최근 MMDetection Open Source를 이용한 Object Detection에 대해서 공부하고 있다.
CNN을 공부할 때보다 새로운 개념도 많고 생각해야 할 부분도 많아서 이렇게 정리해보려고 한다.
한번에 모든걸 다 정리하면 힘들기 때문에 Config에 대해 먼저 공부했다.
Config
MMDetection은 Modular design을 사용한다.
Modular design이란?
모듈러 설계라고 불리는 Modular design은 시스템을 Module이라는 작은 부분으로 세분화하는 설계 방식이다.
Config는 이렇게 세분화된 Module을 configured 시켜주는 역할을 한다.
Config를 이용해서 시스템을 보다 간결하게 작동시킬 수 있다.
Config의 예시로 대표적인 Model Config와 Dataset Config를 알아보자.
MMDetection에서는 여러 Model을 pytorch 기반으로 구현해 놓았다.
나는 이중에서 faster-rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py를 이용해 Config에 대해 공부했다.
MMDetection 공식 github의 configs/faster_rcnn/faster-rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py에 들어가보면 다음과 같이 되어있다.
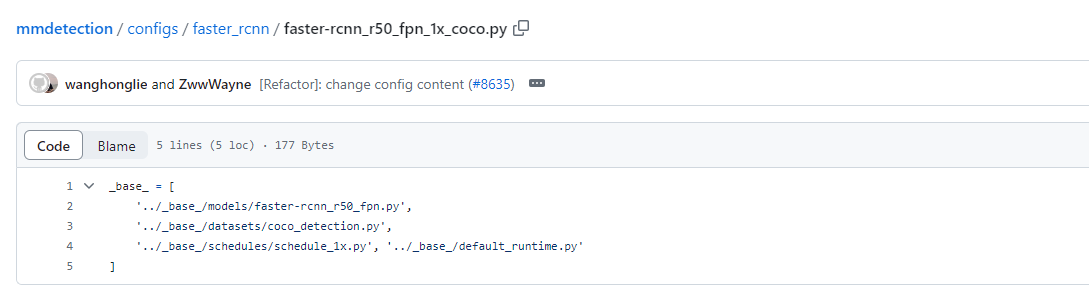
이를 해석해보면 MMDetection 에서 구현한 이 Model은
'_base_/models/faster-rcnn_r50_fpn.py',
'_base_/datasets/coco_detection.py',
'_base_/schedules/schedule_1x.py',
'_base_/default_runtime.py'
를 통해 만들어졌다.
각각은 구현된 Model, 학습에 이용된 Dataset, scheduler, runtime default를 의미한다.
나는 이중에서 Model Config, Dataset Config를 공부했다.
Model Config
Model Config는 다음과 같았다.
전반적으로 Model의 구성요소(?)에 대해 나와있다.
backbone, neck, rpn, roi ...
이중에서도
train_cfg, test_cfg는 Model training, testing hyper parameter에 관한 것이다.
# model settings
model = dict(
type='FasterRCNN',
data_preprocessor=dict(
type='DetDataPreprocessor',
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53],
std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375],
bgr_to_rgb=True,
pad_size_divisor=32),
backbone=dict(
type='ResNet',
depth=50,
num_stages=4,
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3),
frozen_stages=1,
norm_cfg=dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True),
norm_eval=True,
style='pytorch',
init_cfg=dict(type='Pretrained', checkpoint='torchvision://resnet50')),
neck=dict(
type='FPN',
in_channels=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
out_channels=256,
num_outs=5),
rpn_head=dict(
type='RPNHead',
in_channels=256,
feat_channels=256,
anchor_generator=dict(
type='AnchorGenerator',
scales=[8],
ratios=[0.5, 1.0, 2.0],
strides=[4, 8, 16, 32, 64]),
bbox_coder=dict(
type='DeltaXYWHBBoxCoder',
target_means=[.0, .0, .0, .0],
target_stds=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]),
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=True, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='L1Loss', loss_weight=1.0)),
roi_head=dict(
type='StandardRoIHead',
bbox_roi_extractor=dict(
type='SingleRoIExtractor',
roi_layer=dict(type='RoIAlign', output_size=7, sampling_ratio=0),
out_channels=256,
featmap_strides=[4, 8, 16, 32]),
bbox_head=dict(
type='Shared2FCBBoxHead',
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=80,
bbox_coder=dict(
type='DeltaXYWHBBoxCoder',
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]),
reg_class_agnostic=False,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='L1Loss', loss_weight=1.0))),
# model training and testing settings
train_cfg=dict(
rpn=dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.7,
neg_iou_thr=0.3,
min_pos_iou=0.3,
match_low_quality=True,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='RandomSampler',
num=256,
pos_fraction=0.5,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=False),
allowed_border=-1,
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
rpn_proposal=dict(
nms_pre=2000,
max_per_img=1000,
nms=dict(type='nms', iou_threshold=0.7),
min_bbox_size=0),
rcnn=dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.5,
neg_iou_thr=0.5,
min_pos_iou=0.5,
match_low_quality=False,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='RandomSampler',
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False)),
test_cfg=dict(
rpn=dict(
nms_pre=1000,
max_per_img=1000,
nms=dict(type='nms', iou_threshold=0.7),
min_bbox_size=0),
rcnn=dict(
score_thr=0.05,
nms=dict(type='nms', iou_threshold=0.5),
max_per_img=100)
# soft-nms is also supported for rcnn testing
# e.g., nms=dict(type='soft_nms', iou_threshold=0.5, min_score=0.05)
))Dataset Config
Dataset Config는 다음과 같았다.
dataset type은 CocoDataset를 이용했다.
즉, Model 학습시에 CocoDataset을 이용해 학습한 것으로 해석할 수 있다.
Dataset Config는 최종적으로 dataloader를 위해 dataset에 관한 정보, pipeline이 담겨져있다.
train_dataloader를 살펴보면 dataset(pipeline)에 관한 정보와 batch size등의 정보가 들어있다.
즉 train_dataloader에는 Model을 학습시키는 메커니즘이 들어있음을 알 수 있다.
# dataset settings
dataset_type = 'CocoDataset'
data_root = 'data/coco/'
backend_args = None
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile', backend_args=backend_args),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(type='Resize', scale=(1333, 800), keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip', prob=0.5),
dict(type='PackDetInputs')
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile', backend_args=backend_args),
dict(type='Resize', scale=(1333, 800), keep_ratio=True),
# If you don't have a gt annotation, delete the pipeline
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(
type='PackDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_id', 'img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape',
'scale_factor'))
]
train_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=2,
num_workers=2,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=True),
batch_sampler=dict(type='AspectRatioBatchSampler'),
dataset=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
ann_file='annotations/instances_train2017.json',
data_prefix=dict(img='train2017/'),
filter_cfg=dict(filter_empty_gt=True, min_size=32),
pipeline=train_pipeline,
backend_args=backend_args))
val_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=1,
num_workers=2,
persistent_workers=True,
drop_last=False,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=False),
dataset=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
ann_file='annotations/instances_val2017.json',
data_prefix=dict(img='val2017/'),
test_mode=True,
pipeline=test_pipeline,
backend_args=backend_args))
test_dataloader = val_dataloader실제로 학습 데이터가 들어오면 train_dataloader를 작동시켜라 ... 같은 형식의 명령을 하게된다.
# model을 cfg개체의 model로 정하고 train_cfg, test_cfg를 이용하여 model detector 생성
model = build_detector(cfg.model, train_cfg=cfg.get('train_cfg'), test_cfg=cfg.get('test_cfg'))