Heap
heap은 그 자체로 우선 순위 큐의 구현과 일치하다.
heap은 완전이진트리(complete binary tree) 구조로 heap이 되기 위한 조건은 다음과 같다.
- essentially complete binary tree 구조이다.
- min heap의 경우 각 노드에 저장된 값은 자신의 자식 노드들에 저장된 값보다 작거나 같다.
=> root 노드에 저장된 값이 가장 작은 값(min heap)
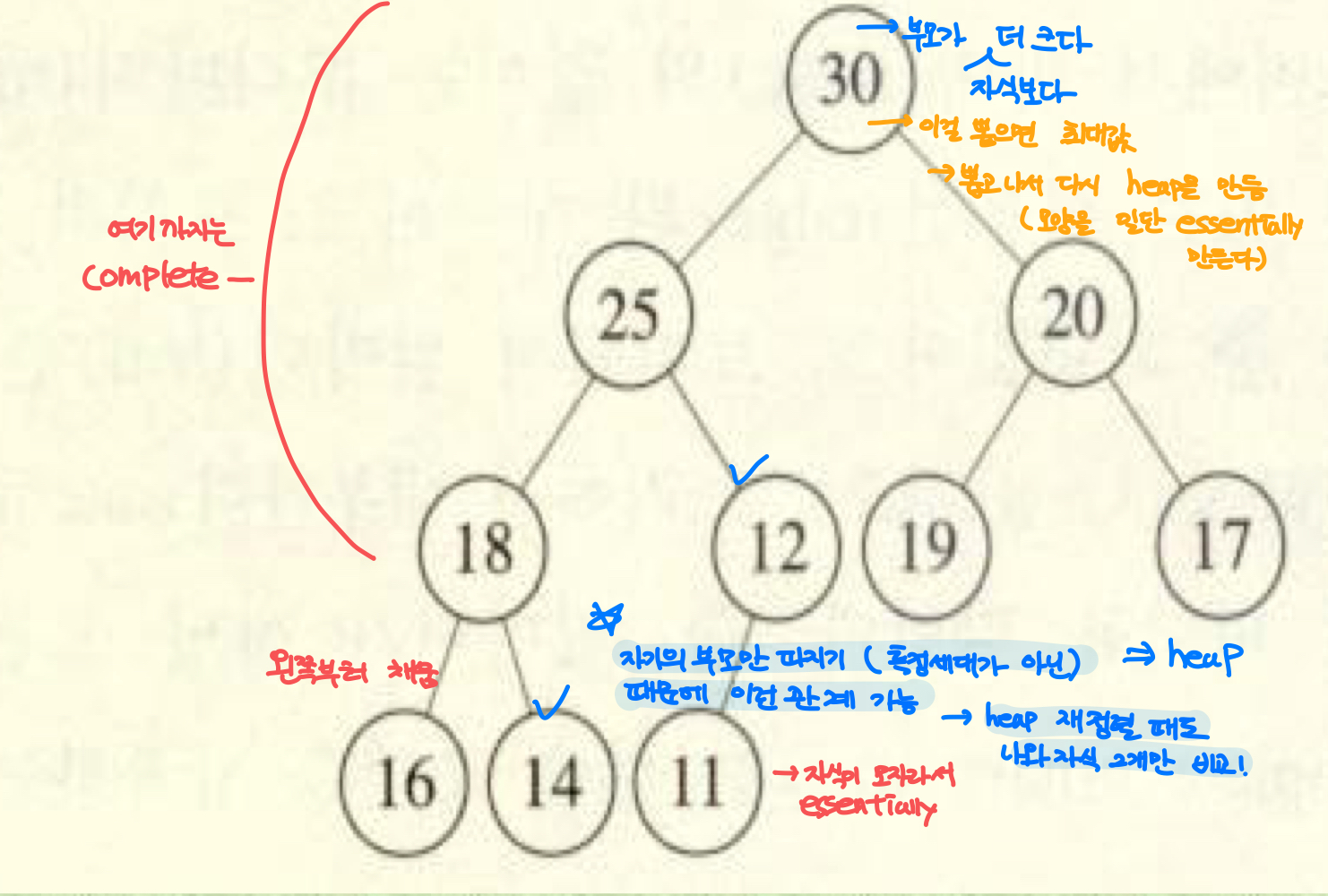
설계된 힙의 속성에 따라 항상 부모가 자식보다 나은 값을 가진다.
max heap의 예
완전 이진 트리( complete binary tree)
2^(k-1)개로 되어있는 element가 2개의 자식을 가진다. 자식이 빈 공간 없이 모두 2개의 자식을 가지면 complete binary tree이고 맨 밑 노드가 꽉 차있지 않으면 essentially binary tree
힙 구현
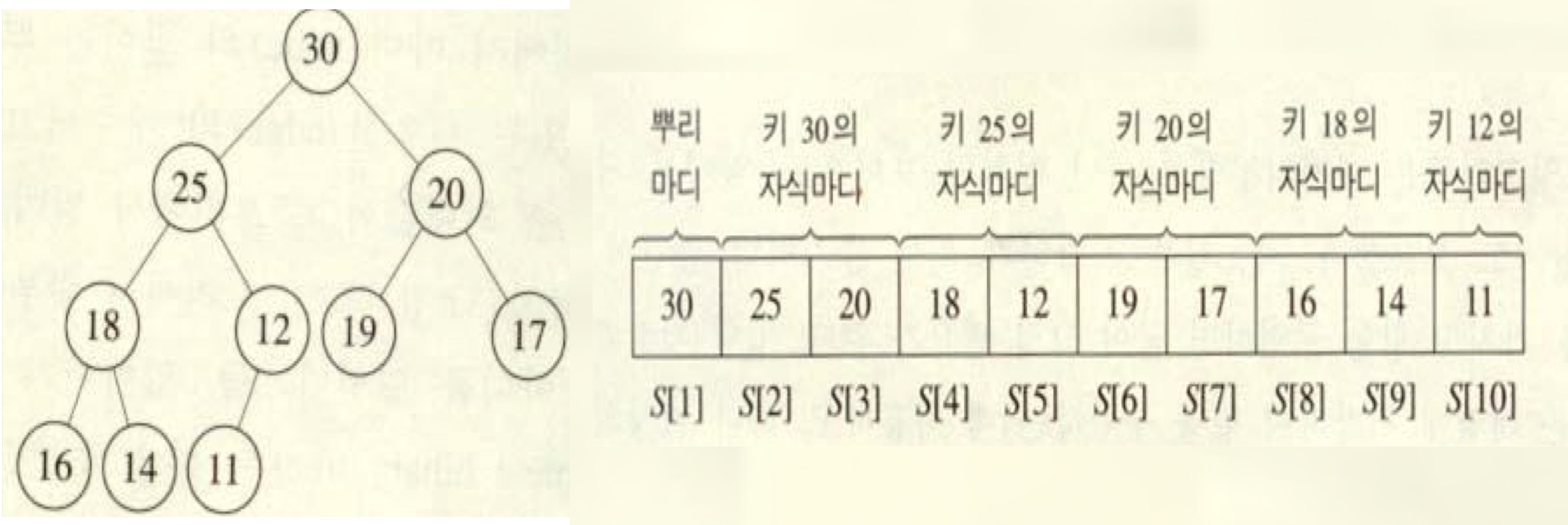
트리는 보통 linked list로 구현한다. 하지만 힙은 트리임에도 불구하고 array 를 기반으로 구현해야한다.
-> 새 노드를 힙의 맨 마지막 위치에 추가해야하는데 이 때 array 기반으로 구현해야 이 과정이 수월하기 때문
- 구현의 편의를 위해 0번 인덱스는 사용하지 않는다.
- 완전 이진 트리의 특성을 활용해 array의 index만으로 부모 자식 관계를 정의
- n 번 째 노드의 left child node = 2n
- n 번 째 노드의 right child node = 2n +1
- n 번 째 노드의 parent node = n/2
heap push()
heap tree 의 높이 : logn
push()를 했을 때 swap 하는 과정이 최대 logN번 반복되기 때문에 시간 복잡도는 O(logn)
heap pop()
pop() 을 했을 때 때 swap 하는 과정이 최대 logN번 반복되기 때문에 시간 복잡도는 O(logn)
의사 코드
void siftdown(heap& H){
node parent, largerchild;
parent = root of H;
largerchild = 큰 key를 가진 parent의 자식마디
while(parent의 키가 largerchild 키보다 작다){
parent 키와 largerchild키 교환;
parent = largerchild;
largerchild = 큰 key를 가진 parent의 자식마디;
}
}keytype root(heap& H){
keytype keyout;
keyout = 루트 노드의 key;
맨끝에 추가된 노드를 루트 노드로 이동;
siftdown(H);
return keyout;
}void removekeys(int n, heap H, keytype S[]){ index i;
for(i=n; i>=1; i--)
S[i] = root(H);
}void makeheap(int n, heap& H){
index i;
heap Hsub;
for(i=d-1; i>=0; i--)
for(all subtree Hsub whose roots have depth i)
siftdown(Hsub);
}힙소트
void heapsort(int n, heap H, keytype S[]){
makeheap(n,H);
removekeys(n,H,S);
}