DOM
-
브라우저의 렌더링 엔진은 HTML 문서를 로드한 후, 파싱하여 객체로 만들고 이들을 브라우저가 이해 할 수 있는 트리 구조로 구성하여 메모리에 적재하는데 이 때, 사용하는 구조 모델을
DOM이라고 한다.📢 DOM은 두 가지 기능을 담당.
- HTML 문서에 대한 모델 구성
- HTML 문서 내의 각 요소에 접근하고 수정 할 수 있는 Property와 method 제공
DOM과 자바스크립트의 관계
- 페이지 콘텐츠(the page content)는 DOM 에 저장되며 자바스크립트는 DOM을 통해 페이지 콘텐츠(the page content)에 접근하거나 조작할 수 있다.
Document
-
웹 페이지는 일종의 문서(document)로 HTML 문서가 웹 브라우저에 로드되면
document 객체가 된다. -
document 객체는 HTML 문서의 루트 노드이다.

- 위에는 개발자 도구에서 document의 type을 출력한 모습이다.
document도 Object임을 알 수 있다.
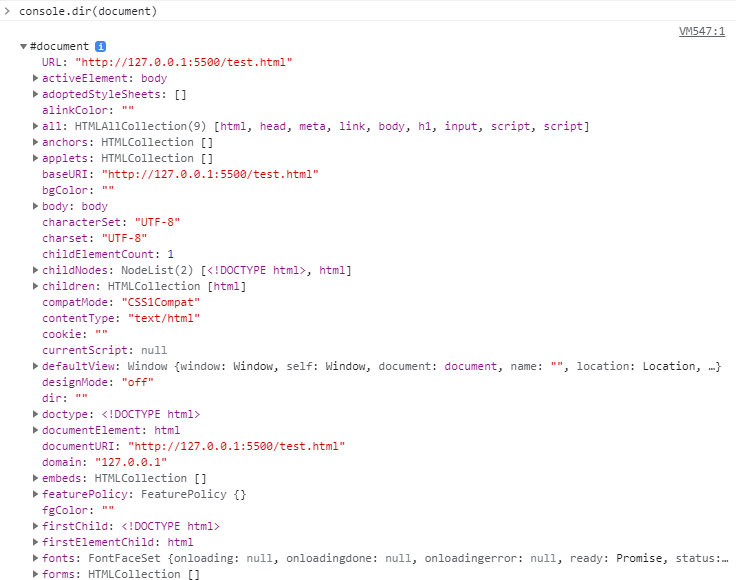
- 위에는 개발자 도구에서 console.dir(document)로 출력한 모습이며
document 객체에는 다양한 property가 있는 것을 알 수 있다.
Dom에 접근할 수 있는 method
1. getElementById ✔️
document.getElementById('id'): 주어진 문자열과 일치하는 id 속성을 가진 요소를 찾고, 이를 나타내는Element를 반환
const element = document.getElementById("id");
element.innerHTML = "바꿀 내용"; // 내용이 바뀐다.
element.style.color = "red"; // 컬러가 바뀐다.2. getElementsByClassName ✔️
document.getElementsByClassName('className'): 주어진 문자열과 일치하는 class 속성을 가진 요소들을 찾고, 이를 나타내는array (vector) of all elements를 반환 (HTMLCollection (live))
const elements = document.getElementsByClassName("class1");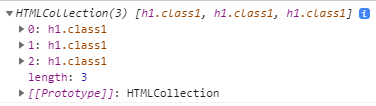
3. getElementsByTagName ✔️
document.getElementsByTagName('tagName'): 특정 태그를 가진 요소들을 찾고, 이를 나타내는array (vector) of all elements를 반환 (HTMLCollection (live))
const elements = document.getElementsByTagName("tagName");4. querySelector ✔️
document.querySelector(selector): 제공한 선택자 또는 선택자 뭉치와 일치하는 문서 내첫 번째 Element를 반환
const element = document.querySelector(".myclass");
/* document에서 "myclass"라는 클래스를 사용하는 첫 번째 요소를 반환 */
const element = document.querySelector("#myId");
/* document에서 "myId"라는 id를 사용하는 첫 번째 요소를 반환 */5. querySelectorAll ✔️
document.querySelectorAll(selector): 제공한 선택자 또는 선택자 뭉치와 일치하는 문서 내모든 Element를 반환(NodeList (non-live))
const elements = document.querySelectorAll(".class1"); 
❓ 참조
HTMLCollection과NodeList는 DOM을 조작하다보면 종종 만나게 되는 컬렉션으로 유사배열이다.차이점
- HTMLCollection은 name, index 등의 항목으로 접근 가능.
- NodeList는 index로만 접근 가능
- live and non-live
DOM에 새로운 element를 append 했을 때 live node는 알아차리고 non-live node는 알아차리지 못한다.📝코드
<ul> <li class="list-item">One</li> <li class="list-item">Two</li> <li id="three">Three</li> </ul>const liveElements = document.getElementsByClassName('list-item'); const nonLiveElements = document.querySelectorAll('.list-item'); console.log(liveElements.length); // length of 2 console.log(nonLiveElements.length); // length of 2 document.getElementById('three').className = 'list-item'; console.log(liveElements.length); // length of 3 console.log(nonLiveElements.length); // length of 2 ### ```
