Day3. DataFiltering - Customers Who Never Order
Problem
Table: Customers
| Column Name | Type |
|---|---|
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
id is the primary key (column with unique values) for this table.
Each row of this table indicates the ID and name of a customer.
Table: Orders
| Column Name | Type |
|---|---|
| id | int |
| customerId | int |
id is the primary key (column with unique values) for this table.
customerId is a foreign key (reference columns) of the ID from the Customers table.
Each row of this table indicates the ID of an order and the ID of the customer who ordered it.
Write a solution to find all customers who never order anything.
Return the result table in any order.
The result format is in the following example.
Example 1:
Input:
Customers table:
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Joe |
| 2 | Henry |
| 3 | Sam |
| 4 | Max |
Orders table:
| id | customerId |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 |
Output:
| Customers |
|---|
| Henry |
| Max |
solution
# my solution
import pandas as pd
def find_customers(customers: pd.DataFrame, orders: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
cus = customers.set_index(keys='id')
n = []
for i in orders['customerId']:
if i not in n:
n.append(i)
cus = cus.drop(i)
cus.rename(columns={'name':'Customers'}, inplace=True)
return cus# check result
data = [[1, 'Joe'], [2, 'Henry'], [3, 'Sam'], [4, 'Max']]
customers = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['id', 'name']).astype({'id':'Int64', 'name':'object'})
data = [[1, 3], [2, 1]]
orders = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['id', 'customerId']).astype({'id':'Int64', 'customerId':'Int64'})
find_customers(customers, orders)
# the others [1], [2]
# 1.
import pandas as pd
def find_customers(customers: pd.DataFrame, orders: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
# Select the customers whose 'id' is not present in the orders DataFrame's 'customerId' column.
df = customers[~customers['id'].isin(orders['customerId'])]
# Build a DataFrame that only contains the 'name' column and rename it as 'Customers'.
df = df[['name']].rename(columns={'name': 'Customers'})
return df
# 2.
import pandas as pd
def customers_who_never_order(customers: pd.DataFrame, orders: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
df = customers.merge(orders, left_on='id', right_on='customerId', how='left')
df = df[df['customerId'].isna()]
df = df[['name']].rename(columns={'name': 'Customers'})
return dfLearn new method - isin method
When check the ohter solution, many people use isin method. So, today I will learn about isinmethod through Pandas API reference. [3]
isinmethod using for check whether each element in the DataFrame is contained in values. Let's look into some example.
# 1. Create DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'num_legs': [2, 4], 'num_wings': [2, 0]},
index=['falcon', 'dog'])
df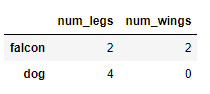
# 2. isin method
df.isin([0, 2])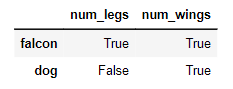 If values is a list, then check whether every value in the DataFrame is present in the list. In this case, If animals haver 0 or 2 legs or wings, then output is True, otherwise output is False.
If values is a list, then check whether every value in the DataFrame is present in the list. In this case, If animals haver 0 or 2 legs or wings, then output is True, otherwise output is False.
# 3. application
~df.isin([0, 2])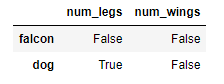 To check values is not in the DataFrame, use the ~ operator. Can check the result is the opposite of the above result.
To check values is not in the DataFrame, use the ~ operator. Can check the result is the opposite of the above result.
reference
probelm
leetcode - 30 Days of Pandas / Customers Who Never Order
[0]
the other solution
the other solution # 1. [1]
Pandas API reference
pandas.DataFrame.isin — pandas 2.0.3 documentation [3]
