Introduction
- Layer normalization (LN) has been often incorporated in systems especially in NLP or Speech, due to its adaptaility to sequential data.
- Not all components in LN are necessary, and some are even detrimental.
- This study focuses on the component-wise analysis on LN.
- This study suggests a new form of normalization, called Adaptive Normalization (AdaNorm).
Preliminary: LN algorithms
LN is a normlalization layer to stabilize training, especially effective for models such as transformers. It first standardize the input feature into zero-mean unit-variance. It then introduce two parameters and for bias and gain, respectively. These two parameters enhance the expressive power of the model for the given datasets.
This study first decomposes the LN components into three; (1) Bias and Gain, (2) Forward normalization, and (3) Backward normalization.
- Bias and Gain
Bias and gain increase the expressivity of the model.
- Forward normalization
The LN normalizes the input vectors so that the tensor flows more stabilizedly in forward propagation.
- Backward normalization
The LN not only normalizes the forward progress, but also the backward propagation. The mean and standard deviation are also functions of the input variables, having gradients that can be back-propagated.
Findings
Are bias and gain effective?
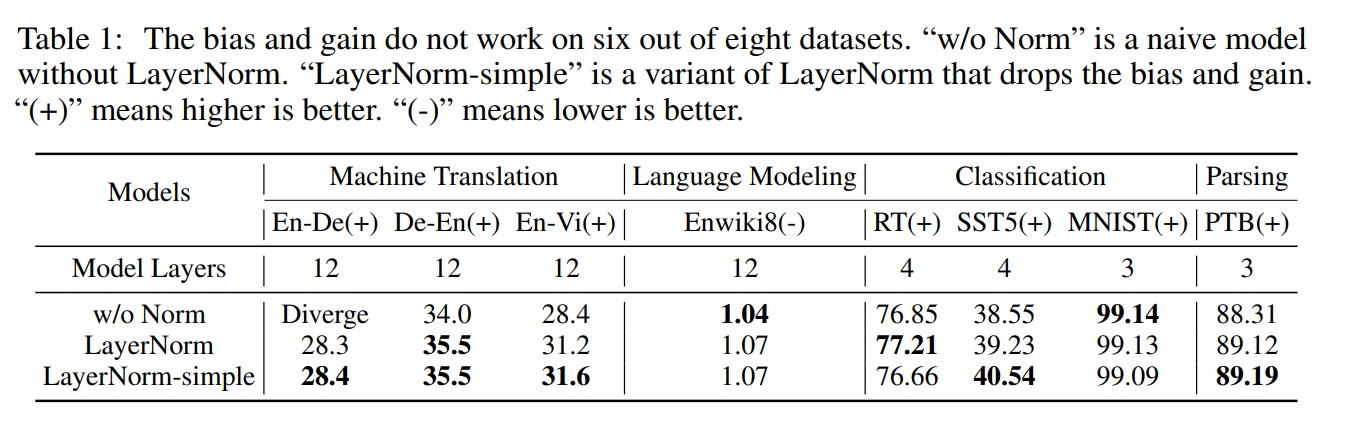
- LayerNorm-simple is LN without bias and gain.
- In 6 out of 8 datasets, bias and gain does not work.
- LN is useful (See the divergene in w/o Norm)
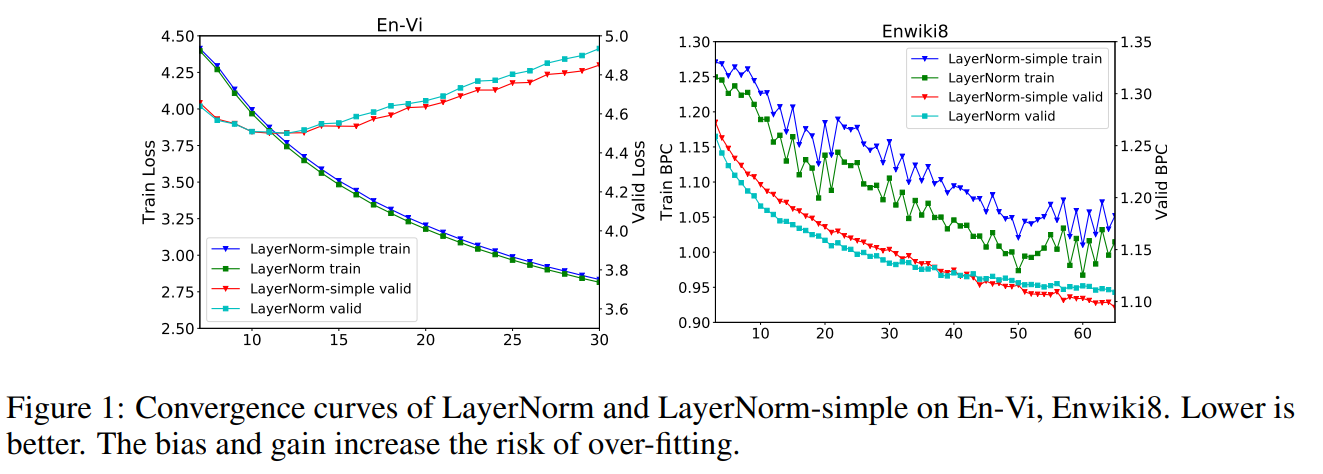
- Valid loss of LN-Simple is lower.
- Training loss of LN-Simple is higher.
--> Bias and gain could lead to overfitting of the model -> lack of generalization power.
Is LN all about forward normalization?
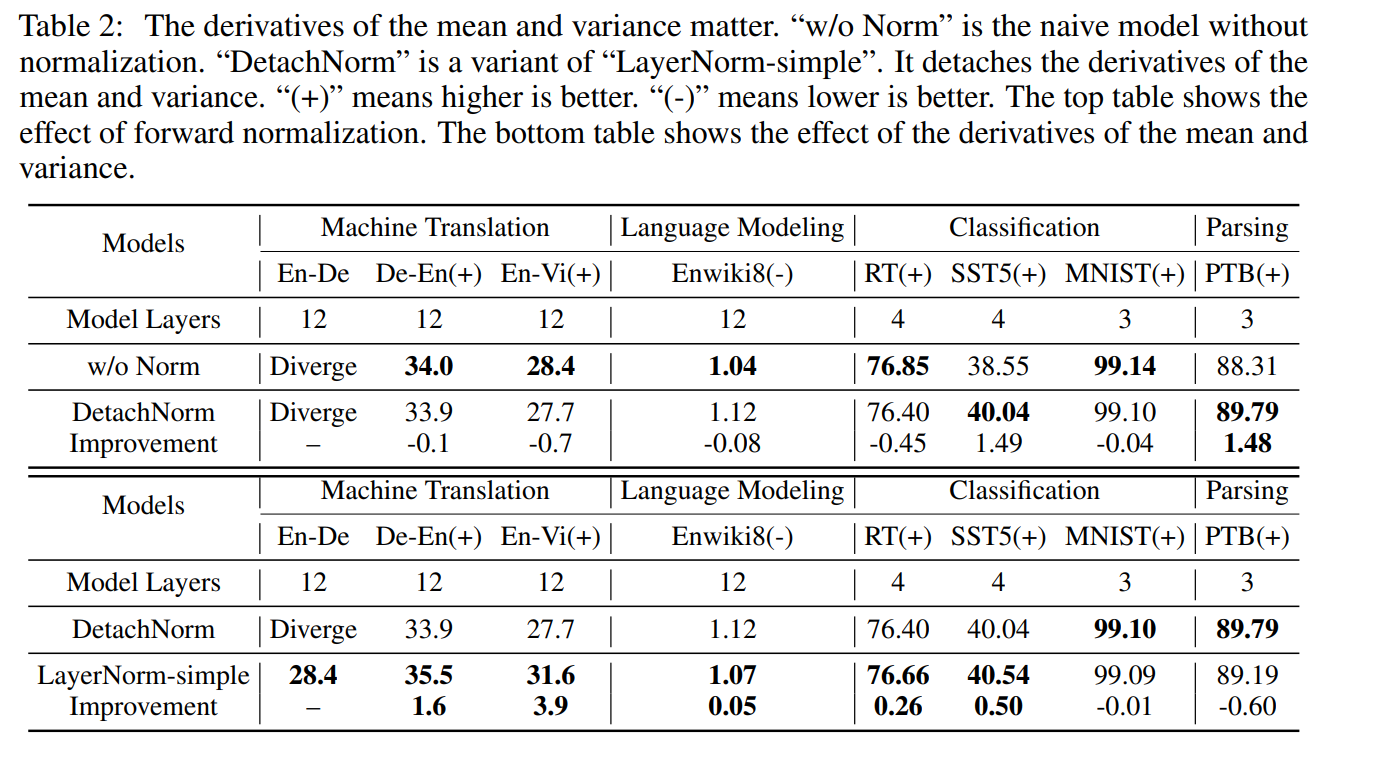
- DetachNorm is LN-simple with derivatives for and detached.
- LN-simple is better than DetachNorm.
--> Backward normalization through gradients in is crucial.
AdaNorm
-
constrains the differentiability, and the average scaling weight, average of output, thus enhancing training stability.
-
AdaNorm adaptively adjusts scaling weights based on inputs -> Not only statistics from training data, but also statistics from given arbitrary data are considered in normalization process.
* Proofs are present in the original paper.
Results
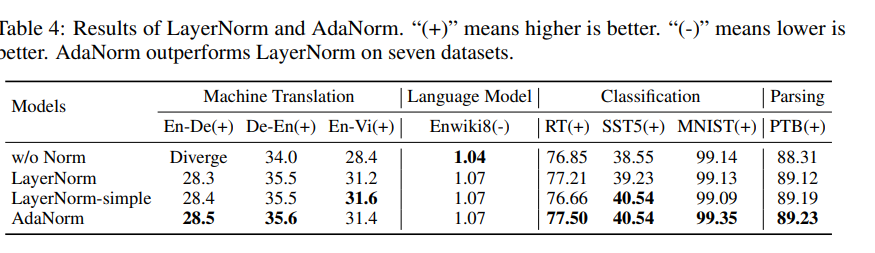
Discussions
Easy-to-understand, well-written paper. Motivations, experimental settings are simple yet effective. It brings much insight. Want to try it on my domain because generalization power matters.
P.S. Mathematical proofs are also present in the full paper.
