Graph as Matrix: PageRank, Random Walks and Embeddings
Graph as Matrix
- We investigate graph analysis and learning from a matrix perspective.
- Treating a graph as matix allows us to:
❍ Determine node importance via random walk (PageRank)
❍ Obtain node embeddings via matrix factorization (MF)
❍ View other node embeddings (e.g. Node2Vec) as MF - Random walk, matrix factorization and node embeddings are closely related!
PageRank
Example: The Web as a Graph
Q: What does the Web "look like" at a global level?
- Web as graph

information → graph 형태로
Ranking Nodes on the graph
- All web pages are not equally "important"
- There is large diversity in the web-graph node connectivity.
- So, let's rank the pages using the web graph link structure!
Link Analysis Algorithms
- We will cover the following Link Analysis approaches to compute the importance of nodes in a graph
❍ PageRank
❍ Personalized PageRank (PPR)
❍ Random Walk with Restarts
Links as Votes
- Idea: Links as Votes
❍ Page is more important if it has more links ; In-coming links? Out-going links? - Think of in-links as votes
- Are all in-links equal?
❍ Links from important pages count more
❍ Recursive question!
PageRank: The "Flow" Model
- A "vote" from an important page is worth more:
❍ Each link's vote is proportional to the importance of its source page
❍ If page i with importance r_i has d_i out_links, each link gets r_i/d_i votes
❍ Page j's own importance r_j is the sum of the votes on its in-links - A page is important if it is pointed to by other important pages
- Define "rank" r_j for node j
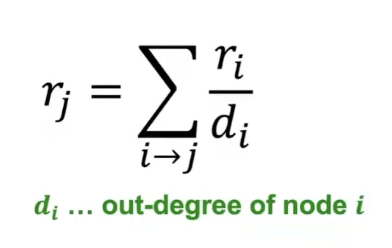
PageRank: Matrix Formulation
- Stochastic adjacency matrix M
❍ Let page j have d_j out_links
❍ If j → i, then M_ij = 1 / d_j (M: column stochastic matrix) - Rank vector r: An entry per page
❍ r_i is the importance source of page i - The flow equations can be written
Connection to Random Walk
- Imagine a random web surfer:
❍ At any time t. surfer is on some page i
❍ At time t+1, the surfer follows an out-link from i uniformly at random
❍ Ends up on some page j linked from i
❍ Process repeats indefinitely - Let:
❍ p(t) ... vector whose ith cordinate is the prob. that the surfer is at page i at time t
❍ so, p(t) is a probability distribution over Given a pages
The Stationary distribution
- Where is the surfer at time t_1?
❍ Follow a link uniformly at random
p(t+1) = M p(t)
❍ Suppose the random walk reaches a state
p(t+1) = M p(t) = p(t)
then p(t) is stationary distribution of a random walk
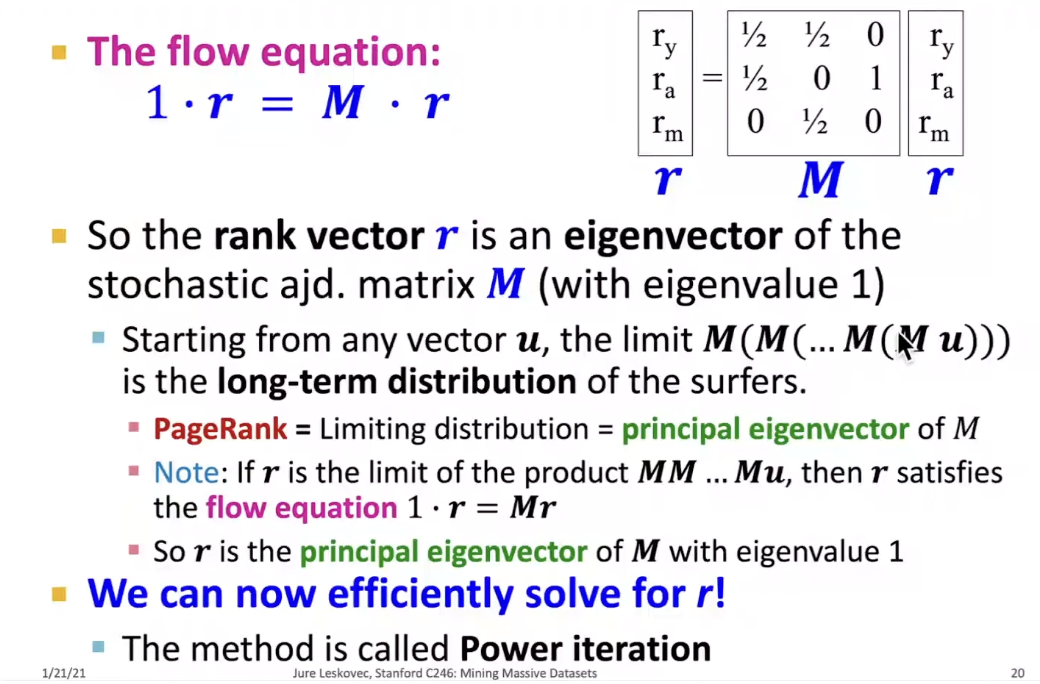
❍ Our original rank vector r satifies r = M * r (so, r is a stationary distribution for the random walk)
Eigenvector Formulation
PageRank: How to solve?
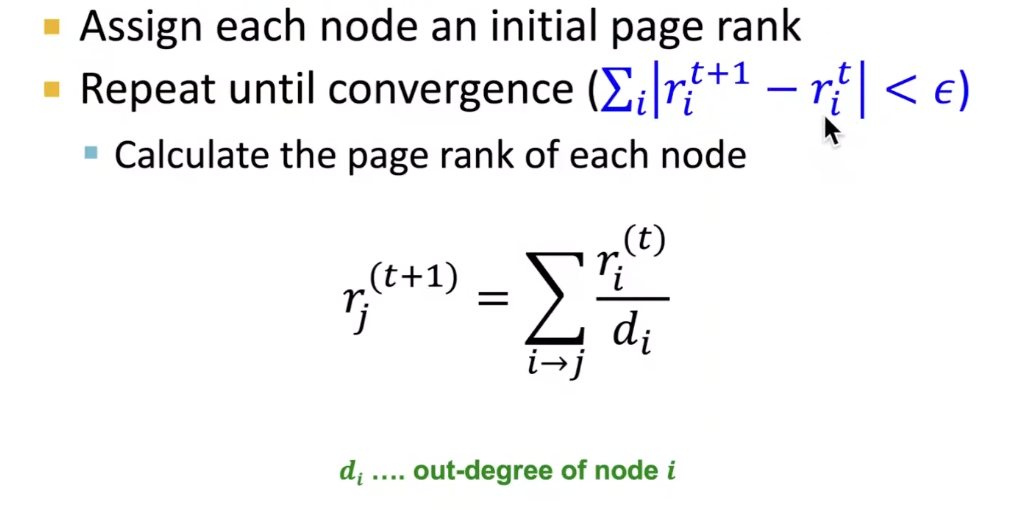
Given a graph with n nodes, we use an iterative procedure:
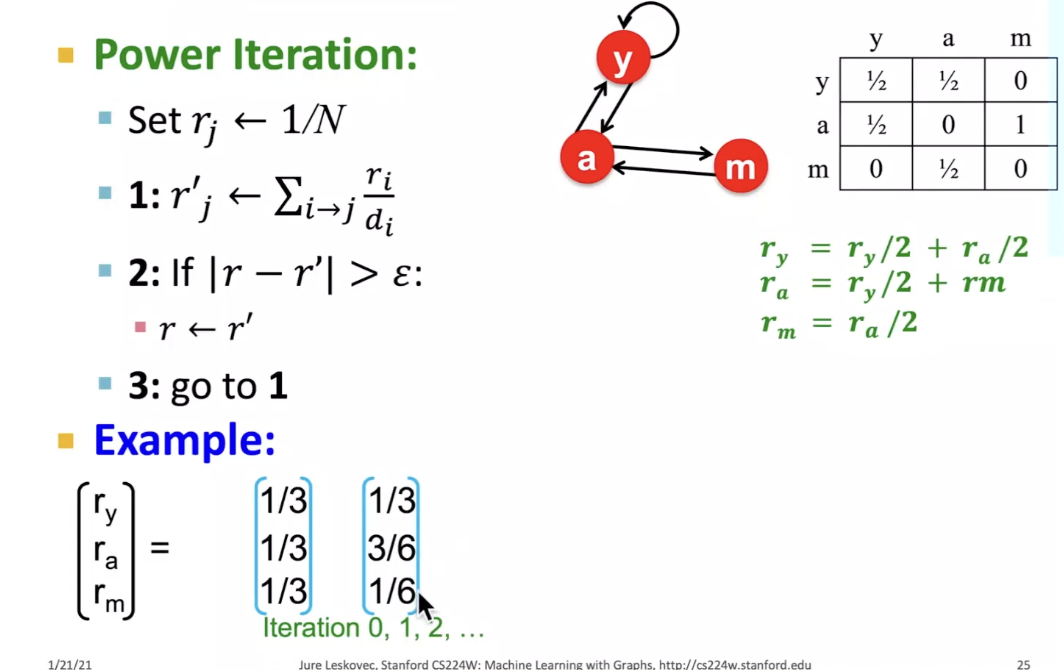
Power Iteration Method
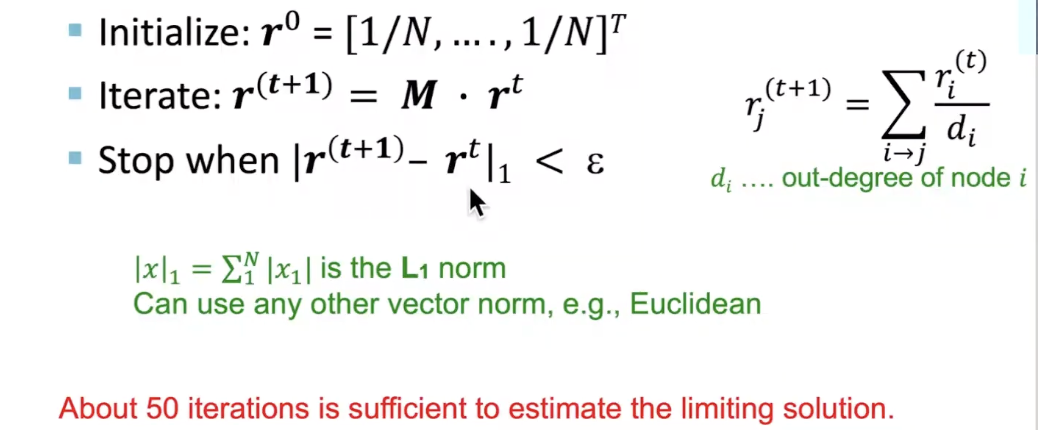
- Given a web graph with N nodes, where the nodes are pages and edges are hyperlinks
- Power iteration: a simple iterative scheme
PageRank: How to solve?
Look careful of Power Iteration part
PageRank: Three Questions
- Does this converge?
- Does it converge to what we want?
- Are results reasonable?
PageRank: Problems
- Some pages are dead ends (have no out-links)
- Such pages cause importance to "leak out"
- Spider traps (all out-links are within the group)
- Eventually spider traps abosrb all importance
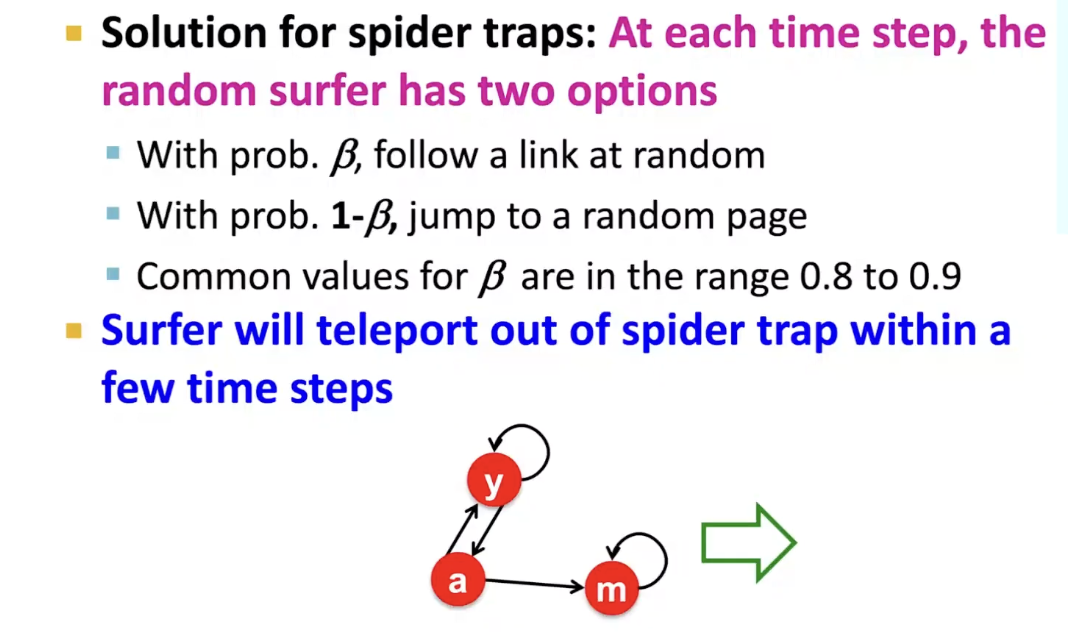
Solution to Spider Traps
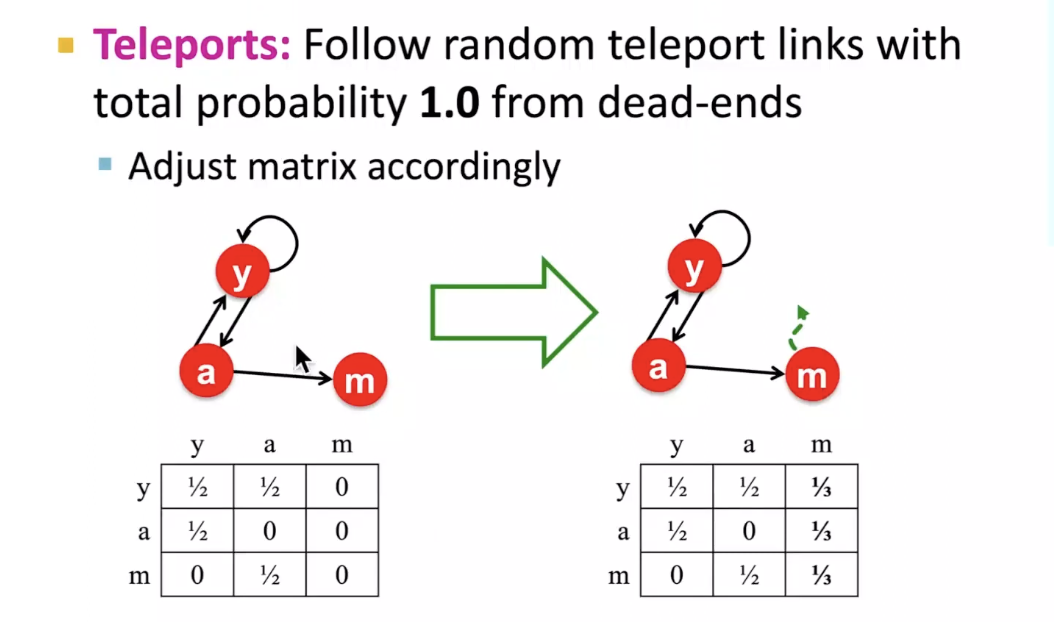
Solution to Dead Ends
Why Teleports Solve the Problem?
Why are dead-ends and spider traps a problem and why teleports solve the problem?
- Spider-traps are not a problem, but with traps PageRank scores are not what we want
❍ Soultion: Never get stuck in a spider trap by teleporting out of it in a finite number of steps - Dead-ends are a problem
❍ The matrix is not column stochastic so our initial assumptions are not met
❍ Soultion: Make matrix column stochastic by always teleporting when there is nowhere else to go
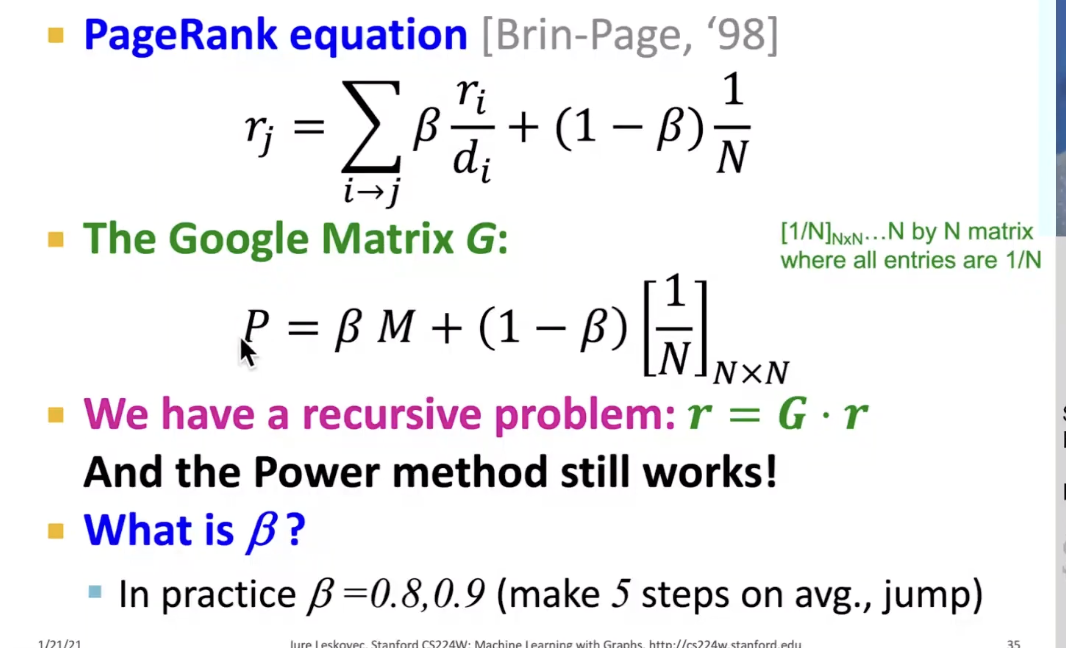
Soultion: Random Teleports

Google matrix
Random Walk with Restarts and Personalized PageRank
Example: Recommendation
Bipartite User-Item Graph

Proximity on Graphs
- PageRank
❍ Ranks nodes by "importance"
❍ Teleports with uniform probability to any node in the network - Personalized PageRank
❍ Ranks proximity of nodes to the teleport nodes S - Proximity on graphs:
❍ Q: What is most related item to Item Q?
❍ Random Walks with Restarts
Idea: Random Walks

Benefits
- "similarity" considers
❍ Multiple connections
❍ Multiple paths
❍ Direct and indirect connections
❍ Degree of the node
Matrix Factorization and Node Embeddings
Connection to Matrix Factorization
- Simplest node similarity: Nodes u, v are similar if they are connected by an edge
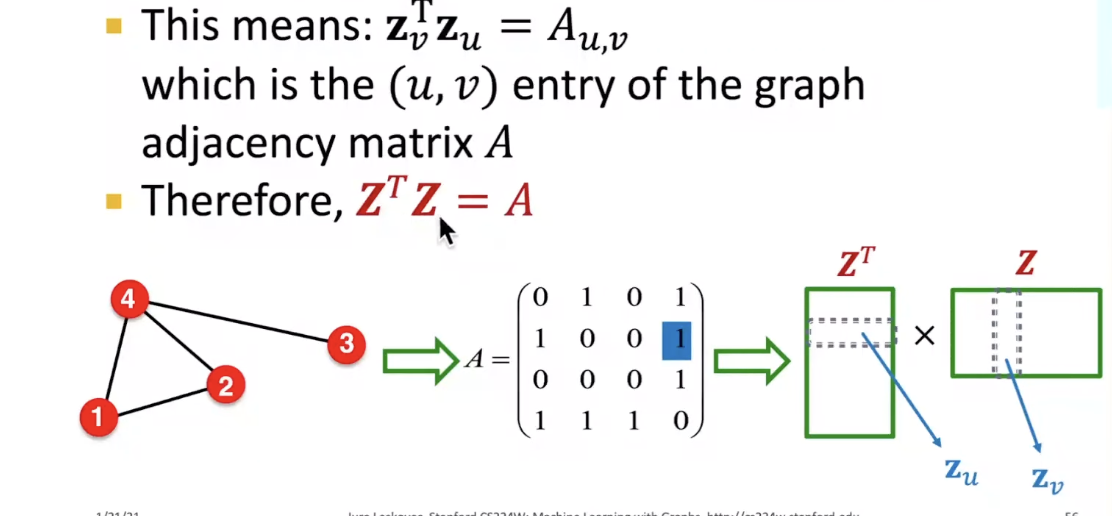
Matrix Factorization

Random Walk-based Similarity
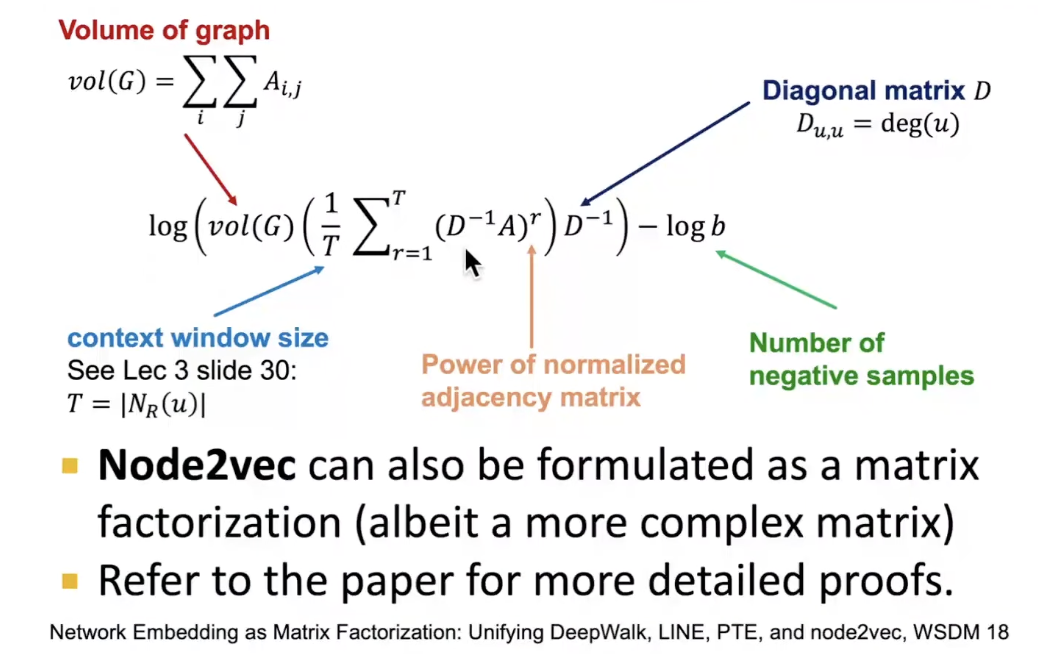

Limitations
- Limitations of node embeddings via matrix factorization and random wlaks
- cannot obtain embeddings for nodes not in the training set
- Cannot capture structural similarity
- DeepWalk and node2vec do not capture structural similarity
- Cannot utilize node, edge and graph features
