dfs, bfs 문제
<3> 음료수 얼려 먹기
dfs와 bfs 둘다 써봄
문제
N x M 크기의 얼음 틀이 있다. 구멍이 뚫려 있는 부분은 0, 캄낙이가 존재하는 부분은 1으로 표시된다. 구멍이 뚫려있는 부분끼리 상,하,좌,우로 붙어있는 경우 서로 연결되어 있는 것으로 간주한다. 이때 얼음 틀의 모양이 주어졌을 때 생성되는 총 아이스크림 개수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력예시
4 5
0 0 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0출력예시
3
package _240627;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class 음료수얼려먹기 {
static int arr[][];
static boolean visit[][];
static int dx[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0};
static int dy[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1};
static int cnt = 0, count = 0, N, M;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(bufferedReader.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
arr = new int[N][M];
visit = new boolean[N][M];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(bufferedReader.readLine());
for(int j=0;j<M;j++){
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
}
}
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
for(int j=0;j<M;j++){
if(arr[i][j] == 0 && !visit[i][j]) {
dfs(i, j);
cnt++;
bfs(i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(cnt + " " + count);
}
static void dfs(int x, int y){
visit[x][y] = true;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nx = dx[i] + x;
int ny = dy[i] + y;
if(nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= N || ny >= M) continue;
if(arr[nx][ny] == 0 && !visit[nx][ny]){
dfs(nx, ny);
}
}
}
static void bfs(int x, int y){
Queue<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{x, y});
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int p[] = queue.poll();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nx = p[0] + dx[i];
int ny = p[1] + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= N || ny >= M) continue;
if(arr[nx][ny] == 0 && !visit[nx][ny]){
queue.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
}
}
}
}
}최단 거리: bfs가 가장 빠름
가중치가 없을 때 -> bfs
분할정복
큰 문제를 작은 문제로 쪼개어서 풀고 다시 합치는 방법
-> 브루트포스 시간초과 날 때 사용
- 반복문
- 재귀호출
dp와 비교됨
초기에 값이 주어지고 점화식 같은 수식을 이용하여 원하는 마지막 부분을 구함.
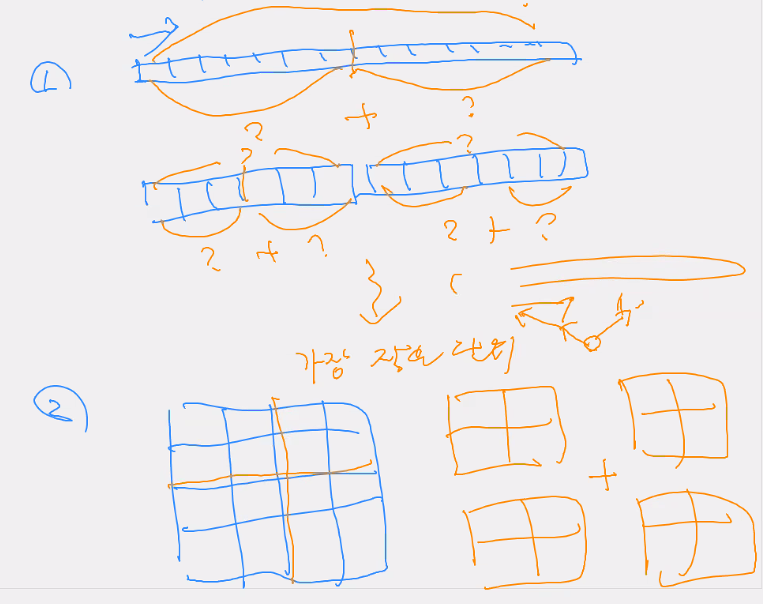
백준 실버1 Z
분할 정복 문제(반복문/재귀)
리니어하거나 공간을 가지는 경우
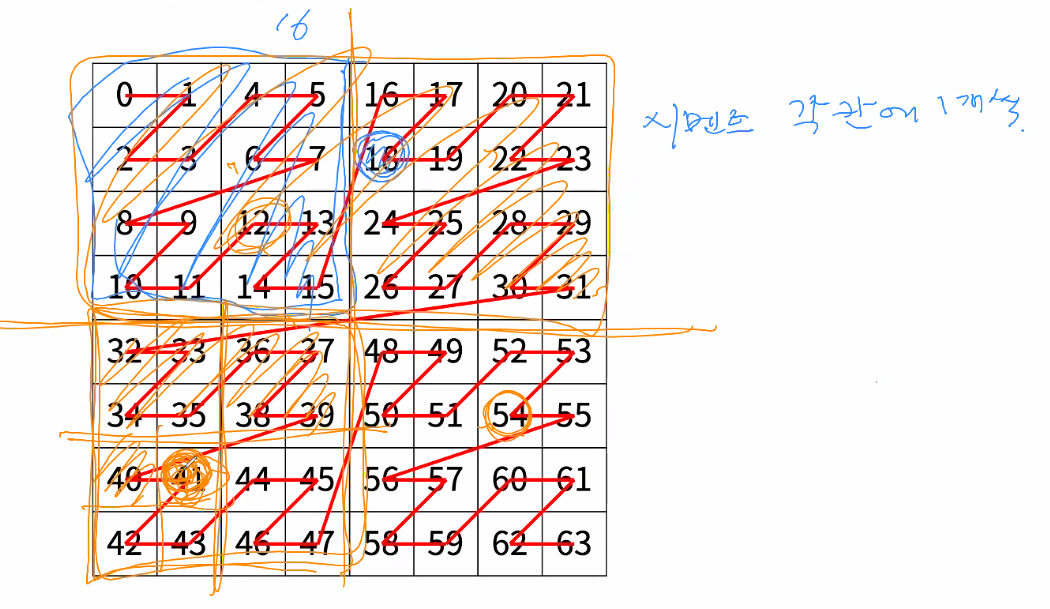
만약 41을 구해야 하면 1, 2사분면의 값은 그냥 고정임
각 사분면의 원점(x, y)를 기준으로 구하려는 값인 r, c이 어디쪽에 있는지 구하고
3사분면이면 1사분면 값 + 2사분면 값 (즉 N N 2)를 한다.
그리고 다시 3사분면 안에서 N을 쪼개서 N=1일 때까지 쪼갠다.
package _240627;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
// 분할 정복
public class BOJ_Z_2 {
static int N, r, c, ans;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = bufferedReader.readLine();
N = Integer.parseInt(str.split(" ")[0]); // 2의 제곱수
r = Integer.parseInt(str.split(" ")[1]);
c = Integer.parseInt(str.split(" ")[2]);
N = (int) Math.pow(2, N); // N을 2^N 으로 보정
z(0,0);
System.out.println(ans);
}
static void z(int y, int x){
if(N==1) return;
N /= 2;
if( r < y + N && c < x + N){
// 분할 영역
z(y, x);
} else if(r<y+N && c >= x + N){ // 2사분면
ans += N * N * 1;
z(y, x+N); // 원점 이동
} else if(r >= y+N && c < x + N){ // 3사분면
ans += N * N * 2;
z(y+N, x); // 원점 이동
} else{ // 4사분면
ans += N * N * 3;
z(y+N, x+N); // 원점 이동
}
}
}백준 실버1 쿼드트리
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1992
분할 정복 문제
size를 통해 크기를 받아와 size만큼 압축이 되면(=모두 0이나 1로 구성되어 있다면) 해당 값 출력,
압축이 되지 않으면 size/=2를 하여 다시 압축이 되는지 검사한다.(재귀)
이때 괄호 (, )는 새로운 분할을 시작할 때와 분할이 끝났을 때 넣는다.
package _240627;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class BOJ_쿼드트리 {
static int arr[][], N;
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(bufferedReader.readLine());
arr = new int[N][N];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
String str = bufferedReader.readLine();
for(int j=0;j<N;j++){
arr[i][j] = str.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
method(0, 0, N);
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
}
static void method(int x, int y, int size){
if(test(x,y, size)){
stringBuilder.append(arr[x][y]);
return;
}
stringBuilder.append("(");
int s = size /= 2;
method(x, y, s); // 1사분면
method(x, y + s, s); // 2사분면
method(x + s, y, s); // 3사분면
method(x + s, y + s, s); // 4사분면
stringBuilder.append(")");
}
static boolean test(int x, int y, int size){
for(int i=x;i<x+size;i++){
for(int j=y;j<y+size;j++){
if(arr[x][y] != arr[i][j]) {
// 압축 불가능
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}