[SK shieldus Rookies 19기][Python] 5일차
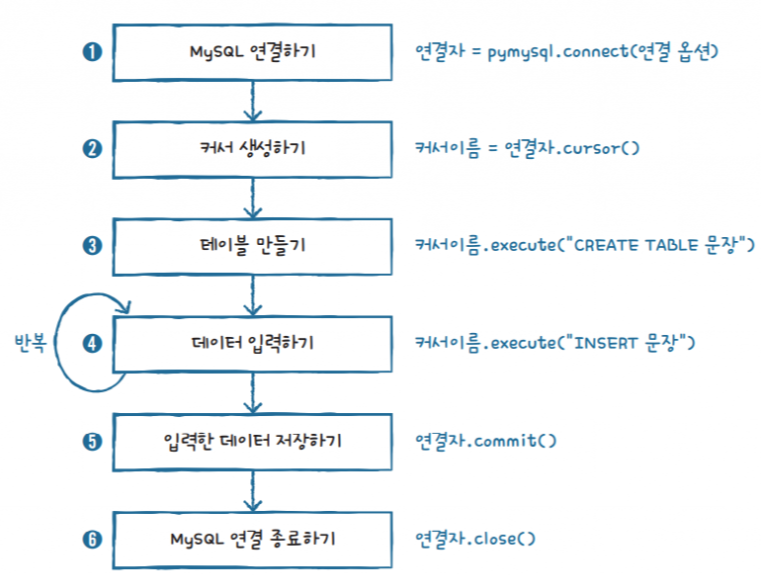
파이썬 데이터베이스 접속
pymysql.connect(host="localhost", # 데이터베이스 주소
port=3306, # 데이터베이스 서비스 포트 (MySQL 기본 포트: 3306)
user="springboot", # 데이터베이스 접속 계정
passwd="p@ssw0rd", # 데이터베이스 사용자 패스워드
db="sampledb" # 사용할 데이터베이스/스키마
autocommit=True|False # INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE 구문 실행 결과를 자동으로 반영할지 여부를 설정
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor # SELECT 결과를 컬럼명과 값으로 구성된 dict 타입으로 반환
) 예시
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb") as conn:cursorclass를 지정하지 않으면 SELECT 결과를 값으로 구성된 튜플 타입으로 반환
(1, '홍길동', 23, 'hong@test.com')
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as conn:cursorclass를 pymysql.cursors.DictCursor으롯 설정하면 SELECT 결과를 컬럼 이름과 값으로 구성된 딕셔너리를 반환
{'member_id': 1, 'member_name': '홍길동', 'member_age': 23, 'member_email': 'hong@test.com'}
데이터 추가 기능을 구현
import pymysql
from faker import Faker
try:
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as conn:
curr = conn.cursor()
fake = Faker('ko-KR')
for i in range(10):
query = f"insert into members (member_name, member_age, member_email) values ('{fake.name()}', {fake.pyint(10, 30)}, '{fake.email()}')"
print(query)
curr.execute(query)
conn.commit() ⇐ 10개의 insert 구문의 실행 결과를 DB에 반영
except pymysql.MySQLError as e:
print(e) 
데이터베이스 연결 시 autocommit 을 True로 설정
import pymysql
from faker import Faker
try:
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor, autocommit=True) as conn:
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
curr = conn.cursor() 트랜잭션 관리가 필요한 경우 False(기본값)으로 설정
commit() 또는 rollback()을 처리
fake = Faker('ko-KR')
for i in range(10):
query = f"insert into members (member_name, member_age, member_email) values ('{fake.name()}', {fake.pyint(10, 30)}, '{fake.email()}')"
print(query)
curr.execute(query)
# conn.commit() ⇐ commit() 함수를 호출하지 않아도 변경사항이 DB에 반영되는 것을 확인할 수 있음
except pymysql.MySQLError as e:
print(e) 데이터 추가 후 조회하도록 수정
fetchone() - 커서로부터 하나의 행(레코드)을 반환
import pymysql
from faker import Faker
try:
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as conn:
curr = conn.cursor()
fake = Faker('ko-KR')
for i in range(10):
query = f"insert into members (member_name, member_age, member_email) values ('{fake.name()}', {fake.pyint(10, 30)}, '{fake.email()}')"
print(query)
curr.execute(query)
conn.commit()
query = "select * from members"
curr.execute(query)
# 조회 결과를 하나씩 가져오기
while True:
result = curr.fetchone()
if result == None: break
print(result)
except pymysql.MySQLError as e:
print(e) fetchall() - 커서로부터 모든 행(레코드)을 반환
import pymysql
from faker import Faker
try:
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as conn:
curr = conn.cursor()
fake = Faker('ko-KR')
for i in range(10):
query = f"insert into members (member_name, member_age, member_email) values ('{fake.name()}', {fake.pyint(10, 30)}, '{fake.email()}')"
print(query)
curr.execute(query)
conn.commit()
query = "select * from members"
curr.execute(query)
# 모든 조회 결과를 반환
results = curr.fetchall()
for result in results:
print(result)
except pymysql.MySQLError as e:
print(e) fetchmany(n) - 커서로부터 n개의 행(레코드)을 반환
import pymysql
from faker import Faker
try:
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as conn:
curr = conn.cursor()
fake = Faker('ko-KR')
for i in range(10):
query = f"insert into members (member_name, member_age, member_email) values ('{fake.name()}', {fake.pyint(10, 30)}, '{fake.email()}')"
print(query)
curr.execute(query)
conn.commit()
query = "select * from members"
curr.execute(query)
# 조회 결과의 일부를 반환
results = curr.fetchmany(10) ⇐ 조회 결과의 첫부분 부터 10개를 가져와서 반환
for result in results:
print(result)
print("*" * 10)
results = curr.fetchmany(10) ⇐ 그 다음(11번째) 부터 10개를 가져와서 반환
for result in results:
print(result)
except pymysql.MySQLError as e:
print(e) 입력한 내용과 일치하는 데이터를 조회
import pymysql
try:
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as conn:
curr = conn.cursor()
name = input("검색할 이름을 입력하세요 : ")
query = f"select * from members where member_name = '{name}'"
curr.execute(query)
results = curr.fetchall()
for result in results:
print(f"ID : {result['member_id']}") ⇐ 컬럼의 이름으로 값을 추출하는 것이 가능
print(f"이름 : {result['member_name']}") DictCursor를 사용하지 않는 경우 result[0]과 같이
print(f"나이 : {result['member_age']}") 튜플 데이터의 인덱스를 사용해야 함
print(f"이메일 : {result['member_email']}")
except pymysql.MySQLError as e:
print(e) 입력한 내용을 포함하고 있는 데이터를 조회
import pymysql
try:
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as conn:
curr = conn.cursor()
name = input("검색할 이름을 입력하세요 : ")
query = f"select * from members where member_name like '%{name}%'"
count = curr.execute(query) ⇐ SELECT 구문인 경우 조회 결과 개수를 반환
print(f"총 {count}건을 조회했습니다.") INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE 구문인 경우 등록, 수정, 삭제된 행의
개수를 반환
results = curr.fetchall()
print(f"총 {len(results)}건을 조회했습니다.")
for result in results:
print(f"ID : {result['member_id']}")
print(f"이름 : {result['member_name']}")
print(f"나이 : {result['member_age']}")
print(f"이메일 : {result['member_email']}")
except pymysql.MySQLError as e:
print(e) 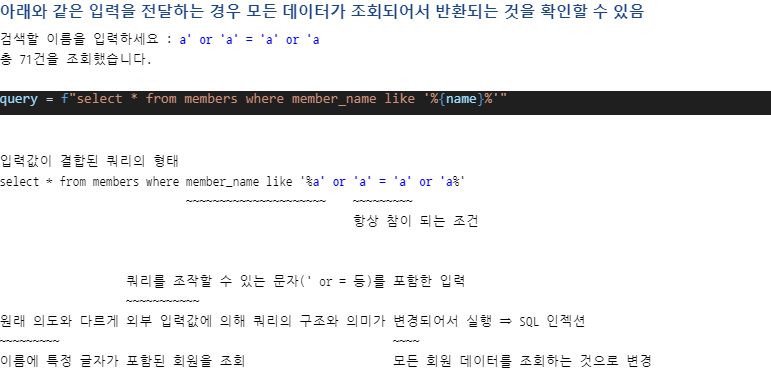
구조화된 쿼리를 실행하는 형태로 변경
import pymysql
try:
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", passwd="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as conn:
curr = conn.cursor()
name = input("검색할 이름을 입력하세요 : ")
query = "select * from members where member_name like %s" # 쿼리문의 구조를 정의
count = curr.execute(query, ('%'+name+'%',)) # execute() 함수의 두번째 인자에 쿼리 실행에
print(f"총 {count}건을 조회했습니다.") 필요한 값을 튜플 또는 딕셔너리를 통해 전달
# execute() 함수가 값을 안전한 형태로
results = curr.fetchall() 변경해서 쿼리를 생성, 실행
print(f"총 {len(results)}건을 조회했습니다.")
for result in results:
print(f"ID : {result['member_id']}")
print(f"이름 : {result['member_name']}")
print(f"나이 : {result['member_age']}")
print(f"이메일 : {result['member_email']}")
except pymysql.MySQLError as e:
print(e) 검색할 이름을 입력하세요 : a' or 'a' = 'a' or 'a
총 0건을 조회했습니다.
해당 입력을 통해서 생성되는 쿼리는 홑따움표가 이스케이프 처리되서 문자 그 자체로 해석
정규표현식
정규표현식(正規表現式, Regular Expression)
문자열 데이터에 특정 패턴을 이용해서 검색, 추출, 치환하는 기능
https://docs.python.org/ko/3/library/re.html
숫자 하나
[0123456789] ⇐ 대괄호 → 나열된 데이터 중 하나
[0-9] ⇐ 대괄호 내의 - ⇒ 가질 수 있는 값의 범위
\d
알파벳 소문자 한 글자
[abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz][a-z]
알파벳 대문자 한 글자
[ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ][A-Z]
알파벳 대소문자 관계 없이 한 글자
[abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ][a-zA-Z]
16진수 한 글자
[0-9a-fA-F]
문자열의 시작을 지정
^ ⇐ circumflex, carrot, hat, cap
문자열의 끝을 지정
$
한글 한 글자
[ㄱ-힣]
반복회수를 지정 ⇒ ? * + {m} {m,n} 등으로 표현
\d? ⇒ 숫자 0회 또는 1회
\d* ⇒ 숫자 0회 이상
\d+ ⇒ 숫자 1회 이상
\d{m} ⇒ 숫자 m개
\d{m, n} ⇒ 숫자 m개 ~ n개
\d - 숫자와 매치된다. [0-9]와 동일한 표현식이다.
\D - 숫자가 아닌 것과 매치된다. [^0-9]와 동일한 표현식이다.
\s - 화이트스페이스(whitespace) 문자와 매치된다. [ \t\n\r\f\v]와 동일한 표현식이다. 맨 앞의 빈칸은 공백 문자(space)를 의미한다.
\S - 화이트스페이스 문자가 아닌 것과 매치된다. [^ \t\n\r\f\v]와 동일한 표현식이다.
\w - 단어 문자(alphanumeric)와 매치된다. [a-zA-Z0-9_]와 동일한 표현식이다.
\W - 단어 문자(alphanumeric)가 아닌 문자와 매치됩니다. [^a-zA-Z0-9_]와 동일한 표현식이다.
import re
p = re.compile('[a-z]+')
print("match 결과 " + "*" * 10)
result = p.match('python')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(0, 6), match='python'>
result = p.match('3 python')
print(result) # None
result = p.match('life is too short')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(0, 4), match='life'>
print("search 결과 " + "*" * 10)
result = p.search('python')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(0, 6), match='python'>
result = p.search('3 python')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(2, 8), match='python'>
result = p.search('life is too short')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(2, 8), match='python'>
print("findall 결과 " + "*" * 10)
results = p.findall('life is too short')
print(results) # ['life', 'is', 'too', 'short']
results = p.findall('3 python')
print(results) # ['python']
print("finditer 결과 " + "*" * 10)
results = p.finditer('life is too short')
print(results) # <callable_iterator object at 0x000002232E003310>
for result in results: print(result)
# <re.Match object; span=(0, 4), match='life'>
# <re.Match object; span=(5, 7), match='is'>
# <re.Match object; span=(8, 11), match='too'>
# <re.Match object; span=(12, 17), match='short'>
results = p.finditer('3 python')
print(results) # <callable_iterator object at 0x000002232E0024A0>
for result in results: print(result)
# <re.Match object; span=(2, 8), match='python'>import re
p = re.compile('[a-z]+')
result = p.search('3 python')
type(result)
print("매치된 문자열 : " + result.group()) # python
print("매치된 문자열의 시작 위치(인덱스) : " + str(result.start())) # 2
print("매치된 문자열의 끝 위치(인덱스) : " + str(result.end())) # 8
print("매치된 문자열의 (시작, 끝) 튜플 : " + str(result.span())) # (2, 8)import re
# p = re.compile('[a-z]+')
# result = p.search('3 python')
result = re.search('[a-z]+', '3 python')
- DOTALL(S) - .(dot)이 줄바꿈 문자를 포함해 모든 문자와 매치될 수 있게 한다.
- IGNORECASE(I) - 대소문자에 관계없이 매치될 수 있게 한다.
- MULTILINE(M) - 여러 줄과 매치될 수 있게 한다. ^, $ 메타 문자 사용과 관련 있는 옵션입니다.
- VERBOSE(X) - verbose 모드를 사용할 수 있게 한다. 정규식을 보기 편하게 만들 수 있고 주석 등을 사용할 수 있게 한다.
옵션을 사용할 때는 re.DOTALL처럼 접미사를 붙여도 되고 re.S처럼 약어를 써도 된다.
import re
p = re.compile('a.b')
result = p.match('a\nb')
print(result) # None
p = re.compile('a.b', re.DOTALL)
result = p.match('a\nb')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(0, 3), match='a\nb'>import re
p = re.compile('[a-z]+')
result = p.match('python')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(0, 6), match='python'>
result = p.match('Python')
print(result) # None
result = p.match('PYTHON')
print(result) # None
p = re.compile('[a-z]+', re.IGNORECASE)
result = p.match('python')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(0, 6), match='python'>
result = p.match('Python')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(0, 6), match='python'>
result = p.match('PYTHON')
print(result) # <re.Match object; span=(0, 6), match='python'>import re
p = re.compile(r'^python\s\w+')
result = p.findall('''python one\nlife...\npython two\nyour nedd python\npython threee
life is too short
python two
your nedd python
python three''')
print(result) # ['python one']
p = re.compile(r"^python\s\w+", re.MULTILINE) # r"^python\s\w+" 또는 "^python\\s\\w+" 형식으로 표기
result = p.findall('''python one # raw string \를 이용해서 이스케이프
life is too short
python two
your nedd python
python three''') # ['python one', 'python two', 'python three']
print(result) 실습
실습. CLI 기반의 CRUD 프로그램을 작성
==========================
메뉴
--------------------------
Q : 종료 ⇒ 프로그램을 종료
I : 등록 ⇒ 등록 화면으로 이동
S : 검색 ⇒ 검색 화면으로 이동
==========================
메뉴를 선택하세요 >>>
==========================
회원 등록
--------------------------
이름 : 홍길동
나이 : 23
이메일 : hong@test.com
==========================
Y : 등록 / N : 취소 ⇒ Y → members 테이블에 입력한 내용을 저장 → 등록했습니다. 출력 후 메뉴 화면으로 이동
N → 메뉴 화면으로 이동
==========================
회원 검색
--------------------------
이름 : 길동
==========================
Y : 검색 / N : 취소 ⇒ Y → members 테이블에 like 검색 → 검색 결과 화면으로 이동
N → 메뉴 화면으로 이동
==========================
회원 검색 결과 (OO건)
--------------------------
1 : 홍길동 ⇐ 검색 결과를 회원아이디 : 회원이름 형식으로 나열
2 : 고길동 검색 결과가 없는 경우 "일치하는 결과 없음" 출력
3 : 신길동
==========================
번호 : 상세 조회 / N : 취소 ⇒ 번호(회원 아이디) → 회원 상세 조회 화면으로 이동
N → 메뉴 화면으로 이동
==========================
회원 상세 조회
--------------------------
아이디 : 1
이름 : 홍길동
나이 : 23
이메일 : hong@test.com
==========================
U : 수정 D : 삭제 / Y : 메뉴로 이동
⇒ D → 해당 회원 삭제 후 "삭제했습니다" 메시지를 출력하고 메뉴 화면으로 이동
U → 수정 화면으로 이동
N → 메뉴 화면으로 이동
==========================
회원 수정
--------------------------
아이디 : 1 ⇐ 회원 정보를 보여주고,
이름 : 홍길동
나이 : 23
이메일 : hong@test.com
==========================
나이 : 43
이메일 : gildong@test.com
수정할까요? (Y : 수정 / N : 메뉴로 이동)
⇐ Y → 나이와 이메일을 입력 받아서 수정 후 "수정했습니다." 메시지를 출력하고
메뉴 화면으로 이동
N → 메뉴 화면으로 이동
회원 등록 및 수정 시 이름, 나이, 이메일의 형식을 정규식을 이용해서 검증 후 등록, 수정 처리해야 함강사님 예시
import pymysql
import re
# 화면 출력에 사용되는 함수들
def print_double_line():
print("======================================")
def print_single_line():
print("--------------------------------------")
def print_title(title):
print()
print_double_line()
print(title)
print_single_line()
def print_tail():
print_double_line()
def show_menu_page():
print_title("메뉴")
print("I: 회원 정보를 등록합니다.")
print("S: 회원을 LIKE 검색합니다.")
print("Q: 프로그램을 종료합니다.")
print_tail()
def check_input(message, valid_inputs, line_yn=False):
if line_yn: print("--------------------------------------")
while True:
i = input(message + " >>> ").upper()
if i in valid_inputs:
return i
else:
print("잘못된 입력입니다. 확인 후 다시 입력해 주세요.")
def main():
show_menu_page()
menu = check_input("메뉴를 선택하세요. (I: 등록 / S: 검색 / Q: 종료)", ("I", "S", "Q"))
if menu == "Q":
print("프로그램을 종료합니다.")
elif menu == "I":
do_insert()
elif menu == "S":
do_search()
def do_insert():
print_title("회원 등록")
name = input("이름 : ")
age = int(input("나이 : "))
email = input("이메일 : ")
# TODO 형식 검증 후 메시지 출력
yn = check_input("등록하시겠습니까? (Y: 등록 / N: 취소)", ("Y", "N"), True)
if yn == "N":
print("회원 등록을 취소합니다.")
elif yn == "Y":
query = "insert into members (member_name, member_age, member_email) value (%s, %s, %s)"
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", password="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb") as connection:
cursor = connection.cursor()
count = cursor.execute(query, (name, age, email))
if count == 1:
print("회원 정보를 정상적으로 등록했습니다.")
connection.commit()
else:
print("회원 정보를 등록하는데 실패했습니다.")
connection.rollback()
main()
def do_search():
print_title("회원 검색")
name = input("이름 : ")
print_tail()
yn = check_input("검색하시겠습니까? (Y: 검색 / N: 취소)", ("Y", "N"))
if yn == "N":
print("회원 검색을 취소합니다.")
elif yn == "Y":
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", password="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as connection:
query = "select * from members where member_name like %s"
cursor = connection.cursor()
count = cursor.execute(query, ("%"+name+"%",))
members = cursor.fetchall()
print_title(f"검색 결과 (총 {count}건)")
if count == 0:
print("일치하는 결과가 없습니다. ")
else:
ids = []
for member in members:
ids.append(str(member['member_id']))
print(f"{member['member_id']} : {member['member_name']}")
do_detail(ids)
main()
def do_detail(ids):
mid = check_input("상세 정보를 조회하시겠습니까? (회원번호: 상세조회 / N: 취소)", ids, True)
if mid == "N":
print("상세 조회를 취소합니다.")
return
else:
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", password="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as connection:
query = "select * from members where member_id like %s"
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute(query, (mid,))
member = cursor.fetchone()
print_title("회원 상세 조회")
print(f"ID: {member['member_id']}")
print(f"이름: {member['member_name']}")
print(f"나이: {member['member_age']}")
print(f"이메일: {member['member_email']}")
udn = check_input("회원 정보를 수정 또는 삭제하시겠습니까? (U: 수정 / D: 삭제 / N: 메인 화면으로 이동)", ("U", "D", "N"), True)
if udn == "U":
do_update(member['member_id'])
elif udn == "D":
do_delete(member['member_id'])
elif udn == "N":
return
def do_delete(id):
yn = check_input("회원 정보를 삭제하시겠습니까? (Y: 삭제 / N: 취소)", ("Y", "N"))
if yn == "N":
print("회원 정보 삭제를 취소합니다.")
elif yn == "Y":
query = "delete from members where member_id = %s"
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", password="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", autocommit=True) as connection:
cursor = connection.cursor()
count = cursor.execute(query, (id,))
if count == 1:
print("회원 정보를 정상적으로 삭제했습니다.")
else:
print("회원 정보를 삭제하는데 실패했습니다.")
def do_update(id):
with pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user="springboot", password="p@ssw0rd", db="sampledb", cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) as connection:
query = "select * from members where member_id like %s"
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute(query, (id,))
member = cursor.fetchone()
print_title("회원 정보 수정")
print(f"ID: {member['member_id']}")
print(f"이름: {member['member_name']}")
print(f"나이: {member['member_age']}")
print(f"이메일: {member['member_email']}")
print_tail()
age = int(input("변경할 나이 : "))
email = input("변경할 이메일 : ")
# TODO 형식 검증 후 메시지 출력
yn = check_input("회원 정보를 수정하시겠습니까?", ("Y", "N"), True)
if yn == "N":
print("회원 정보 수정을 취소합니다.")
else:
query = "update members set member_age = %s, member_email = %s where member_id = %s"
cursor = connection.cursor()
count = cursor.execute(query, (age, email, id))
if count == 1:
print("회원 정보를 정상적으로 수정했습니다.")
connection.commit()
else:
print("회원 정보를 수정하는데 실패했습니다.")
connection.rollback()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()내 코드
#작성중~