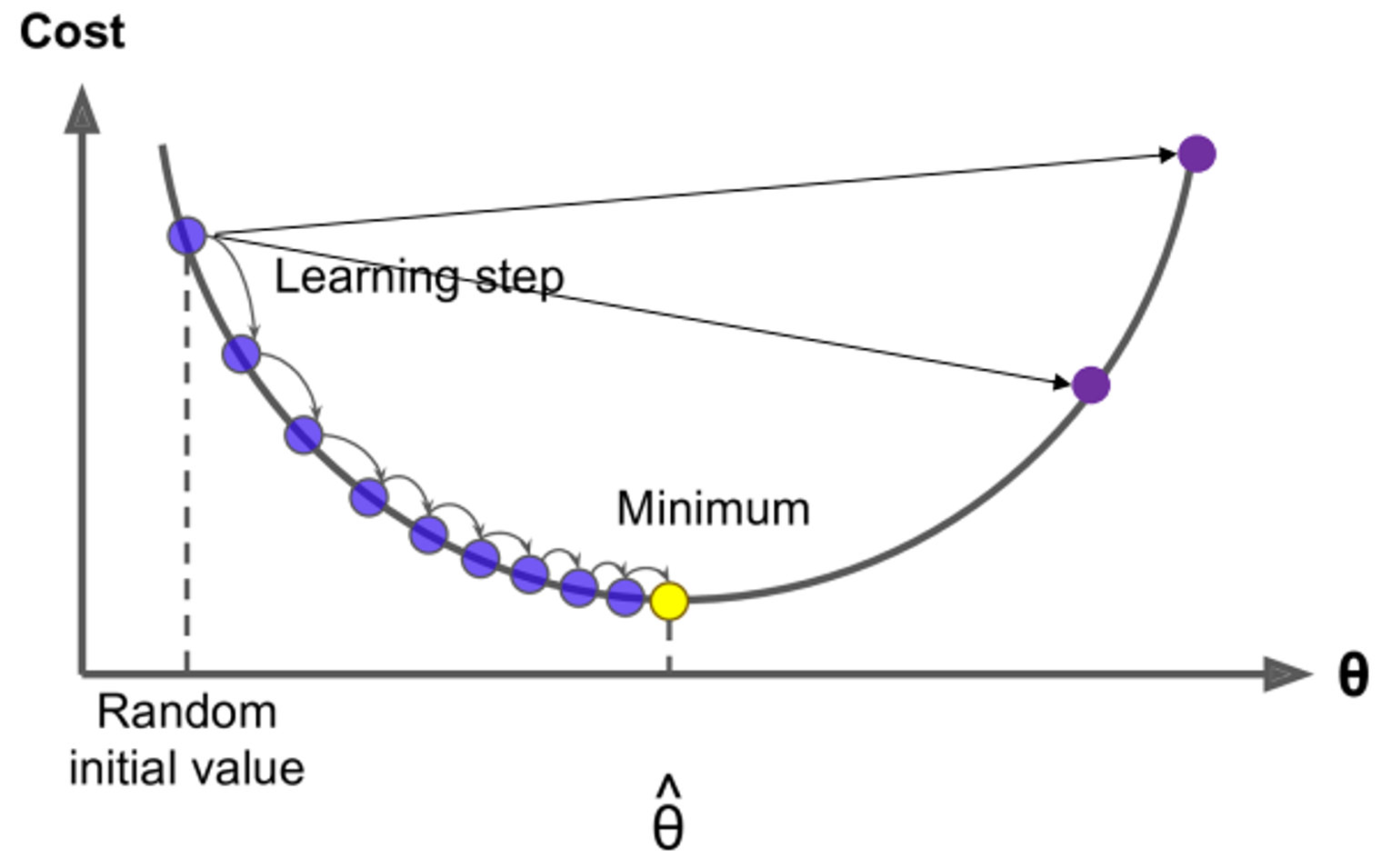
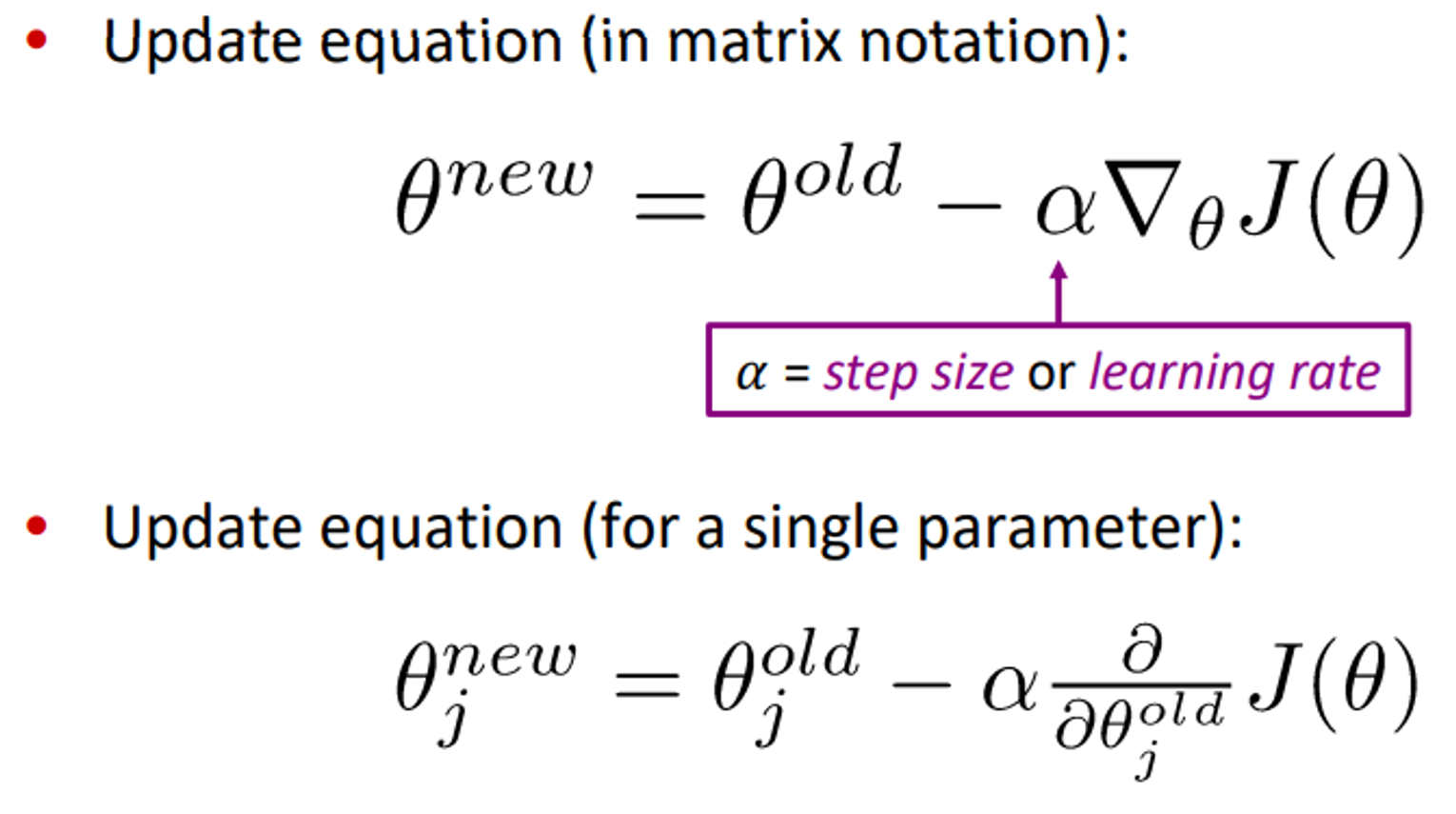
Optimization : Gradient Descent
GD is an argorithm to minize by changing
Idea: from current value of , calculate gradient of , then take small step in the
direction of negative gradient. Repeat.
Problem: is a function of all windows in the corpus
• So is very expensive to compute
solution : stochastic gradient descent(SGD)

select sample window from corpus then learn with the window’s gradient
(update )
SGD를 이용한다면, is very sparse so updating all for per step is so expensive.
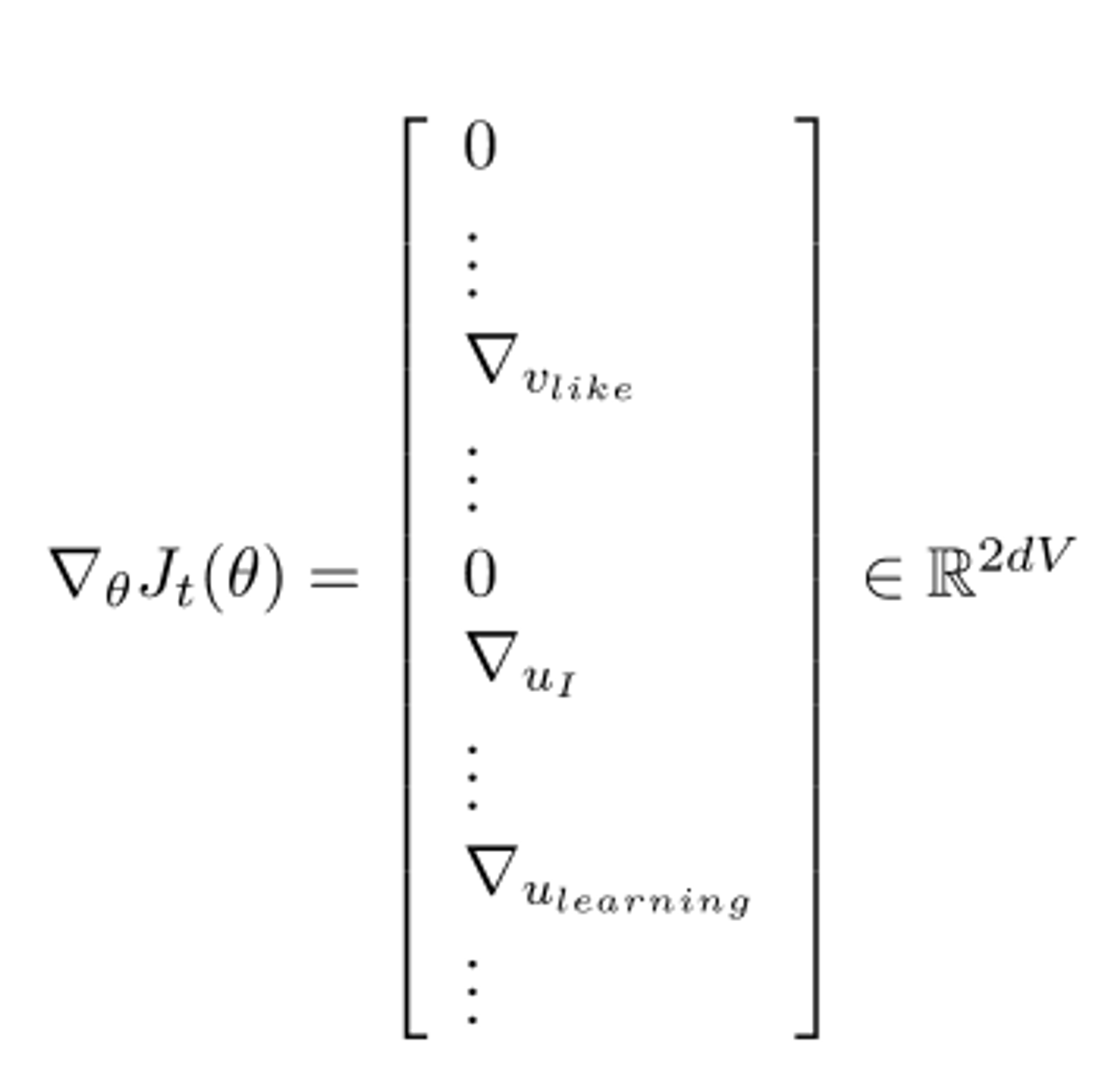
for many frame work(like “pytorch”) a word vector is row vector
with hash-table we update each row that needs updating

Word2vec algorithm family : More details
- Skip-grams(SG) : predict context words form given center word
- Continuous Bag of Words(CBOW) : predict center word from given Bag of words(from context)
- Negative sampling
Skip-gram with negative sampling
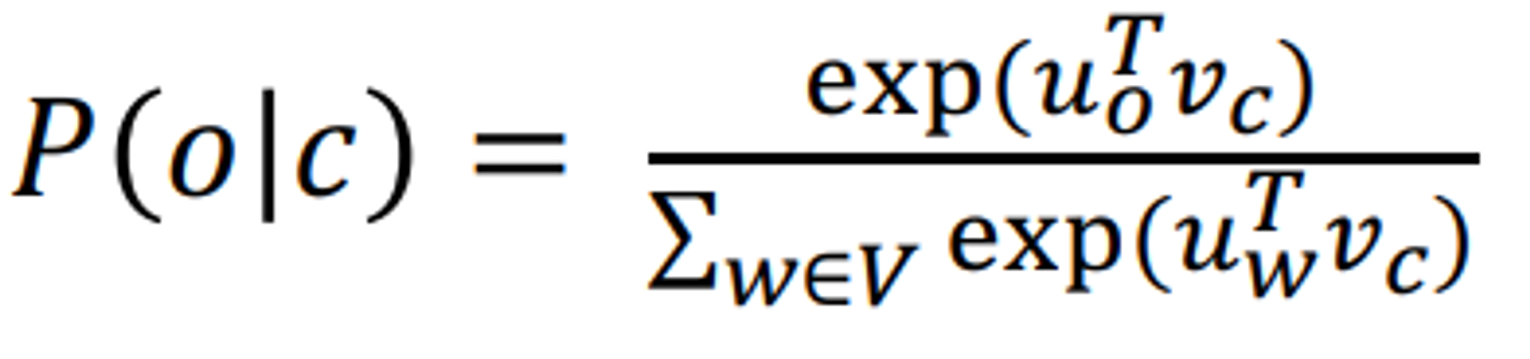
from this difinition of P the denominator term is expensive(V is very large)
solution
Idea : train binary logistic regressions for a true pair(center word with word in its window) vs noise pairs(center word paired with a random word)
Loss function (average of all )
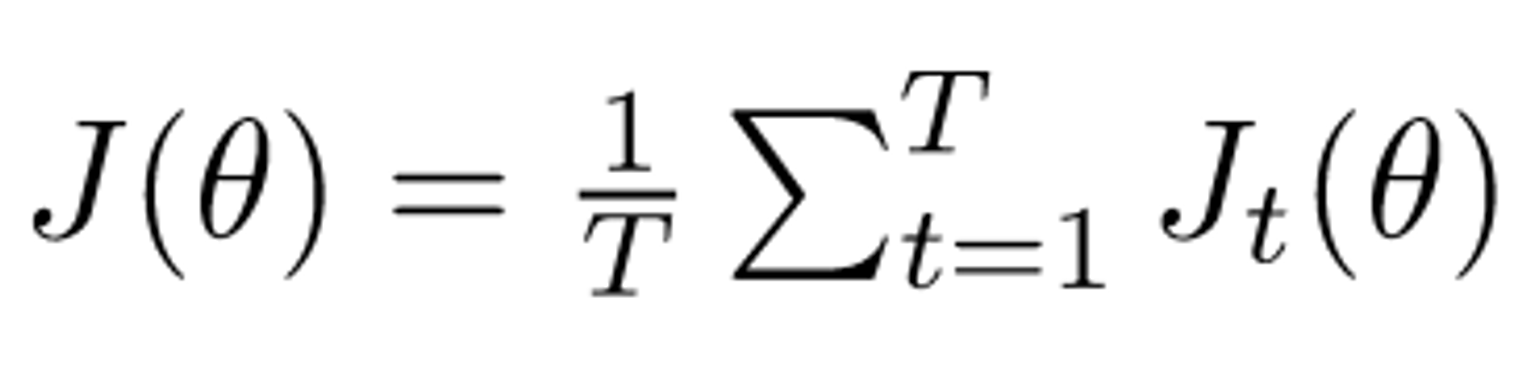
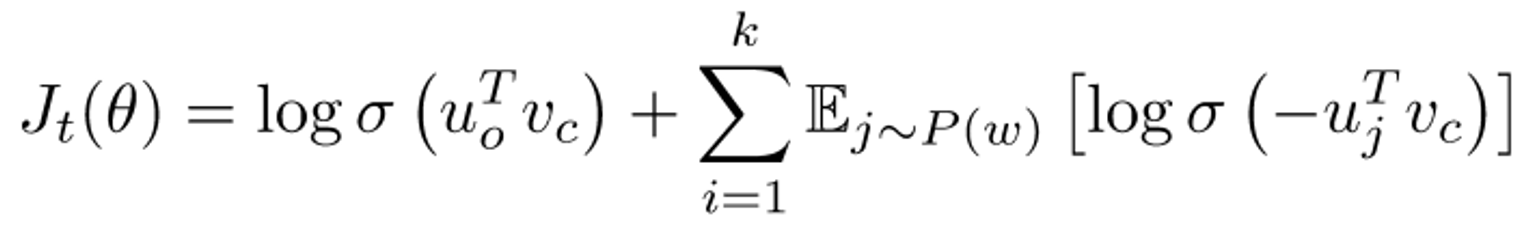
이를 조금만 더 쉽게 표현하면

이와같다. 여기서 U는 unigram function으로 U(w)는 corpus 내에서 w의 등장 확률에 관한 함수이다.
To normalize this unigram function use this function
The power(3/4) makes less frequent words be sapmpled more often.
Co-occurrence
- window를 기준으로 : similar to word2vec → captures some syntatic and semantic information
- full document : will give general topics leading to “Latent semantic Analysis”(LSA, 잠재 의미 분석)
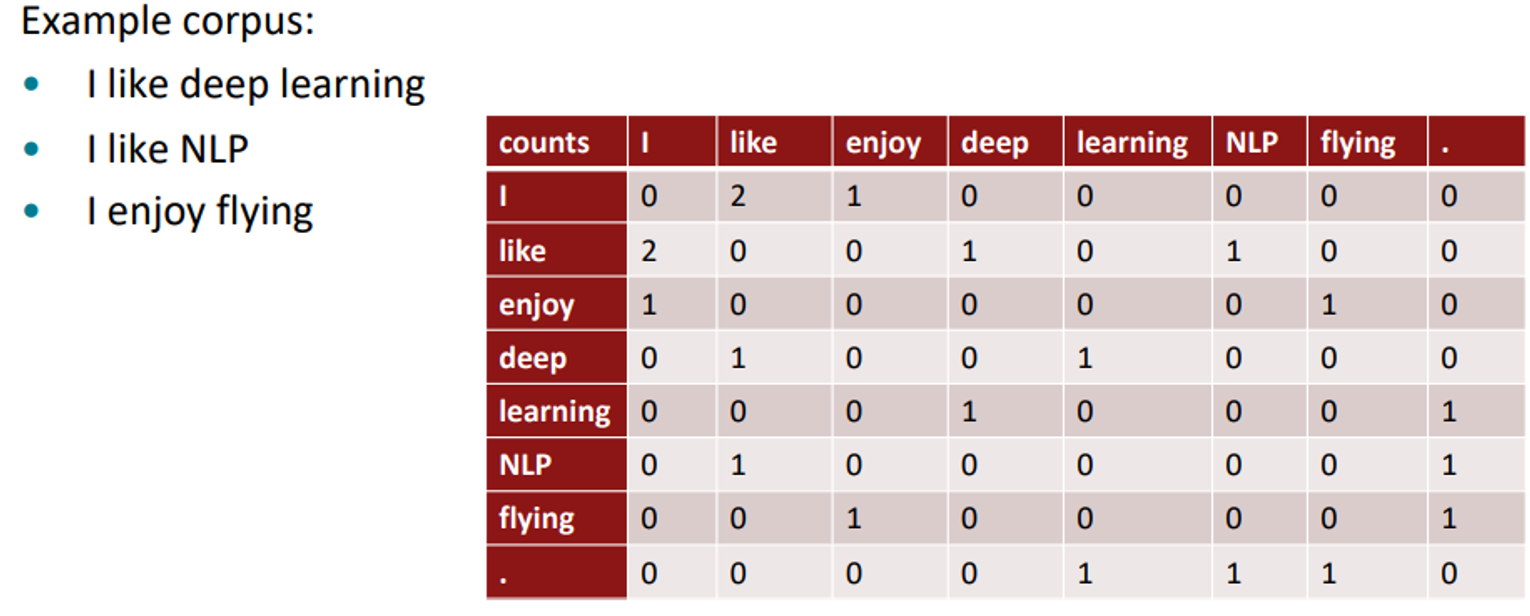
window size = 1
Co-occurrence matrix X를 singular value decomposition을 통해 나누어준다.
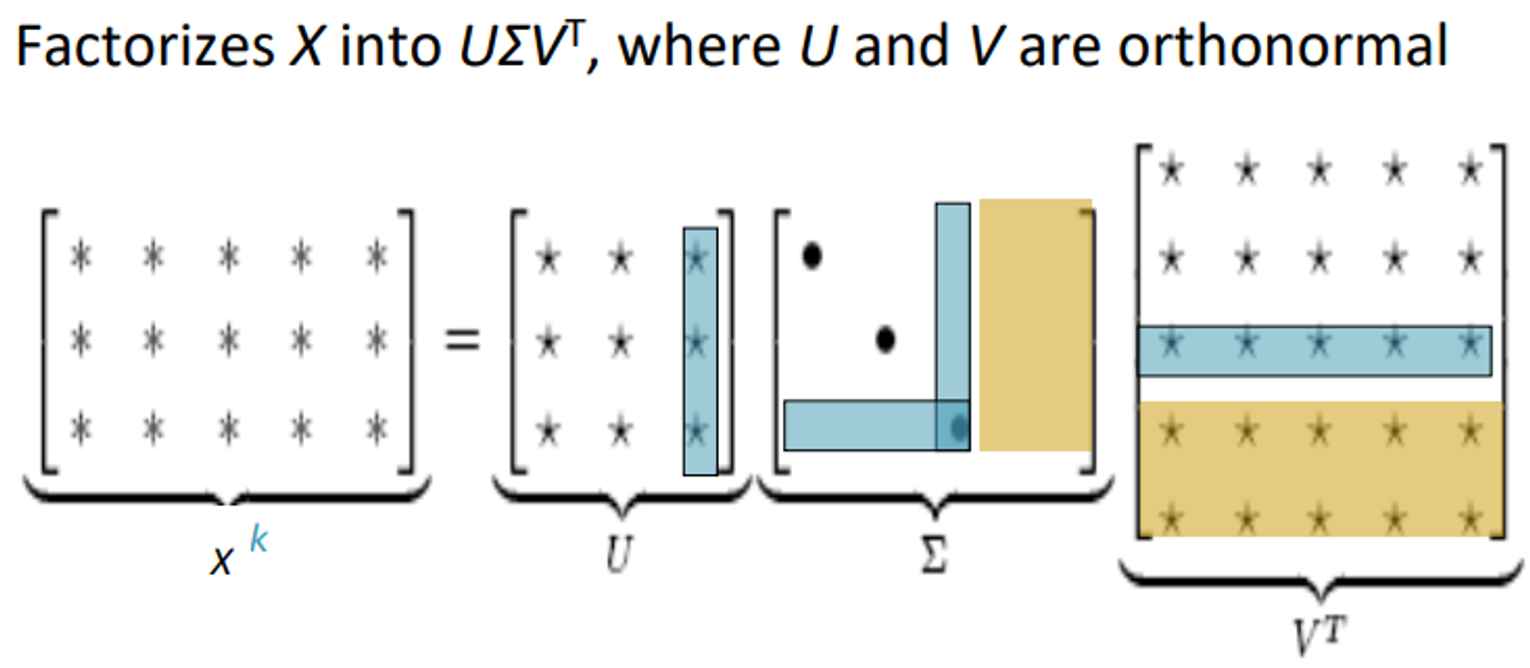
하지만 SVD를 그대로 이용하는것은 잘 되지는 않음
따라서 다음 기법들을 이용해볼 수 있음.
-
scaling the counts : scaling counts in the cells can help a lot
problem : function words (the, he, has) are too frequent → syntax has too much impact. some fixes : min(X, t) with
-
Ramped windows : 가까운것은 가중치를 크게 두고(counts more) 먼 것은 가중치를 적게 두어서 계산하는 방법
-
Pearson correlations instead of counts.
-
ect…
COALS model
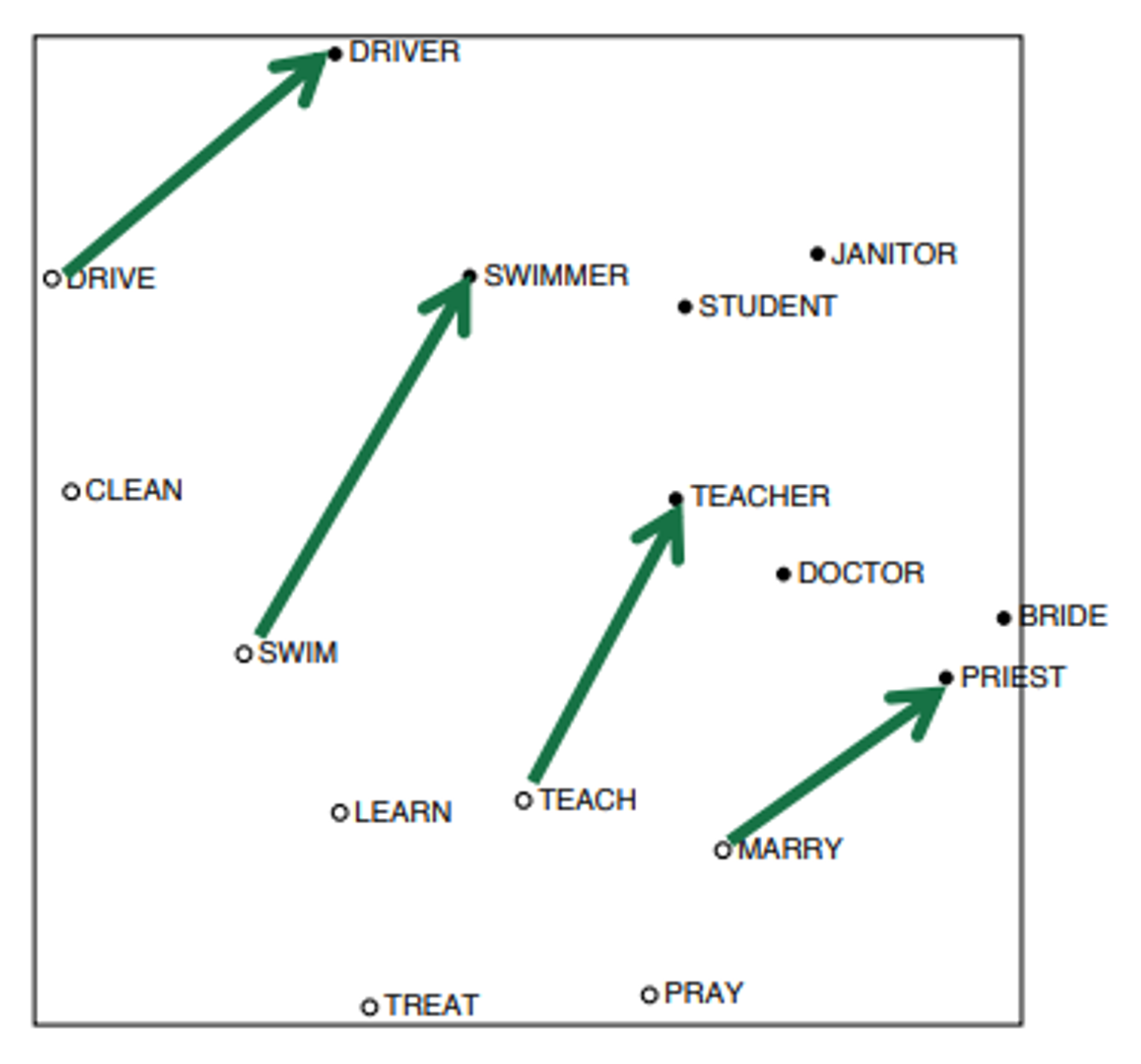
scaling을 통해 다음과 같은 semantic patterns를 발견할 수 있다.
Towards GloVe : Count based vs. direct prediction
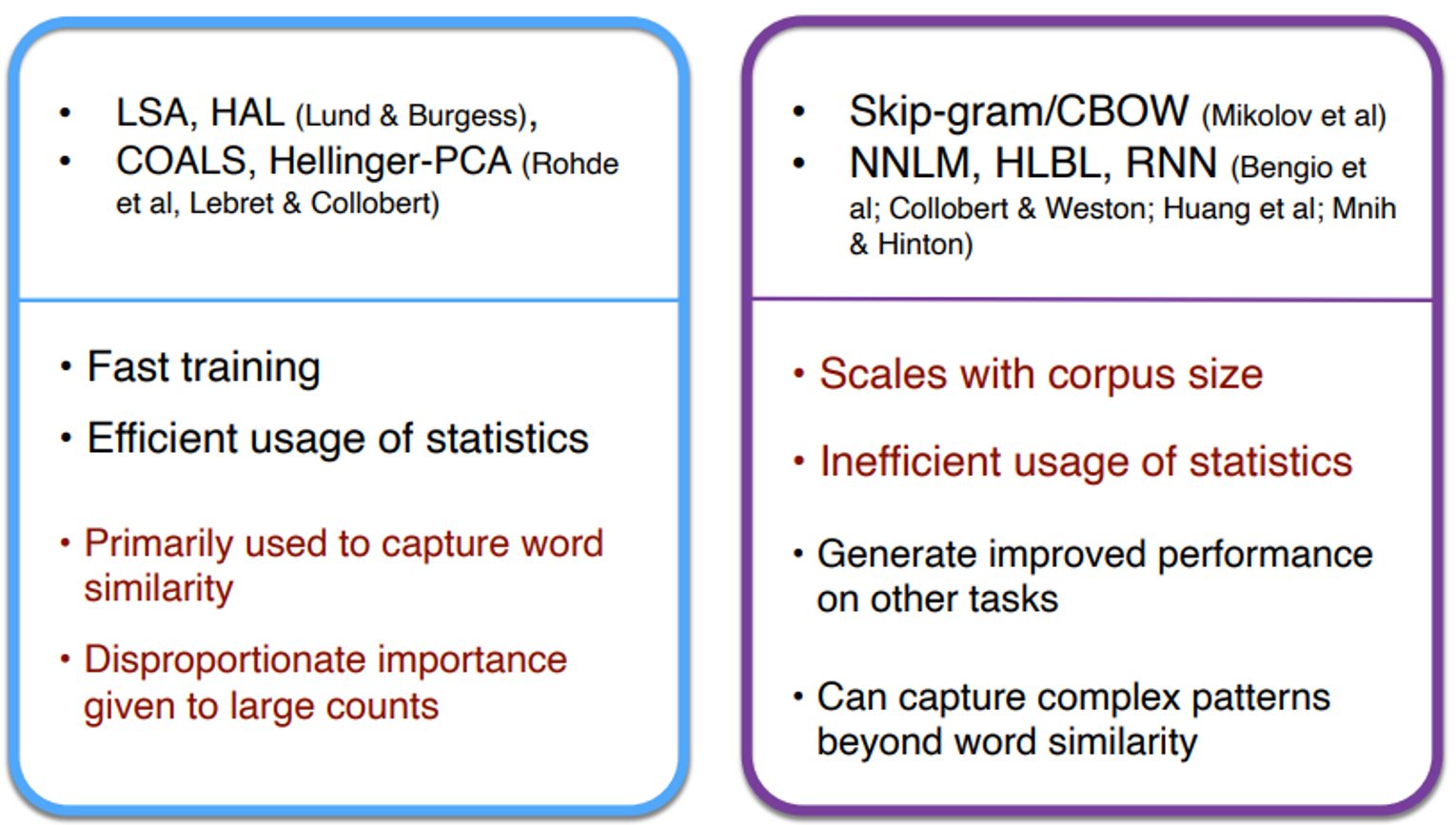
EMNLP(Encoding meaning conponents in vectors differences)
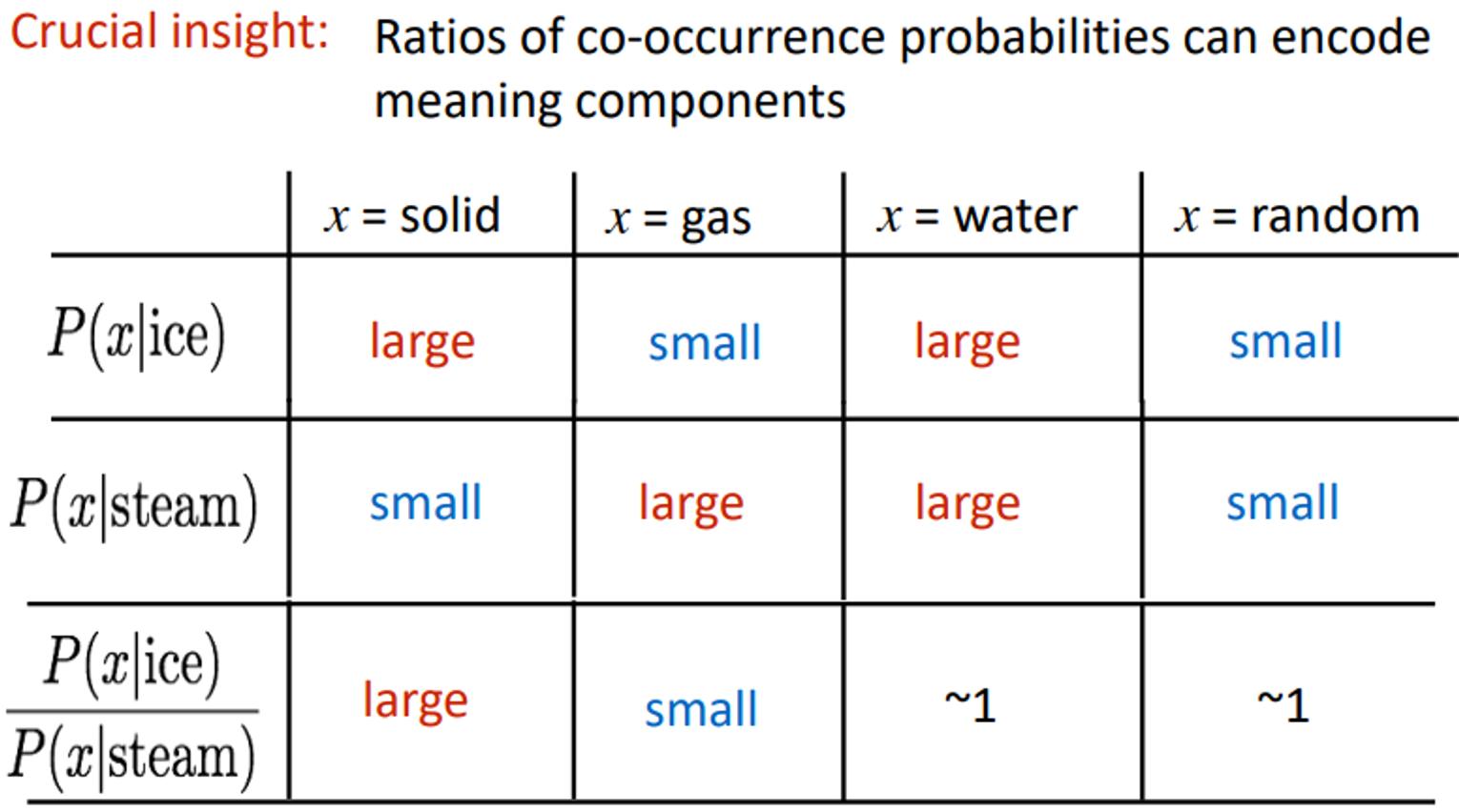
ratio of co-occurrence probabilities 를 meaning conponents로 encode할 수 있다.
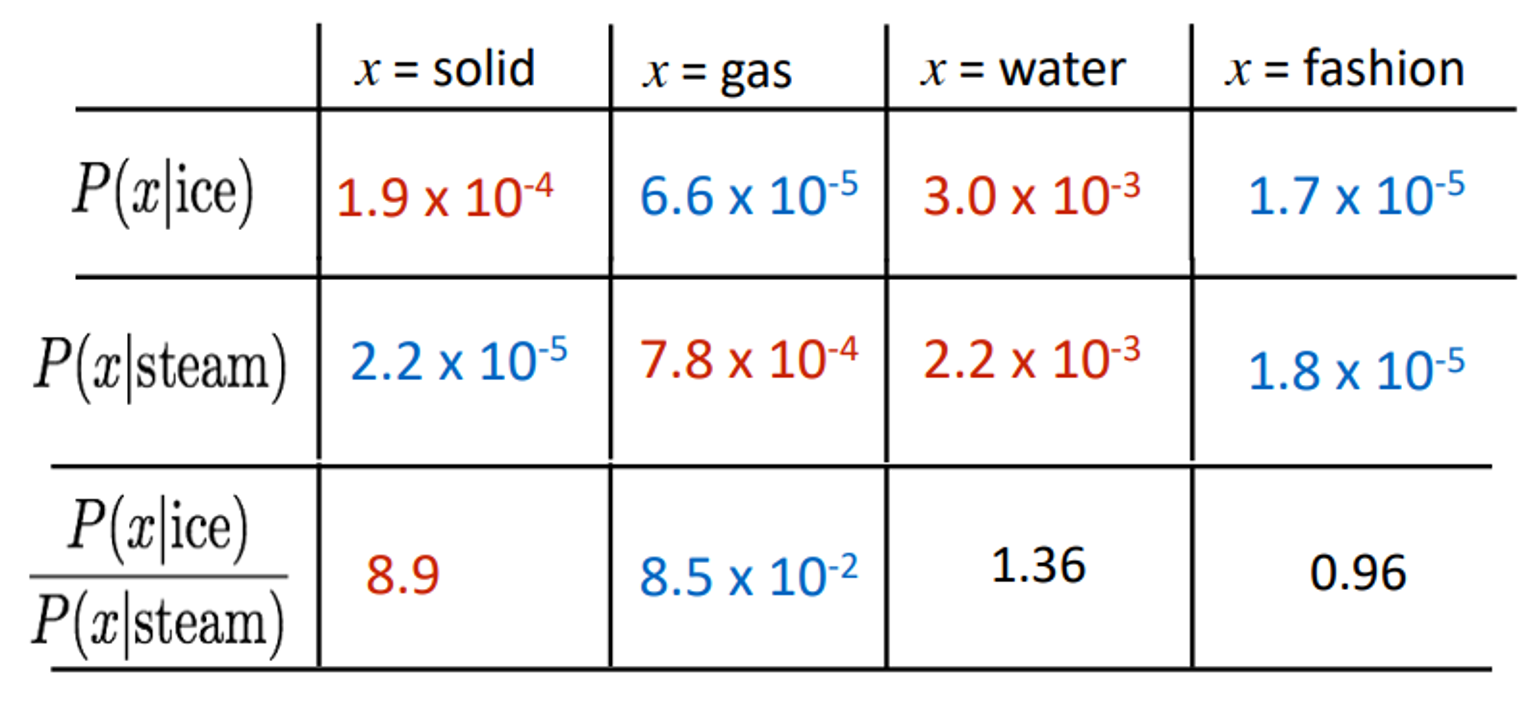
이를 실제로 linear vector component로 표현하려면
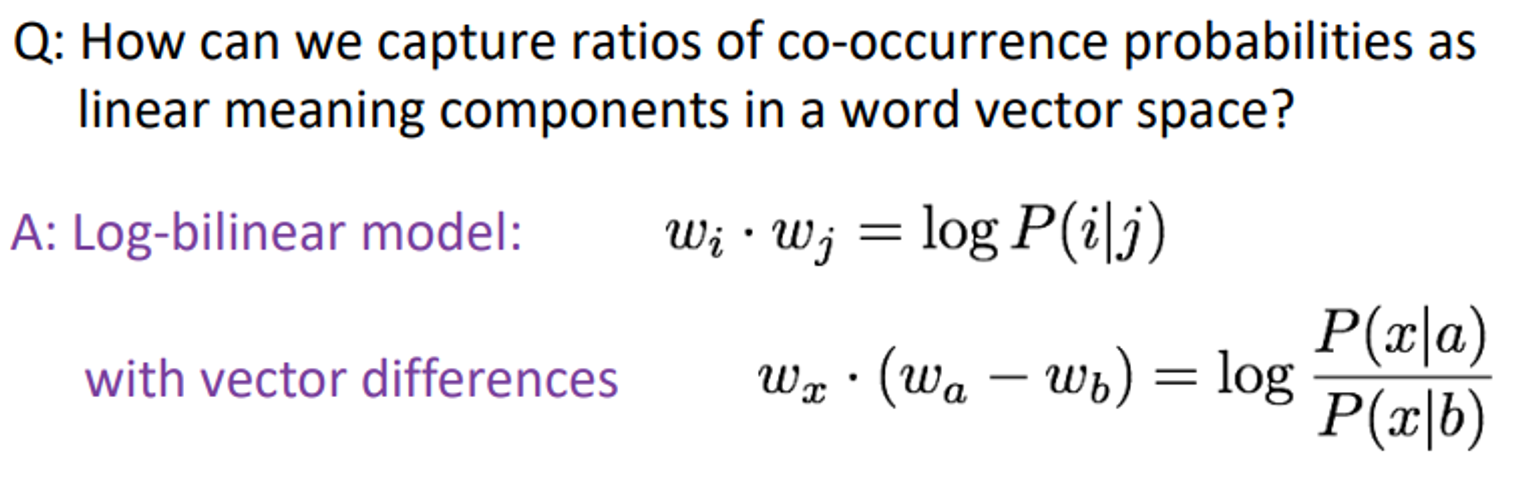
다음과 같은 log-bilinear model을 생성한다.
위의 기법들을 합쳐
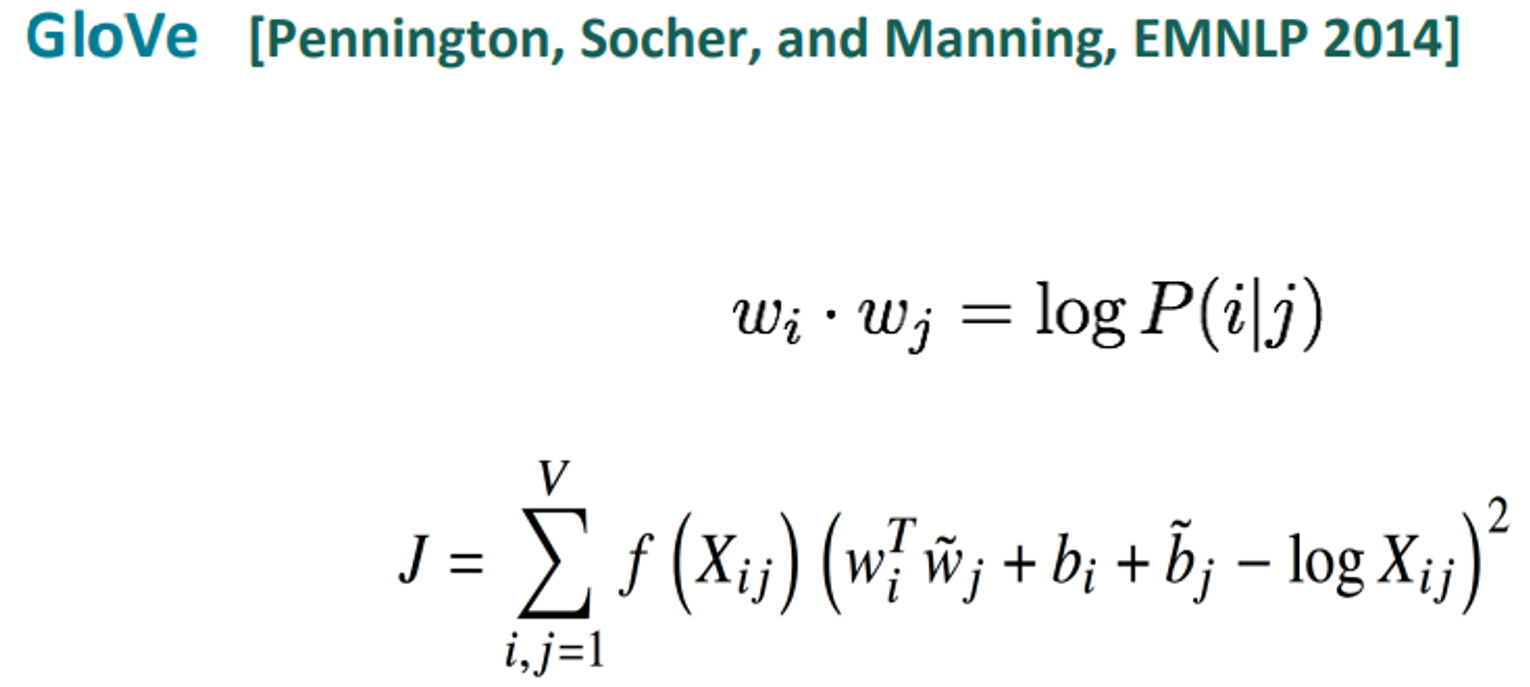
GloVe model은 다음과 같다.
: Log-bilinear model
pros : Fast training, Scalable to huge corpora, Good performance even with small corpus and small vectors
Evaluate word vectors
Intrinsic
• Evaluation on a specific/intermediate subtask
• Fast to compute
• Helps to understand that system
• Not clear if really helpful unless correlation to real task is established
Extrinsic
• Evaluation on a real task
• Can take a long time to compute accuracy
• Unclear if the subsystem is the problem or its interaction or other subsystems
• If replacing exactly one subsystem with another improves accuracy à Winning!
Intrinsic evaluation
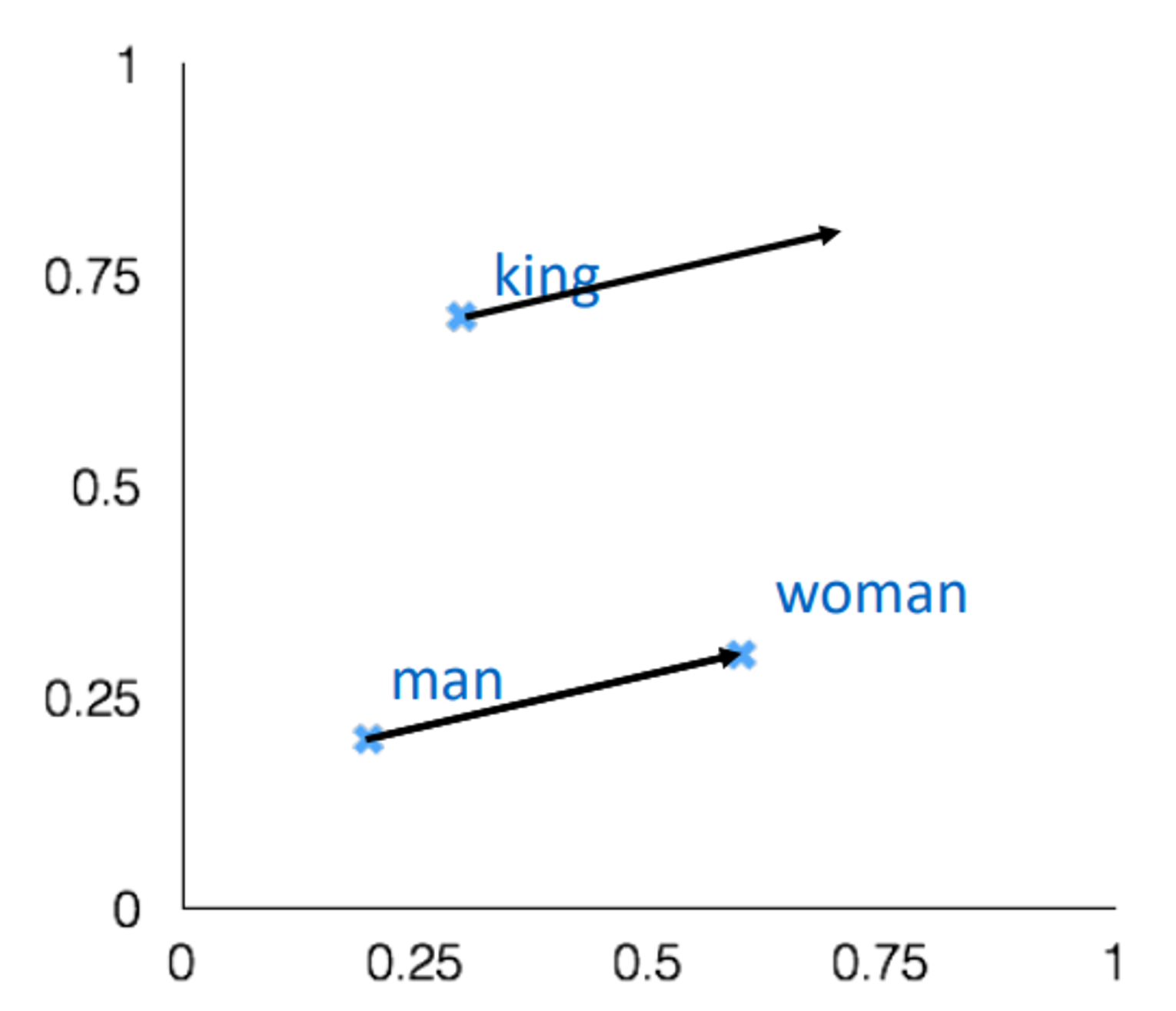
intrinsic evaluation is evaluate word vectors by “how well their cosine distance after addition captures intuitive semantic and syntactic analogy questions”
For example question can be something like “man is to woman as king is to ?”
- 해석(이해가 안돼서 GPT 돌렸습니다..) 단어 벡터의 품질을 평가하는 방법 중 하나는 벡터를 더한 후의 코사인 거리가 직관적인 의미와 구문론적 유추 문제들을 얼마나 잘 포착하는지를 보는 것입니다. 여기서 말하는 '유추 문제'란 'man is to woman as king is to ?'와 같은 문제를 말하는데, 단어 벡터가 이러한 유추를 잘 해결한다면, 그 벡터들은 의미적이고 구문론적인 관계를 잘 표현하는 것으로 간주됩니다.
vector cosine distance
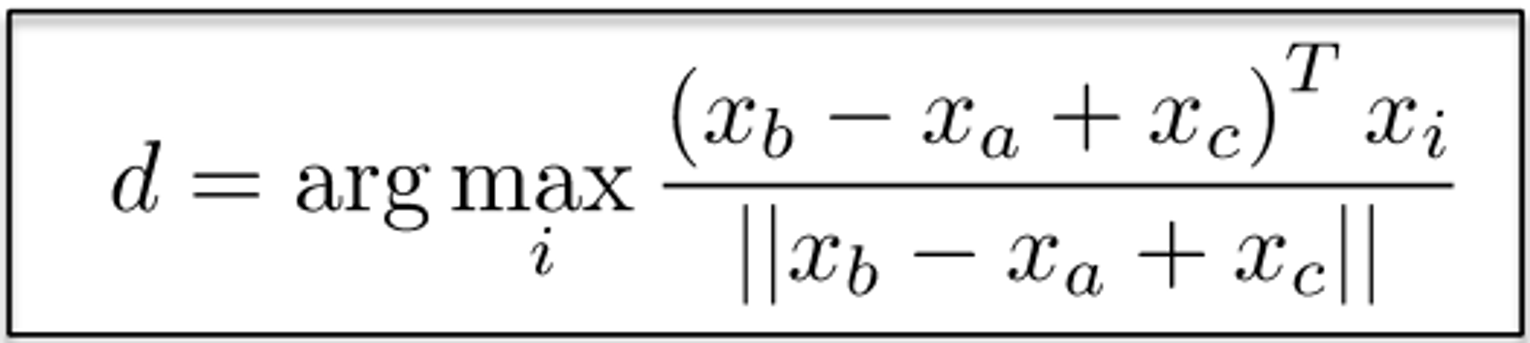
Human judgment(intrinsic)
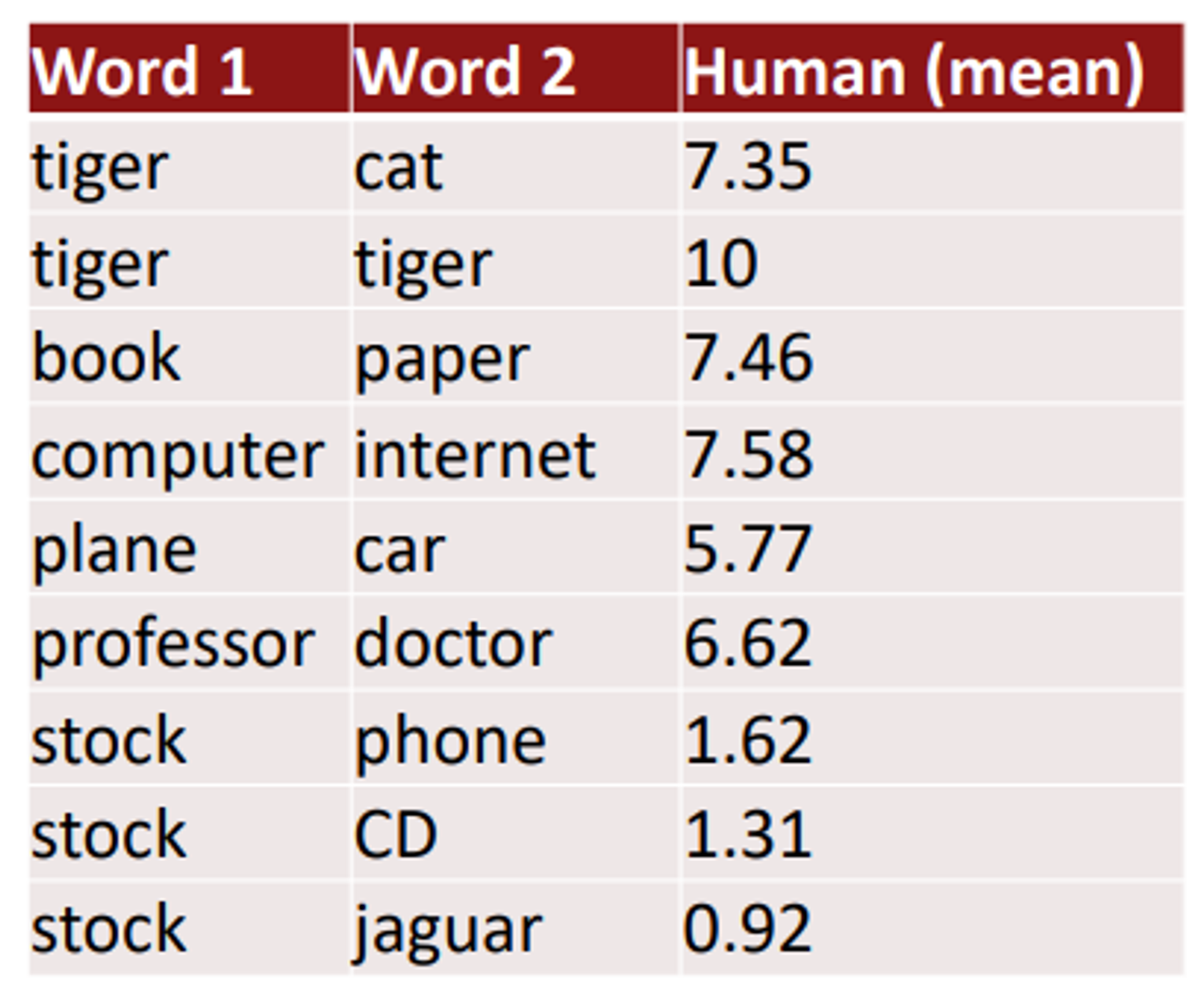
이런식으로 사람의 평가를 통해 evaluate할 수 있따.
Extrinsic evaluation
All subsequent NLP task in this class.(사실 모든 NLP task가 extrinsic evaluation이다)
NER : if we have good wordvectors NER task → good
Word senses and word sense ambiguity
단어들은 많은 의미를 가지고 있다(다의어)
이런 단어들의 vector은 어떤식으로 처리해야하는지에 대해.
하나의 벡터가 모든 의미를 담아야 하는지 or 여러개의 벡터로 나누어야하는지.
ex : pike
• A sharp point or staff
• A type of elongated fish
• A railroad line or system
• A type of road
• The future (coming down the pike)
• A type of body position (as in diving)
• To kill or pierce with a pike
• To make one’s way (pike along)
• In Australian English, pike means to pull out from doing something: I reckon he could
have climbed that cliff, but he piked!
Word representations via Global Context and Multiple word prototypes
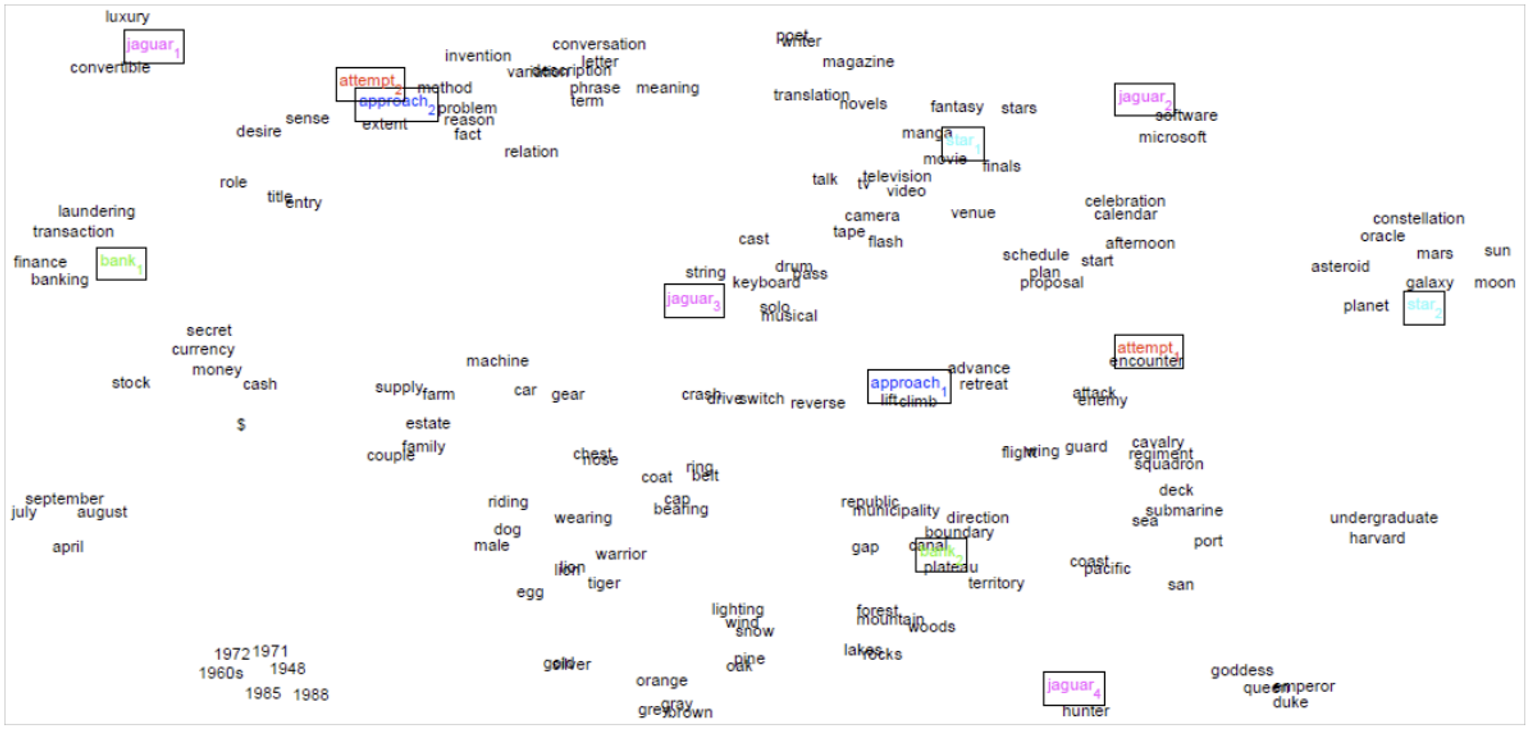

Linear Algebraic Structure of Word Senses, with Application to Polysemy
다음과 같이 다의어의 여러 sense들을 중첩해서 저장하는 것이다.
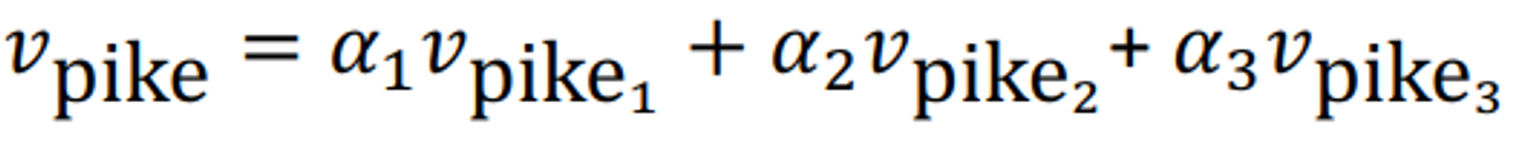
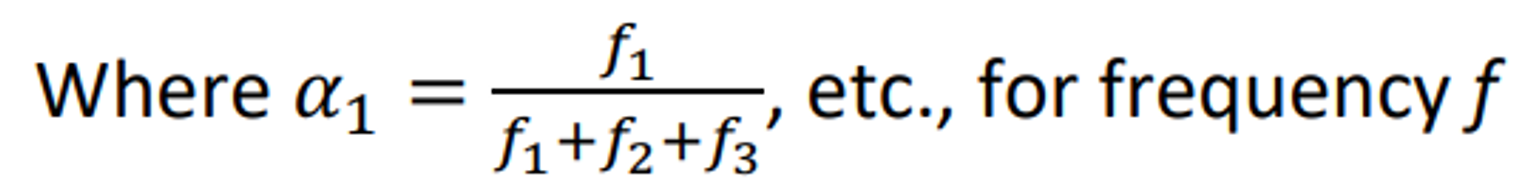
Q. What if the superposioned vecter’s sense means totally other word?
A. That can’t be problem because the encoded vector space is so broad and sparse
강의에서는 "Sparse coding"이라는 단어가 등장하는데, 이것이 무엇을 의미하는지 잘 이해가 안돼서 찾아보았다. 이는 다음 아티클에...
