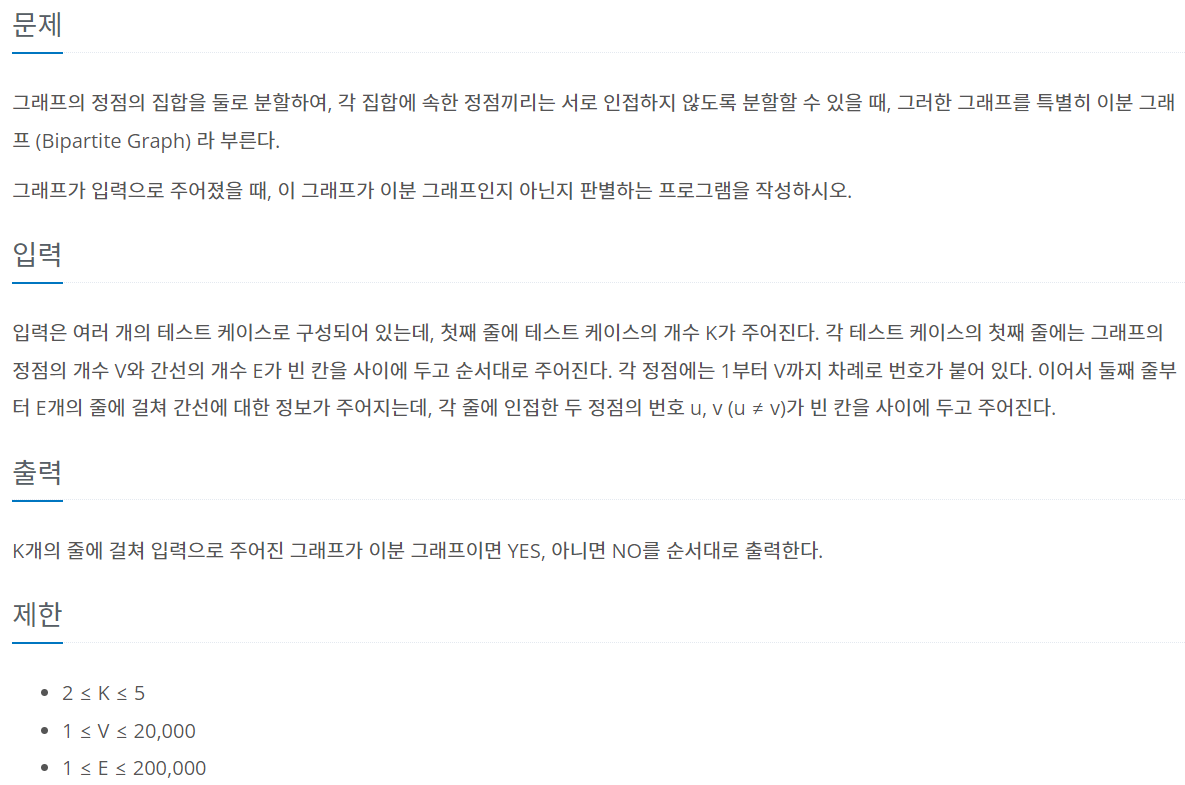
이분 그래프
이분 그래프는 정점을 두 개의 집합으로 나눌 수 있는 그래프이며, 이때 그래프의 모든 엣지는 서로 다른 집합에 속한 정점끼리만 연결되어야 한다.
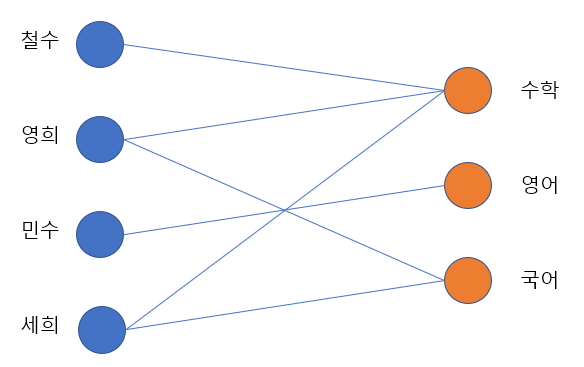
학생 목록과 수업 목록이 있을 때, 학생들이 어떤 수업을 수강하고 있는지를 이분 그래프로 표현할 수 있다.
또한 넷플릭스와 같은 비디오 스트리밍 플랫폼에서 제공되는 영화 목록과 시청자 사이의 관계도 또한 이분 그래프로 표현할 수 있다.
접근 방법과 예제 문제: 이분 그래프_백준
이분 그래프를 판별하는 알고리즘은 DFSF를 조금 변형하여 만들 수 있다.
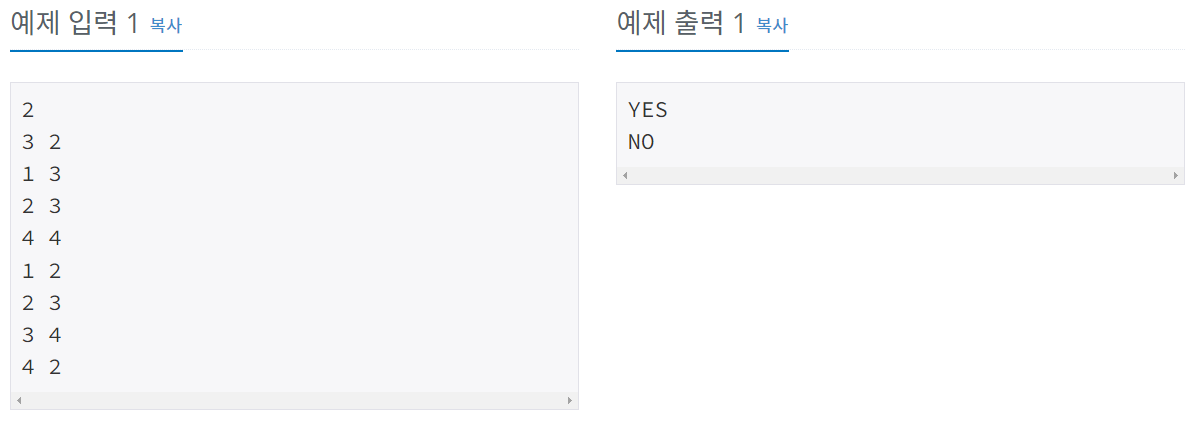
reference: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1707
풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int numOfNodes;
int numOfEdges;
bool DFS(int node, map<int, short>& teamMap, const vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
short nowNodeTeam = teamMap[node];
// 탐색
for (int i = 0; i < graph[node].size(); i++) {
int nextNode = graph[node][i];
// 팀이 부여되지 않은 노드라면(방문되지 않은 노드)
if (teamMap.find(nextNode) == teamMap.end()) {
teamMap.insert({ nextNode, (nowNodeTeam + 1) % 2 });
bool retBool = DFS(nextNode, teamMap, graph);
if (!retBool)
return false;
}
// 팀이 부여된 노드라면
else {
short nextNodeTeam = teamMap[nextNode];
// 같은 팀에 속한 노드라면 이분 그래프가 아님
if (nowNodeTeam == nextNodeTeam)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool solution(const vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
// 색상을 표현하는 맵
map<int, short> teamMap;
// 1번 노드부터 시작
int node = 1;
// 1번노드는 팀_제로에 속하게 한다.
teamMap.insert({ node, 0 });
// 무조건 하나로 연결된 그래프가 아님을 가정해야 한다.
// int answer = DFS(node, teamMap, graph);
// return answer;
for (int i = 1; i <= numOfNodes; i++) {
if (!DFS(i, teamMap, graph)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
int testCase;
cin >> testCase;
vector<string> answers;
for (int t = 0; t < testCase; t++) {
cin >> numOfNodes;
cin >> numOfEdges;
// 1번 노드부터 시작
vector<vector<int>> graph(numOfNodes+1);
for (int e = 0; e < numOfEdges; e++) {
int n1, n2;
cin >> n1 >> n2;
graph[n1].push_back(n2);
graph[n2].push_back(n1);
}
bool answer = solution(graph);
if (answer)
//cout << "YES" << endl;
answers.push_back("YES");
else
//cout << "NO" << endl;
answers.push_back("NO");
}
for (int t = 0; t < testCase; t++) {
cout << answers[t] << endl;
}
return 0;
}