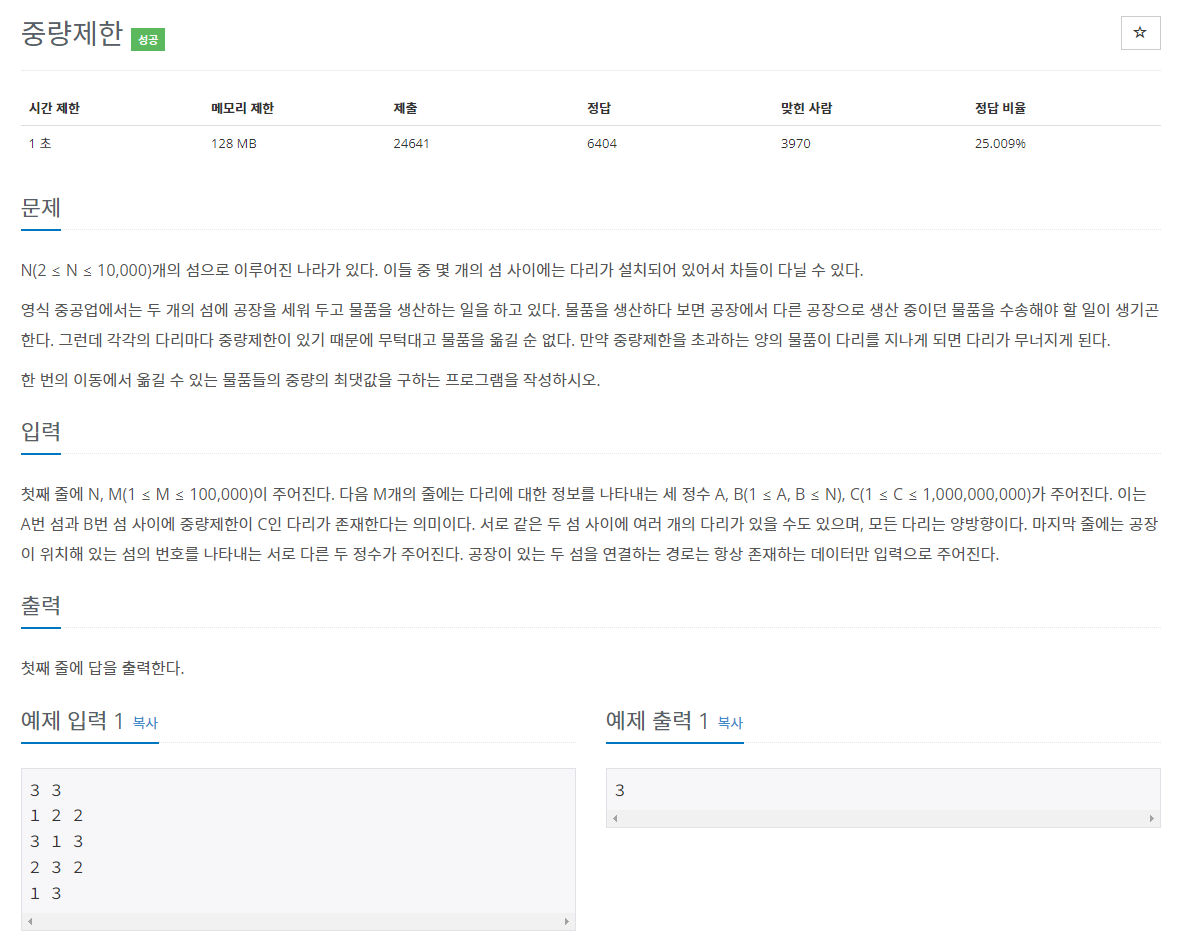
중량제한_백준
source: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1939
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const pair<pair<int, int>, int>& p1, const pair<pair<int, int>, int>& p2) {
return p1.second < p2.second;
}
};
int N, M;
int S, E;
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> graph(100000 + 1);
int solution() {
int minWeight = 1e9;
vector<int> visited(N + 1, 0);
priority_queue<pair<pair<int, int>, int>, vector<pair<pair<int, int>, int>>, cmp> pq;
visited[S] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[S].size(); i++) {
pair<int, int> p = graph[S][i];
int nextLoc = p.first;
int nextCost = p.second;
int minCost = p.second;
pq.push({ {nextLoc, nextCost}, minCost });
}
while (!pq.empty()) {
pair<pair<int, int>, int> now = pq.top(); pq.pop();
int nowLoc = now.first.first;
int nowCost = now.first.second;
int minCost = now.second;
if (nowLoc == E)
return minCost;
if (minCost < visited[nowLoc])
continue;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[nowLoc].size(); i++) {
pair<int, int> next = graph[nowLoc][i];
int nextLoc = next.first;
int nextCost = next.second;
if (visited[nextLoc] < min(nextCost, minCost)) {
pq.push({ {nextLoc, nextCost}, min(nextCost, minCost) });
visited[nextLoc] = min(nextCost, minCost);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b, cost;
cin >> a >> b >> cost;
graph[a].push_back({ b, cost });
graph[b].push_back({ a, cost });
}
cin >> S >> E;
cout << solution() << endl;
return 0;
}
2022/06/17 풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const pair<int, int>& p1, const pair<int, int>& p2) {
return p1.second < p2.second;
}
};
int N, M;
int solution(const vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>& BRIDGES, int start, int destination) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, cmp> pq;
vector<int> maxLimit(N + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < BRIDGES[start].size(); i++) {
pair<int, int> p = BRIDGES[start][i];
pq.push(p);
maxLimit[p.first] = p.second;
}
while (!pq.empty()) {
pair<int, int> p = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int nowNode = p.first;
int bridgeLimit = p.second;
if (nowNode == destination)
return maxLimit[nowNode];
if (maxLimit[nowNode] > bridgeLimit)
continue;
for (int i = 0; i < BRIDGES[nowNode].size(); i++) {
pair<int, int> nextp = BRIDGES[nowNode][i];
int nextNode = nextp.first;
int nextBridgeLimit = nextp.second;
int minBridgeLimit = min(bridgeLimit, nextBridgeLimit);
if (maxLimit[nextNode] < minBridgeLimit) {
pq.push({ nextNode, minBridgeLimit });
maxLimit[nextNode] = minBridgeLimit;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M;
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> BRIDGES(N+1);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int from, to, limit;
cin >> from >> to >> limit;
BRIDGES[from].push_back({ to, limit });
BRIDGES[to].push_back({ from, limit });
}
int start, destination;
cin >> start >> destination;
int answer = solution(BRIDGES, start, destination);
cout << answer << endl;
}
2022/08/31 풀이(최신)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_WEIGHT = 1e9;
int N, M;
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> graph(10000 + 1);
int START, END;
struct LoadInfo {
int node;
int BeforeMaxWeight;
};
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const LoadInfo& info1, const LoadInfo& info2) {
return info1.BeforeMaxWeight < info2.BeforeMaxWeight;
}
};
int solution() {
priority_queue<LoadInfo, vector<LoadInfo>, cmp> pq;
LoadInfo startInfo = { START, MAX_WEIGHT };
pq.push(startInfo);
vector<vector<bool>> visited(N + 1, vector<bool>(N + 1, false));
while (!pq.empty()) {
LoadInfo info = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int nowNode = info.node;
int bMaxWeight = info.BeforeMaxWeight;
if (nowNode == END)
return bMaxWeight;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[nowNode].size(); i++) {
int nextNode = graph[nowNode][i].first;
int edgeWeight = graph[nowNode][i].second;
if (visited[nowNode][nextNode])
continue;
LoadInfo nextInfo = { nextNode, min(bMaxWeight, edgeWeight) };
pq.push(nextInfo);
visited[nowNode][nextNode] = true;
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M;
map<pair<int, int>, int> edgeMap;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
pair<int, int> p = { min(a, b), max(a, b) };
if (edgeMap.find(p) == edgeMap.end())
edgeMap.insert({ p, c });
else {
edgeMap[p] = max(edgeMap[p], c);
}
}
for (auto iter = edgeMap.begin(); iter != edgeMap.end(); iter++) {
int a = (*iter).first.first;
int b = (*iter).first.second;
int c = (*iter).second;
graph[a].push_back({ b, c });
graph[b].push_back({ a, c });
}
cin >> START >> END;
int answer = solution();
cout << answer << endl;
}
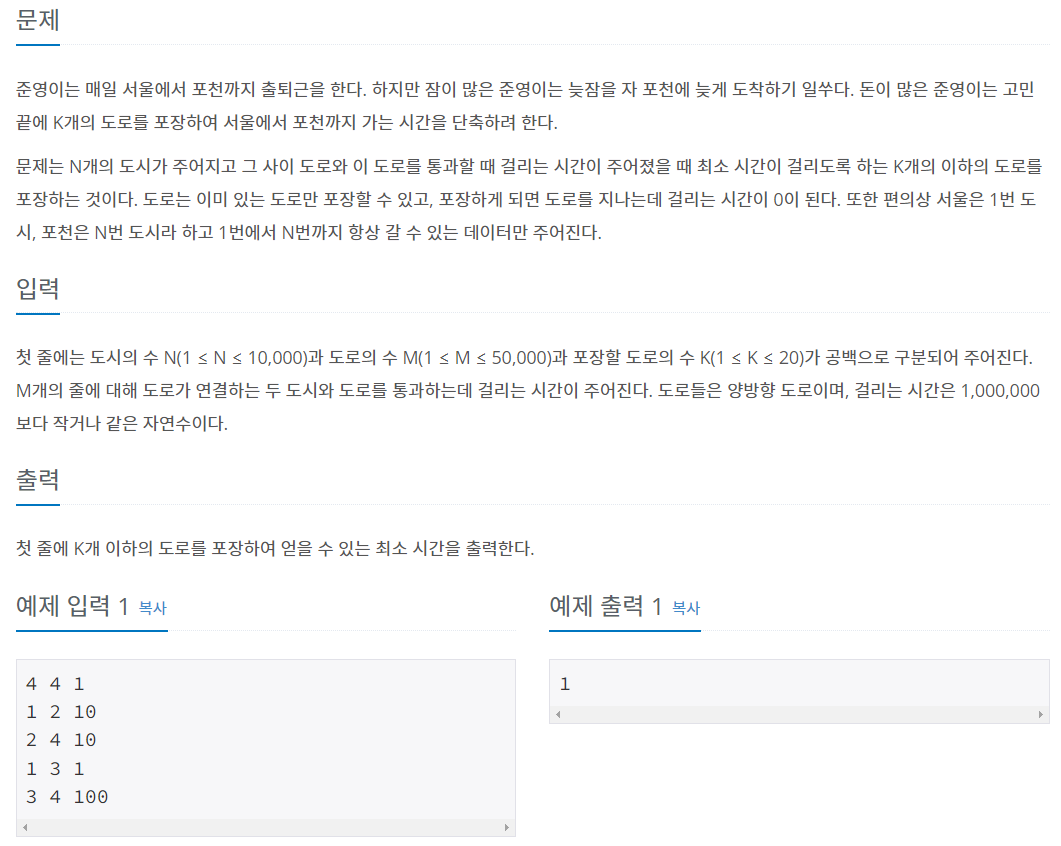
도로포장_백준
source: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1162
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const pair<pair<int, int>, long long>& p1, const pair<pair<int, int>, long long>& p2) {
if (p1.second != p2.second)
return p1.second > p2.second;
else if (p1.first.second != p2.first.second)
return p1.first.second < p2.first.second;
else
return p1.first.first < p2.first.first;
}
};
int N, M, K;
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> graph(10000 + 1);
long long solution() {
int Start = 1;
int End = N;
if (N == 1)
return 0;
vector<vector<long long>> minCostTable(N + 1, vector<long long>(K + 1, 1e12));
priority_queue<pair<pair<int, int>, long long>, vector<pair<pair<int, int>, long long>>, cmp> pq;
for (int i = 0; i <= K; i++) {
minCostTable[Start][i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph[Start].size(); i++) {
int nextNode = graph[Start][i].first;
long long nextCost = graph[Start][i].second;
pq.push({ {nextNode, K}, nextCost });
minCostTable[nextNode][K] = nextCost;
pq.push({ { nextNode, K - 1 }, 0 });
minCostTable[nextNode][K - 1] = 0;
}
while (!pq.empty()) {
pair<pair<int, int>, long long> now = pq.top(); pq.pop();
int nowNode = now.first.first;
int resChance = now.first.second;
long long nowCost = now.second;
if (nowNode == End)
return nowCost;
if (minCostTable[nowNode][resChance] < nowCost)
continue;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[nowNode].size(); i++) {
int nextNode = graph[nowNode][i].first;
long long nextCost = graph[nowNode][i].second;
if (minCostTable[nextNode][resChance] > nowCost + nextCost) {
pq.push({ {nextNode, resChance}, nowCost + nextCost });
minCostTable[nextNode][resChance] = nowCost + nextCost;
}
if (resChance >= 1) {
if (minCostTable[nextNode][resChance - 1] > nowCost) {
pq.push({ {nextNode, resChance - 1}, nowCost });
minCostTable[nextNode][resChance - 1] = nowCost;
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M >> K;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b, cost;
cin >> a >> b >> cost;
graph[a].push_back({ b, cost });
graph[b].push_back({ a, cost });
}
cout << solution() << endl;
}
2022/08/31 풀이(최신)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll MAX_COST = (ll)50000 * 1000000;
int N, M, K;
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> graph(10000+1);
struct Node {
int city;
ll totalCost;
int resChance;
};
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const Node& n1, const Node& n2) {
if (n1.totalCost != n2.totalCost) {
return n1.totalCost > n2.totalCost;
}
else
return n1.resChance < n2.resChance;
}
};
ll solution() {
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, cmp> pq;
Node nStart = { 1, 0, K };
pq.push(nStart);
vector<vector<ll>> minCostTable(N + 1, vector<ll>(20 + 1, MAX_COST));
minCostTable[1][K] = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
Node nowNode = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int city = nowNode.city;
ll totalCost = nowNode.totalCost;
int resChance = nowNode.resChance;
if (city == N)
return totalCost;
if (minCostTable[city][resChance] < totalCost)
continue;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[city].size(); i++) {
int nextCity = graph[city][i].first;
ll cost = graph[city][i].second;
if (resChance > 0) {
if (totalCost < minCostTable[nextCity][resChance-1]) {
Node wrappingNode = { nextCity, totalCost + 0, resChance - 1 };
pq.push(wrappingNode);
minCostTable[nextCity][resChance - 1] = totalCost;
}
}
if (totalCost + cost < minCostTable[nextCity][resChance]) {
Node unWrappingNode = { nextCity, totalCost + cost, resChance };
pq.push(unWrappingNode);
minCostTable[nextCity][resChance] = totalCost + cost;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M >> K;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
graph[a].push_back({ b, c });
graph[b].push_back({ a, c });
}
ll answer = solution();
cout << answer << endl;
return 0;
}


