[CrashCourse CS] #7 The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
CPU : Central Processing Unit
- CPU's job is to execute programs.
- Programs are made up of a series of individual operations, called instructions, b/c they instruct computer what to do.
- Hypothetical example of an instruction table:
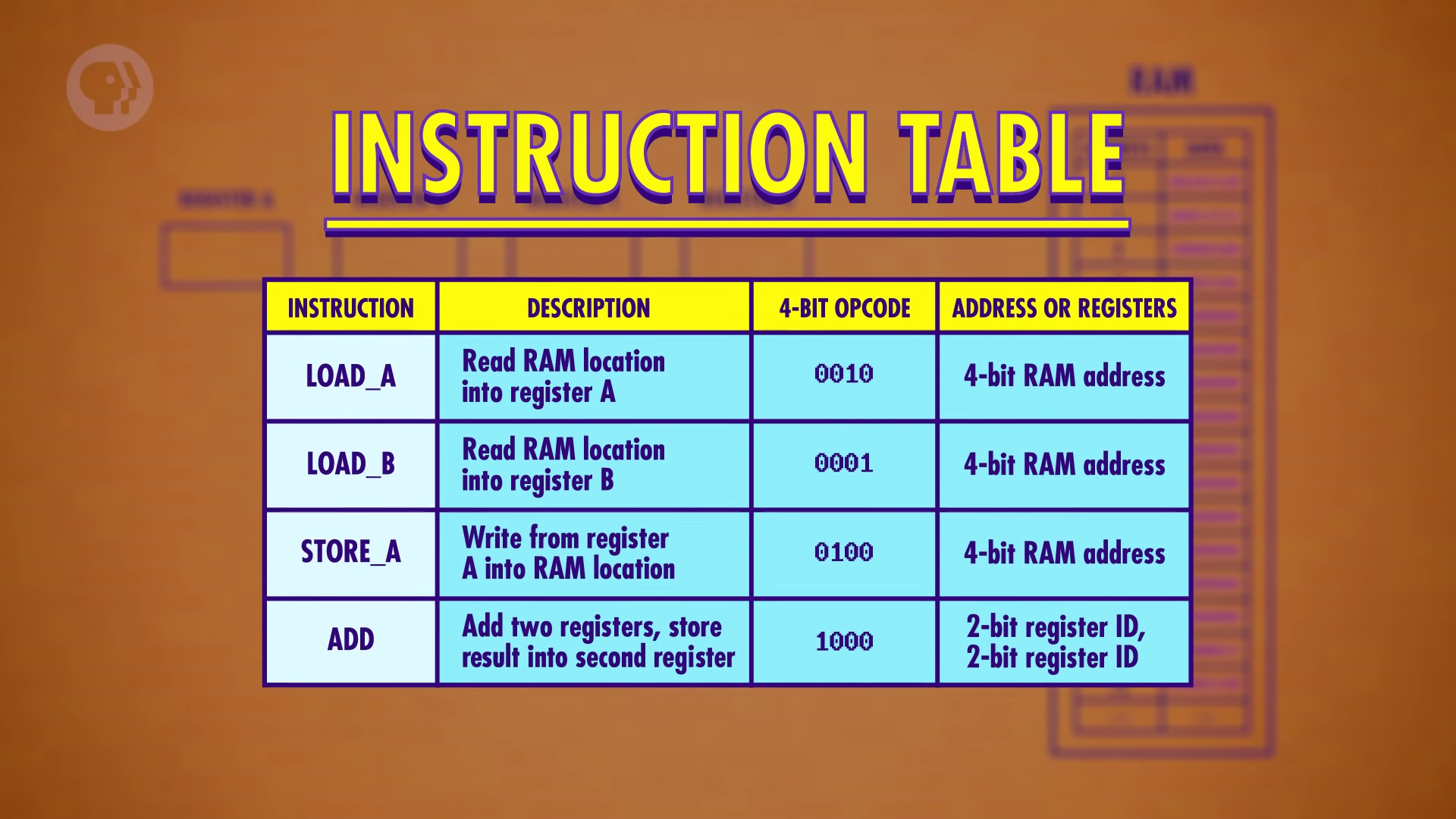
- The first 4 bit contains operation codes (opcodes), and the last four bit specify where the data for that operation should come from.
- ex) 0010 1110 at RAM address 0
0010 : opcode (LOAD_A : Read RAM location into register A)
1110 : data address (register the data in address 1110)
CPU Structure and Cycle
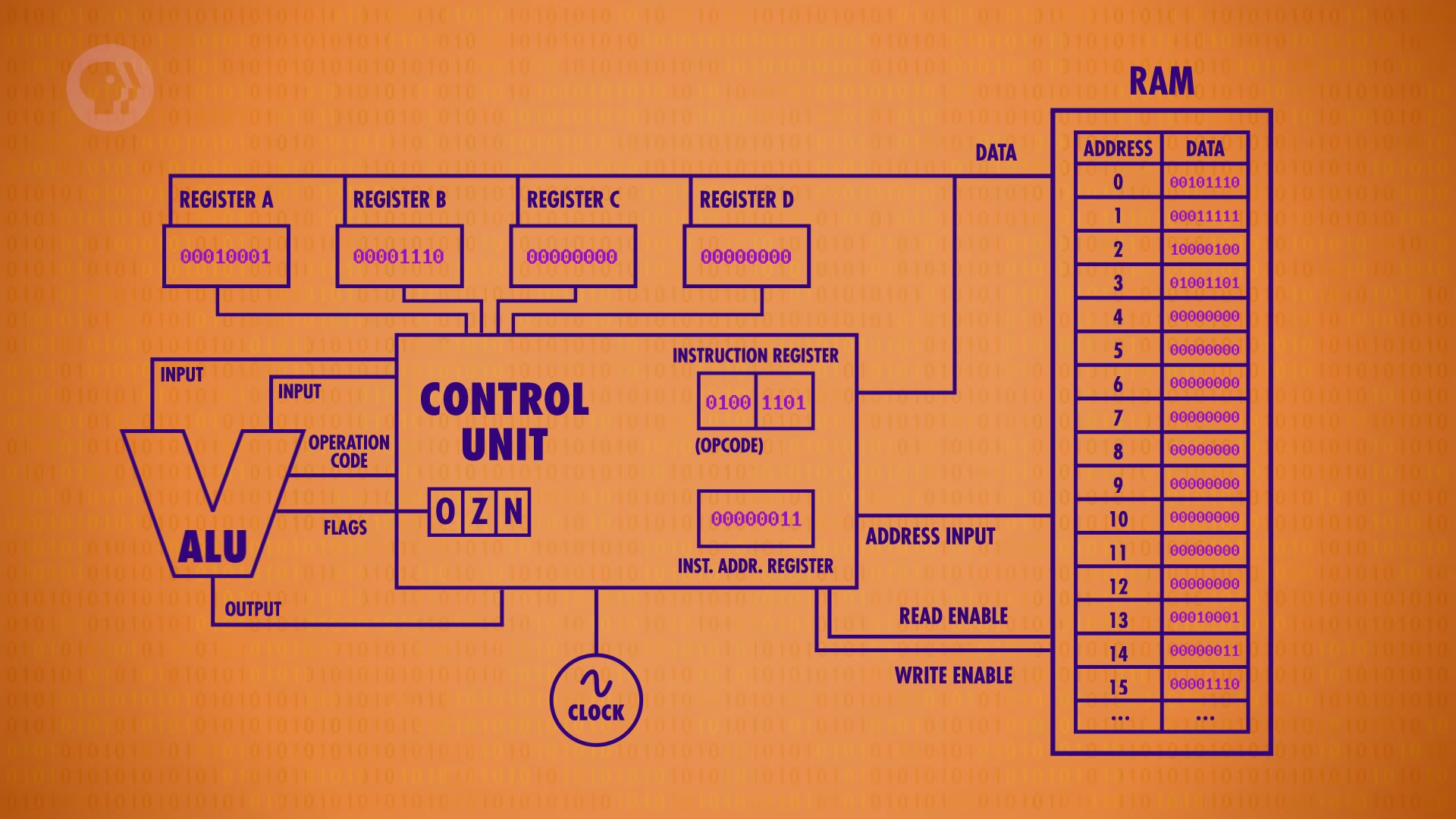
- Memory Registors (A, B, C, D) - temporarily store and manipulate vaules.
- Control Unit directs all of the different parts of the CPU.
- Instruction Address Register - stores the memory address of the current instruction.
- Instruction Register - stores the current instruction.
- Clock
- Triggers an electrical signal at a precise and regular inerval.
- Its signal is used by the Control Unit to advance the internal operation of the CPU.
1. Fetch Phase
- When we first boot up our computer, all of the registers start at 0.
- First phase of a CPU's operation - retrieve first instruction.
- Instruction Address Register input 0 to RAM.
- RAM returns the data stored in address 0, which is copied to the instruction register.
2. Decode Phase
- Figure out what the instructions is.
- Check instruction's OPcode with logic gates.
3. Execute Phase
Clock Speed
- The speed at which a CPU can carry out each stop of the fetch - decode - execute cycle is called its Clock Speed.
- Measured in Hertz, a unit of frequency.
- 1 Hertz = 1 cycle per second.
- Today's CPU - Gigahertz : Billions of CPU cycles every single second.
- Overclocking - modify the clock to speed up the tempo of the CPU.
- CPUs are designed to handle a little bit of overclocking.
- Too much can overheat or make errors.
- Underclocking - slowing the CPU down.
- Modern processors have Dynamic Frequency Scaling - change clock speed based on demand.
영어 표현
- ram : 들이받다.
- gobbledygook : language that is meaningless or is made unintelligible by excessive use of abstruse(=complex) technical terms; nonsense.
- beef up : strengthen, increase.
Thoughts
- CPU 파트가 처음엔 이해가 안돼서 여러번 돌려봤다. 그러니까 이해가 됬다.
- It is all about increasing the level of abstraction.


