Day4. Data Filtering - Article Views I
Problem
Table: Views
| Column Name | Type |
|---|---|
| article_id | int |
| author_id | int |
| viewer_id | int |
| view_date | date |
There is no primary key (column with unique values) for this table, the table may have duplicate rows.
Each row of this table indicates that some viewer viewed an article (written by some author) on some date.
Note that equal author_id and viewer_id indicate the same person.
Write a solution to find all the authors that viewed at least one of their own articles.
Return the result table sorted by id in ascending order.
The result format is in the following example.
Example 1:
Input:
Views table:
| article_id | author_id | viewer_id | view_date |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 2019-08-01 |
| 1 | 3 | 6 | 2019-08-02 |
| 2 | 7 | 7 | 2019-08-01 |
| 2 | 7 | 6 | 2019-08-02 |
| 4 | 7 | 1 | 2019-07-22 |
| 3 | 4 | 4 | 2019-07-21 |
| 3 | 4 | 4 | 2019-07-21 |
Output:
| id |
|---|
| 4 |
| 7 |
Solution
# my solution
import pandas as pd
def article_views(views: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
n = []
m = 0
for i in views['author_id']:
if (i == views['viewer_id'].iloc[m]) & (i not in n):
n.append(i)
m += 1
n.sort()
ans = pd.DataFrame({'id': []})
for i in n:
ans.loc[len(ans)] = [i]
return ans# check result
data = [[1, 3, 5, '2019-08-01'], [1, 3, 6, '2019-08-02'], [2, 7, 7, '2019-08-01'], [2, 7, 6, '2019-08-02'], [4, 7, 1, '2019-07-22'], [3, 4, 4, '2019-07-21'], [3, 4, 4, '2019-07-21']]
Views = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['article_id', 'author_id', 'viewer_id', 'view_date']).astype({'article_id':'Int64', 'author_id':'Int64', 'viewer_id':'Int64', 'view_date':'datetime64[ns]'})
article_views(Views)
# other solutions [1], [2]
# 1.
import pandas as pd
def article_views(views: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
# Filter rows where author_id and viewer_id are the same (authors viewing their own articles)
authors_viewed_own_articles = views[views['author_id'] == views['viewer_id']]
# Get unique author_ids from the filtered data
unique_authors = authors_viewed_own_articles['author_id'].unique()
# Sort the unique author_ids in ascending order
unique_authors = sorted(unique_authors)
# Create a DataFrame with the sorted unique author_ids and rename the 'author_id' column to 'id'
result_df = pd.DataFrame({'id': unique_authors})
return result_df
# 2.
def article_views(views: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
return views.loc[
views['author_id'] == views['viewer_id'], ['author_id']
].drop_duplicates().rename(columns={
'author_id': 'id',
}).sort_values(
by=['id'],
)Learn New method
When check popular solution, They didn't use for loop and, solution is more simple than my solution. So, today I learn about new method which is core of best solution through Pandas API reference. [3], [4]
Pandas.Series.unique
Series.unique() return unique values of Series object as a NumPy array. uniques are returned in order of appearance. So, If you want sort, you have to use other methods to sort. Let's look into some example.
pd.Series([2, 1, 3, 3], name='A').unique()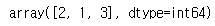 If you check above code and result, you could confirm
If you check above code and result, you could confirm unique method return values that exist in Sereies without duplication.
exam = pd.Series([2, 1, 3, 3], name='A').unique()
exam.sort()
exam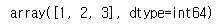 In addition, If you use
In addition, If you use sort method, you can sort the result.
Pandas.DataFrame.drop_duplicates
DataFrame.drop_duplicates( subset = None , * , keep = 'first' , inplace = False , ignore_index = False ) return DataFrame with duplicate rows removed. By default use all of the columns. But if you want to consider certain columns, you can by using subset parameter. Let's look into some example.
df = pd.DataFrame({
'brand': ['Yum Yum', 'Yum Yum', 'Indomie', 'Indomie', 'Indomie'],
'style': ['cup', 'cup', 'cup', 'pack', 'pack'],
'rating': [4, 4, 3.5, 15, 5]
})
df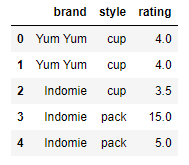
df.drop_duplicates()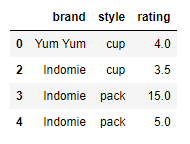 If you check above result, you could confirm df removed duplicate rows.
If you check above result, you could confirm df removed duplicate rows.
df.drop_duplicates(subset=['brand'])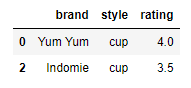 In addition, If you use subset parameter, you could remove duplicates on specific column(s).
In addition, If you use subset parameter, you could remove duplicates on specific column(s).
reference
problem
leetcode - 30 Days of Pandas / Article Views I [0]
other solutions
other solutions 1. [1]
Pandas API reference
pandas.Series.unique — pandas 2.0.3 documentation
[3]
