Tree
그래프의 일종으로 한 루트 노드에서 시작해서 자기 자신에게 돌아오지 못하는 순환이 없는 그래프이다.
- root node : 최상위 노드
- leaf node : 자식 노드가 없는 노드
- internal node : leaf node가 아닌 노드 ( 내부 노드 )
Binary Tree
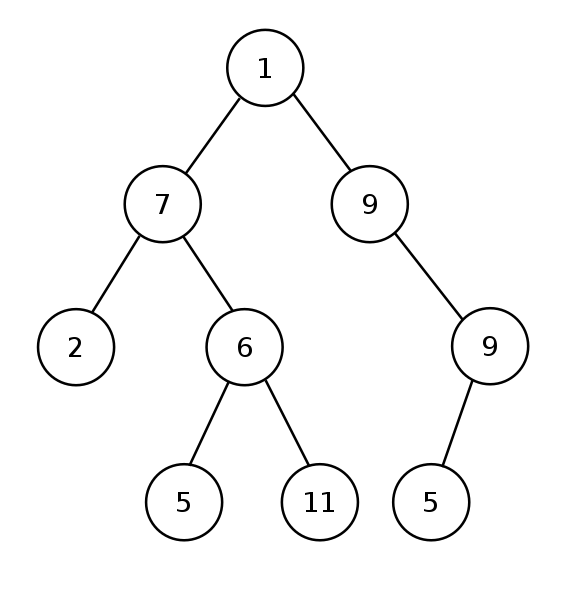
각각의 부모 노드가 최대 2개의 자식 노드를 가질 수 있는 트리
구성 요소
- val ( 데이터 )
- left child
- right child
sturct Node{
int val;
Node* left, *right;
};Binary Tree의 종류
1. Full Binary Tree
모든 부모 노드들이 2개의 자식 노드를 가지거나 가지지 않는 트리
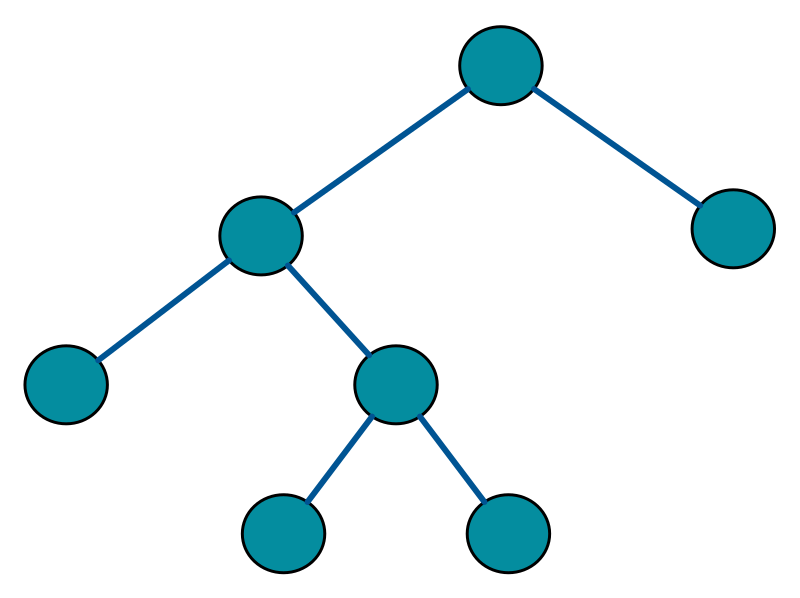
i = the number of internal nodes ( 내부 노드 = 자식을 가진 노드 )
n = be the total number of nodes
l = number of leaves
λ = number of levelsl = i + 1
n = 2i + 1 // i + l = i + (i + 1)
i = (n-1)/2 // (2i + 1 - 1)/2 = i
l = (n+1)/2 // (2i+1+1)/2 = 2i+1
n = 2l-1 // 2(i+1)-1
i = l-1 // i+1-1
(max)l: 2^(λ - 1) // 최대 leaf개수Full Binary Tree를 체크하는 예제
struct Node
{
int key;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int k)
{
key = k;
}
};
bool isFullBinaryTree(Node *root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
if (root->left && root->right)
{
return isFullBinaryTree(root->left) && isFullBinaryTree(root->right);
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
Node *root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->left->right->left = new Node(6);
root->left->right->right = new Node(7);
if (isFullBinaryTree(root))
{
cout << "Is Full Binary Tree" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Is not Full Binary Tree" << endl;
}
return 0;
}2. Complete Binary Tree
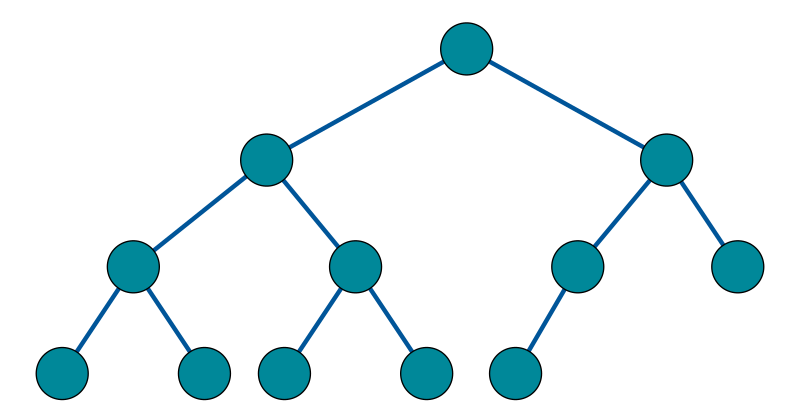
Full Binary Tree와 비슷하지만 차이점이 있음
- 모든 레벨들이 채워져있어야 함
- leaf 요소들이 왼쪽으로 치우쳐야 함
- 마지막 leaf 요소는 Full Binary가 아니여도 됨 ( 0개 혹은 1개의 자식만 있어도 됨 )
left child = 2i + 1
right child = 2i + 2
parent node = (i-1) / 2
iternal range = [0, n/2 - 1]
leaf range = [n / 2, n - 1]Complete Binary Tree 체크하는 예제
struct Node
{
int key;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int key)
{
this->key = key;
this->left = nullptr;
this->right = nullptr;
}
};
int getTotalCount(Node *root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
return 1 + getTotalCount(root->left) + getTotalCount(root->right);
}
bool checkCompleteTree(Node *root, int idx, int total)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
if (idx >= total)
{
// nullptr이아니고(노드가 존재하고) idx가 total 을 넘어서면 complete tree가 아니다.
return false;
}
return checkCompleteTree(root->left, 2 * idx + 1, total) && checkCompleteTree(root->right, 2 * idx + 2, total);
}
int main()
{
Node *root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
// root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
int total = getTotalCount(root);
if (checkCompleteTree(root, 0, total))
{
cout << "Complete Tree" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Is not complet tree" << endl;
}
}Complete Binary Tree Applications
- Heap-based data structures
- Heap sort
3. Balanced Binary Tree
노드의 왼쪽 트리와 오른쪽 트리의 높이 차이가 0혹은 1인 트리
Balanced Binary Tree 체크하는 예제
class Solution {
public:
int dfsHeight (TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int leftHeight = dfsHeight (root -> left);
if (leftHeight == -1) return -1;
int rightHeight = dfsHeight (root -> right);
if (rightHeight == -1) return -1;
if (abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) return -1;
return 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode *root) {
return dfsHeight (root) != -1;
}
};