[CrashCourse CS] #4 Representing Numbers and Letters with Binary
Crash Course Computer Science
목록 보기
5/41
How to represent things beyond just two values (true, false)?
Decimal
- 263 represents:
| 100's | 10's | 1's |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 6 | 3 |
- Add these together to make 263.
- Each multiplier is 10 times larger than the one to the right, b/c each column has 10 possible digits to work with, 0 through 9, after which you carry on to the next column.
- Base ten notation, decimal.
Binary
- Binary number 101:
| 4's | 2's | 1's |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
- Add these together to make 5.
- Each multiplier is 2 times larger than the one to the right, b/c each column has 2 possible digits to work with, 0 through 2, after which you carry on to the next column.
- It means that each multiplier has to be two times larger than the column to its right.
Bit
- Each of these binary digits, 1 or 0, is called "bit".
- ex) 1011 1111 -> 8 bit number, with lowest value of 0 (0000 0000), highest value of 255 (1111 1111).
- 256 different values, or 2^8.
- 8 bit computers, 8bit graphics, audio -> do most of their operations in chunks of 8bits.
- 256 colors
- 8 bit = 1 byte.
- 32 bit / 64 bit computers - they operate in chunks of 32 or 64 bits.
- Largest number you can represent with 32 bits is under 4.3 billion.
- Computers use 32 bit color graphics - makes photo smooth.
How to represent positive/negative numbers
- Most computers use first bit for the sign.
- 0 for +, 1 for -
- Use the remaining 31 bits for the number itself.
- 32 bit can represent +/- 2 billion numbers.
- 64 bit can represent +/- 9.2 quintillion numbers.
Numbers that are not whole numbers(정수): 2.415, ...
- They are called "Floating Point Numbers", because the decimal point can float around in the middle of a number.
- The most common method to represent floating point numbers is IEEE754.
- 625.9 = 0.6259 x 10^3
- 0.6259 : significand
- 10^3 : exponent
- In 32-bit floating point number:
- 1st bit : represents +/-
- next 8 bits : store exponent (10^3)
- remaining 23 bits : store significand (.6259)
Computer uses numbers to represnet letters.
- ASCII : the American Standard Code for Information Interchange
- 7-bit code, stores 128 different values
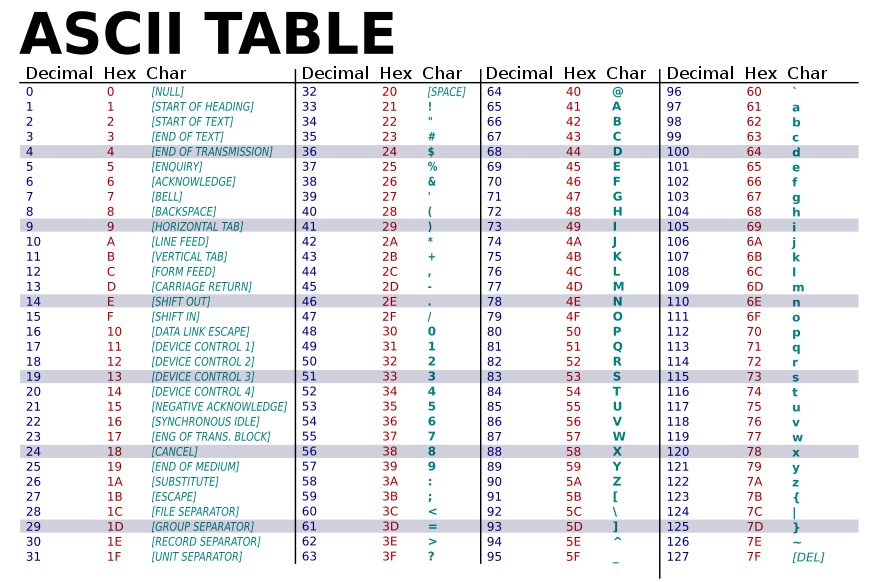
- ASCII becomes the standard, allowing different computers built by different companies to exchange data : Inter-operability(상호운용성)
- Each country invented multi-byte encoding schemes, all of which were mutually incompatible.
- UNICODE was devised in 1992 for one universal encoding scheme.
Other file formats like MP3 or GIF use binary numbers to encode sounds or colors of a pixel.
Everything on computer is a long sequence of 1's and 0's.
Thoughts
- Float 타입이 소수점이 float 할 수 있어서 그런 이름이 붙여진게 흥미로웠다.
