Overview
- NVIDIA에서 낸 Decoder 기반의 Embedding 모델로 GPT-4 합성 데이터 없이, 공개 데이터로만 학습한 모델
- MTEB(embedding 관련 리더보드) 에서 1등 기록중
- https://huggingface.co/nvidia/NV-Embed-v1 에 모델 공개
Introduction
- 최근 몇 년 동안 대형 언어 모델(LLM)은 다양한 자연어 처리 작업에서 뛰어난 성능을 보여주고 있음.
- 하지만 전통적인 LLM 임베딩 모델은 특정 응용 프로그램에 맞춰 미세 조정되어 범용성과 일반적 적용에 한계
- 따라서 이 논문은 LLM을 범용 임베딩 모델로 훈련시키기 위한 새로운 접근법인 NV-Embed 모델 제안
- 모델 구조 관점: Latent attention Layer 제안
- 모델 훈련 관점: 2단계 Contrastive instruction-tuning
Method
- 두 가지 관점 모델 구조 / 모델 훈련
1. Bidirectional Attention
- 여기서는 단순히 LLM Decoder에서 contrastive learning 할때 causal attention mask를 없앰
2. Latent Attention Layer
- sequence of tokens의 embedding을 얻는 2가지 주요 방법은 다음과 같음
- (1) mean pooling: bidirectional embedding모델에서 주로 사용
- (2) <eos> token embedding: decoder 기반 LLM 기반 embedding 모델에서 주로 사용
- 그러나 두 방법은 명확한 단점(한계점)이 존재
- (1)의 경우에는 단순히 token embedding을 평균내기때문에 key phrases의 정보를 dilute(희석) 할 수 있음
- (2)의 경우에는 마지막 <eos> token embedding을 쓰면서 recency bias (처음 / 중간 정보를 잊는) 문제를 겪을 수 있음
- 따라서 이 논문에서는 Latent attention Layer를 제안함
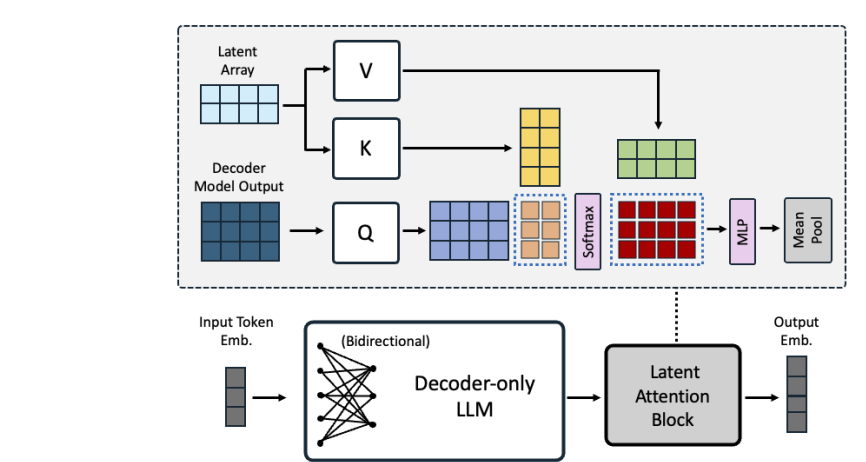
- Q: LLM에서 나오는 output
- K/V: trainalbe matrix

3. Two-stage Instruction-Tuning
- 2단계 instruction Tuning 진행
- (1) 검색 관련 task
- contrastive training
- in-batch negatives and hard-negative examples
- (2) 검색 & 비검색 관련 task 합쳐서
- contrastive training
- in-batch negative 는 적용 X
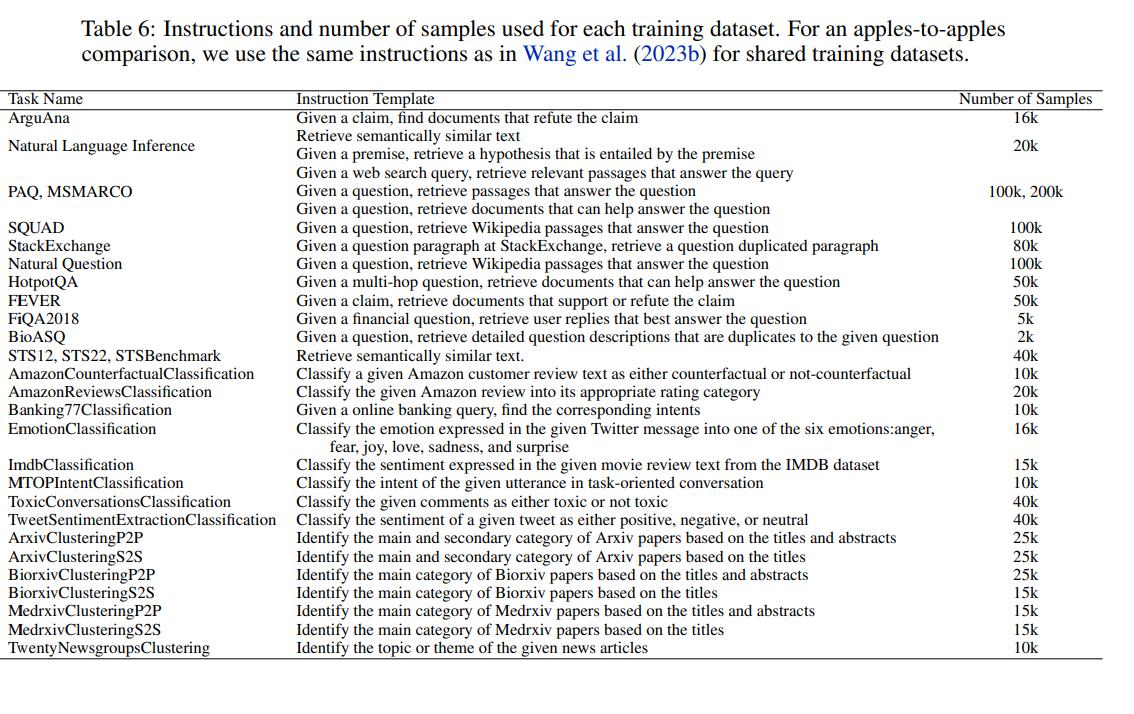
Training Data
- Instruction Dataset
Instruct: task_definition Query: q
- 그 후 공개 데이터 수집(검색 / 비검색 task)
Experiment
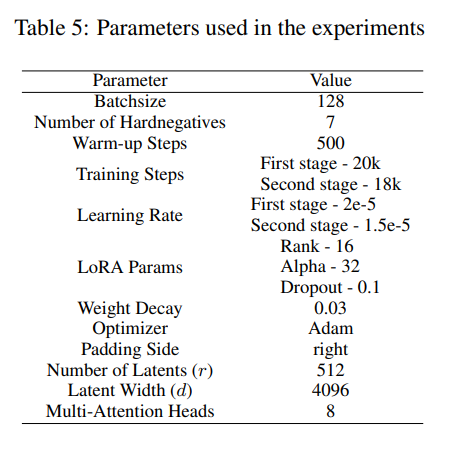
Training
- PEFT, LoRA 사용
Main Result
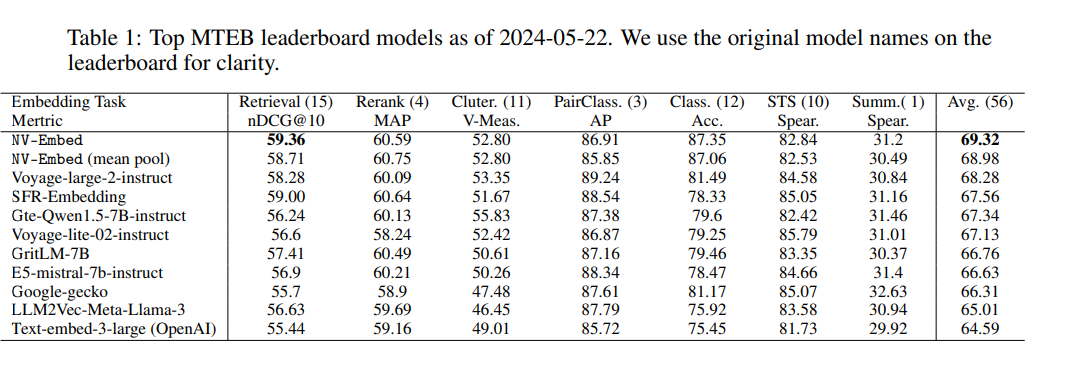
- Avg 점수 기준 SOTA 달성
Pooling Method
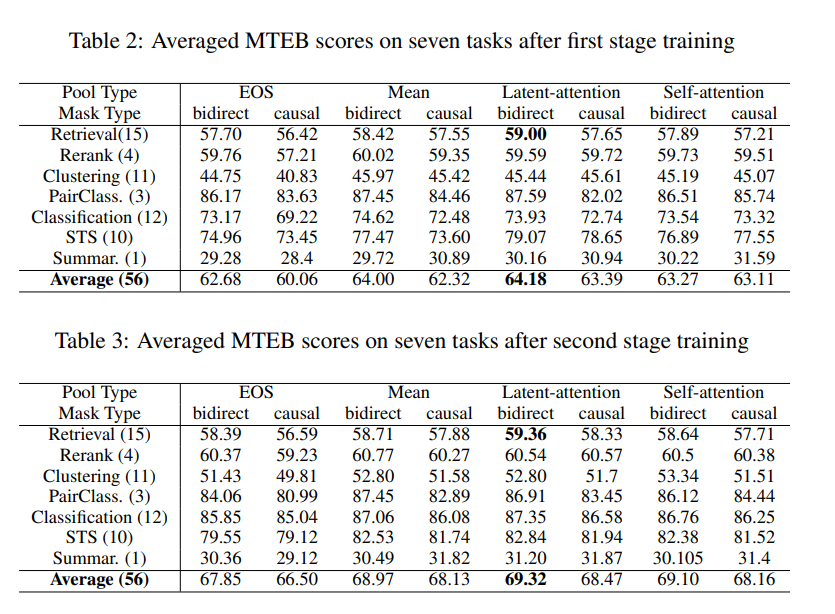
-
mean pooling > last-token embedding
- recency bias의 영향
-
latent-attention은 성능이 향상
