정렬이 중요한 이유
- 컴퓨팅 작업에서 가장 많은 시간을 차지하는 것은 저장과 검색
- 정렬된 데이터의 검색은 , 정렬되지 않은 데이터의 검색은
- 이 큰 경우 정렬 시간의 차이로 인한 컴퓨팅 효율의 차이 역시 매우 크게 변화
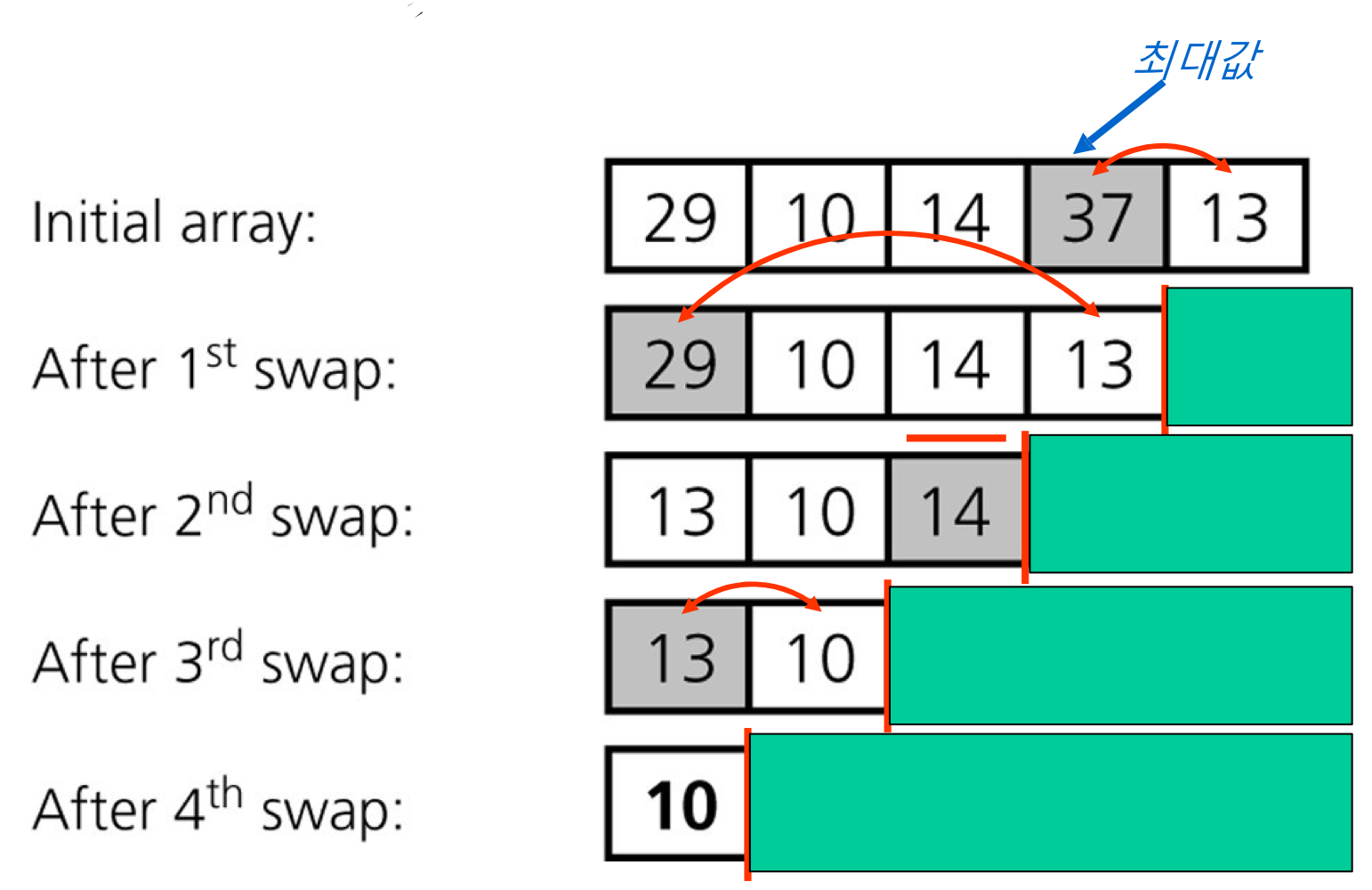
Selection Sort
- Algorithm
1. 리스트에서 가장 큰 원소를 찾는다.
2. 그 원소와 맨 오른쪽 원소를 교환한다.
3. 맨 오른쪽 원소를 제외한다.
⠀⠀ - Complexity :
- Code
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
int max = arr[0];
int max_i = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
if (arr[j] > max) {
max = arr[j];
max_i = j;
}
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[max_i];
arr[max_i] = temp;
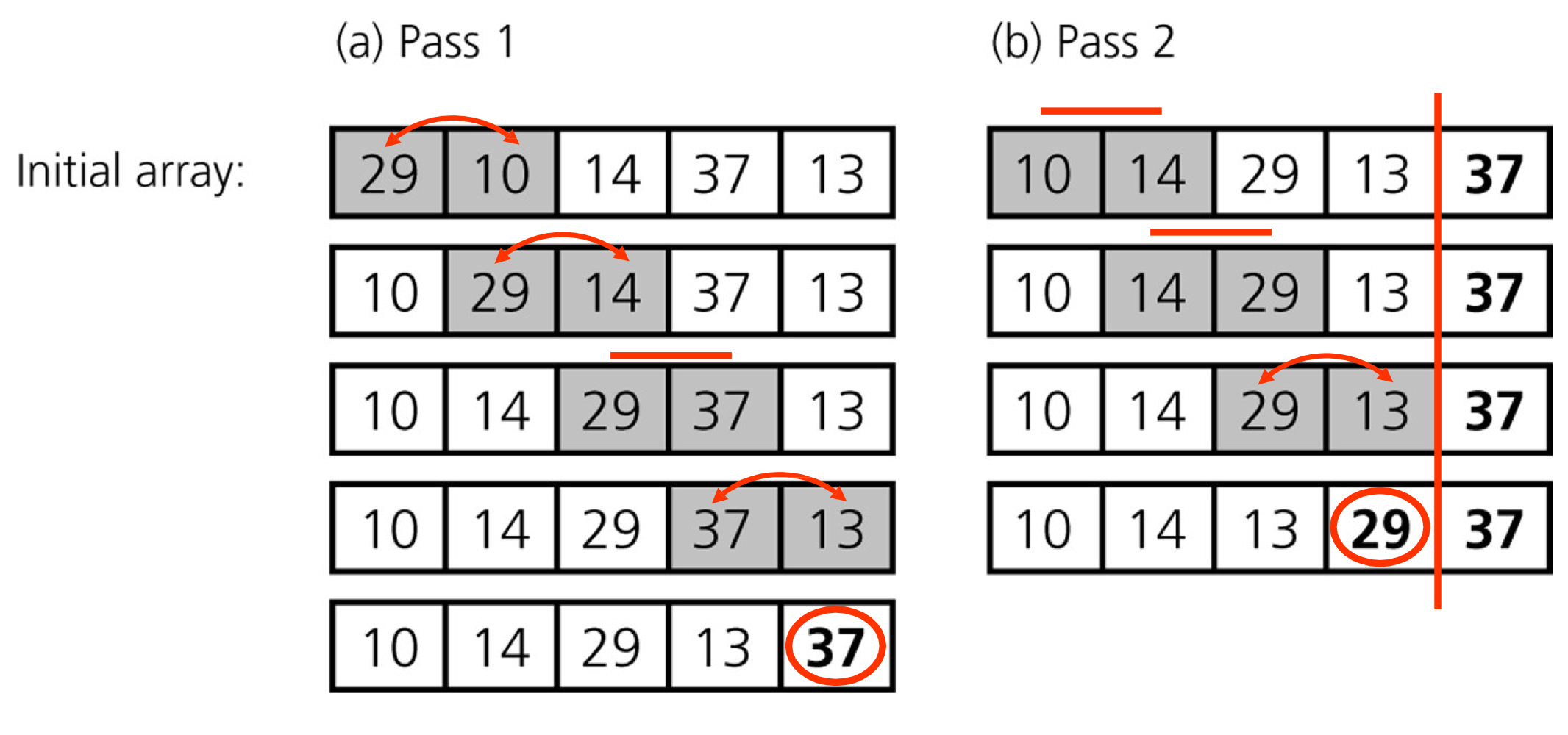
}Bubble Sort
- Algorithm
1. 리스트의 처음부터 뒤로 이동하며 인접한 두 개의 원소를 비교한다.
2. 뒤의 값이 작으면 앞의 값과 교환하고, 그렇지 않으면 다음 원소로 넘어간다.
3. 맨 오른쪽 원소를 제외한다.
⠀⠀ - Complexity :
⠀⠀
⠀⠀ - Code
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++)
if(arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
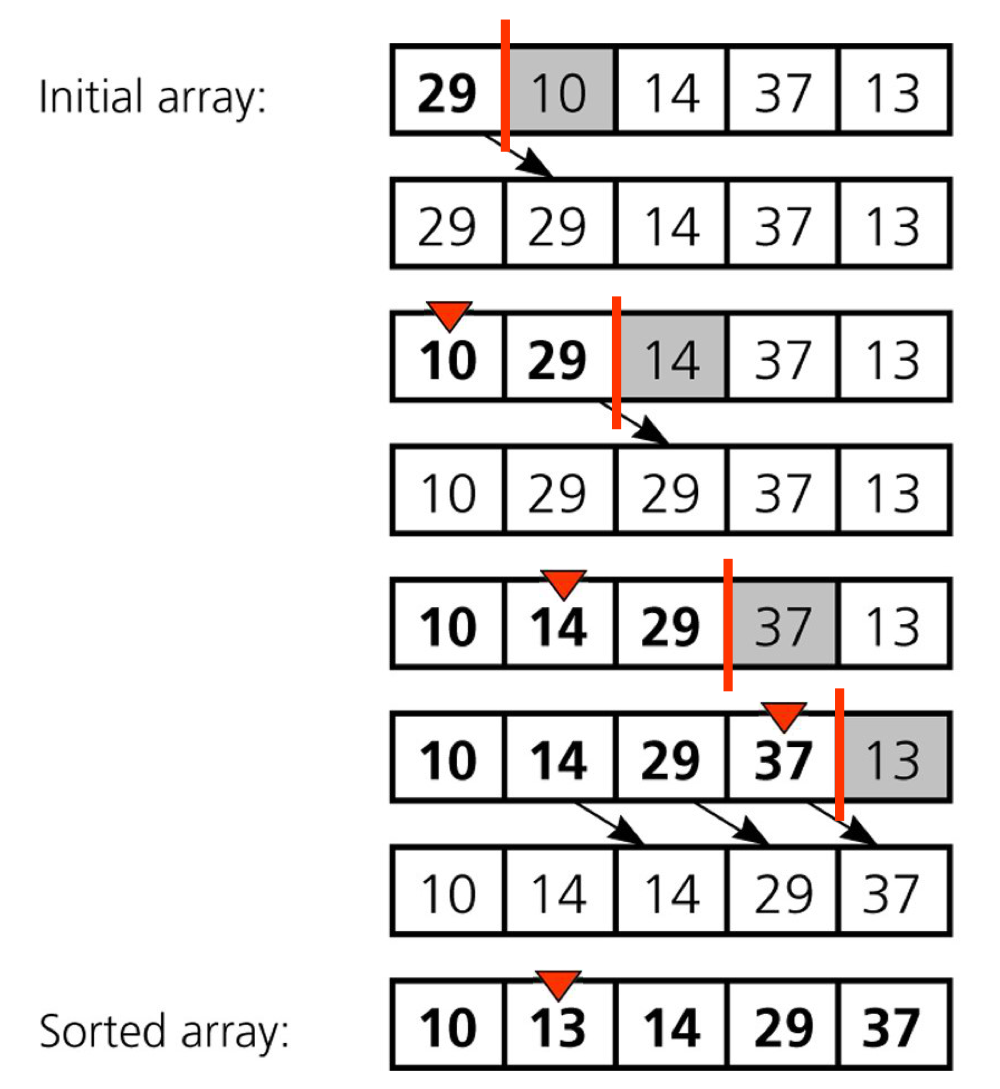
}Insertion Sort
- Algorithm
- 크기 순으로 정렬된 길이 의 배열에 번째 숫자를 삽입
⠀⠀ - Complexity
- Worst / Average Case :
- Best Case :
- Code
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--){
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
else break;
}
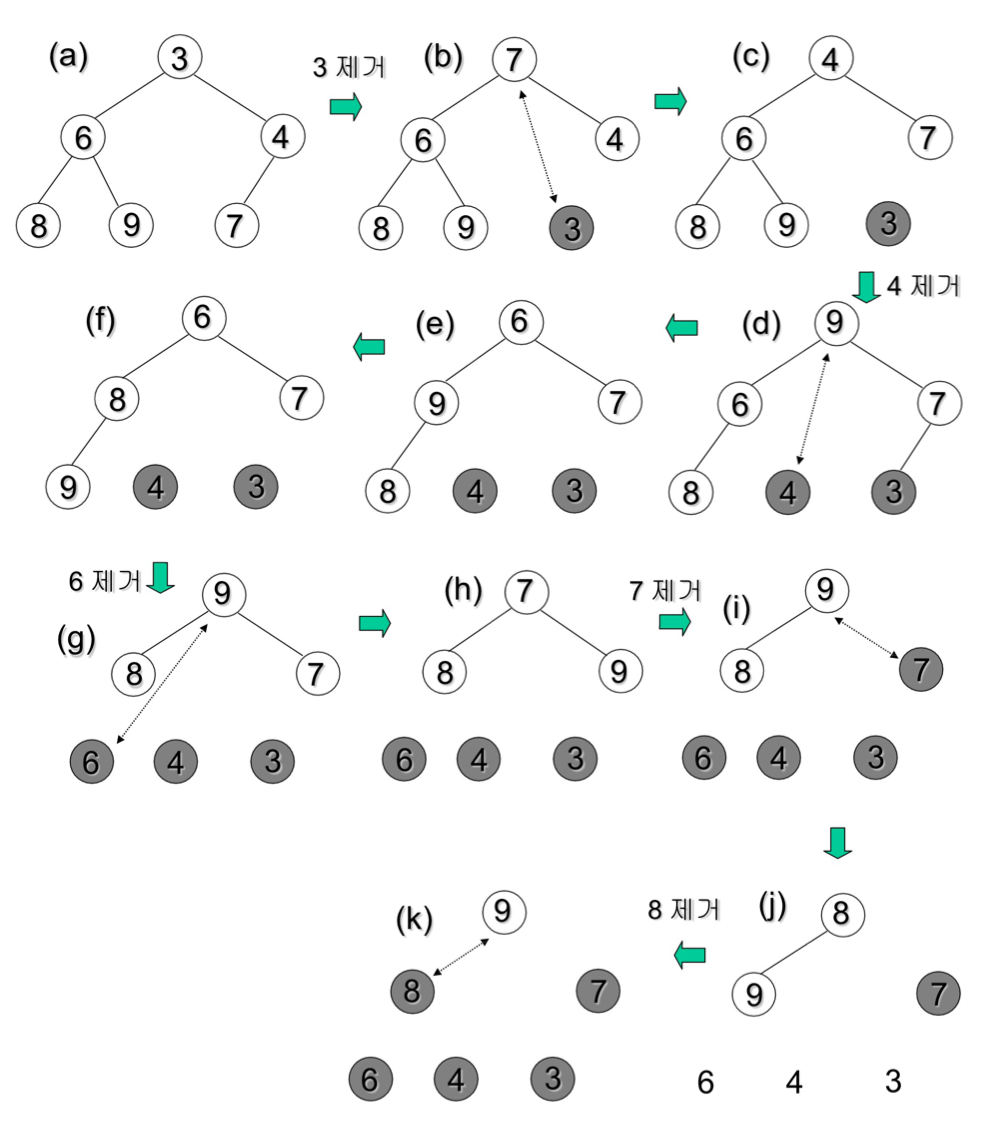
}Heap Sort
- Algorithm
- 주어진 리스트를 heap으로 만든 다음 하나씩 heap에서 제거하며 정렬
⠀⠀ - Complexity :
⠀⠀ - Heap : 각 노드의 값이 자신의 자식 노드의 값보다 크지 않은 Complete Binary Tree
⠀⠀
⠀⠀ - Code (배열을 Heap으로 만들기)
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
pos = i;
while (pos > 0 && A[pos] < A[(pos - 1) / 2]) {
swap(A[pos], A[(pos - 1) / 2]);
pos = (pos - 1) / 2;
}
while (pos > 0 && A[pos] < A[(pos - 2) / 2]) {
swap(A[pos], A[(pos - 2) / 2]);
pos = (pos - 2) / 2;
}
}⠀⠀
- Code (Heap에서 오름차순으로 출력하기)
while(len > 0) {
printf("%d ", A[0]);
len--;
temp = A[0];
A[0] = A[len];
A[len] = temp;
rearrange(len, A);
}
void rearrange(int len, int A[]) {
int pos = 0;
int left, right;
while (pos < len) {
left = pos * 2 + 1;
right = pos * 2 + 2;
if (left >= len)
return;
if (right >= len) {
if (A[left] < A[pos])
swap(A[left], A[pos]);
return;
}
else if ((A[left] <= A[right] && A[left] < A[pos])) {
swap(A[left], A[pos]);
pos = left;
}
else if (A[right] <= A[left] && A[right] < A[pos]) {
swap(A[right], A[pos]);
pos = right;
}
}
return;
}조건이 필요한 정렬
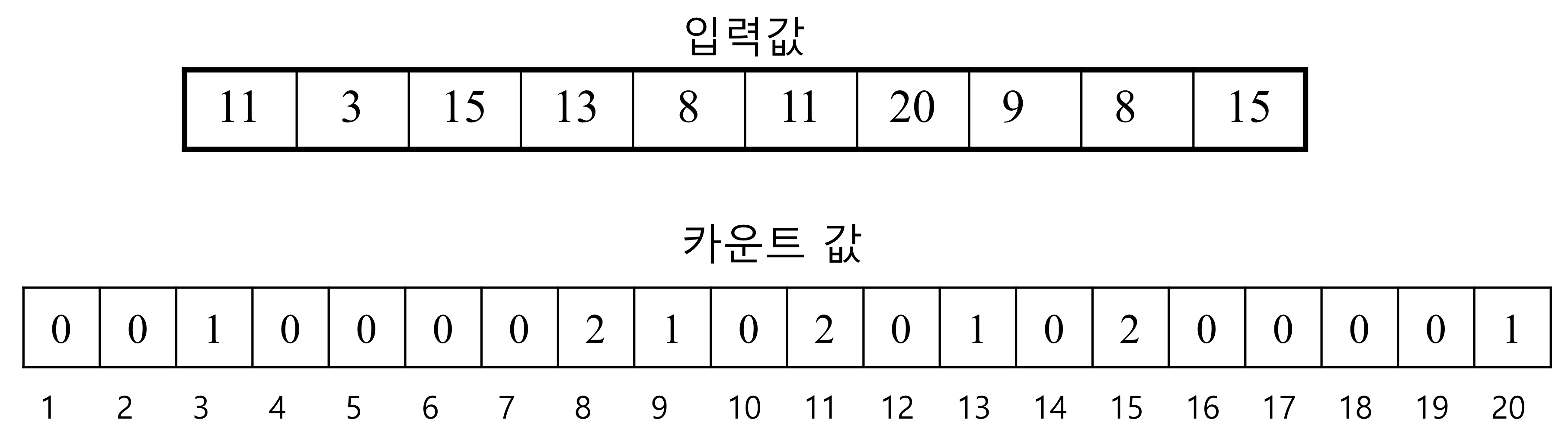
Counting Sort
- 시작값과 끝값을 알고 있는 경우에 사용 가능
⠀⠀ - Algorithm
1. 개의 빈 리스트를 생성하고 0으로 초기화
2. 입력값을 순서대로 읽어서 해당 값을 리스트 인덱스로 하여 값을 1 증가
3. 리스트를 순서대로 읽으면서 해당 인덱스의 값을 출력
⠀⠀ - Complexity :
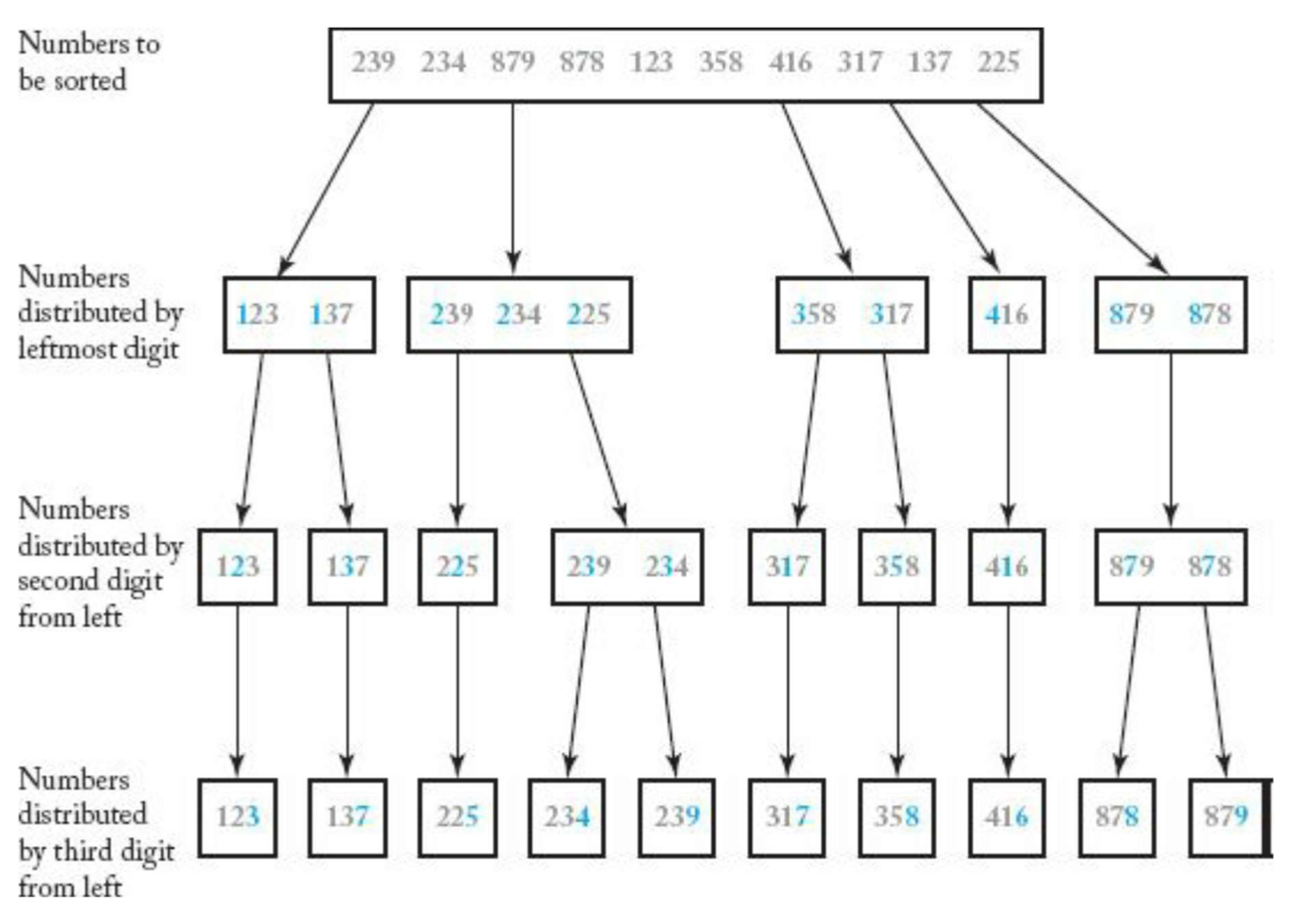
Radix Sort
- 원소들이 모두 이하의 자릿수를 가질 때 사용 가능
⠀⠀ - Algorithm
1. 0 ~ 9까지의 Bucket 준비
2. 모든 데이터에 대하여 가장 낮은 자릿수에 해당하는 Bucket에 차례로 데이터 저장
3. 0부터 차례대로 Bucket에서 데이터를 가져옴
4. 자릿수를 높여가며 위의 과정을 반복
⠀⠀ - Complexity
- Average Case :
- Worst Case :
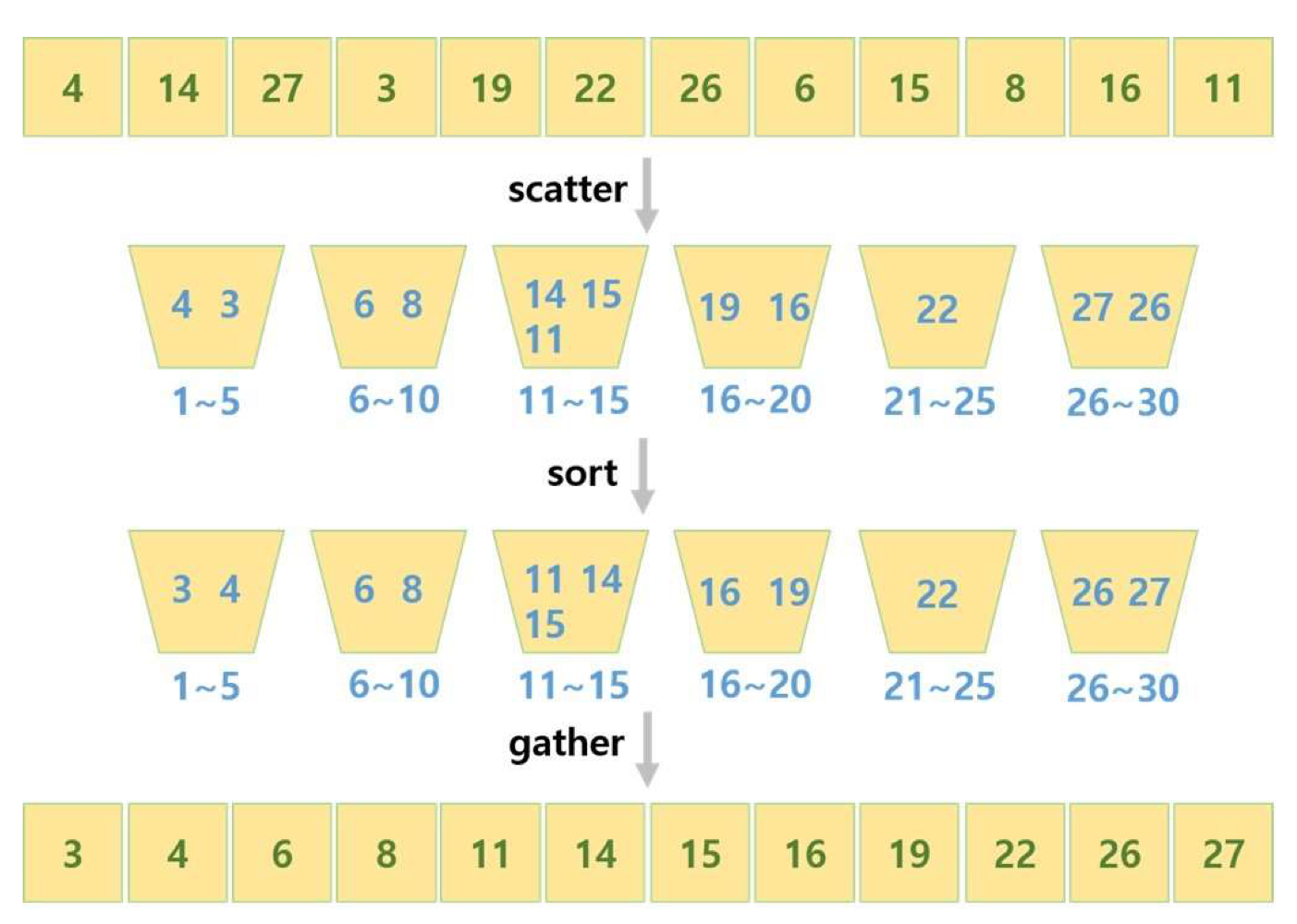
Bucket Sort
- 원소들이 특정한 그룹으로 분류 가능할 때 사용 가능
⠀⠀ - Algorithm
1. 원소들을 버킷 단위로 분류
2. 버킷 내부에서 정렬 후 병합
⠀⠀ - Complexity
- Average Case :
- Worst Case :
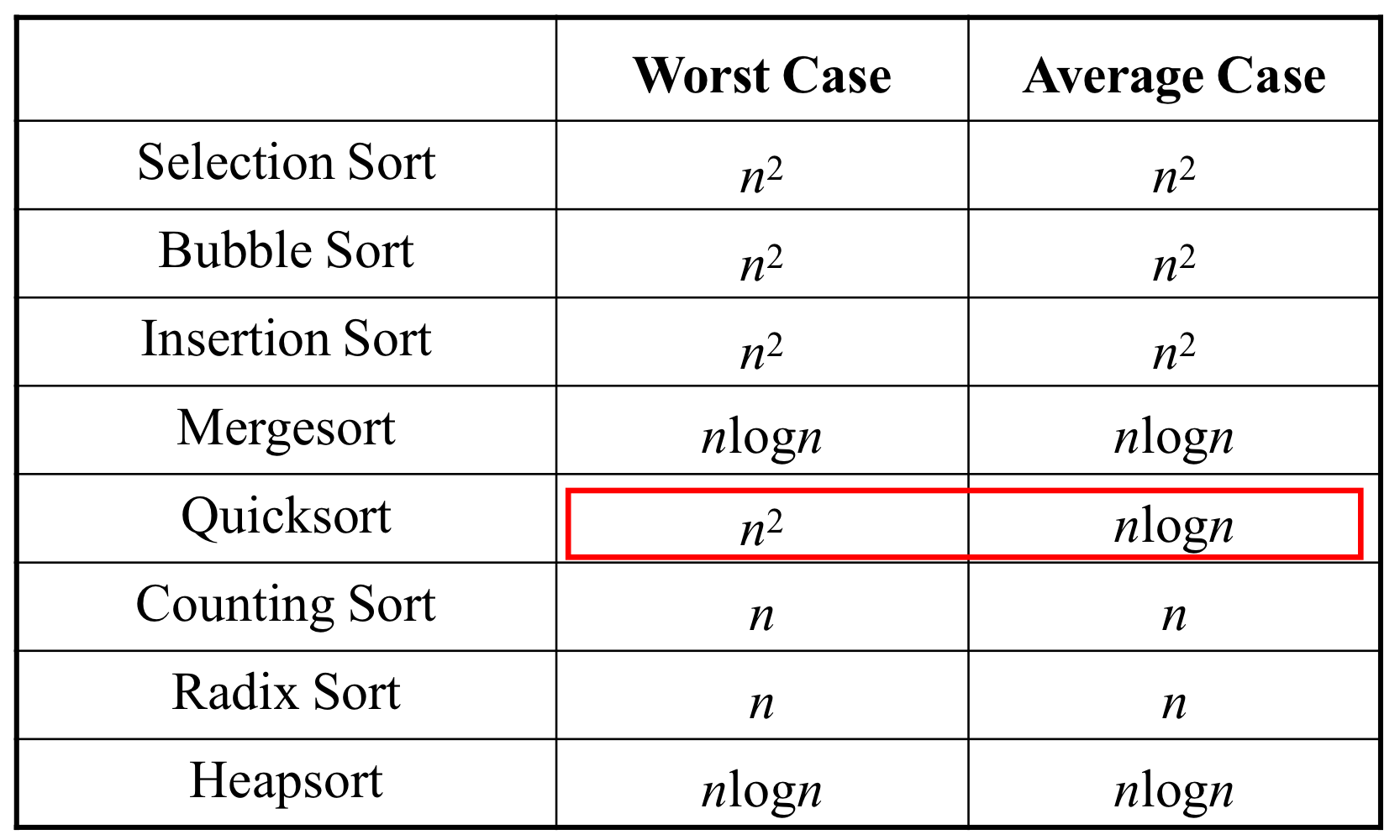
효율성 비교
많은 종류의 정렬을 다루다보니 분량이 많아졌다. 아직도 자료구조 수업 복습하는 느낌? 오히려 좋아.
