모든 Weak entity의 attribute를 포함하는 Composite attribute가 될 수 있다.)
- 식별하는 Relationship type에 관계된 parent entity
- Typically, parent's ID
- E.g.
- EMPLOY_ID- Notation in an ER diagram

- Notation in an ER diagram
- Identified by the combination of (= Weak Key + Strong key)
6. REFINING THE ER DESIGN FOR THE COMPANY DATABASE
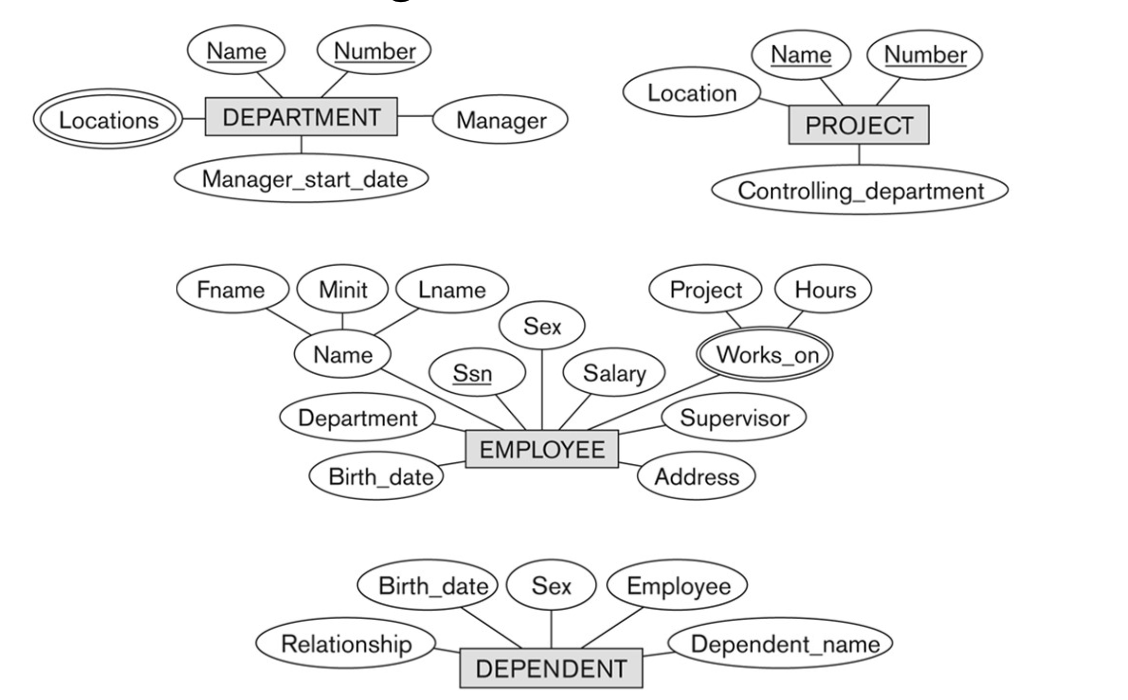
6-1. Recall the Initial Design of the Four Entity Types
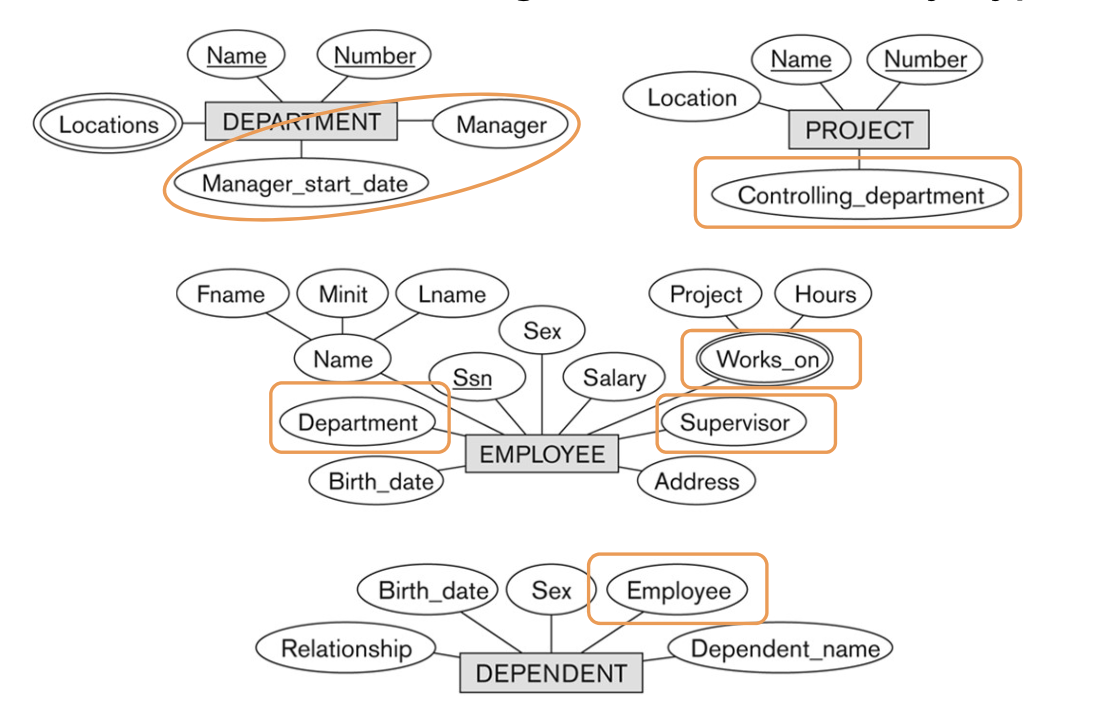
6-2. Identifying Relationships between Entity Types
- Six relationship types are identified after examining the previous requirements.
- Note that all are "binary" relationship
- Listed below with their participating entity types
- WORKS_FOR: EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT
- MANAGES: EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT
- CONTROLS: DEPARTMENT and PROJECT
- WORKS_ON: EMPLOYEE and PROJECT
- SUPERVISION: EMPLOYEE (as supervisor) and EMPLOYEE (as supervisee)
- DEPENDENTS_OF: EMPLOYEE and DEPENDENT
6-3. Discussion of Relationship Types
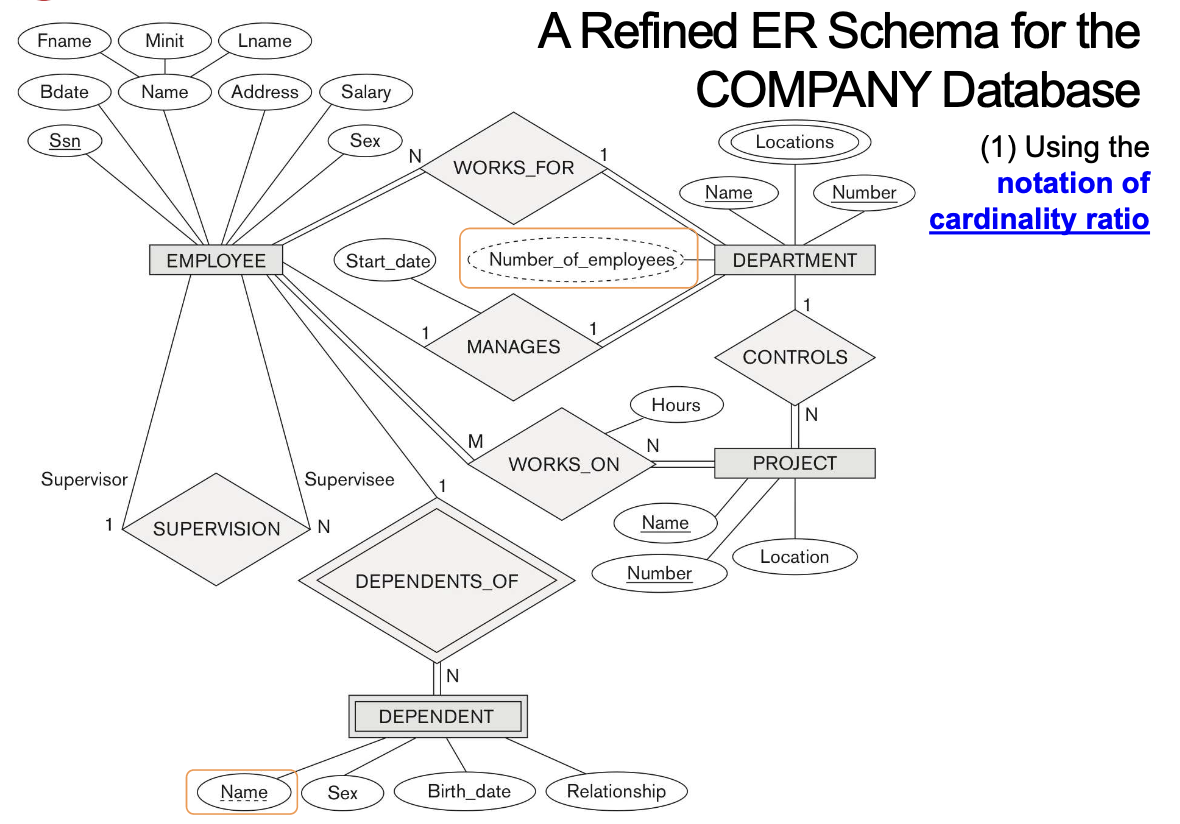
- In a refined design, Initial Entity types의 몇 attribute가 relationship으로 refine될 수 있다.
- Manager of DEPARTMENT -> MANAGES
- Works_On of EMPLOYEE -> WORKS_ON
- Department of EMPLOYEE -> WORKS_FOR
- Controlling_Department of PROJECT -> CONTROLS
- Supervisor of EMPLOYEE -> SUPERVISON
- In general, relationships에 참여하고 있는 동일한 entity types 사이에 하나 이상의 relationship types가 존재할 수 있다.
- 이러한 경우에서는 다른 의미와 다른 relationship instances가 필요하다.
- E.g.
- MANAGES and WORKS_FOR: distinct relationship types between EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT
6-4. Additional Discussion on Relationship Structural Constraints
- Relationship type R에 참여하는 Entity type E의 participation에 대한 constraints를 특정해야 한다.
- 각 Entity Type E에 대한 Instance e는 최소 min, 최대 max 만큼 relation instances in R에 참여
- Denoted by (mix,max)
- Default(no constraint) min = 0 (partial participation), max = n (no limit)
- By all means, min <= max, min >= 0, max >= 1
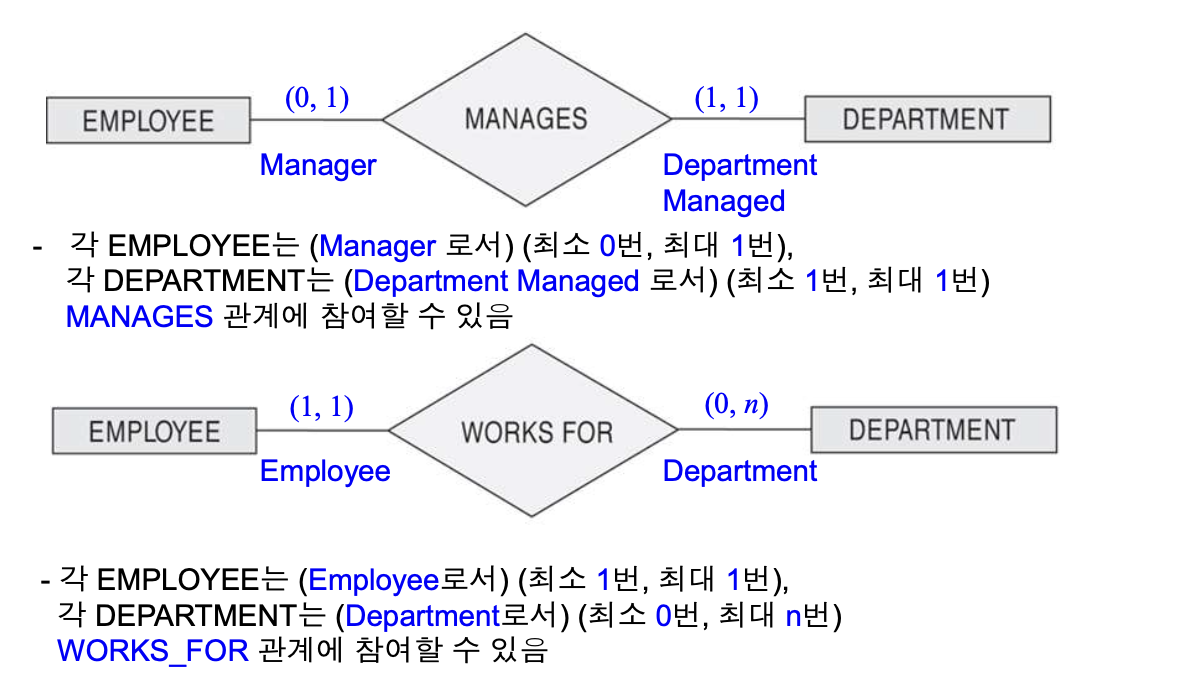
- [Example]
- A department has exactly one manager, and an employee can manage at most one department.
- Translated to (1, 1) for participation of DEPARTMENT in MANAGES
- Translated to (0, 1) for participation of EMPLOYEE in MANAGES
- An employee can work for exactly one department, but a department can have any number of employees.
- Translated to (1, 1) for participation of EMPLOYEE in WORKS_FOR
- Translated to (0, n) for participation of DEPARTMENT in WORKS_FOR
- 각 Entity Type E에 대한 Instance e는 최소 min, 최대 max 만큼 relation instances in R에 참여
6-5. Notation for Relationships in ER Diagrams
6-6. Examples of Relationships in ER Diagrams
6.7. The Initial Design of the COMPANY Database
6-8. A Refined ER Schema for the COMPANY Database
- (1) Using the notation of cardinality ratio
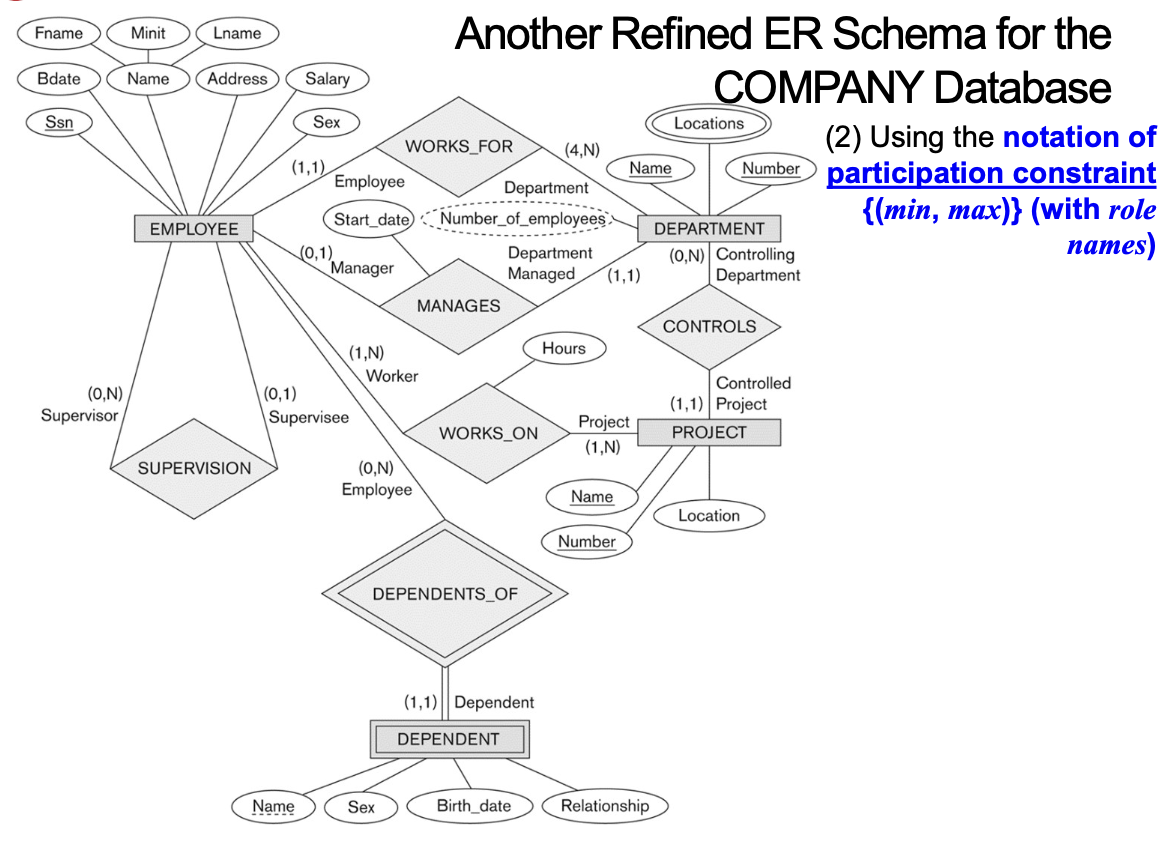
6-9. Another Refined ER Schema for the COMPANY Database
- (2) Using the notation of participation constraint{(min, max)} (with role name)
Reference
Database System Concepts | Abraham Silberschatz
데이터베이스 시스템 7th edition