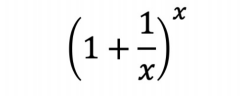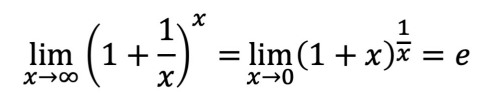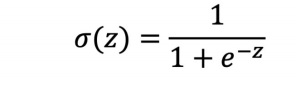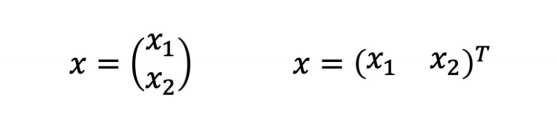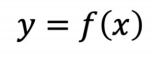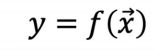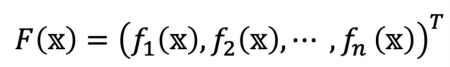기초 수학 개념
- 회귀 모델
- 내가 가지고 있는 데이터를 직선으로 만들어 두고, 각 값들을 예측하는 것
- (회귀 모델 예측 결과) : 연속된 변수값
- 분류 모델
- 구분이 명확함
- 몇개의 종류에서 값을 찾아내는 것 (iris, 와인 프로젝트)
- 이진 분류
- 0 과 1
- 맞다, 아니다
- 전체 데이터 에서 실제 1의 값을 가진 데이터
- TP = 실제 1인데 1로 맞춘 것
- FN = 실제 1인데 틀리게 예측한 값
- 전체 데이터 에서 0의 값을 가진 데이터(아래)
- TN = 0을 0으로 맞춤
- FP = 0을 1이라고 클리게 맞춤
- Accuracy
- 전체 데이터 중 맞게 예측한 것의 비율
- Precision
- 내가 1이라고 말한(예측한) 것들 중에서 실제 1인 것의 비율
- recall (재현율)
- 실제 1일 데이터 중에서 1이라고 예측
- fall out (FPR)
- 실제 0 중에서 1이라고 잘못 예측한 것
- F1-Score (조합평균)
- recall + recision 결합한 지표
- 어느 한쪽으로 치우치지 않고 둘다 높은 값을 가질 수록 높은 값을 가짐
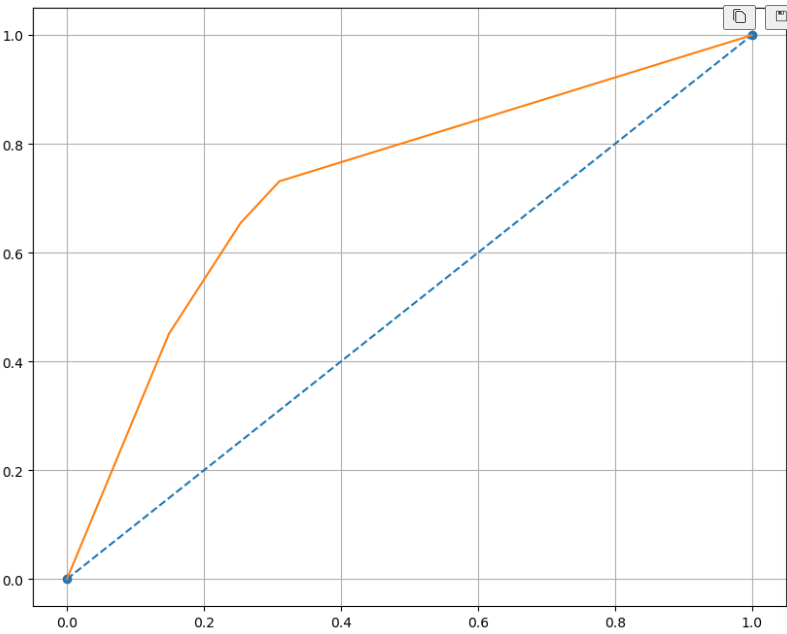
- ROC 곡선
- FPR(= fall out)이 변할때 TPR(= Recall)의 변화를 그린 그림
- FPR을 X축, TPR을 Y축
- 직선에 가까울 수록 머신러닝 모델의 성능이 떨어지는 것으로 판단
- AUC
- ROC 커브의 밑에 면적
1. ROC 커브 그리그
# 1) 데이터 불러오기 & concat
import pandas as pd
red_url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PinkWink/ML_tutorial/master/dataset/winequality-red.csv'
white_url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PinkWink/ML_tutorial/master/dataset/winequality-white.csv'
red_wine = pd.read_csv(red_url, sep=';')
white_wine = pd.read_csv(white_url, sep=';')
red_wine['color'] = 1.
white_wine['color'] = 0.
wine = pd.concat([red_wine, white_wine])
# 2) 맛 분류를 위한 데이터 정리
wine['taste'] = [1. if grade > 5 else 0 for grade in wine['quality']]
X = wine.drop(['taste','quality'], axis= 1)
y = wine['taste']
# 3) 의사 결정 나무 모델 확인
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=13)
wine_tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2, random_state=13)
wine_tree.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_tr = wine_tree.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test = wine_tree.predict(X_test)
print('Train Acc: ', accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_tr))
print('Test Acc: ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_test))Train Acc: 0.7294593034442948
Test Acc: 0.7161538461538461
# 4) 각 수치 구하기
from sklearn.metrics import (accuracy_score, precision_score,
recall_score, f1_score, roc_auc_score, roc_curve)
print('accuracy : ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_test))
print('recall :', recall_score(y_test, y_pred_test))
print('precision :', precision_score(y_test, y_pred_test))
print('AUC score : ', roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_test))
print('F1-score', f1_score(y_test, y_pred_test))accuracy : 0.7161538461538461
recall : 0.7314702308626975
precision : 0.8026666666666666
AUC score : 0.7105988470875331
F1-score 0.7654164017800381
wine_tree.predict_proba(X_test)array([[0.61602594, 0.38397406],
[0.61602594, 0.38397406],
[0.12197802, 0.87802198],
...,
[0.12197802, 0.87802198],
[0.61602594, 0.38397406],
[0.12197802, 0.87802198]])
# 5) 그리기
# 모듈
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# X_test에 대한 predict_proba를 먼저 찾음
# 위에서 학습한 wine_tree의 predict_proba 함수에 X_test에를 넣어 줌
# [:, 1] : 1인 확률들만 취득 (위 결과값의 배열 = [0,1])
pred_proba = wine_tree.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
# pred_proba : 위 결과값
# pred_proba를 roc_curve에 넣고 확률값을 확인
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, pred_proba)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
plt.plot([0,1], [0,1], 'o', ls='dashed')
# x축, y축
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.grid()
plt.show()2.함수의 기초
1) 다항함수
# 1) 기본
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.style.use('seaborn-whitegrid')
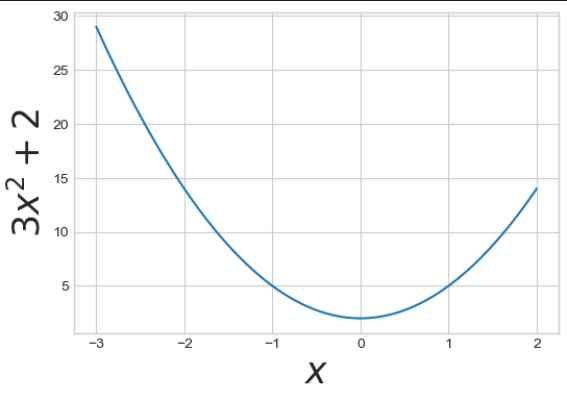
# -3 ~ 2 까지 100개 만들기
x = np.linspace(-3,2,100)
y = 3*x**2 + 2
plt.figure(figsize=(6,4))
plt.plot(x,y)
# 수학 기호 (이탤릭체)
plt.xlabel('$x$', fontsize=25)
plt.ylabel('$3x^2 +2$', fontsize=25)
plt.show()# 2) x축 방향 이동
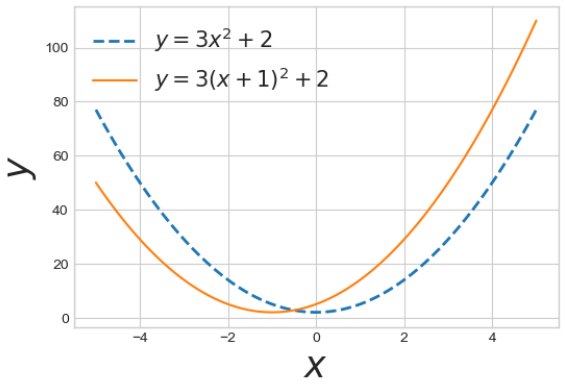
x = np.linspace(-5,5,100)
y1 = 3*x**2 +2
y2 = 3*(x+1)**2 +2
plt.figure(figsize=(6,4))
plt.plot(x, y1, lw=2, ls='dashed', label='$y=3x^2 +2$')
plt.plot(x, y2, label='$y=3(x+1)^2 +2$')
plt.legend(fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel('$x$', fontsize=25)
plt.ylabel('$y$', fontsize=25)
plt.show()2) 지수함수
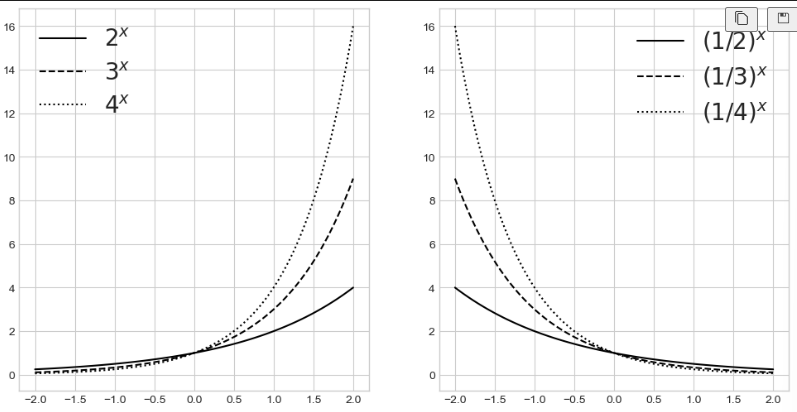
x = np.linspace(-2,2,100)
a11, a12, a13 = 2,3,4
y11, y12, y13 = a11**x, a12**x, a13**x
a21, a22, a23 = 1/2, 1/3, 1/4
y21, y22, y23 = a21**x, a22**x, a23**x# 1) 그래프
# plt.subplots(1행, 2열, 사이즈)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 6))
ax[0].plot(x, y11, color='k', label=r"$2^x$")
ax[0].plot(x, y12, '--', color='k', label=r"$3^x$")
ax[0].plot(x, y13, ':', color='k', label=r"$4^x$")
ax[0].legend(fontsize=20)
ax[1].plot(x, y21, color='k', label=r"$(1/2)^x$")
ax[1].plot(x, y22, '--', color='k', label=r"$(1/3)^x$")
ax[1].plot(x, y23, ':', color='k', label=r"$(1/4)^x$")
ax[1].legend(fontsize=20)3)특이한 지수
# 어떤 함수 인지 대략 확인
import numpy as np
x = np.array([10,100,1000,10000,100000])
(1+1/x)**xarray([2.59374246, 2.70481383, 2.71692393, 2.71814593, 2.71826824])
=> x 값이 커질 수록 어떠한 값으로 수렴(----)하는 함수임을 확인
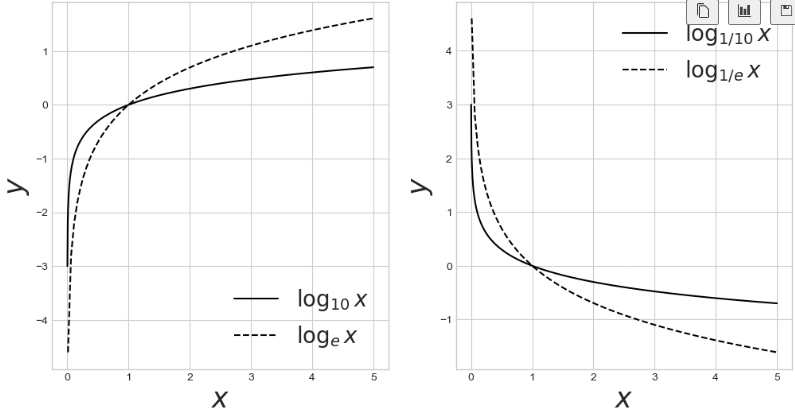
4) 로그함수
# 데이터 준비
# 로그함수를 만들고 싶다면
def log(x, base):
# 밑수(base)를 return으로 지정
return np.log(x)/np.log(base)
x1 = np.linspace(0.0001, 5, 1000)
x2 = np.linspace(0.01, 5, 100)
y11, y12 = log(x1, 10), log(x2, np.e)
y21, y22 = log(x1, 1/10), log(x2, 1/np.e)# 그리기 준비
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(12, 6))
ax[0].plot(x1, y11, color='k', label=r'$\log_{10} x$')
ax[0].plot(x2, y12, '--', color='k', label=r'$\log_{e} x$')
ax[0].set_xlabel('$x$', fontsize=25)
ax[0].set_ylabel('$y$', fontsize=25)
ax[0].legend(fontsize=20, loc='lower right')
ax[1].plot(x1, y21, color='k', label=r'$\log_{1/10} x$')
ax[1].plot(x2, y22, '--', color='k', label=r'$\log_{1/e} x$')
ax[1].set_xlabel('$x$', fontsize=25)
ax[1].set_ylabel('$y$', fontsize=25)
ax[1].legend(fontsize=20, loc='upper right')
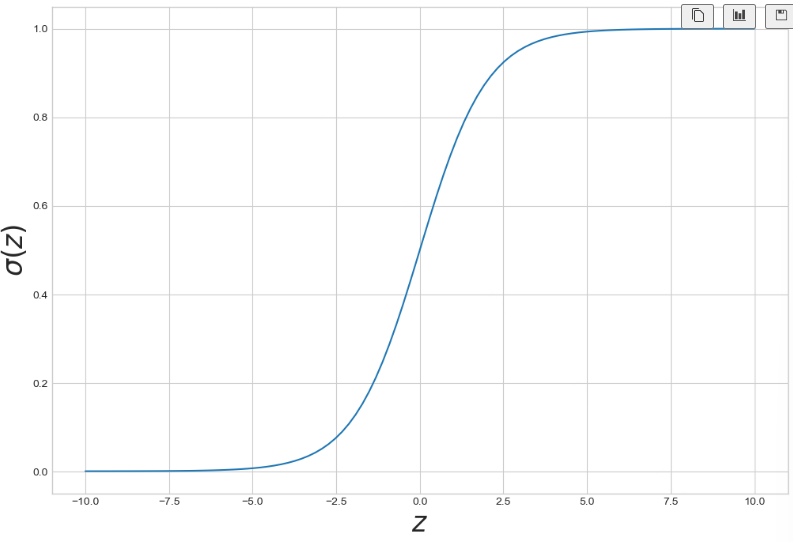
plt.show()5) 시그모이드
0 과 1사이의 값을 가진다
0으로 수렴하지 않음
무조건 1로 수렴함
z = np.linspace(-10,10,100)
sigma = 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.plot(z, sigma)
plt.xlabel('$z$', fontsize=25)
plt.ylabel('$\sigma(z)$', fontsize=25)
plt.show()3. 함수의 표현
1_벡터의 표현
2_스칼라 함수
-
단일변수 스칼라함수
-
다중변수 스칼라 함수
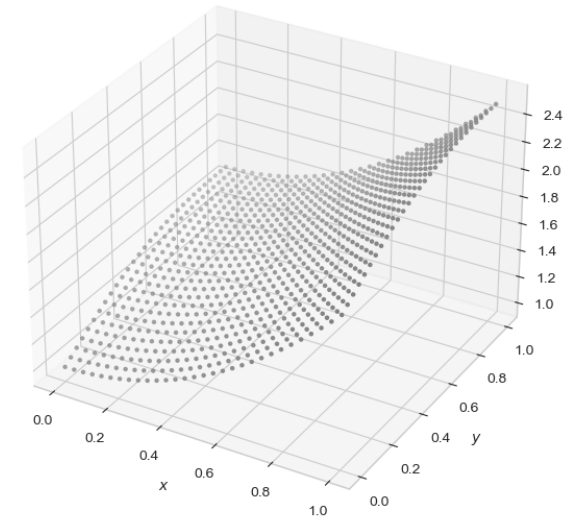
3_다변수 벡터 함수
u = np.linspace(0,1,30)
v = np.linspace(0,1,30)
# np.meshgrid : u,v의 많은 값을 한번에 계산(점찍고)하고 싶을 때 meshgrid를 사용
U, V = np.meshgrid(u, v)
Z = (1+U**2) + V/(1+V**2)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7,7))
# projection : 3D로 그리는 명령어
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.xaxis.set_tick_params(labelsize=10)
ax.yaxis.set_tick_params(labelsize=10)
ax.zaxis.set_tick_params(labelsize=10)
ax.set_xlabel('$x$',fontsize=10)
ax.set_ylabel('$y$',fontsize=10)
ax.set_zlabel('$z$',fontsize=10)
ax.scatter3D(U, V, Z, marker='.', color='gray')
plt.show()4_함수의 합성
log 함수는 x가 크면 조금 변하고, x가 작으면 많이 변한다
-
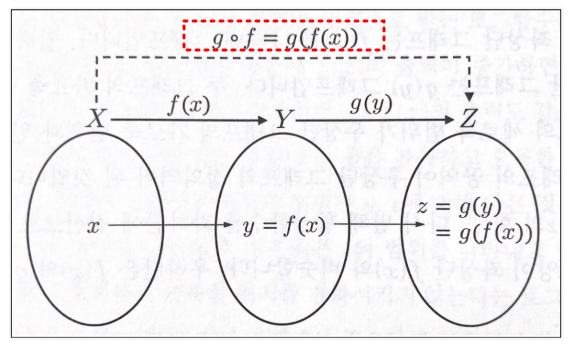
-
각 함수의 모양 확인
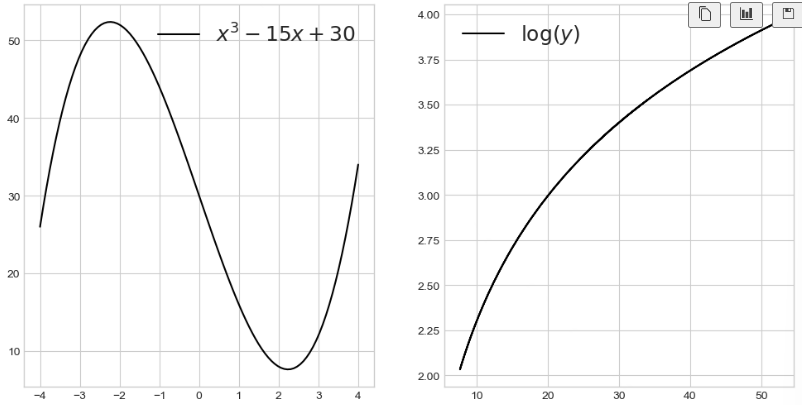
x = np.linspace(-4, 4, 100)
# f(x)
y = x**3 - 15*x + 30
# g(y)
z = np.log(y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 6))
ax[0].plot(x, y, label=r'$x^3 - 15x + 30$', color='k')
ax[0].legend(fontsize=18)
ax[1].plot(y, z, label=r'$\log(y)$', color='k')
ax[1].legend(fontsize=18)
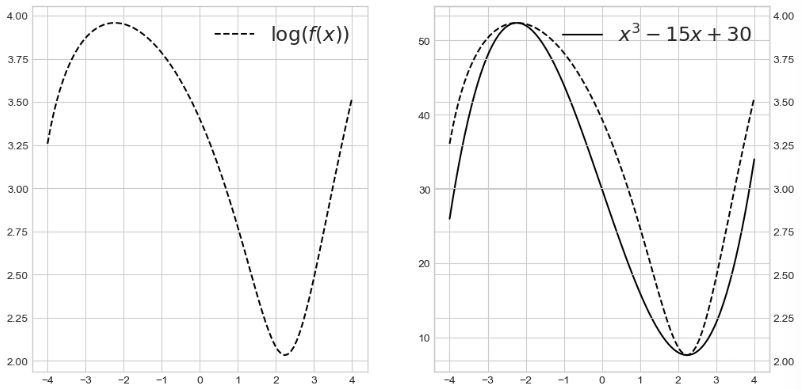
plt.show()- 합성 함수 모양 확인
x = np.linspace(-4, 4, 100)
# f(x)
y = x**3 - 15*x + 30
# g(y)
z = np.log(y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 6))
ax[0].plot(x, z, '--', label=r'$\log(f(x))$', color='k')
ax[0].legend(fontsize=18)
ax[1].plot(x, y, label=r'$x^3 - 15x + 30$', color='k')
ax[1].legend(fontsize=18)
# 2번째 그림에서 x축을 하나 더 만들라는 명령
ax_tmp = ax[1].twinx()
ax_tmp.plot(x,z, '--', label=r'$\log(f(x))$', color='k')
plt.show()4. boxplot
boxplot을 이용해서
몇% 지점의 데이터를 찾아서 버리거나 검토하는 용도를 배우고자 함
-
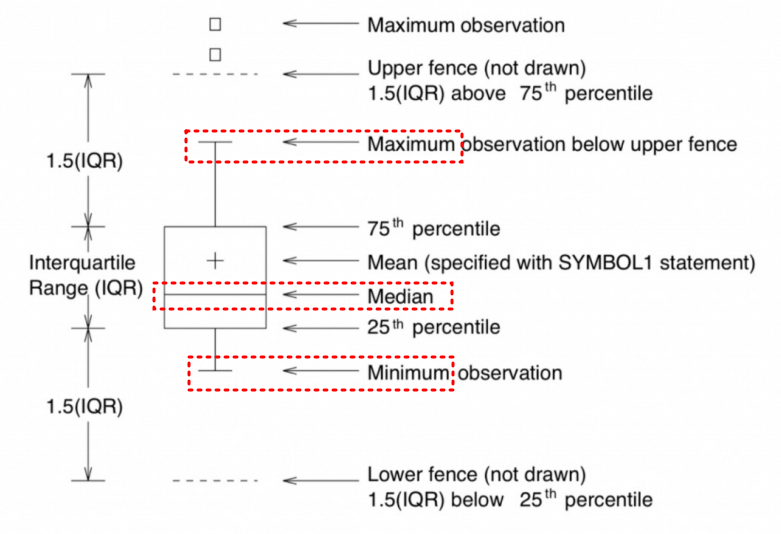
-
예제
# 모듈
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
samples = [1,7,9,16,36,39,45,45,46,48,51,100, 101]
# [1]이 len(sample) 만큼 있기를 기대함
tmp_y = [1]*len(samples)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,4))
plt.scatter(samples, tmp_y)
plt.grid()
plt.show()-
-
각 지표 찾는 방법
-
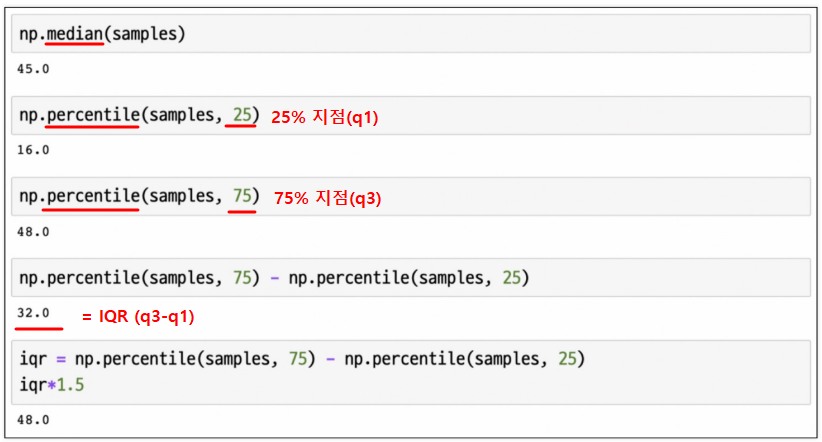
그래프로 아웃라이어 확인
# 중간값
import numpy as np
np.median(samples)
# # 25프로 지점 찾기
# np.percentile(samples, 25)
# # 75프로 지점 찾기
# np.percentile(samples, 75)
# # 중앙값 찾기
# np.percentile(samples, 75) - np.percentile(samples, 25)
iqr = q3 - q1
q1 = np.percentile(samples, 25)
q2 = np.median(samples)
q3 = np.percentile(samples, 75)
# IQR
upper_fence = q3 + iqr*1.5
lower_fence = q1 - iqr*1.5
plt.figure(figsize=(12,4))
plt.scatter(samples, tmp_y)
plt.axvline(x=q1, color='black')
plt.axvline(x=q2, color='red')
plt.axvline(x=q3, color='black')
plt.axvline(x=upper_fence, color='black', ls='dashed')
plt.axvline(x=lower_fence, color='black', ls='dashed')
plt.grid()
plt.show()-
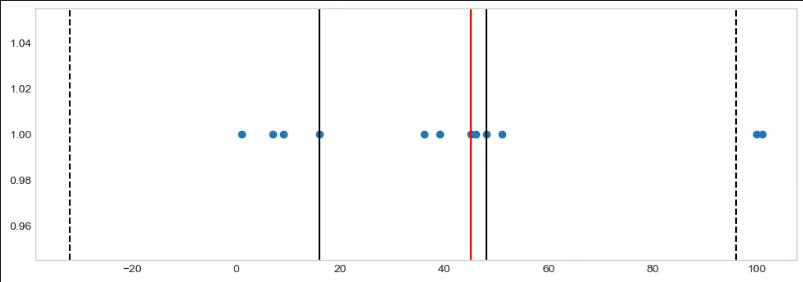
-
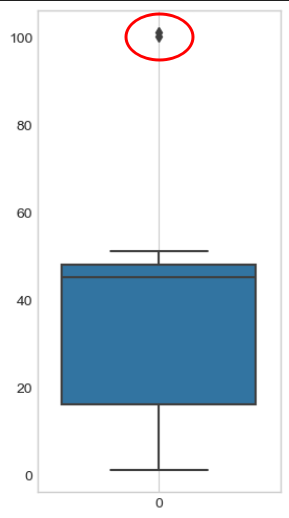
seaboen boxplot
import seaborn as sns
plt.figure(figsize=(3,6))
sns.boxplot(samples)
plt.grid()
plt.show()