이 문제는 힙으로 풀었어야 했다. 첫 시도는 힙으로 풀지 않아 효율성에선 통과하지 못하였다.
힙을 사용하지 않은 방식
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(vector<int> &vec, int idx1, int idx2){
int temp = vec[idx1];
vec[idx1] = vec[idx2];
vec[idx2] = temp;
}
void simpleSort(vector<int> &vec, int start){ // 시간복잡도: O(n)
int vecSize = vec.size();
for(int i = start+1; i < vecSize; i++){
if(vec[i-1] > vec[i])
// swap
swap(vec, i-1, i);
else
break;
}
}
void quickSort(vector<int> &vec, int start, int end){ // 퀵소트 시간복잡도: O(nlogn)
if(start >= end)
return;
int p = start;
int ll = start+1;
int rr = end;
while(ll <= rr){
while(ll <= end && vec[ll] <= vec[p]) ll++;
while(rr >= start+1 && vec[rr] >= vec[p]) rr--;
if(ll > rr){
int tmp = vec[rr];
vec[rr] = vec[p];
vec[p] = tmp;
}
else{
int tmp = vec[rr];
vec[rr] = vec[ll];
vec[ll] = tmp;
}
}
quickSort(vec, start, rr-1);
quickSort(vec, rr+1, end);
}
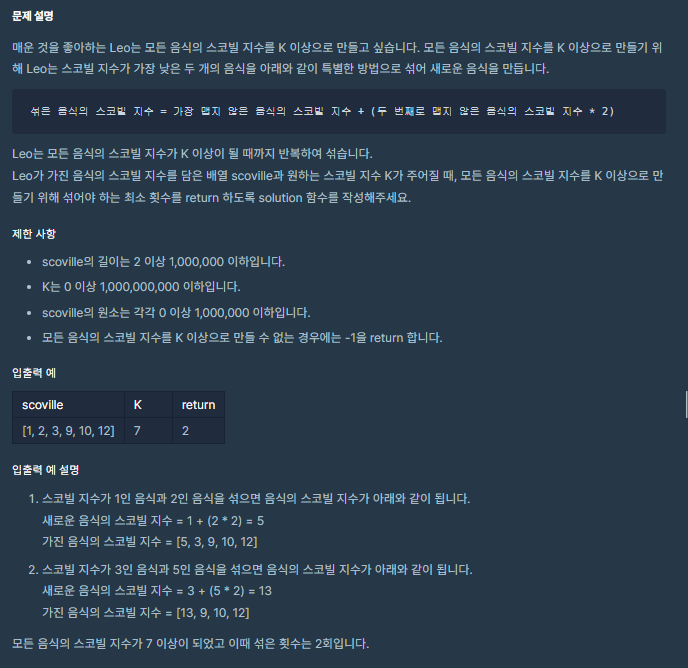
int solution(vector<int> scoville, int K) {
int answer = 0;
// 오름차순 정렬
quickSort(scoville, 0 , scoville.size()-1); // O(nlogn)
int idx = 0;
while(true){ // O(N)
if(scoville[idx] < K){ // idx는 스코빌이 가장 작은 음식(원소) 위치에 해당하는 인덱스
// 더 이상 합칠 수 없다면
if(idx+1 >= scoville.size())
return -1;
// 섞은 음식 만들기 => 제일 작은 값(idx) + 두번째로 작은 값(idx+1)*2
int newScov = scoville[idx] + scoville[idx+1]*2;
scoville[idx+1] = newScov;
idx++;
simpleSort(scoville, idx); // O(N) => 총 O(N^2) <= 다시 정렬하는 부분에서 최소 O(logn)을 보장해야 효율성에서 통과할 문제라 추측.
// N의 범위(스코빌 벡터 길이): ~ 1,000,000이다.
// 이 범위는 최소 O(nlogn)의 시간 복잡도를 가진 알고리즘을 사용해야 한다.
// 새로운 원소를 삽입해서 정렬까지 이루어지는 부분이 O(logn) 시간 복잡도의 알고리즘이 되어야 한다.
// 이는 결국 우선순위 큐의 삽입 시간 복잡도와 같다.
answer++;
}
else
break;
}
return answer;
}Heap 사용
priority_queue 이용
#include <queue>
주요 메서드
push(): 삽입 <= 시간복잡도: O(logN)
top(): 반환 <= 시간복잡도: O(1), 반환만 하고 힙에서 삭제를 하지 않는다.
pop(): 삭제 <= 시간복잡도: O(logN)
c++의 priority_queue는 디폴트가 최대 힙이므로 최소 힙으로 사용하려면 삽입, 삭제 때 마이너스(-)를 붙여야 한다.
/* priority_queue(heap)을 사용한 solution
*
*/
// cmp 구조체
struct cmp {
bool operator()(int a, int b){
// 오름차순
return a > b;
}
};
// 스코빌 벡터 길이: ~ 1,000,000
// K: ~ 1,000,000,000
int solution(vector<int> scoville, int K) {
int answer = 0;
// 우선순위 큐 선언
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, cmp> pq;
// 우선순위 큐에 모든 요리 스코빌 지수 담기
// 시간 복잡도: O(nlogn)
for(int i=0; i<scoville.size(); i++){
pq.push(scoville[i]);
}
// 반복적으로 섞기 수행
while(!pq.empty()){
// 가장 작은 스코빌
int first = pq.top(); pq.pop();
if(first >= K)
// 가장 작은 스코빌이 K이상이라는 뜻은 모든 스코빌 지수가 K이상이란 뜻
break;
int second;
if(!pq.empty()) {
second = pq.top();
pq.pop();
}
else
return -1; // K 이상을 충족하지 못하였는데 더 섞을 스코빌 지수가 없음
// 섞기
int newScov = first + second*2;
pq.push(newScov); // => 최종 O(nlogn)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
answer++;
}
return answer;
}