확장 가능 비즈니스를 위한 Web Scalability for Startup Engineers


- 📝 Web Scalability for Startup Engineers 을 읽고 정리한 글입니다.
- 이 책은 HTTP-based systems (websites, REST APIs, SaaS, and mobile application backends)에 관련된 Scalability를 다루고 있습니다. 특히, 스타트업이 겪을 수 있는 다양한 challenges와 issues들에 대해서 깊이 있고 실용적인 방법을 소개합니다.
- 작성 일자: 2020-05-12
1. Core Concepts for Scalability
* What is Scalability?
=>
Scalabilitywould decidehow many more users you can handleandhow many more requests they can sendwithout degrading the user experience. scalability of a software product may be constrained byhow many engineers can be working on the system.
1. Handling more data:
더 많은 데이터를 저장하고, 더 많은 유저, 더 많은 제품을 저장하고, 더 많은 데이터를 sort, search, read, write 등을 해야하는 상황
2. Handling higher concurrency levels:
제한된 CPU와 threads를 가진 server가 동시에 많은 user의 접속이 이루어졌을 때 user의 경험을 해치지 않아야하는 상황.
- need tosynchronize parallel executionof your codeto ensure consistency of your data
- more open connection, more active threads, more messages being processed at the same time, more CPU context switches
3. Handling higher interaction rates:
Rate of interactions은 얼마나 clients가 servers속에서 정보 교환이 이루어지는 지를 의미함.
ex) 15초~20초마다 유저가 page를 넘기는 웹사이트, 초당 mulitple messages가 발생하는 모바일 게임
-Latency가 제일 중요한 challenge.Rate of Interactions가 증가할수록 서버의 빠른 응답속도를 요한다.
4. How many engineers can be working on system:
If your system is very tightly interconnected, you may struggle to scale your engineering team, as everyone will work on the same codebase.
* 서버 1개로부터 글로벌 서비스로 확장되어가는 과정
1) Single-server Configuration
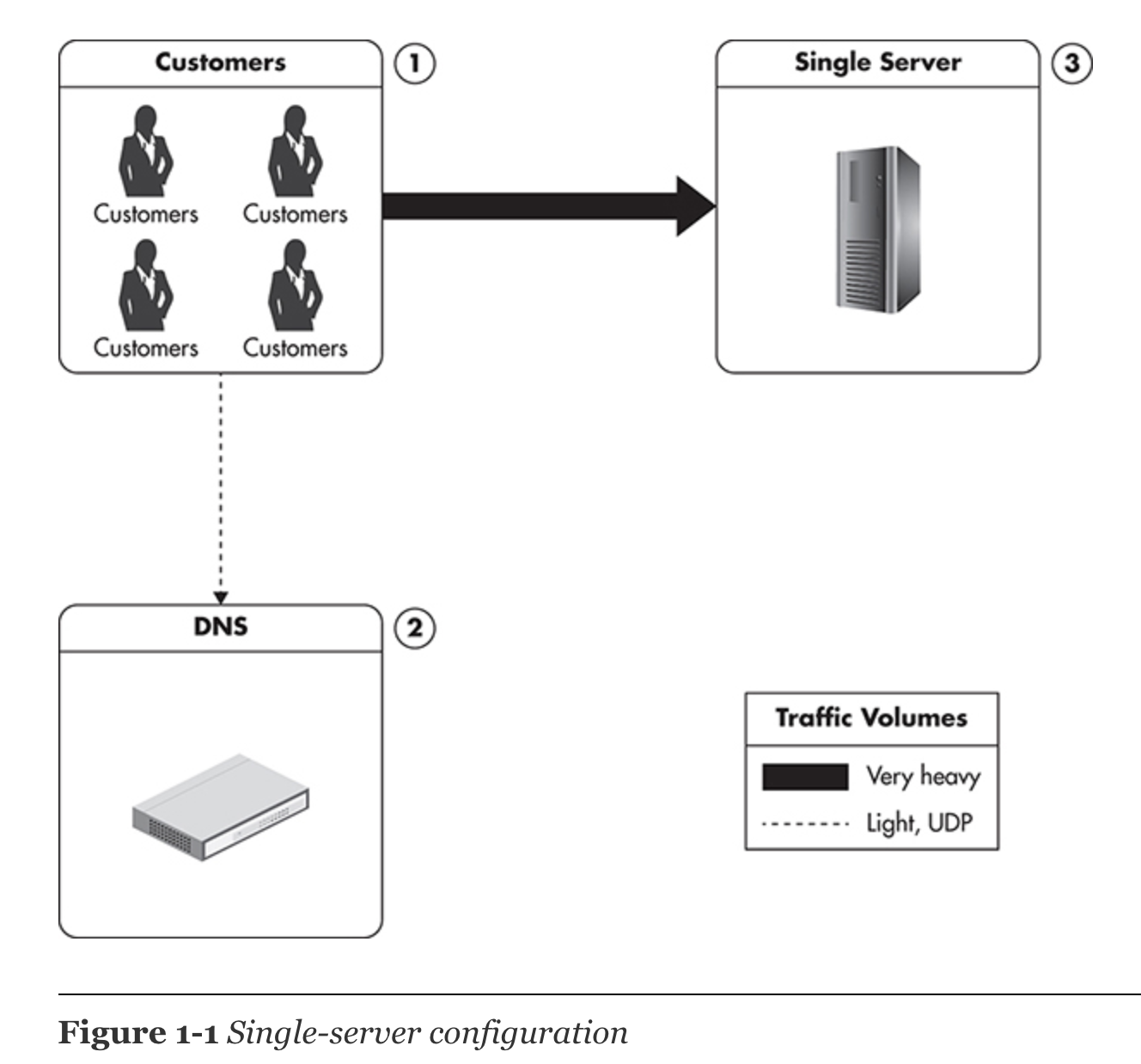
상황: client가 DNS에 처음에 connect하고, DNS는 domain name에 맵핑되어있는 IP address에 연결시켜준다. 그 다음에 HTTP를 이용하여 다양한 resources들을 요청하기 시작할 것이다.
해결책1) VPS 사용: VPS 가격도 저렴하고 좋음. multiple instances가 하나의 physical machine에서 동시에 존재 가능.
참고)
*Virtual private server is a term used by hosting providers to describe a virtual machine for rent.
상황:
- user수 증가: each user consumes more resources, including memory, CPU time, and disk input/output (I/O).
- database 크기 증가: your database queries begin to slow down due to the extra CPU, memory, and I/O requirements.
- 시스템에 기능 추가: makes user interactions require more system resources.
2) Single server, but stronger
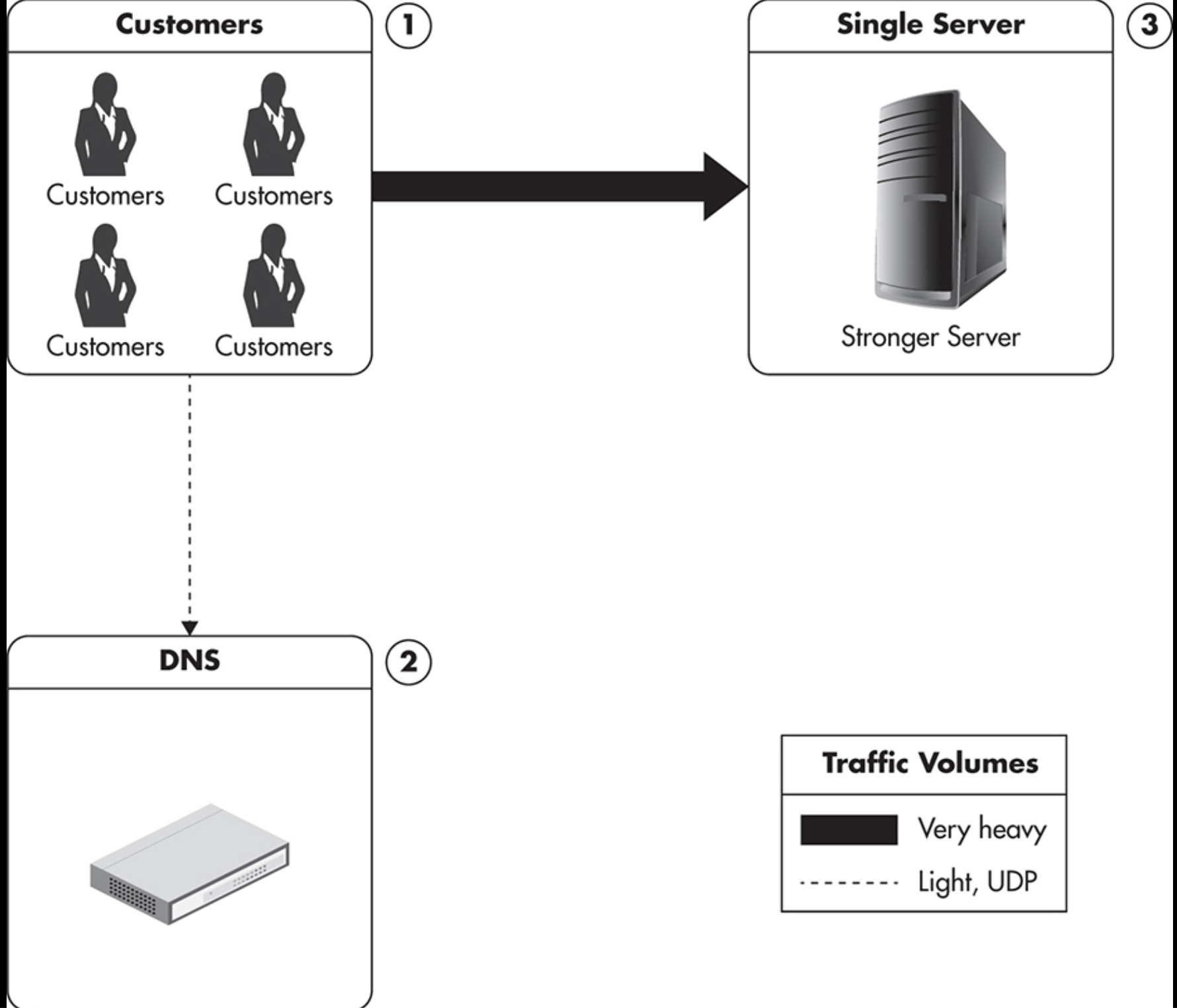
해결책2) Scaling Vertically: 서버, 하드웨어 크기를 업그레이드하는 방법
장점: 아키텍처를 바꾸지 않고, 쉽게 scaling 가능
단점: 가격이 비싸고, 어느 순간 scaling하는데 있어서 한계점이 옴.
ex) 계속 CPU를 추가시킴으로써 MySQL을 Scaling하다보면 한계점이 온다. 왜냐하면 lock contention 현상이 증가하기 때문이다.
- Adding more I/O capacity by adding more hard drives in Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) arrays.
- Improving I/O access times by switching to solid-state drives (SSDs). Random reads and writes using SSDs are between 10 and 100 times faster. Unfortunately, sequential reads and writes are not much faster. In fact, most open-source databases (like MySQL) optimize data structures and algorithms to allow more sequential disk operations rather than depending on random access I/O. Cassandra use solely sequential I/O for all writes and most reads, making SSD even less attractive.
- Reducing I/O operations by increasing RAM
- Improving network throughput by upgrading network interfaces or installing additional ones
- Switching to servers with more processors or more virtual cores => CPU를 공유할 뿐만 아니라, fewer context switches to excute multiple processess on core 효과도 있음.
참고)
*Vertical scalability is accomplished by upgrading the hardware and/or network throughput. it does not require architectural changes to your application.
*Locks are used to synchronize access between execution threads to shared resources like memory or files.
3) Configuration with separate services residing on different servers
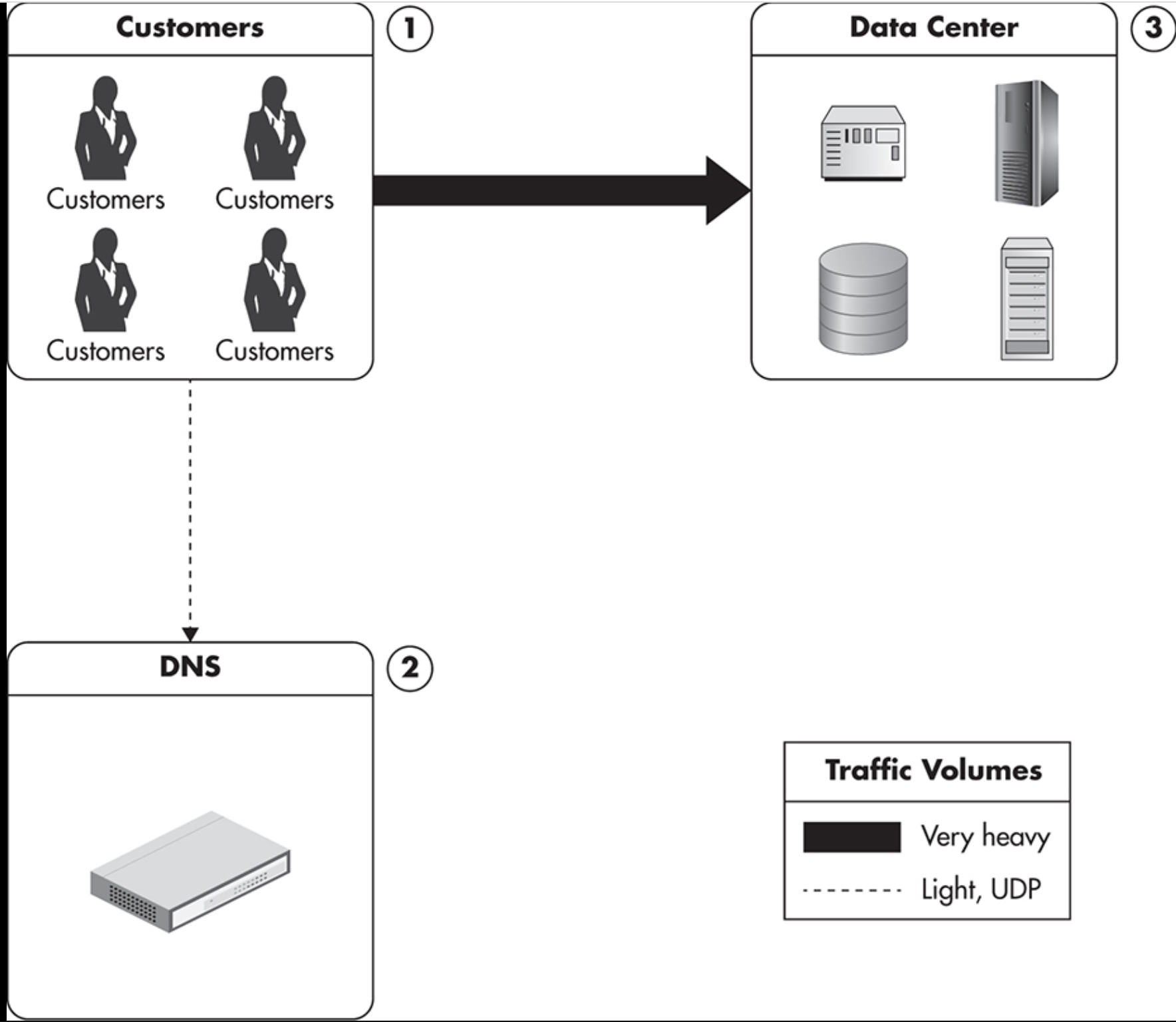
4) Configuration showing functional partitioning of the application
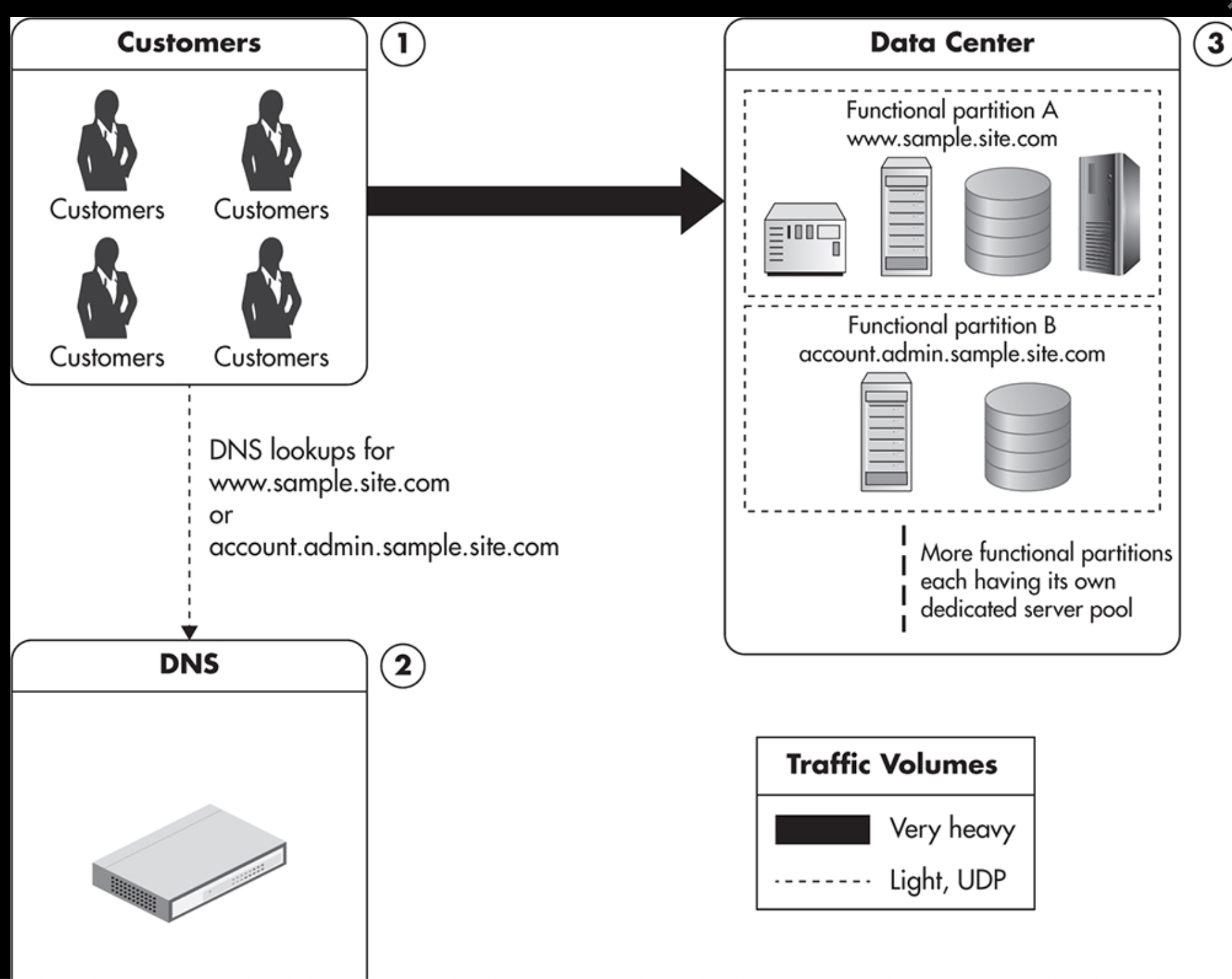
해결책3)4) Functional partitioning: Service를 분리해서 각기 다른 physical machine에 install 시킨다.
- separate webserver와 separate database를 가짐으로써 자원활용을 극대화시킨다.
- Each server has a certain role, such as web server, database server, FTP, or cache.
- a web application uses functional partitioning to distribute the load among even more servers.
- different partitions may have different servers installed, and they may also have different vertical scalability needs. The more flexibility we have in scaling each part of the system, the better.
참고)
*Cache is a server/service focused on reducing the latency and resources needed to generate the result by serving previously generated content
5) Integration with a content delivery network(CDN) provider
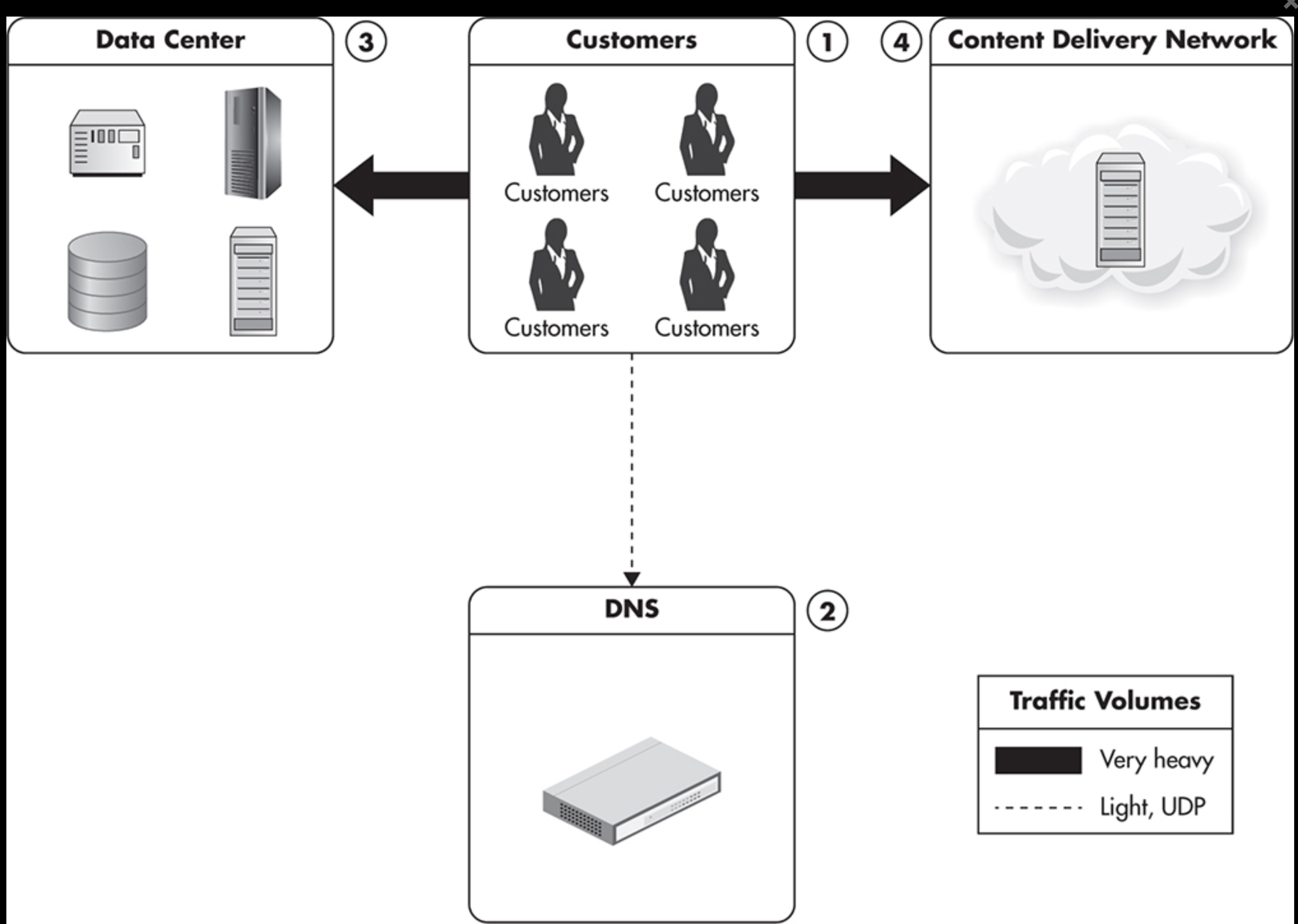
해결책5) scaling using a third-party service such as CDN.
참고)
*A content delivery network(CDN) is a hosted service that takes care of global distribution of static files like images, JavaScript, CSS, and videos. It works as an HTTP proxy. Once the file is cached by the CDN, subsequent clients are served without contacting your servers at all. Finally, your clients may benefit from better resource locality. CDN providers are usually global companies with data centers located all around the world.
6) Distributing the Traffic: Horizontal Scalability
- Multiple servers dedicated to each role
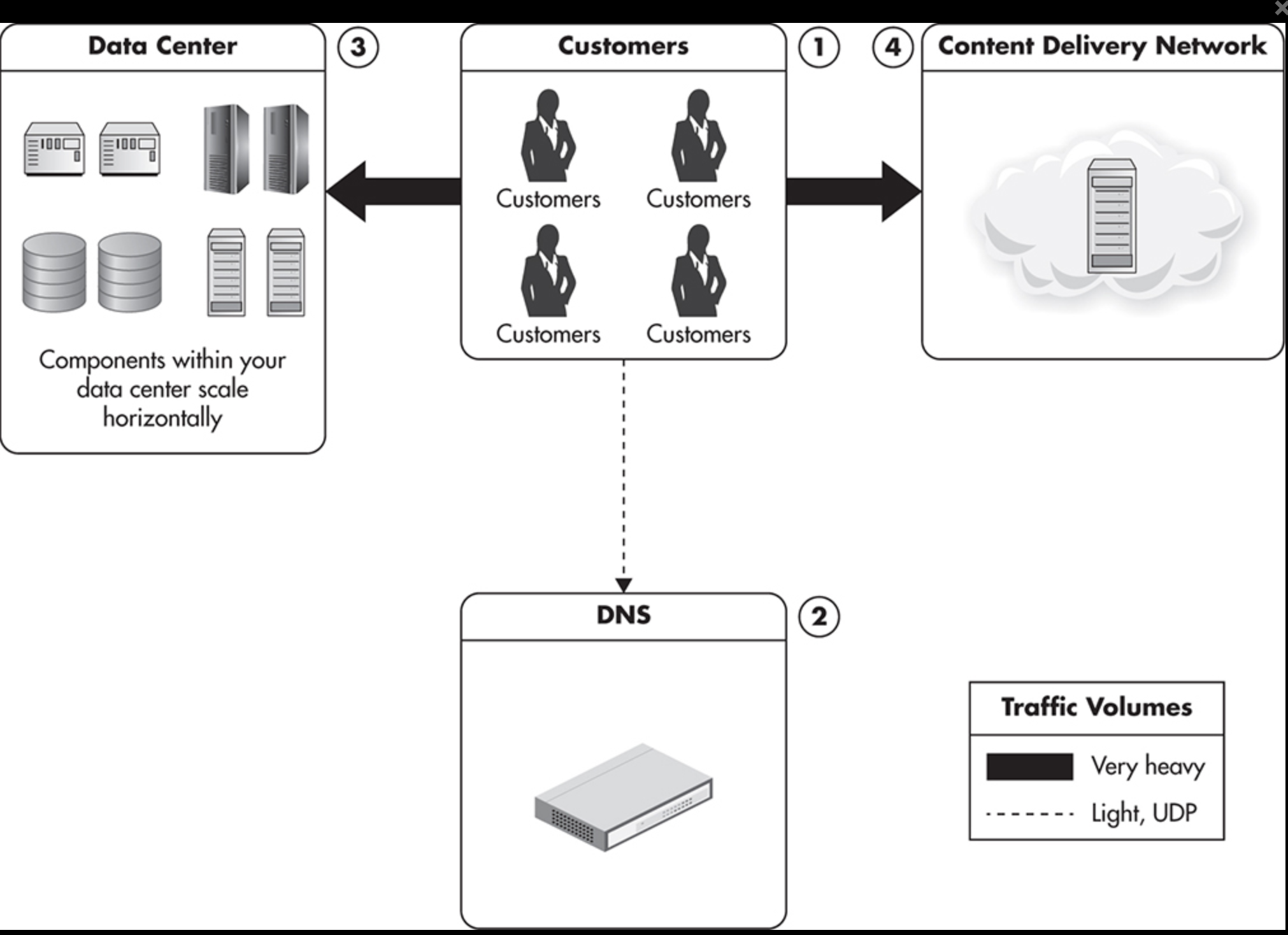
해결책6) horizontal scalability: 각각의 server들의 role에 따라 분리시킴
- Achieving true horizontal scalability is usually difficult and expensive. it is the easiest to achieve, like web servers and caches, and then tackle the more difficult areas, like databases or other persistence stores.
- The more traffic you generate, the more you are charged by the provider, but the cost per capacity unit remains constant.
참고)
*Round-robin DNS is a DNS server feature allowing you to resolve a single domain name to one of many IP addresses. Thus, round-robin DNS allows you to map the domain name to multiple IP addresses, each IP pointing to a different machine
7) Scalability for a Global Audience(geoDNS)
- Customers from different locations are served via local edge caches.
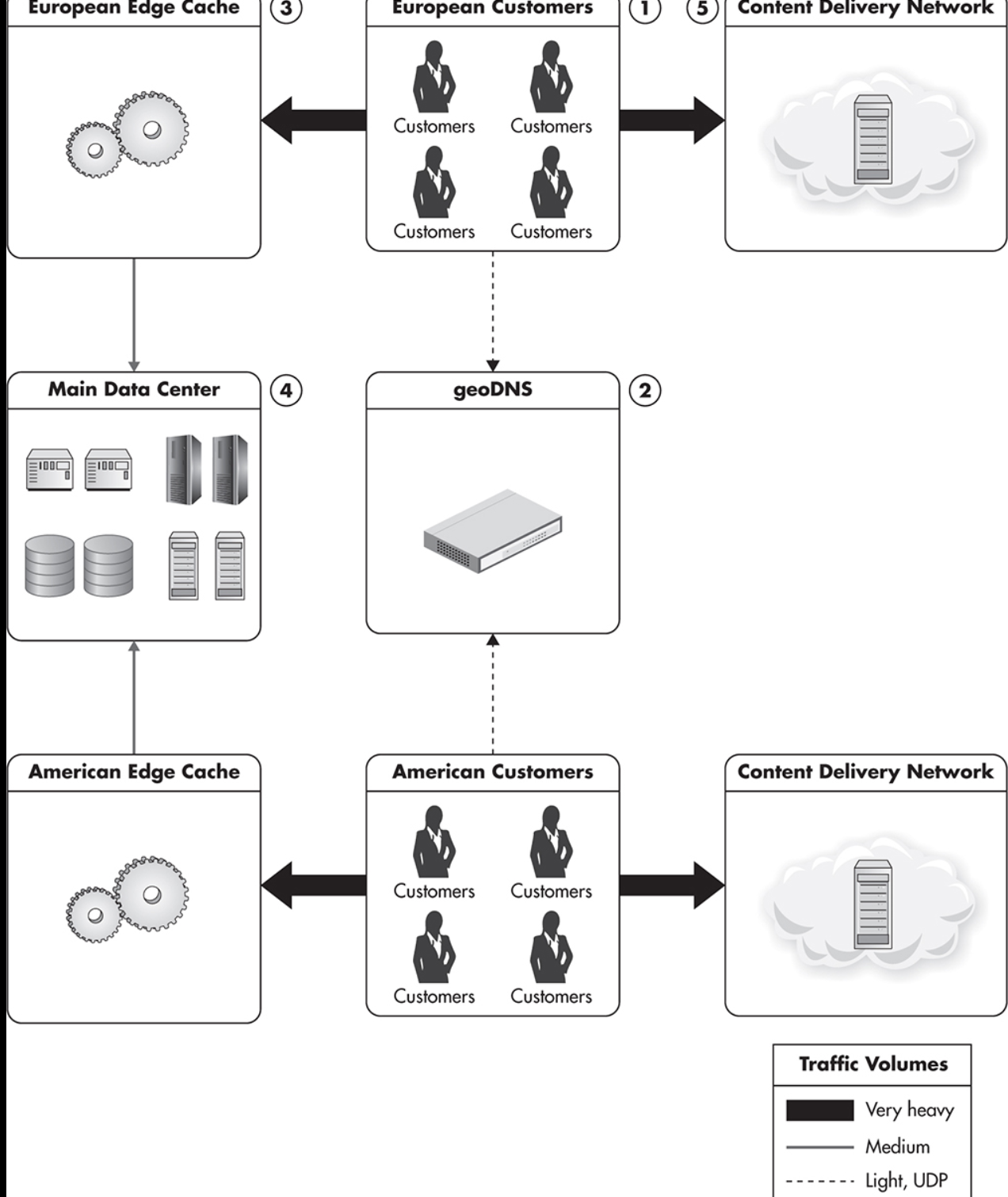
해결책7) 글로벌급으로 서비스가 커졌을 경우 geoDNS를 통해 지역별 DNS를 따로 준다. 또한 multiple edge cache servers를 글로벌하게 운영함으로써 network latency를 낮춘다.
참고)
*Edge cache is a HTTP cache server located near the customer, allowing the customer to partially cache the HTTP traffic. Edge-cache servers can serve entire pages or cache fragments of HTTP responses.
* Overview of a Data Center Infrastructure
- High-level overview of the data center infrastructure
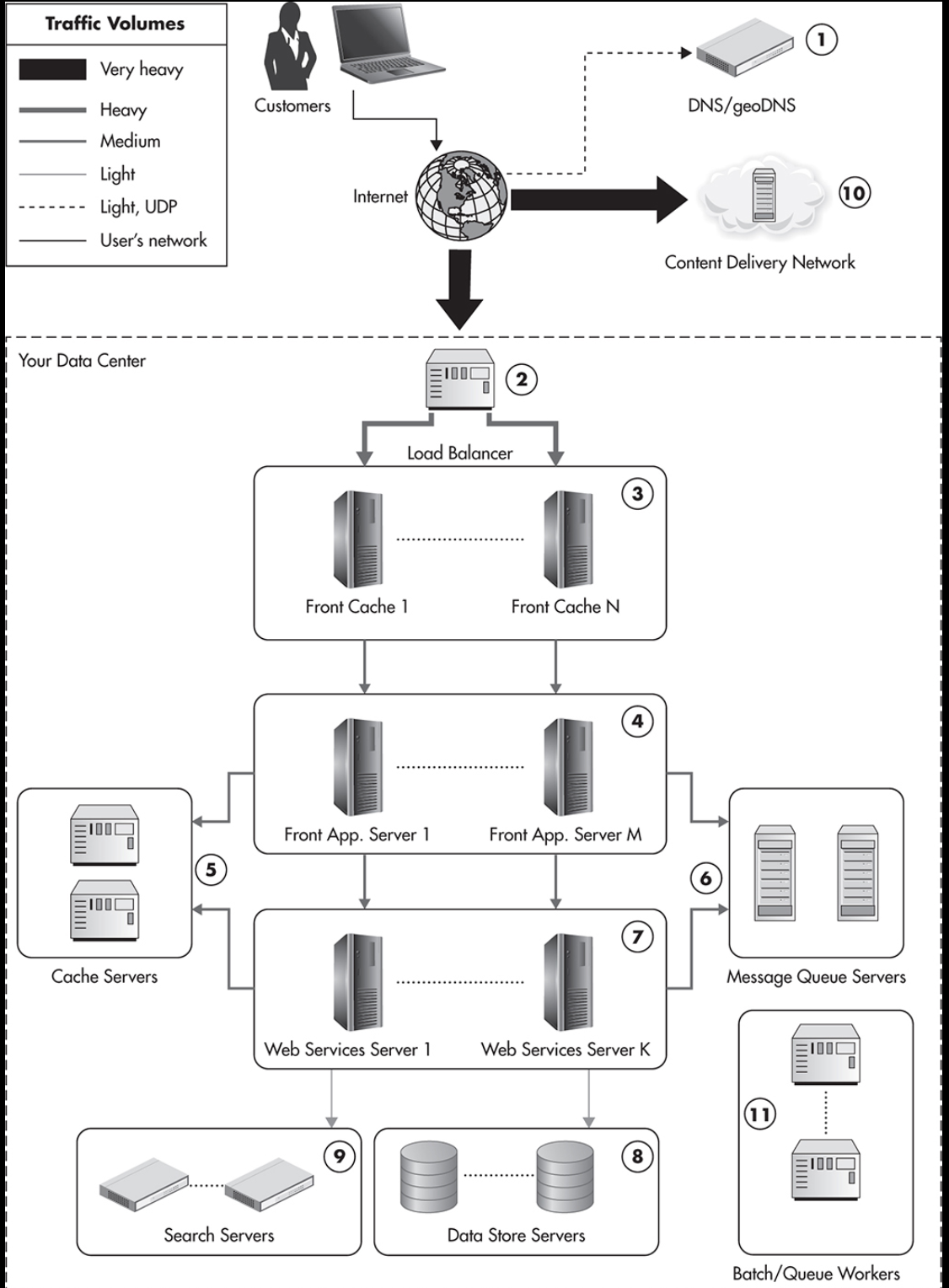
Data Center Infrastructure 구성 요소
1. Front line:
1) client request가 geoDNS로 감 2) load balancer로 전달됨 3) 그 다음 cash server로 전달되거나 web application layer로 넘어감
2. Web Application Layer:
4)html 생성 역할, html client request를 handling하는 역할. simple하게 만들어야하는게 특징
3. Web Services Layer:
7)비즈니스 로직 수행
4. Additional Components:
5)object cache servers, 6)message queues, 11)batch-processing server, jobs
5. Data Persistence Layer
8)Mysql, Nosql 9) Search engines
참고)
*load balancer is a software or hardware component that distributes traffic coming to a single IP address over multiple servers. Load balancers are used to share the load evenly among multiple servers and to allow dynamic addition and removal of machines.
*Object cache servers are used by both front-end application servers and web services to reduce the load put on the data stores and speed up responses by storing partially precomputed results
*Message queues are used to postpone some of the processing
*batch-processing server, jobsare not involved in generating responses to users’ requests. they are offline job-processing servers providing features like asynchronous notifications, order fulfillment, and other high-latency functions.
* Overview of the Application Architecture
- High-level view of an application architecture
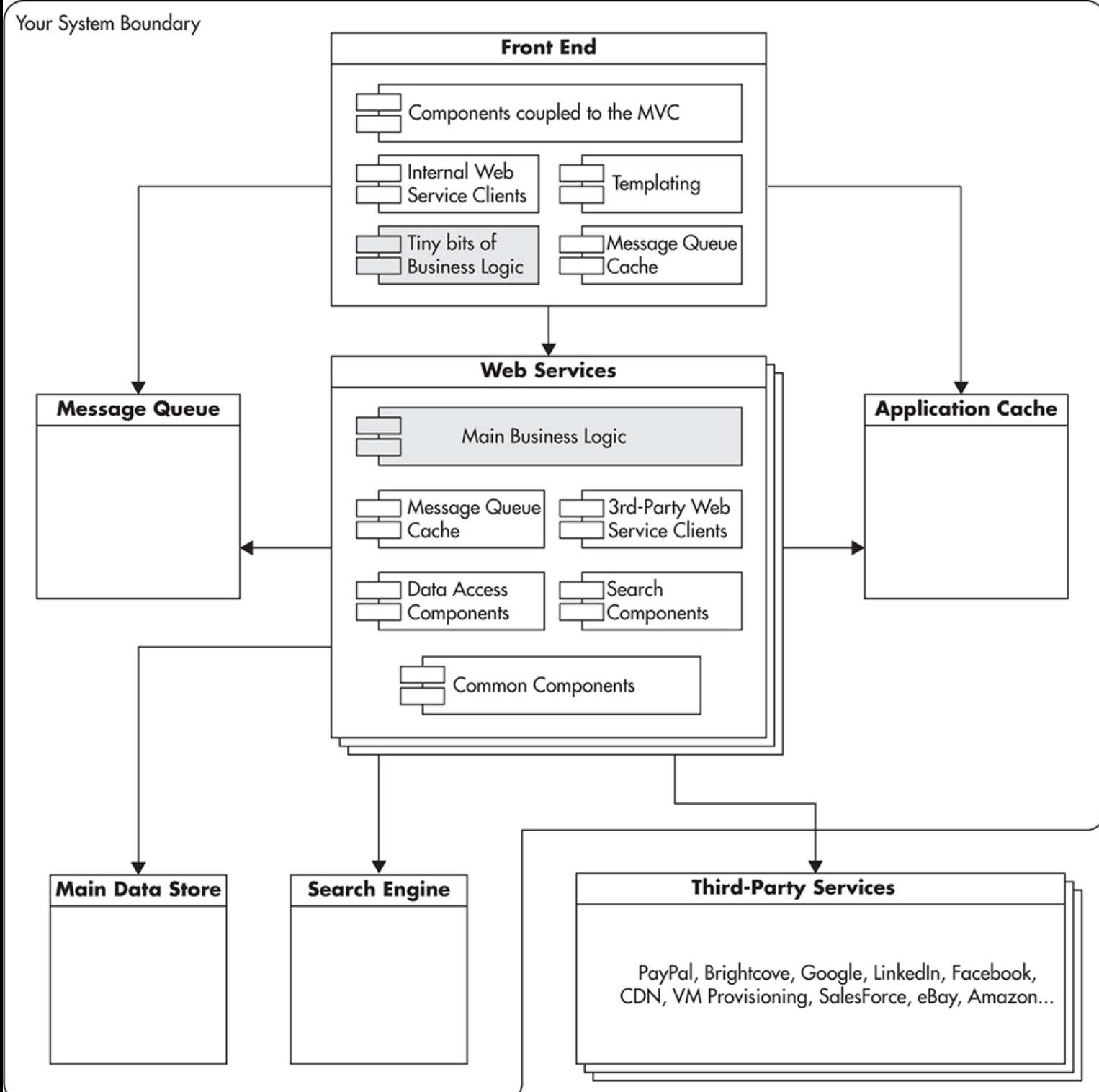
- Doman-Driven-Design(도메인 주도 설계)를 생각하면 됨. 이미 다른 포스팅에서 도메인 주도 설계를 다루었기 때문에 자세한 설명대신에 그림으로 설명을 대체하도록 하겠다.
참고)
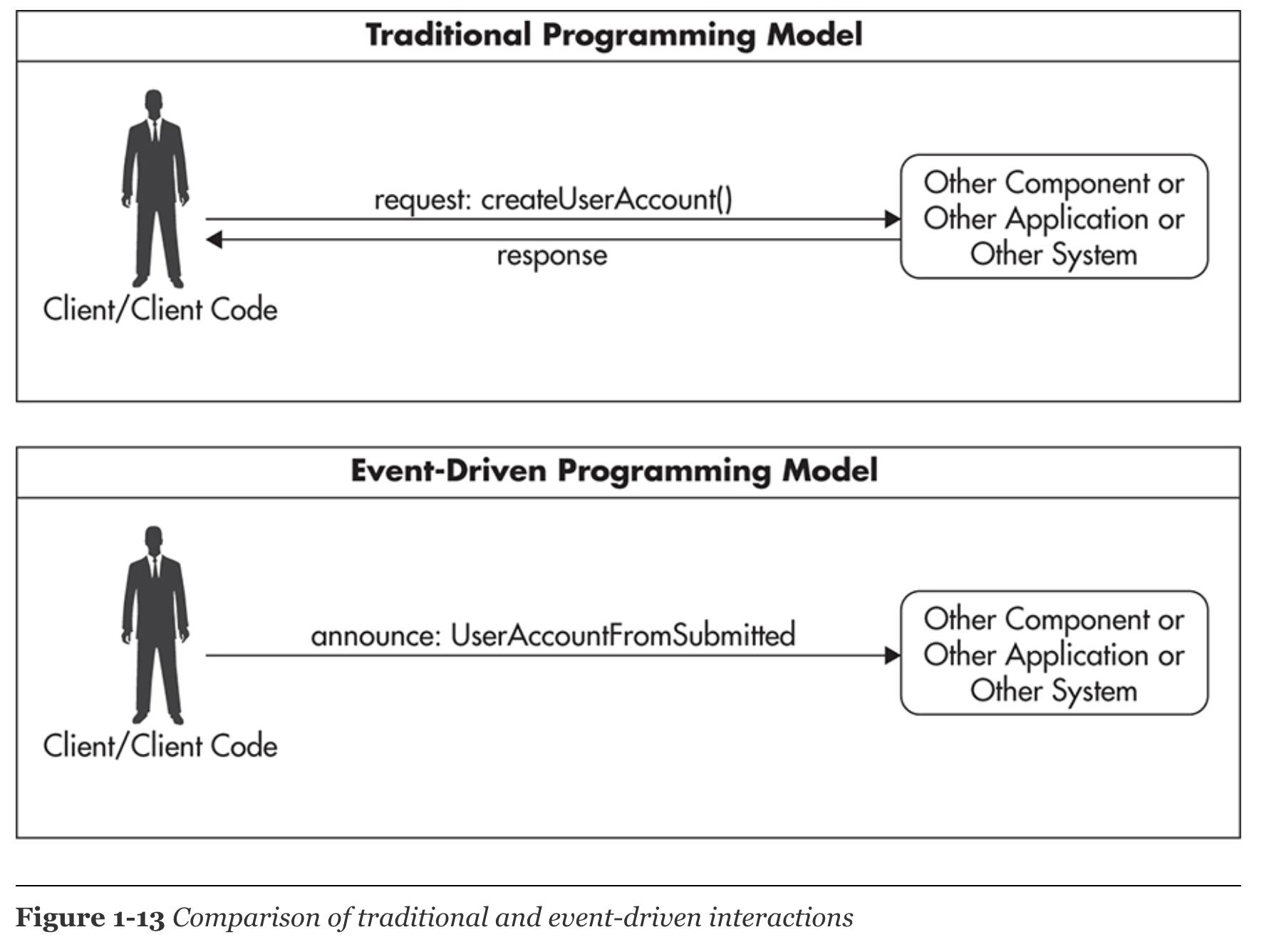
*Event-driven model, we don’t wait for things to be done. Whenever we have to interact with other components, we announce things that have already happened and proceed with our own processing
-
Comparison of traditional and event-driven interactions
-
Conceptual view of services in the web services layer
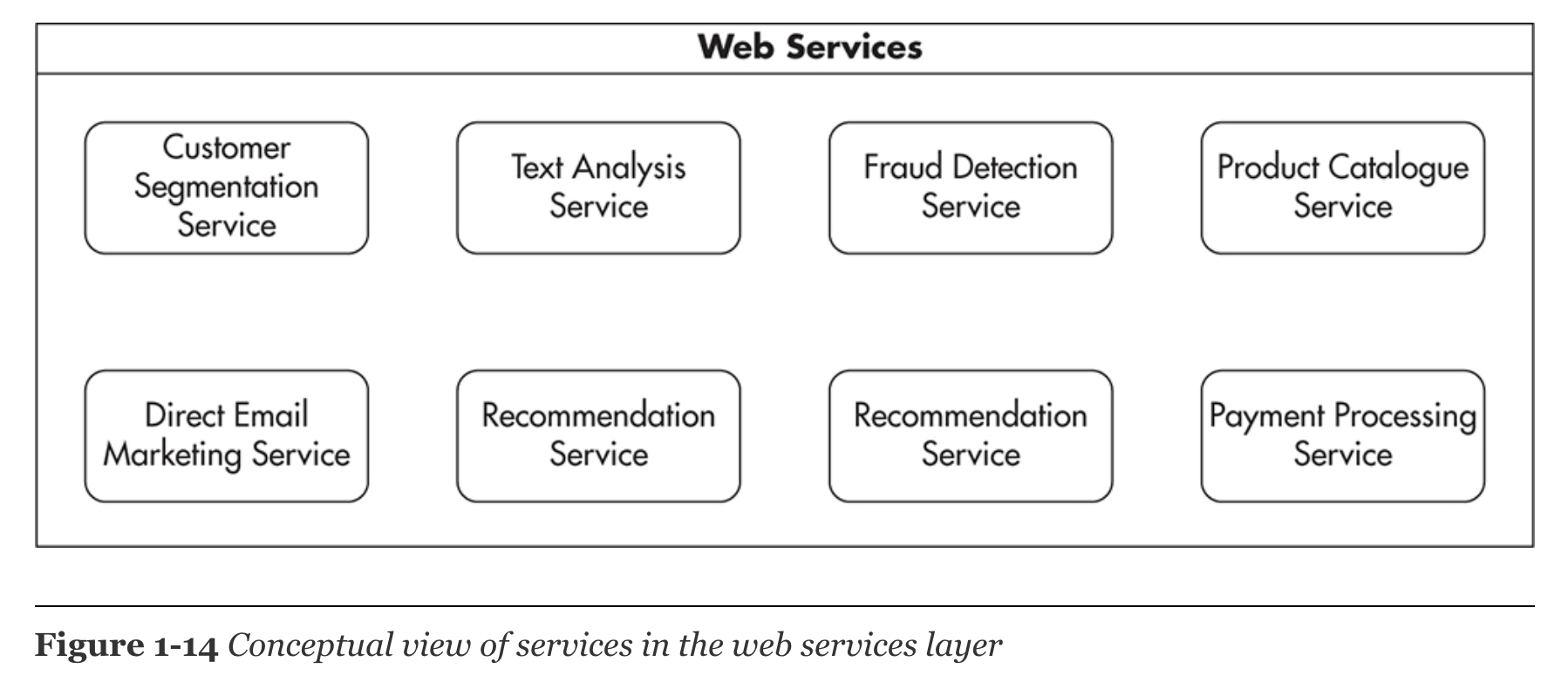
-
Each web service would be fully independent.
-
Think of the data store as you think of caches, search engines, and message queues—as plug-and-play extensions. If you decide to switch to a different persistence store or to exchange your caching back ends, you should be able to do it by replacing the connectivity components, leaving the overall architecture intact
🏝이 글이 도움이 되셨다면 추천 클릭을 부탁드립니다 :)
참고 자료

어려운 개념이라 올리신 포스트 보면서 개념공부중입니다. 감사해요