다음 내용은 아주대학교 김상훈 교수님 운영체제 강의 및 강의 자료와 Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces(https://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~remzi/OSTEP/)을 참고하여 작성한 글입니다.
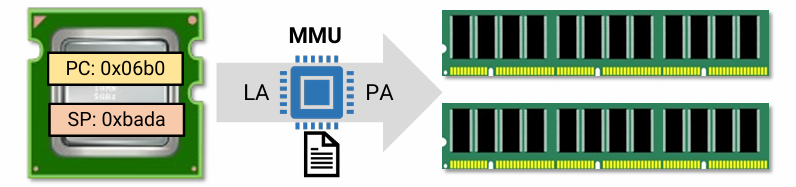
Address in Computers
- Physical address (PA)
- Address seen by the memory unit
- Logical address (LA) or virtual address (VA)
- Generated by the CPU
- Processes see logical address
- Memory Management Unit (MMU) translates LA to PA
- Modern architectures have MMU as part of CPU core
- 각각의 process는 자신의 logical한 address space가 독립적으로 있고, 그 space를 physical address space로 mapping 해 주는 역할을 MMU가 한다.
Fixed Partitions
Definition
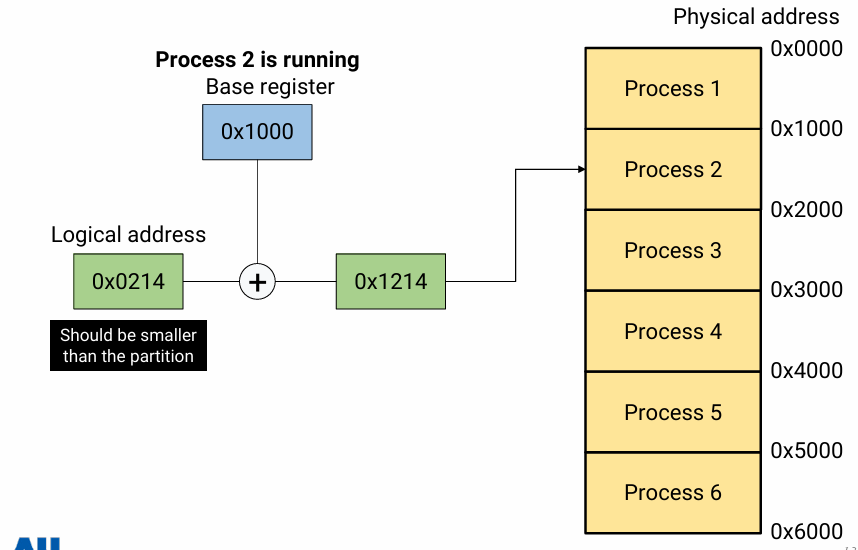
- Break up physical memory into same-sized partitions
- Physical address = base address + logical address
- Cannot access beyond its partition
- 0 <= Logical address < Partition size
- The number of partitions = degree of multiprogramming (= 한 번에, 동시에 돌릴 수 있는 program 수)
Example
- fixed partition을 사용할 때 logical address는 base address로부터의 offset을 의미한다.
- 이 offset 값은 partion size보다는 작아야 한다. offset이 partition size보다 크다는 것은 총 공간 크기가 10인데, 50만큼의 공간을 원한다는 것이다.
- base register는 process의 PCB에 저장돼 있다.
- fixed partion을 쓰는 시스템에서는 address translation을 위해 partition의 시작 주소를 가리키고 있는 base register 하나만 있으면 된다.
Advantage
- Easy to implement
- Easy to validate access
- compare logical address to the partition size
- Fast context switch
- Just save/restore the base register on context switch
Problem
- Partition size: One size does not fit all
- Process마다 사용하고 싶은 mem 크기는 다른데 이를 만족하지 못한다.
- partition 크기보다 큰 process는 돌릴 수 없다.
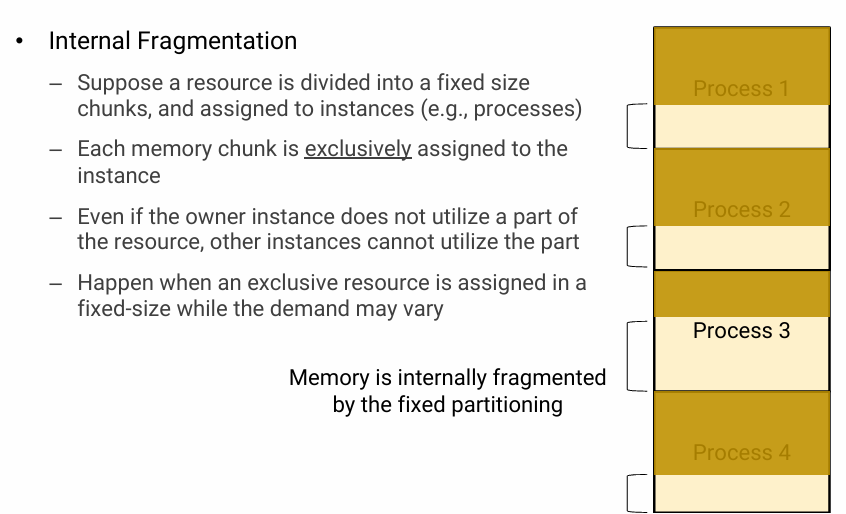
- Internal Fragmentation
- Each memory chunk is exclusively assigned to the instance
- other instances cannot utilize the part
- 어떤 resource를 fixed size로 잘라서 instance에게 나누어 주면, 낭비되는 part가 생기더라도 다른 instance가 사용할 수 없다.
Variable Partitions
- Assume OS knows the memory size that processes need in advance
- 원하는 memory 크기만큼 hole(현재 allocate 되지 않은 부분)에서 찾아서 contiguous하게 주겠다.
- Allow variable partition sizes
- No internal fragmentation
Example
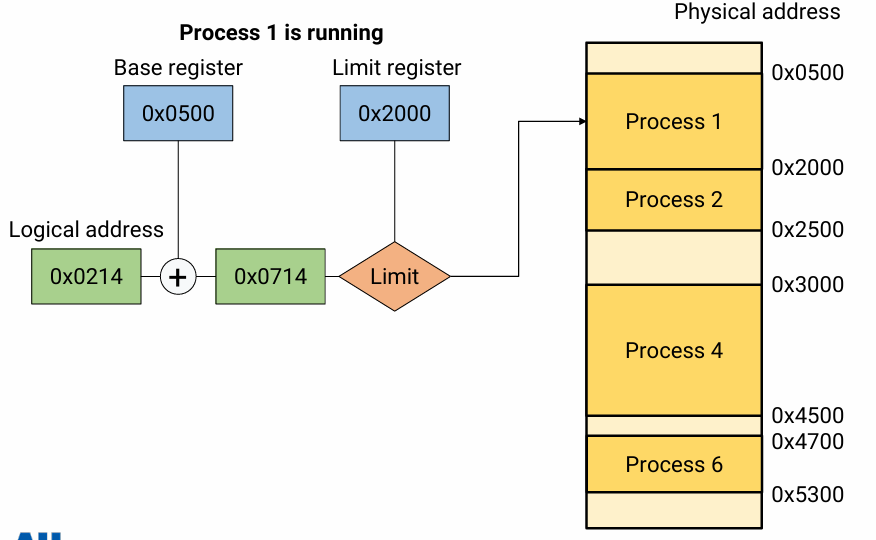
-
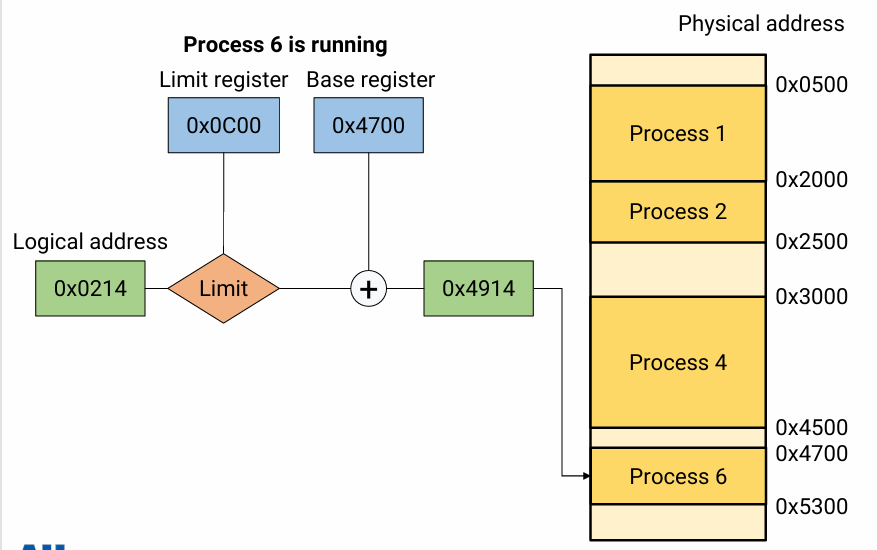
이 예시에서 Limit register는 이 process가 참조할 수 있는 maximum physical address이다. 즉 logical addr + base register 값이 마지노선 값을 넘는지 안 넘는지 판단하는 것이다.
-
컵이 있고, 매실 원액이 있고, 물이 있을 때 매실 원액과 물을 섞은 양이 이 컵에 담기나? 판단하는 과정이다.
-
이 예시에서 Limit register는 이 process가 참조할 수 있는 maximum logical address이다. 즉 logical addr 값이 마지노선 값을 넘는지 안 넘는지 판단하는 것이다.
-
컵에 물을 넣었을 때, 더 넣을 수 있는 양을 이미 알고 있다고 가정하자. 이 더 넣을 수 있는 양과 내가 넣으려는 매실의 양을 비교하는 과정이다.
Problem
-
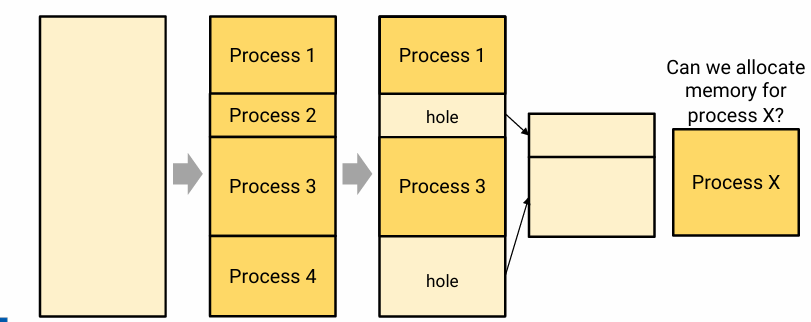
External fragmentation
- As OS load and unload processes, holes are left unscattered throughout physical memory
- Become unable to allocate a contiguous chunk even though the sum of holes is greater than required chunk
- memory를 두고 생각해 보면, 안 쓰고 있는 mem chunk는 많은데 이 mem chunk가 contiguous 하지 않아서 process한테 allocate할 수 없는 상황이다.
-
Allocate strategies
- hole을 줄 수는 있는데 어떤 hole을 줘야 하지?
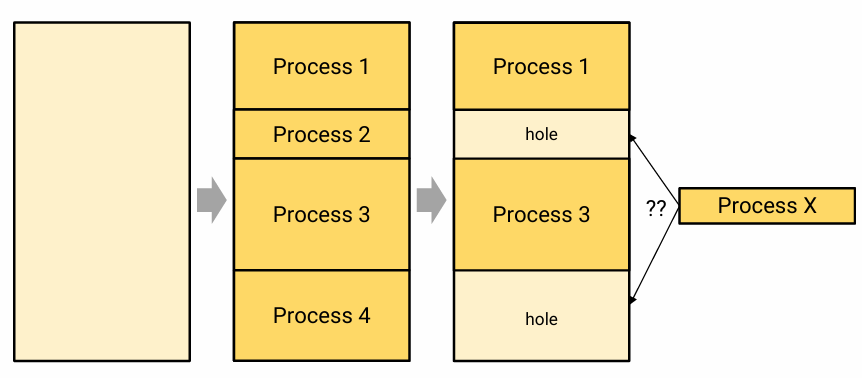
- First fit: 처음으로 발견한 hole 주기
- 보통 N개의 block을 할당한다고 하면, 0.5N개는 external fragmentation이 발생한다고 한다.
- Best fit: 가장 크기가 비슷한 hole 주기
- 비슷한 크기의 hole을 주면서 매우 작은 크기의 hole들이 많이 생긴다. 결과적으로 external fragmentation이 매우 빈번히 생긴다.
- Worst fit: 가장 크기가 큰 hole 주기
- external fragmentation control이 가장 낫다고 한다.
- hole을 줄 수는 있는데 어떤 hole을 줘야 하지?
Partitions
- 여태까지의 partition 방법은 process 1개당 1개의 partition만 할당했다. 이런 방식은 place/manage 하기도 어렵고(e.g., internal/external fragmentation), partition을 grow/shrink 할 수도 없다.
- 그러면서 생긴 아이디어가, '왜 process addr space를 1개의 contiguous addr로 만들어야 해? process addr space는 4개의 section(Code, Data, Heap, Stack)으로 구성돼 있는데, 이 section을 따로따로 각자 다른 곳에 두면 안 되나?' 이거다.
Segmentation
- An extension of variable partitions
- Divide address space into logical segments
- Multiple segments per process
- segment 단위는 CODE/HEAP/STACK/DATA
- Physically discontiguous, logically contiguous
Example
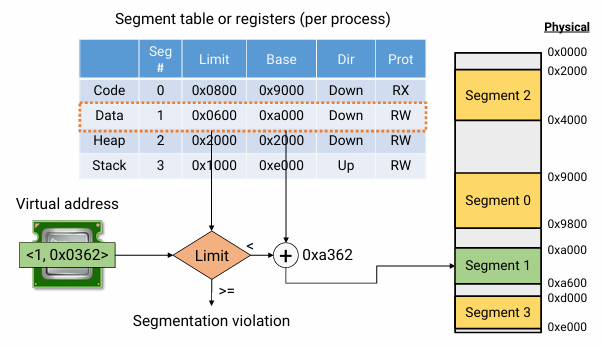
- '#'번째 segment
- limit은 offset의 최대 size가 될 수도 physical address 마지노선이 될 수도 있다.
- dir은 direction이다. Down이면 주어진 base address에서 밑으로 확장하면 된다.
- prot는 protection이다. RX이면 read/execute는 할 수 있지만 write는 할 수 없다.
- Virtual address는 <segment #, offset>으로 표현된다.
- 여기서는 첫 번째 segment의 virtual address를 physical address로 translation 하는 과정이다. 먼저 offset 값이 limit보다 작은지 확인한다. 만약 작다면, 그 값을 base register에 더해서 physical address를 만든다. 만약 limit보다 크다면 MMU가 process에게 signal을 날린다. 그러면 그 process는 segmentation fault를 남기고 죽는다.
- Each process has its own segment table
- table의 행, 열의 수는 architecture마다 다르다.
- table은 memory에 위치하고 있으며, 이 table은 segment-table base register, STBR 이 가리키고 있다. 따라서 translation 시 MMU는 STBR에 저장된 addr만 읽으면 된다.
- context switch 시 STBR만 바꾸면 된다.
- Segment ID는 explicit 하게 혹은 implicit 하게 표현될 수 있다.
- Explicit: <segment ID, offset>
- <0x01, 02a31>, <0x21, 0x23c2>
- Implicit: Use n-MSBs(Most Significant Bit) as segment ID
- ID: #1, offset: 0x068
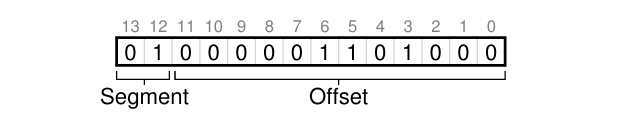
- ID: #1, offset: 0x068
- Explicit: <segment ID, offset>
Advantage
- Enable sparse allocation of address space
- can grow and shrink stack and heap independently
- can dynamically relocate each segment
- 옮기는 단위가 작다. variable 같은 경우는 옮기는 단위가 전체라 힘들다.
- easy to protect segments
- read-only for code
Problem
-
# of supported segments vs. segment table size overhead
- segment table을 memory에 두고, STBR로 참고하면 context switch는 가볍고(단순히 STBR만 바꾸면 됨) process가 가질 수 있는 segment 개수에 제한이 없다고 봐도 무방하다. 그러나 context switch 때마다 MMU가 무조건 한 번은 memory에 가야 하는 상황이 발생한다. 즉 메모리 접근으로 인한 overhead가 발생한다.
- segment table을 segment registers에 기록하면 memory에 접근할 필요가 없어 translation은 빠를 테지만, context switch overhead가 매우 크다(registers를 새로운 process의 table 내용으로 모두 교체해야 함). 또 process가 가질 수 있는 segment 개수에 bound가 생긴다.
-
특성 메모리에 테이블(STBR 사용) 레지스터에 테이블 저장 Context Switch 오버헤드 낮음 높음 주소 변환 속도 느림 (MMU가 메모리 접근 필요) 빠름 (MMU가 레지스터 참조) 세그먼트 개수의 유연성 제한 없음 제한 있음 (레지스터 개수에 의해 제한)
-
External fragmentation
- 비록 sparse한 형태라 internal fragmentation은 없겠지만 본질적으로 아직도 exclusive한 memory를 variable size로 de/allocation 반복하는 형식이다. 필연적으로 external fragmentation이 발생할 수밖에 없다.
