Dependency 확인
앞의 튜토리얼에서 만들었던 패키지의 의존성을 확인
$ rospack depends1 beginner_tutorials roscpp rospy std_msgs
이렇게 한 패키지에 의존성이 어떻게 설정되어 있는지 알수있다.
Publisher 작성
#!/usr/bin/env python
# license removed for brevity
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import String
def talker():
pub = rospy.Publisher('chatter', String, queue_size=10)
rospy.init_node('talker', anonymous=True)
rate = rospy.Rate(10) # 10hz
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
hello_str = "hello world %s" % rospy.get_time()
rospy.loginfo(hello_str)
pub.publish(hello_str)
rate.sleep()
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
talker()
except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
pass주의: Python 노드를 작성한 후 실행 가능 모드(executable)로 바꿔주어야 한다 : 참고
$ chmod +x talker.py
작성 후, CMakeLists.txt에 다음을 추가한다.
catkin_install_python(PROGRAMS scripts/talker.py DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION} )
패키지를 빌드한다.
$ cd ~/catkin_ws $ catkin_make
Subscriber 작성
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import String
def callback(data):
rospy.loginfo(rospy.get_caller_id() + "I heard %s", data.data)
def listener():
# In ROS, nodes are uniquely named. If two nodes with the same
# name are launched, the previous one is kicked off. The
# anonymous=True flag means that rospy will choose a unique
# name for our 'listener' node so that multiple listeners can
# run simultaneously.
rospy.init_node('listener', anonymous=True)
rospy.Subscriber("chatter", String, callback)
# spin() simply keeps python from exiting until this node is stopped
rospy.spin()
if __name__ == '__main__':
listener()만든 Python 노드를 실행 가능 모드로 변경
$ chmod +x talker.py
CMakeLists.txt에 추가
catkin_install_python(PROGRAMS scripts/talker.py scripts/listener.py DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION} )
패키지 빌드
$ cd ~/catkin_ws $ catkin_make
실행
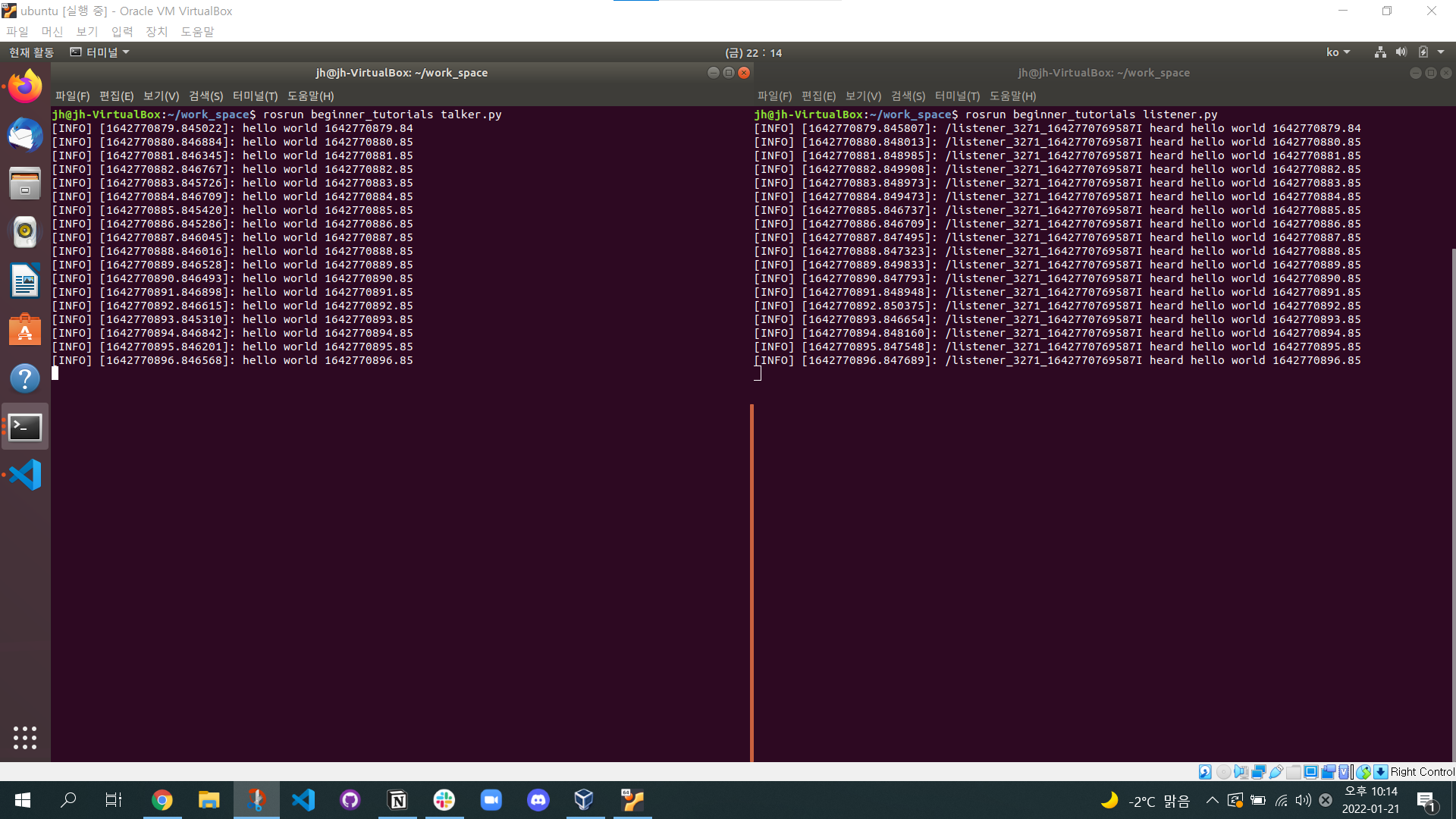
터미널을 3개 열고, 각 터미널마다 다음을 실행
roscorerosrun beginner_tutorials talker.pyrosrun beginner_tutorials listener.pyPublisher 노드에서 나온 topic을 Subscriber의 callback 함수에서 받아 출력하는 것을 알 수 있다.