
Hashing
- 딕셔너리의 탐색, 삽입, 삭제를 에 가능하게 하는 자료구조
Static Hashing
정적 해싱 소개
hash table이라 불리는 테이블에 딕셔너리 쌍(키, 값)이 저장 →b개의 버킷으로 구분(ht[0], .., ht[b-1])- 버킷: 개당
s개의 슬롯을 가지고 있음. 각 슬롯은 하나의 딕셔너리 쌍을 가질 수 있을 정도로 충분한 크기 hash function: 키가k인 딕셔너리 쌍의 주소 공간을 결정하는 함수. 즉 키를 버킷에 매핑하는 함수 → 모든 키k에 대해서h(k) → 0 ~ b-1h(k)는 따라서 키 값k의 주소 공간
정적 해싱의 정의
- Key Densitiy: 가능한 키의 개수
T중 테이블에 존재하는 딕셔너리 (키, 값) 쌍의 개수n이 어느 정도인지에 따라 결정.n/T - Loading Density / Loading Factor: 버킷의 개수
b과 버킷이 개당 가지고 있는 슬롯의 개수s를 곱하면 저장 가능한 총 공간이 나오는데, 이 총 공간에 현재 어느 정도로 딕셔너리 (키, 값) 쌍이 저장되어 있는지 보여줌.a=n/(sb)
해시 테이블
- 버킷의 개수는 일반적으로 가능한 키의 개수보다 적기 때문에 동일한 버킷에 여러 개의 키가 들어갈 수 있음
- 두 개의 키 , 는 해시 함수 값이 같다면() 서로 같은
synonym으로 판단 overflow: 딕셔나리 (키, 값) 쌍을 이미 버킷이 가득 찬 곳에 삽입하려 할 때 발생collision: 새로운 딕셔너리 (키, 값) 쌍에 대한 버킷이 삽입하는 순간 비어 있지 않은 상태. 즉 다른 딕셔너리 쌍이 차지하고 있는 상태.
해시 함수
overflow가 없다면 삽입, 삭제, 탐색은 현재 해시 테이블 상에 저장된 딕셔너리 (키, 값) 쌍의 개수n과 상관없이 (1). 해시 함수 연산 시간 (2). 하나의 버킷을 탐색하는 시간 두 가지를 합한 시간 복잡도.- 해시 함수로 인한
collsion이 최소화될 때 총 연산 비용 감소 - 동일한 해시 함수를 들어오는 모든 입력값에 사용
1. Division
- 가장 흔한 해시 함수
- 키 값이 음수가 아닌 경우 가정
- 버킷은 모듈러 연산(%)의 값을 담음
- 이기 때문에 버킷 인덱스는 (
0...D-1)이고, 적어도D개의 사이즈는 되어야 함 D는 일반적으로 소수로 정하는데, (1). 작으면 홈 버킷의 분포도가 커지고 (2). 크다면 바이어스의 정도가 감소한다.
2. Mid-Square
- 주어진 키의 제곱근을 구하고 근삿값을 해시하는 함수
3. Folding
- 주어진 키 값
k가 여러 개의 부분으로 나눠지는데, 가능한 같은 크기로 나뉜다. - E.g.) 으로 14비트. (3/3/3/3/2)의 다섯 부분으로 나뉠 수 있다. →
- Shift Folding: 마지막 부분을 제외한 다른 모든 부분들이 오른쪽으로 시프트 연산된다. 각 라인의 LSD(
least significant digit)는 마지막 부분의 상응하는 디지트와 매칭. 다른 부분이 해시 함수를 구하기 위해 가산된다. - Folding at the boundaries: 분할이 이루어지는 경계 선상에 키가 나뉘고, 같은 곳으로 떨어지는 디지트가 해시 함수를 구하기 위해 서로 더해진다.
- Shift Folding →
- Folding at the boundaries: folding의 경계는 과 , 과 다. 각 두 번째 위치에 존재하는 파티션의 수를 거꾸로 한 뒤 가산한다. 즉
4. Digit Analysis
- 사전에 주어진 모든 키 값을 알 수 있는 정적 파일에 유용한 방법
- 키 → 라딕스
r을 사용하는 수로 번역 - 라딕스를 통해 각 키의 디지트를 검사. 가장 휜 정도가 심한 디지트가 삭제됨
- 디지트 삭제가 충분히 이루어진다면 남아 있는 디지트는 주소 공간의 범위를 결정하는 데 많은 영향을 주지 않기 때문에 해시 함수로 기능
오버플로우 다루기
오픈 어드레싱
- 네 가지 방법 존재.
1. Linear Probing
- 키 값이
k인 딕셔너리 쌍을 삽입할 때 해시 테이블을 순서대로 탐색 - 탐색 중 아직 딕셔너리 쌍이 없는 빈 버킷 공간을 발견하면 탐색 종료. 그 버킷에 삽입할 딕셔너리 쌍을 삽입한다.
- 빈 버킷이 없을 때(
overflow): 테이블 사이즈를 늘려야 함 loading density가 0.75 이상일 때 테이블 사이즈를 늘리는 게 해시 함수 비용에 이로움해시 테이블 사이즈를 늘리면 해시 함수 역시 새롭게 만들어야 한다!
import Foundation
struct CustomHash {
private var dictionary: [String?]
// bucket == slot == 1
private var bucketSize:Int
private let primeNumber = 13
init(bucketSize: Int) {
self.bucketSize = bucketSize
dictionary = Array(repeating: nil, count: bucketSize)
}
private func getHashValue(_ key: String) -> Int {
let asciiSum = key.map{Int($0.asciiValue ?? 0)}.reduce(0, +)
return asciiSum % primeNumber
}
mutating private func makeDoubleDictionary() {
let newDictionary:[String?] = Array(repeating: nil, count: bucketSize)
bucketSize *= 2
dictionary += newDictionary
}
mutating func insert(_ key: String) {
let hashValue = getHashValue(key)
for i in 0..<bucketSize {
let validIdx = (hashValue + i) % bucketSize
if dictionary[validIdx] == nil {
dictionary[validIdx] = key
return
}
}
// overflow 발생 -> 해시 테이블 사이즈 2배로 늘리고 한 번더 insert 실행
makeDoubleDictionary()
insert(key)
}
func printDictionary() {
for item in dictionary.enumerated() {
if item.element != nil {
print("Index \(item.offset) : \(item.element!)")
}
}
}
}
var customHash = CustomHash(bucketSize: 5)
customHash.insert("dog")
customHash.insert("cat")
customHash.insert("tiger")
customHash.insert("lion")
customHash.printDictionary()
// Index 0 : cat
// Index 1 : tiger
// Index 2 : dog
// Index 3 : lion
customHash.insert("panda")
customHash.insert("horse")
customHash.insert("monkey")
customHash.insert("human")
customHash.insert("sheep")
customHash.printDictionary()
// Index 0 : cat
// Index 1 : tiger
// Index 2 : dog
// Index 3 : lion
// Index 4 : panda
// Index 5 : horse
// Index 6 : human
// Index 7 : sheep
// Index 9 : monkey2. Quadratic Probing
linear probing에서i를 제곱하여 사용함
3. Rehashing
- 일련의 해시 함수를 계속해서 사용함
4. Random Probing
체이닝
Linear Probing: 키 값 탐색이 다른 해시 값을 가지고 있는 딕셔너리 쌍과의 비교하기 때문에 효율적으로 좋지 않음- 버킷 당 하나의 리스트가 있다면 해시 값을 리턴했을 때 곧바로 그 버킷에 주어진 키를 삽입할 수 있다. → 각 키스트가 모든
synonyms를 가지고 있음 - 해시 연산 시간: (1). 해시 주소 계산 (2). 해시 주소에 해당 키가 존재하는지 검사하는 시간
import Foundation
struct CustomChainingHash {
private var dictionary: [[String]]
private var bucketSize: Int
private let primeNumber = 13
init(bucketSize: Int) {
self.bucketSize = bucketSize
dictionary = Array(repeating: [String](), count: bucketSize)
}
private func getHashValue(_ key: String) -> Int {
let asciiSum = key.map{Int($0.asciiValue ?? 0)}.reduce(0, +)
return asciiSum % primeNumber
}
mutating func insert(_ key: String) {
let hashValue = getHashValue(key)
dictionary[hashValue % bucketSize].append(key)
// 특정 키가 버킷 리스트 내에 존재한다 하더라도 탐색하지 않고 그대로 삽입 (중복 키 존재 가능)
// 딕셔너리 버킷 아이템 내 키 존재 여부를 통해 결정 가능
}
func printDictionary() {
for item in dictionary.enumerated() {
if !item.element.isEmpty {
print("Index \(item.offset) :", terminator: " ")
for key in item.element {
print(key, terminator: " ")
}
print()
}
}
}
}
var customChainHash = CustomChainingHash(bucketSize: 5)
customChainHash.insert("lion")
customChainHash.insert("tiger")
customChainHash.insert("whale")
customChainHash.insert("cat")
customChainHash.insert("cow")
customChainHash.printDictionary()
// Index 0 : lion cat
// Index 1 : tiger
// Index 4 : whale cow
customChainHash.insert("sheep")
customChainHash.insert("fish")
customChainHash.insert("human")
customChainHash.insert("monkey")
customChainHash.insert("ape")
customChainHash.insert("zibra")
customChainHash.insert("pig")
customChainHash.printDictionary()
// Index 0 : lion cat sheep fish
// Index 1 : tiger ape
// Index 3 : zibra pig
// Index 4 : whale cow human monkey
Dynamic Hashing
동적 해싱 소개
- 정적 해싱의
loading density→ 스레드홀드 초과 시 해시 테이블의 사이즈를 변경 + 해시 함수 변경해야 하는 오버헤드 존재 - 동적 해싱: 재구축(
rebuild)이 단 한 개의 버킷에서만 일어나도록 하는 해싱 기법. 즉 적절한 해시 테이블 퍼포먼스를 보장하는 방법 - : 의 LSB 에 의해 만들어지는 정수
Directory
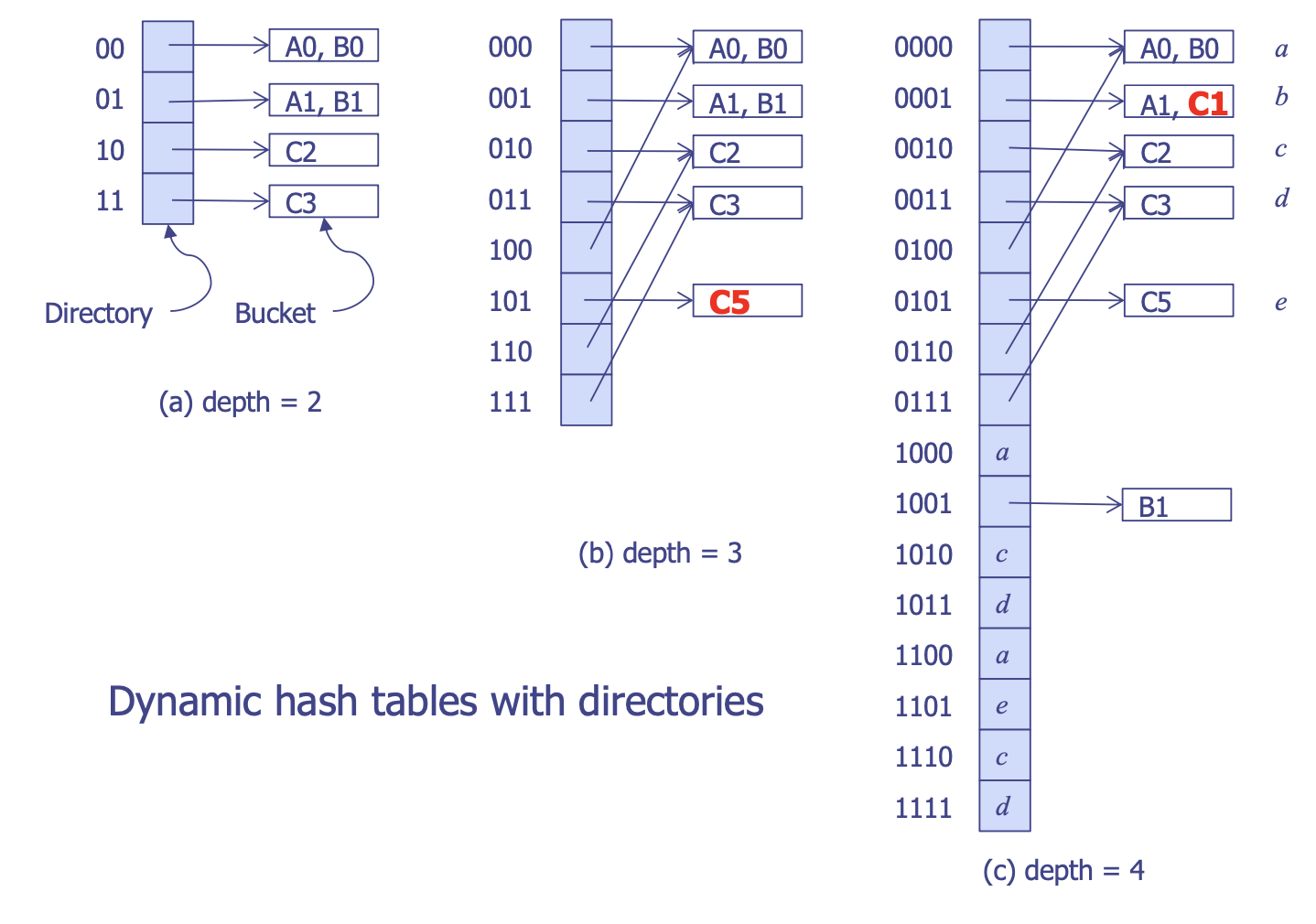
- 버킷 포인터에 대한 디렉토리
d사용: 디렉토리 크기는 디렉토리 인덱스를 알아내기 위한 해시 함수 가 가지는 비트 개수에 따라 달라짐 - 일 때 디렉토리 크기는 으로 결정
- 의 비트 개수는 디렉토리 패스(
directory path)라고 불림 - 추가로 Directoryless 기법도 존재
import Foundation
struct DirectoryHash {
private var directories = Array(repeating: [String](), count: 4)
private var curDepth = 2
private let bucketSize = 2
private func getHashValue(_ key: String) -> Int {
// 각 키의 비트 값은 사전에 미리 딕셔너리로 기록
let hashDict = ["A0" : "100000", "A1" : "100001", "B0" : "101000", "B1" : "101001", "C1" : "110001", "C2" : "110010", "C3" : "110011", "C5" : "110101"]
guard let bits = hashDict[key] else { return -1 }
let bitsArray = Array(bits).map{String($0)}
var LSBString = ""
for idx in (bitsArray.count-curDepth+1)..<(bitsArray.count) {
LSBString += bitsArray[idx]
}
guard let LSB = Int(LSBString) else { return -1 }
return LSB
}
mutating func insert(_ key: String) {
let hashValue = getHashValue(key) % directories.count
if hashValue == -1 {
return
}
if directories[hashValue].count < bucketSize {
directories[hashValue].append(key)
} else {
let newDepthDirectories = Array(repeating: [String](), count: Int(pow(2.0, Double(curDepth))))
directories += newDepthDirectories
curDepth += 1
relocate(hashValue)
insert(key)
}
}
mutating func relocate(_ hashValue: Int) {
var removedKeys = [String]()
for key in directories[hashValue] {
let newHashValue = getHashValue(key)
if newHashValue != hashValue {
removedKeys.append(key)
}
}
for key in removedKeys {
guard let removedIdx = directories[hashValue].firstIndex(of: key) else { continue }
directories[hashValue].remove(at: removedIdx)
}
for key in removedKeys {
insert(key)
}
}
func printDirectories() {
for directoryItem in directories.enumerated() {
if !directoryItem.element.isEmpty {
print("idx: \(directoryItem.offset)", terminator: " ")
for item in directoryItem.element {
print(item, terminator: " ")
}
print()
}
}
}
}
var directoryHash = DirectoryHash()
directoryHash.insert("A0")
directoryHash.insert("B0")
directoryHash.insert("A1")
directoryHash.insert("B1")
directoryHash.insert("C2")
directoryHash.insert("C3")
directoryHash.printDirectories()
// idx: 0 A0 B0
// idx: 1 A1 B1
// idx: 2 C2
// idx: 3 C3
directoryHash.insert("C5")
directoryHash.printDirectories()
// idx: 0 A0 B0
// idx: 1 A1 B1
// idx: 2 C2
// idx: 3 C3
// idx: 5 C5
directoryHash.insert("C1")
directoryHash.printDirectories()
// idx: 0 A0 B0
// idx: 1 A1 C1
// idx: 2 C2
// idx: 3 C3
// idx: 5 C5
// idx: 9 B1- 특정 키값이 입력될 때 해당 LSB를 읽을 수 있도록 문자열 딕셔너리로 가볍게 구현, 딕셔너리 포인터가 가리키는 버킷 역시 최대 사이즈 2의 문자열 배열로 구현
