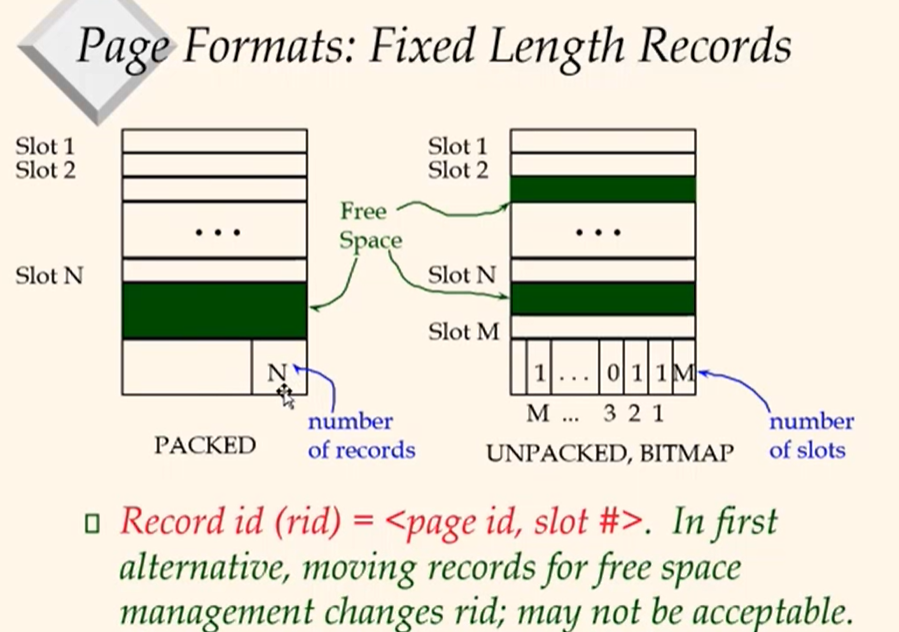
Page Formats: Variable Length Records
When delete the record, all the offset at bottom would be changed. By deleting it, the grey area would get bigger. Rid would not be changed.
Files: a collection of logical records
- Files as a collection of pages when doing I/O
- But higher levels operate on logical records:
- Search/insert/delete/modify the records by field values(e.g., Majos = CS, like SQL)
- Heap Files support file scan and search by record id
- Indexed files support files as a colleciton of logical records.
Heap Files
- Contain records in no particular order
- Good for insert, file scan, search by rids, but finding records by field values needs a file scan
- Keep track of pages with data and pages with free space
- As file grows and shrinks, disk pages are allocated and de-allocated.
Heap Files as a Linked List
-> It could take time a lot in the worst case to find a page with free space(linked list). Each page is one I/O.
Heap File as a Page Directory
Indexed Files
- Heap files support only file scan and rid based search
- Often, files are searched as a collection of logical records through value-based search:
- Find all students in "CS" department (equality search); find all students with a gpa > 3 (range search)
- Indexed files enable value-based search efficiently.
Sorted/Hashed Files
- Search key: fields on which the file is sorted or hashed; need not uniquely identify records:
- Sorted files: records are sorted by search key. Good for equality and range search
- Hashed files: records are grouped into buckets by hash value of search key. Good for equality search
- Used with sorted index and hashed index, more later
Sorted but not stored sequentiallly on 10 disk pages
(number represents age which is one of attributes in records)
System Catalogs
- For each file (relation):
-name, structure(e.g.,Heap file), attributes and types, indexes, integrity constraints, etc. - For each index:
- Name, structure (e.g., sorted or hashed) and search key
- For each view:
view name and definition - Plus statistics, authorization, buffer pool size, page size, etc.
- Catalogs are themselves stored as relations!
Indexing
start from (1,2,3) -> (3,3,4) -> (4,5,5) -> (5,6,7) -> (7,8,8)
Indexes
- A heap file allows retrieving records:
- by rid, or
- by file scan (too slow for large files)
- Often we want to retrieve records to answer value-based queries, e.g.,
- Find all students in the "CS" department
- Find all studetns with a gpa > 3
- Indexes built on sorted/hashed files can answer such quries without file scan
Sorted/Hashed Files
- Search key: a set of fields on which the file is sorted or hashed; need not uniquely identify records.
- Sorted files: records are sorted by search key. Good for equality and range serach
- Hashed files: records are grouped into buckets by search key. Good for equality search
Indexes
- Each index is associated with a search key. It speeds up records retrieval based on the search key.
- Any set of fields can be the search key (e.g.,
<Major, Year>) - Multiple records may have the same search key value
- Possible to have more than 1 index on a file, each having its own search key.
- Any set of fields can be the search key (e.g.,