Elliptic Curve 엘립틱 커브는 정말 안쓰이는 곳이 없는 암호학의 총아다. 수학적으로 우아하고 아름답다. 안전하며 키 관리, 증명도 빠르고 쉽다. 복잡도가 올라가고 연산량이 많아지면 많은 자원을 필요로 한다.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is a form of public-key cryptography that leverages the mathematical properties of elliptic curves to create secure cryptographic protocols. It is known for providing strong security with smaller key sizes compared to other cryptographic methods like RSA.
(https://blog.humminglab.io/posts/tls-cryptography-11-ecc/)
(https://blog.cloudflare.com/a-relatively-easy-to-understand-primer-on-elliptic-curve-cryptography).
What are Elliptic Curves?
An elliptic curve is a mathematical construct defined by a cubic equation in two variables, typically (x) and (y). The general form of the equation is:
[ y^2 = x^3 + ax + b ]
where (a) and (b) are constants. One of the unique properties of elliptic curves is that if you take any two points on the curve and perform an operation known as "point addition," the result will always be another point on the curve.
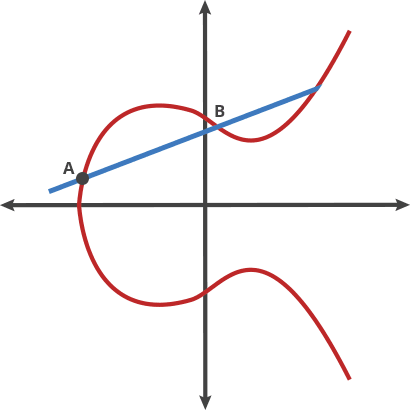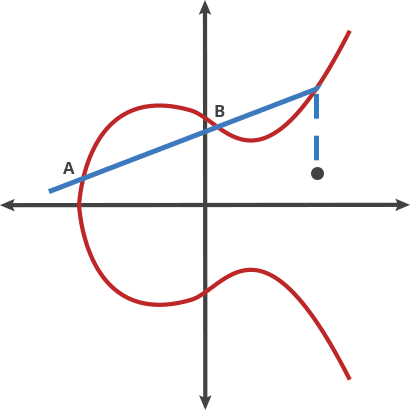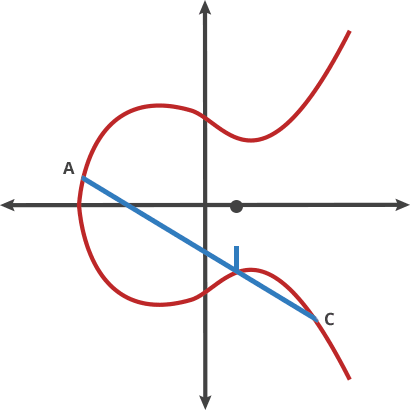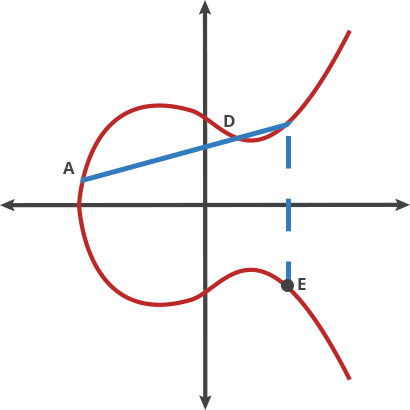
Key Properties of Elliptic Curves
-
Non-singularity: An elliptic curve is smooth, meaning it has no sharp points or cusps. This property ensures that the curve is well-behaved and suitable for cryptographic use.
-
Symmetry: Elliptic curves are symmetric about the x-axis. If you reflect a point on the curve across the x-axis, you get another point on the curve.
-
Point at Infinity: The elliptic curve has a special point called the "point at infinity," which acts as the identity element in the group formed by the points on the curve.
How Does ECC Work?
ECC security relies on the difficulty of the Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem (ECDLP). Given two points (A) and (B) on an elliptic curve, it is computationally challenging to determine the scalar (k) such that (A = kB).
Here’s how ECC is used in cryptographic systems:

-
Key Generation:
- Choose a large prime number (p) and define an elliptic curve (E) over the finite field (F_p).
- Select a base point (G) on the curve.
-
Public Key:
- Compute (Q = nG), where (n) is the private key.
- The public key consists of the tuple ((Q, E, G, p)).
-
Private Key:
- The private key (n) is kept secret and is used for decryption or signing.
-
Encryption:
- To encrypt a message (m), choose a random integer (r) and compute the ciphertext (C = (rG, M + rQ)), where (M) is the encoded message.
-
Decryption:
- Using the private key (n), recover the plaintext (M) by computing (M = C_2 - nC_1), where (C_1 = rG) and (C_2 = M + rQ).
Advantages of ECC
-
Smaller Key Sizes: ECC provides equivalent security to RSA but with much smaller key sizes, leading to faster computations and reduced storage requirements.
-
Faster Computations: Operations like point multiplication in ECC are more efficient than modular exponentiation in RSA, making ECC well-suited for resource-constrained environments.
-
Quantum Resistance: While still a subject of research, ECC is believed to offer better resistance to attacks from future quantum computers compared to RSA.
Common Applications of ECC
-
Secure Web Browsing: Many web browsers use ECC certificates to establish secure HTTPS connections.
-
Digital Signatures: ECC-based digital signatures, such as those generated by ECDSA, provide authenticity and integrity for digital documents and transactions.
-
Cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum rely on ECC algorithms to secure transactions and manage digital assets.
Popular ECC Variants Include:
- ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm)
- Ed25519
- X25519
Challenges and Limitations of ECC
-
Implementation Complexity: ECC requires careful implementation, particularly in handling arithmetic operations on elliptic curves and choosing secure curve parameters.
-
Side-Channel Attacks: Implementations must be protected against side-channel attacks, such as timing and power analysis, which can leak private keys during computations.
ECC offers a powerful combination of security, efficiency, and compactness, making it a cornerstone of modern cryptographic systems. However, its implementation must be done with care to avoid vulnerabilities.

