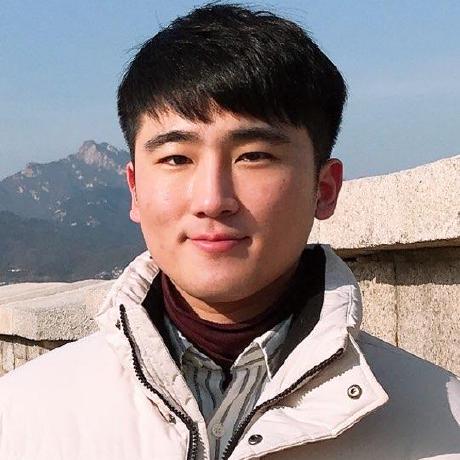
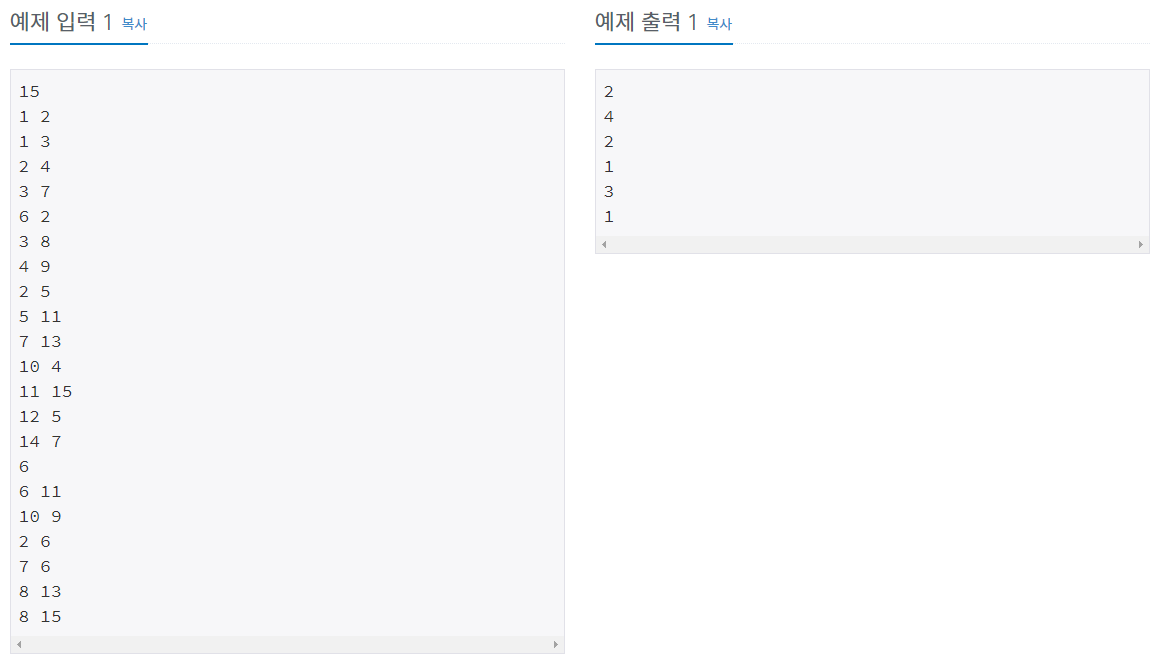
1. LCA Basic
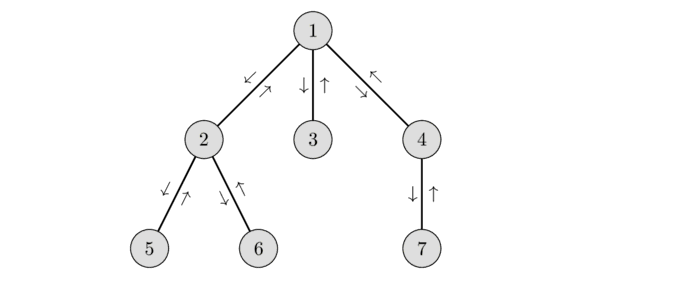
위와 같은 그림이 있다. 그림의 트리는 전재조건이 있다.
1) 자식노드의 번호는 부모노드의 번호보다 작다.
2) 같은 깊이에서 왼쪽 노드의 번호가 더 작다.
이 경우 두 노드의 가장 가까운 노드를 찾는 것은 쉽다.
1) 전위 순회를 한다.
2) 전위 순회 시 경로를 기록한다. 이미 거쳐간 노드도 다시 거쳐진다면 기록한다.
3) 기록한 경로에서 두 노드의 범주를 잡고, 범주 내 가장 작은 수의 번호를 가진 노드가 정답이 된다.
6번 노드와 4번 노드의 LCA
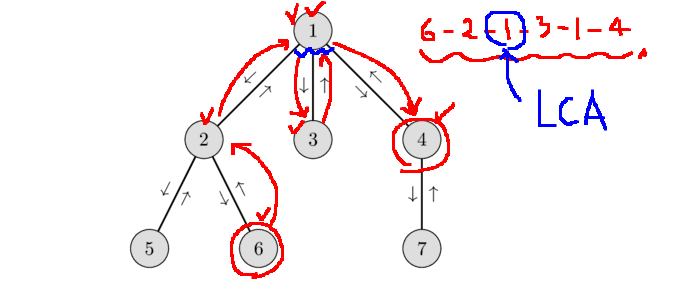
=> 1 - 2 - 5 - 2 - 6 - 2 - "1" - 3 - 1 - 4 - 7 - 4 - 1
2번 노드와 6번 노드의 LCA
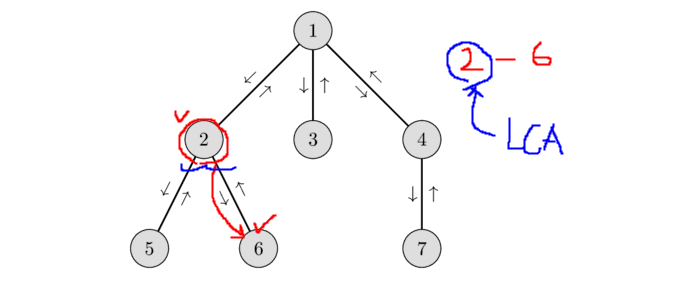
=> 1 - 2 - 5 - "2" - 6 - 2 - 1 - 3 - 1 - 4 - 7 - 4 - 1
코드는 다음과 같다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n; // 노드 갯수
void dfs(int root, vector<int>& route, vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
// 루트 먼저 방문 체크
route.push_back(root);
//cout << root << " ";
// 탐색
for (int i = 0; i < graph[root].size(); i++) {
int nextNode = graph[root][i];
dfs(nextNode, route, graph);
route.push_back(root); // 다시 루트로 돌아옴
//cout << root << " ";
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
cin.ignore();
vector<vector<int>> graph(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int nowNode;
//cin >> nowNode;
//cin.ignore();
string line;
stringstream ss;
getline(cin, line);
ss.str(line);
ss >> nowNode;
string child;
while (ss >> child) {
graph[nowNode].push_back(stoi(child));
}
}
// 전위 순휘 경로 생성
vector<int> route;
dfs(1, route, graph);
int numOfQuery;
cin >> numOfQuery;
vector<int> answers;
for (int i = 0; i < numOfQuery; i++) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int start;
int end;
int startIdx;
bool flag = false;
for (int j = 0; j < route.size(); j++) {
if (route[j] != a && route[j] != b)
continue;
startIdx = j;
if (route[j] == a) {
start = a;
end = b;
}
else {
start = b;
end = a;
}
flag = true;
break;
}
if (!flag) {
answers.push_back(-1); // 잘못된 노드 입력
continue;
}
int minNum = n;
for (int j = startIdx; j < route.size(); j++) {
if (minNum > route[j])
minNum = route[j];
if (route[j] == end)
break;
}
answers.push_back(minNum);
}
// 전체 정답
for (int i = 0; i < answers.size(); i++) {
cout << answers[i] << '\n';
}
}(입력)
7 // 노드 수
1 2 3 4 // 1번 노드는 2,3,4번 노드를 자식으로 둠
2 5 6
3
4 7
5
6
7
2 // 쿼리 수
2 6 // 2번 노드와 6번 노드의 LCA는?
6 4 // 6번 노드와 4번 노드의 LCA는?
(출력)
1
2
2. LCA (전제 조건이 없을 때)
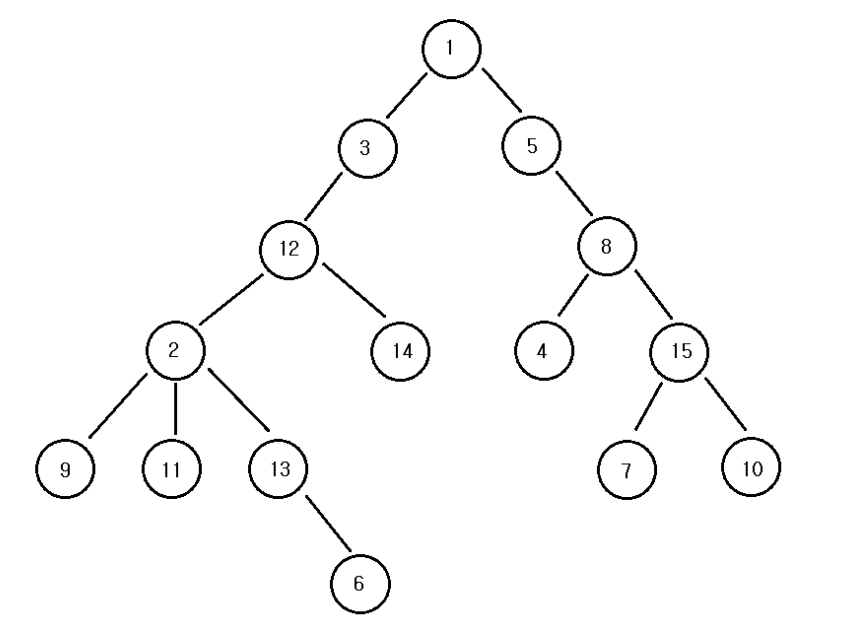
하지만 위 그림과 같이 전제조건이 보장되지 않는다면 어떨까?
전제 조건
1) 자식노드의 번호는 부모노드의 번호보다 작다.
2) 같은 깊이에서 왼쪽 노드의 번호가 더 작다.
기존의 로직대로 2번 노드와 14번 노드의 LCA를 찾으면 LCA가 2번 노드가 된다. 정답은 12번 노드임에도 불구하고 말이다.
따라서 이를 해결하기 위해 노드 번호가 아닌 트리의 깊이로 최소 노드, 즉 LCA를 선정해야한다.
1) 노드 번호를 인덱스 삼아, 해당 노드가 몇번째 레벨에 속하는지 알 수 있는 배열을 하나 만들어야 한다.
2) 만들어진 경로를 탐색하는 과정에서 낮은 노드의 번호가 먼저 발견된다 보장할 수 없다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void dfs(int root, vector<int> &route, vector<vector<int>> &graph){
// 루트 먼저 방문 체크
route.push_back(root);
// 탐색
for(int i=0; i<graph[root].size(); i++){
int nextNode = graph[root][i];
dfs(nextNode, route, graph);
route.push_back(root); // 다시 루트로 돌아옴
}
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
// graph 자료구조
vector<vector<int>> graph(n+1);
// 트리 레벨 info를 위한 자료구조
vector<int> depthInfo(n+1, 0); // 처음은 모두 0번 레벨로 초기화
// 루트는 1번
depthInfo[1] = 1; // 루트는 1번 레벨
/*
반례 케이스
3
2 3
1 2
1
2 3
=> 1번노드 연결정보가 먼저 입력되지 않는 경우도 있다. 이 경우를 처리해야한다.
*/
vector<pair<int, int>> edges;
for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++){
int nodeA, nodeB;
cin >> nodeA >> nodeB;
edges.push_back({nodeA, nodeB});
}
bool checkFlag = false;
while(!checkFlag){
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++){
int nodeA = edges[i].first;
int nodeB = edges[i].second;
if(depthInfo[nodeA] == 0 && depthInfo[nodeB] == 0){
checkFlag = true;
continue; // 아직 알 수 없는 정보는 skip.
}
if(depthInfo[nodeA] != 0 && depthInfo[nodeB] != 0)
continue;
if(depthInfo[nodeA] > depthInfo[nodeB]){ // 이미 트리에 달려진 노드 아래에 새로운 노드가 붙는다.
depthInfo[nodeB] = depthInfo[nodeA]+1;
graph[nodeA].push_back(nodeB);
}
else {
depthInfo[nodeA] = depthInfo[nodeB]+1;
graph[nodeB].push_back(nodeA);
}
}
if(checkFlag){
checkFlag = false;
continue;
}
else
break; // 완성
}
vector<int> route;
dfs(1, route, graph);
// 순회 체크
//for(int i=0; i<route.size(); i++){
// cout << route[i] << " ";
//}
//cout << '\n';
int numOfQuery;
cin >> numOfQuery;
vector<int> answers;
for(int i=0; i<numOfQuery; i++){
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
for(int j=0; j<route.size(); j++){ // 루트 탐색
bool flag = false;
if(route[j] == a){
flag = true;
// 구간 잡기
int minNode = a;
int minDepth = depthInfo[a];
for(int k=j; k<route.size(); k++){
int tempNode = route[k];
if(minDepth > depthInfo[tempNode]){
minNode = tempNode;
minDepth = depthInfo[tempNode];
}
if(tempNode == b)
break;
}
answers.push_back(minNode);
}
else if(route[j] == b){
flag = true;
// 구간 잡기
int minNode = b;
int minDepth = depthInfo[b];
for(int k=j; k<route.size(); k++){
int tempNode = route[k];
if(minDepth > depthInfo[tempNode]){
minNode = tempNode;
minDepth = depthInfo[tempNode];
}
if(tempNode == a)
break;
}
answers.push_back(minNode);
}
if(flag)
break;
}
}
// 전체 정답
for(int i=0; i<answers.size(); i++){
cout << answers[i] << '\n';
}
}번외) 부모의 레벨을 이용한 방법
1) 두 노드의 레벨이 다르다면, 아래 쪽에 위치한 노드를 더 상위 레벨로 한칸 올린다. => 반복
2) 레벨이 같아진다면 일단 같은 노드인지 확인한다. 만약 다르다면 각각 한 레벨씩 더 올리고 다시 비교 확인한다. => 반복
int a, b; // <= 두 노드의 LCA를 찾자!
cin >> a >> b;
// (1) 먼저 같은 레벨로 맞춘다.
while(depthInfo[a] != depthInfo[b]){
if(depthInfo[a] < depthInfo[b])
b = parent[b];
else
a = parent[a];
}
// (2) 레벨이 같아졌으면 서로 한칸씩 위로 이동하며 공통 부모를 찾는다.
while(true){
if(a == b){ // 같은 부모!
answers.push_back(a);
break;
}
else{
// 한칸 씩 올리기
a = parent[a];
b = parent[b];
}
}