인코딩과 범주화
1. 인코딩
📌 1. 인코딩(Encoding)
- 실제 데이터셋은 수치형(numerical)과 범주형(categorial) 변수가 혼재한다
- 인코딩은 컴퓨터가 처리하기 용이하도록 기존의 데이터를 변경하는 것
- 범주형 데이터 : 일반적으로 문자열(string)로 되어있다 ---> 숫자로 변환
: 레이블 인코딩(Label Encoding) - 수치형 데이터 : 분류(classification)문제에서 종속변수가 볌주형이어야 하므로 ---> 범주형으로 변환
: 이진화(Binarization), 이산화(Discretization) - 범주형 변수 : 회귀모형, 신경망 모형에서 독립변수는 수치형이어야 하므로 ---> 수치형으로 변환
: 원핫인코딩(One-hot encoding), 더미변수화(Dummy encoding) - 텍스트 데이터 : 자연어 처리를 위해 ---> 토큰화(tokenizing) 과정
: 정수인코딩(Integer encoding)
- 범주형 데이터 : 일반적으로 문자열(string)로 되어있다 ---> 숫자로 변환
- 인코딩된 코드를 원래의 데이터로 변환
: 디코딩(Decoding)
📌 2. 인코딩 분류
- 범주형 데이터 ---> 이산 수치형 데이터
- OrdinalEncoder() (1:1)
: 범주형 데이터를 정수로 인코딩
: 여러 컬럼(독립변수)에 사용 가능 - LabelEncoder() (1:1)
: 범주형 데이터를 정수로 인코딩
: 하나의 컬럼(종속변수, 타겟)에만 사용가능 - TargetEncoder() (1:1)
:범주형 데이터를 특정한 컬럼(타겟)값의 크기와 비례한 숫자로 인코딩
- 범주형 데이터 ---> 이진 데이터
- Binarizer() (1:1)
: 연속 수치형 데이터를 기준값(threshold)을 기준으로 이진수로 인코딩 - LabelBinarizer() (1:M)
: 연속형 데이터를 이진수 컬럼으로 인코딩
: 하나의 컬럼(종속변수, 타겟)에만 사용 가능 - MultiLabelBinzrizer() (1:M)
: multi-class(여러개의 범주가 있는) 데이터를 이진수 컬럼으로 인코딩
: 하나의 컬럼(종속변수, 타겟)에만 사용 가능
2. 인코딩 방법
📌 1. 범주형 --> 이산 수치형
- 테스트를 위한 데이터 세트 생성하기
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'weight' : [40, 80, 60, 50, 90],
'height' : [162, 155, 182, 173, 177],
'sex' : ['f', 'm', 'm', 'f', 'm'],
'blood_type' : ['O', 'A', 'B', 'O', 'A'],
'health' : ['good', 'excellent', 'bad', 'bad', 'good'],
})
df
weight height sex blood_type health
0 40 162 f O good
1 80 155 m A excellent
2 60 182 m B bad
3 50 173 f O bad
4 90 177 m A good- Ordinal Encoder
: 범주형 데이터를 정수로 인코딩
from sklearn.preprocessing import OrdinalEncoder
#데이터프레임 복사
df_oe = df.copy()
#OrdinalEncoder 에 대한 객체 생성
oe = OrdinalEncoder()
#데에터로 OrdinalEncoder 학습
oe.fit(df)
print(f'{oe.categories_ = }')
df_oe = pd.DataFrame(oe.transform(df), columns = df.columns)
df_oeoe.categories_ = [array([40, 50, 60, 80, 90]), array([155, 162, 173, 177, 182]), array(['f', 'm'], dtype=object), array(['A', 'B', 'O'], dtype=object), array(['bad', 'excellent', 'good'], dtype=object)]
weight height sex blood_type health
0 0.0 1.0 0.0 2.0 2.0
1 3.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 1.0
2 2.0 4.0 1.0 1.0 0.0
3 1.0 2.0 0.0 2.0 0.0
4 4.0 3.0 1.0 0.0 2.0- OrdinalEncoder는 수치형 Weight와 Height도 범주형으로 인식하여 변경하므로 주의
df_oe = df.copy()
oe = OrdinalEncoder()
oe.fit(df[['sex', 'blood_type']])
print(f'{oe.categories_ = }')
df_oe.iloc[:,2:4] = oe.transform(df[['sex', 'blood_type']])
df_oeoe.categories_ = [array(['f', 'm'], dtype=object), array(['A', 'B', 'O'], dtype=object)]
weight height sex blood_type health
0 40 162 0.0 2.0 good
1 80 155 1.0 0.0 excellent
2 60 182 1.0 1.0 bad
3 50 173 0.0 2.0 bad
4 90 177 1.0 0.0 good- 디코딩(Decoding)
oe.inverse_transform(df_oe.iloc[:, 2:4])array([['f', 'O'],
['m', 'A'],
['m', 'B'],
['f', 'O'],
['m', 'A']], dtype=object)- Label Encoder
: 범주형 데이터를 정수로 인코딩
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
df_le = df.copy()
le = LabelEncoder()
#LabelEncoder는 하나의 변수에 대해서만 변환 가능
#객체 생성과 fit을 동시에 적용
health_le = le.fit(df.health)
df_le['health'] = health_le.transform(df.health)
df_le
weight height sex blood_type health
0 40 162 f O 2
1 80 155 m A 1
2 60 182 m B 0
3 50 173 f O 0
4 90 177 m A 2- TargetEncoder
: 범주형 데이터를 특정한 컬럼(타겟)의 값의 크기와 비례한 숫자로 인코딩
📌 2. 범주형 --> 이진 데이터
- OneHot Encoder
: 하나의 컬럼에 있는 범주형 데이터를 여러개의 이진수 컬럼(수치형)으로 인코딩
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
#데이터프레임 복사
df_one = df.copy()
#OneGot Encoder에 대한 객체 생성
oneHot = OneHotEncoder().fit(df_one[['blood_type']])
print(f'{oneHot.categories_=}')
#학습된 결과 적용하여 새로운 컬럼 삽입
#OneHot Encoder는 결과를 sparse matrix로 반환하므로 toarray()를 통해 ndarray로 변환
df_one[oneHot.categories_[0]] = oneHot.transform(df_one[['blood_type']]).toarray()
df_one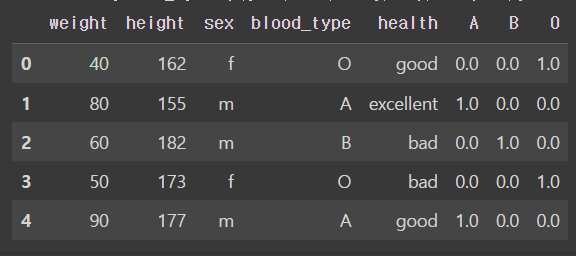
- Dummy Encoding
: pandas에서 제공하는 get_dummies는 One Hot Encoding과 동일한 기능
: 회귀분석에서 범주형 변수 고려할 때 사용
pd.get_dummies(df, columns = ['sex', 'blood_type'], drop_first = False)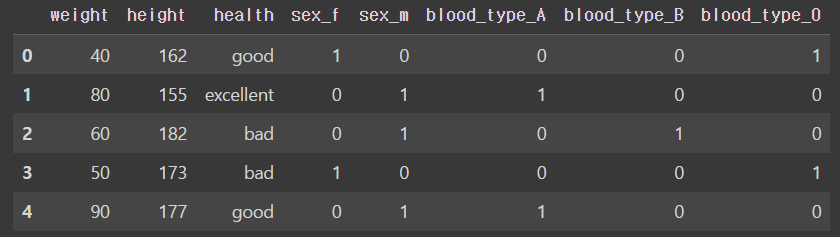
📌 3. 연속 수치형 --> 이진 데이터
- Binarizer
: 연속 수치형 데이터를 기준값(threshold)를 기준으로 이진수로 인코딩
from sklearn.preprocessing import Binarizer
df_bin = df.copy()
#Binarizer 객체 생성과 fit, transform을 동시에 적용
#Binarizer는 수치형 변수에 대해서만 변환 가능
df_bin['weight_bin'] = Binarizer(threshold = 50).fit_transform(df.weight.values.reshape(-1,1))
df_bin['height_bin'] = Binarizer(threshold = 170).fit_transform(df.height.values.reshape(-1,1))
df_bin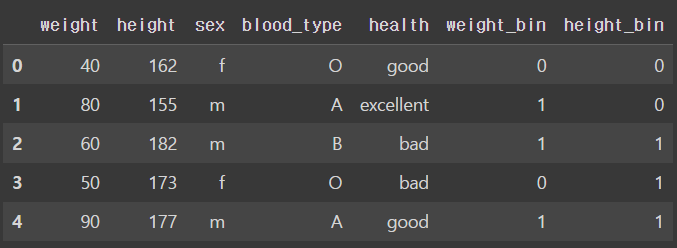
- Label Binarizer
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
df_lb = df.copy()
lb = LabelBinarizer().fit(df.health)
print(f'{lb.classes_=}')
#lb.transform() : 인코딩 변환
health_lb = lb.transform(df.health)
print('health_lb = \n', health_lb)
#인코딩한 데이터를 df로 변환
df_lb[lb.classes_] = health_lb
df_lbhealth_lb =
[[0 0 1]
[0 1 0]
[1 0 0]
[1 0 0]
[0 0 1]] 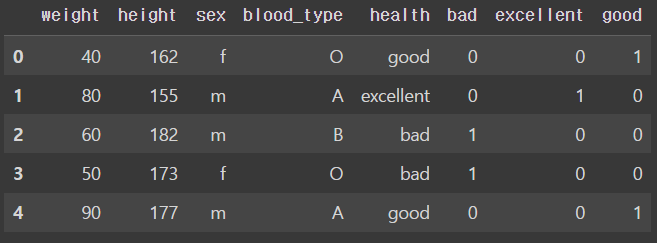
- Multi Label Binarizer
: multi class(여러개의 범주가 있는) 데이터를 이진수 컬럼으로 인코딩
: 하나의 컬럼(종속변수, 타겟)에만 사용 가능
from sklearn.preprocessing import MultiLabelBinarizer
df_mlb = df.copy()
df_mlb['test'] = [['math', 'english'], ['math', 'science'], ['science'],
['math', 'english'], ['science']]
df_mlb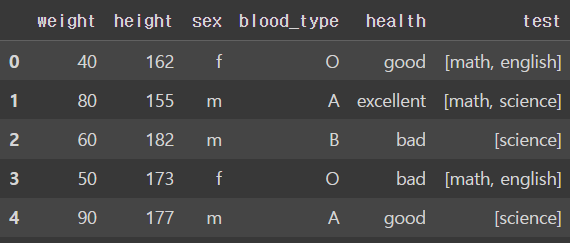
mlb = MultiLabelBinarizer().fit(df_mlb.test)
#classes_ 속성을 이용해 어떤 클래스가 인코딩 되었는지 확인 가능
print(f'{mlb.classes_=}')
df_mlb[mlb.classes_] = mlb.transform(df_mlb.test)
df_mlb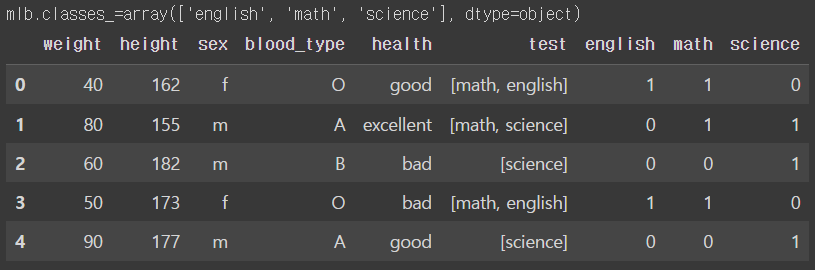
3. 범주화
📌 1. 범주화(Discritization)
: 연속형 변수를 구간별로 나누어 범주형 변수로 변환
: quantization(양자화), binning
- K-bins discretization
from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer
df_kbd = df.copy()
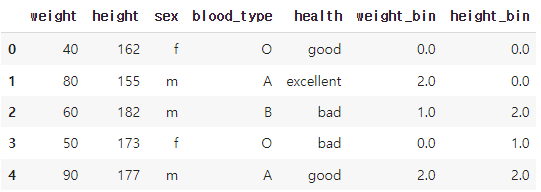
kbd = KBinsDiscretizer(n_bins = 3, encode = 'ordinal').fit(df[['weight', 'height']])
#kbd.transformer() : 인코딩 변환
df_kbd[['weight_bin', 'height_bin']] = kbd.transform(df[['weight', 'height']])
df_kbd