Signal-dependent noise determines motor planning
psychophysics 대가이신 Wolpert 교수님의 논문이다. 기존에 여러 motor planning 을 설명하는 모델이 있었지만 이에 대해 hidden state (control signal) 가 control signal 의 크기와 비례하는 variance 를 가진 noise (signal-dependent noise) 에 의해 corrupt 된다는 가정과 함께, shape of the trajectory 는 최종 position 의 variance 를 minimization 하는 형태로 결정된다는 이론을 설명한다. 이는 기존 Fitts' Law 를 통합적으로 설명하고 있고, 다른 bang-bang control 등 보다 더 biologically plausible 한 description 을 제공한다.
- signal-dependent noise
- minimum-variance theory
Liear Models
논문이 좀 짧아서 가장 핵심적인 모델링 부분에 대해서 간단히 정리하려 한다.
여기서 의 분산은 이다. - signal dependent noise
는 control signal 이다. (like hidden state vector)
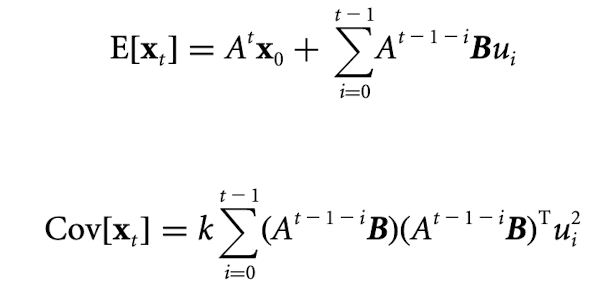
식의 유도:
일 때:
일 때:
이를 일반화하면 주어진 식이 된다.
식의 유도:
이를 대입하고 전개하면:
이 재귀 관계를 부터 까지 반복 적용하면 주어진 식이 된다.
이 때 사진에 나와있는 각항에 대해 설명하면 은 시점의 입력이 시점의 상태에 미치는 영향이라 할 수 있고, 은 시점의 input에 의한 noise의 variance 이다. 사진의 최종 cov 식은 각 시점의 입력이 최종 상태의 공분산에 미치는 영향을 모두 합한 것이다.
Results
Fitts Law 관련
movement time (MT), target distance (A), target width (w)
: Fitts Law
타겟 크기 작을수록 ( 더 큰 control signal 요하므로) 시간이 오래걸림
타겟 거리가 더 멀수록 (더 큰 control signal 요하므로) 시간이 오래걸림
++ 내용 추가
other papers
The physics of optimal decision making: A formal analysis of models of performance in two-alternative forced-choice tasks, Bogacz et al. (2006)
Here, we showed that humans effectively use the predictability of forthcoming events to modulate the distance to the threshold of their decisions, substituting predictive information for sensory information in the decision process to speed up action selection without loss of accuracy
Decision threshold modulation in the human brain, Domenech & Dreher (2010)
여러 모델이 결국 DDM (drift-dissufion model) 으로 귀결.
불확실성이 높은 상황과 아닌 상황에서 decision threshold 의 변화
- 불확실성이 높은 상황에서:
최적의 결정 임계값은 (모든 작업 관련 delay 합)에 의존 - 불확실성이 낮은 상황에서:
bias가 낀 결정을 할 때, delay 가 threshold 이하인 경우, 참가자는 더이상의 계산 안하고 가장 확률이 높거나 보상이 높은 대안을 즉시 선택함.
이런걸 보면 또 마냥 불확실성이 낮다고 해서 결정이 느린 것도 아님. 너무 낮으면 즉시 결정을 내림.
