Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks
- German to English translations
- 모델은 하나의 시퀀스를 다른 시퀀스로 변환하는 문제에도 적용 가능 (요약)
Introduction
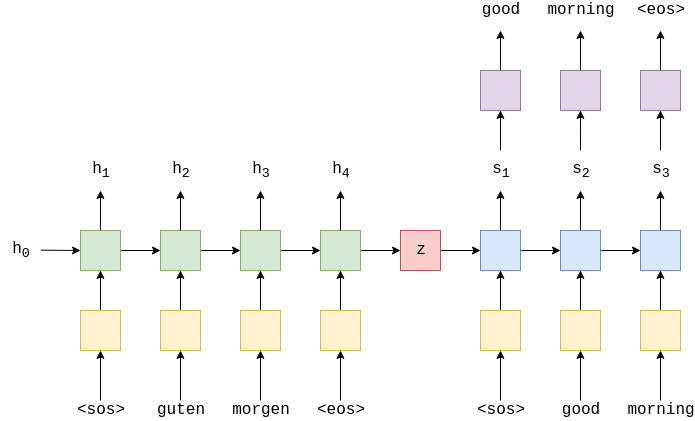
Preprocessing
- PyTorch와 torchtext를 사용하여 필요한 모든 전처리 작업을 수행
- 데이터의 토큰화를 돕기 위해 spaCy도 사용
1. Preparing Data 데이터 준비
# set the random seed
# random seed: 임의의 값을 랜덤하게 생성하나, 한번 정해진 random seed값은 다음 random seed에서도 동일하게 산출됨
SEED = 1234
random.seed(SEED) # Python의 내장 random 모듈의 시드를 설정
np.random.seed(SEED) # NumPy 라이브러리의 시드를 설정
torch.manual_seed(SEED) # PyTorch 라이브러리의 시드를 설정
torch.cuda.manual_seed(SEED) # CUDA를 사용하여 GPU 가속을 활용하는 경우, GPU에서의 시드도 설정
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True # cuDNN의 동일한 결과를 얻기 위한 옵션을 활성화2. Create the tokenizers
- Tokenizer는 문장을 구성하는 개별 토큰으로 이루어진 목록으로 변환하는 데 사용됨
- ex) "good morning!" ⇒ ["good", "morning", "!"]
# 영어와 독일어 모델을 설치하기 위해 명령 줄에서 다음 명령을 실행
python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm
python -m spacy download de_core_news_sm# SpaCy 라이브러리를 사용하여 각각 독일어(de_core_news_sm)와 영어(en_core_web_sm)에 대한 자연어 처리 모델을 로드
spacy_de = spacy.load('de_core_news_sm') # 독일어 문장을 토큰화, 형태소 분석, 구문 분석 및 개체 인식을 수행하는 데 사용됨
spacy_en = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm') # 영어 문장을 토큰화, 형태소 분석, 구문 분석 및 개체 인식을 수행하는 데 사용됨3. Create Tokenizer functions
# 독일어와 영어 텍스트를 토큰화하는 함수들
# SpaCy 모델을 사용하여 텍스트를 토큰(단어 또는 서브워드)으로 분할하는 역할
# source 문장만 단어 순서를 뒤집음
def tokenize_de(text): # 독일어 텍스트를 입력으로 받음
"""
Tokenizes German text from a string into a list of strings (tokens) and reverses it
"""
return [tok.text for tok in spacy_de.tokenizer(text)][::-1]
# spacy_de.tokenizer(text)를 사용하여 독일어 텍스트를 토큰화함
# [::-1]를 사용하여 토큰 리스트를 역순으로 변환함 이로써 독일어 텍스트의 단어 순서가 뒤집힘
# 토큰 리스트(토큰들의 문자열)를 반환함
def tokenize_en(text): # 영어 텍스트를 입력으로 받음
"""
Tokenizes English text from a string into a list of strings (tokens)
"""
return [tok.text for tok in spacy_en.tokenizer(text)]
# spacy_en.tokenizer(text)를 사용하여 영어 텍스트를 토큰화함
# 토큰 리스트(토큰들의 문자열)를 반환함# PyTorch의 torchtext 라이브러리를 사용하여 데이터 필드(Field)를 설정하는 부분을 보완
# 각 데이터 필드는 해당 언어에 대한 토큰화 함수를 설정함
SRC = Field(tokenize = tokenize_de, # 독일어 텍스트 토큰화
init_token = '<sos>', # start of sequence" 토큰을 설정
eos_token = '<eos>', # end of sequence" 토큰을 설정
lower = True) # 모든 단어를 소문자로 변환할 것인지를 설정/ True로 설정되면 데이터의 모든 단어가 소문자로 변환됨.이렇게 하면 대소문자의 차이를 무시할 수 있음
TRG = Field(tokenize = tokenize_en, # 영어 텍스트 토큰화
init_token = '<sos>', # start of sequence" 토큰을 설정
eos_token = '<eos>', # end of sequence" 토큰을 설정
lower = True) # 모든 단어를 소문자로 변환할 것인지를 설정/ True로 설정되면 데이터의 모든 단어가 소문자로 변환됨.이렇게 하면 대소문자의 차이를 무시할 수 있음4. Load the train, validation and test data
train_data, valid_data, test_data = Multi30k.splits(exts = ('.de', '.en'),
fields = (SRC, TRG))- exts 변수: 이 변수는 언어 쌍(영어-독일어)을 지정하여 인풋과 아웃풋 설정함
예제 수를 출력하여 올바르게 로드했는지 확인함
print(f"Number of training examples: {len(train_data.examples)}")
print(f"Number of validation examples: {len(valid_data.examples)}")
print(f"Number of testing examples: {len(test_data.examples)}")print(vars(train_data.examples[0]))- 훈련 데이터셋(train_data)의 첫 번째 예제를 출력하는 코드
- 출력된 내용은 딕셔너리 형태로 표시
출력된 내용:
{'src': ['.', 'büsche', 'vieler', 'nähe', 'der', 'in', 'freien', 'im', 'sind', 'männer', 'weiße', 'junge', 'zwei'], 'trg': ['two', 'young', ',', 'white', 'males', 'are', 'outside', 'near', 'many', 'bushes', '.']} - 독일어(소스) 문장의 시작에 점이 있으므로 문장이 올바르게 뒤집혔음을 확인함
5. Build the vocabulary for the source and target languages
- 어휘를 빌드하는 작업은 훈련 데이터(train_data)를 기반으로 진행
SRC.build_vocab(train_data, min_freq = 2) # SRC 필드에 대한 어휘 구축함
TRG.build_vocab(train_data, min_freq = 2) # TRG 필드에 대한 어휘 구축함- min_freq 인자: 어휘에 포함될 토큰의 최소 빈도수 지정. 설정된 빈도수 조건을 충족하지 못하는 토큰은 "unk" 토큰으로 대체 (여기서 기준은 2회)
- 이를 통해 희귀한 단어가 제한되고 모델이 더 효과적으로 학습 가능
- 어휘 구축은 모델의 입력 및 출력 데이터를 정수 시퀀스로 변환하는 데 사용됨
# 어휘 구축 작업을 통해 각 언어의 고유 토큰의 수를 출력
print(f"Unique tokens in source (de) vocabulary: {len(SRC.vocab)}")
print(f"Unique tokens in target (en) vocabulary: {len(TRG.vocab)}")- 고유 토큰의 수가 많을수록 어휘 크기가 커지며, 이는 모델의 훈련 및 추론에 필요한 계산 리소스를 늘릴 수 있음
- Unique tokens in source (de) vocabulary: 7853
Unique tokens in target (en) vocabulary: 5893
6. Create the iterators
# 디바이스(장치) 설정(CPU또는 GPU를 나타냄)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')- torch.cuda.is_available(): 현재 시스템에서 GPU를 사용할 수 있는지를 확인함
# 데이터를 미니배치로 나누는 작업
BATCH_SIZE = 128
train_iterator, valid_iterator, test_iterator = BucketIterator.splits(
(train_data, valid_data, test_data),
batch_size = BATCH_SIZE, # 미니배치의 크기 지정
device = device) # 모델이 지정한 디바이스에서 연산 수행Building the Seq2Seq Model
Encoder
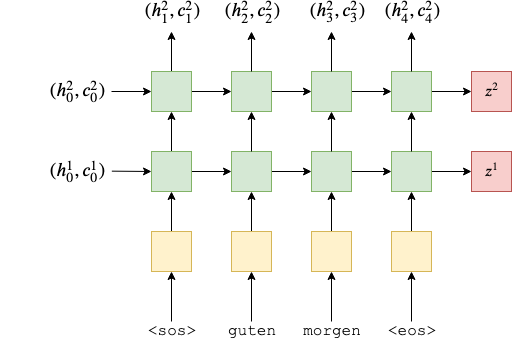
# Encoder 클래스는 PyTorch의 nn.Module 클래스를 상속
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout): # 초기화
super().__init__()
self.hid_dim = hid_dim
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_dim, emb_dim)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout = dropout)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, src):
#src = [src len, batch size]
embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(src))
#embedded = [src len, batch size, emb dim]
outputs, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedded)
#outputs = [src len, batch size, hid dim * n directions]
#hidden = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hid dim]
#cell = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hid dim]
#outputs are always from the top hidden layer
return hidden, cell-
forward 메서드: 이 메서드에서는 인코더의 순방향 계산을 수행. src 인수로 입력 문장을 받아 처리하며, 다음과 같은 단계로 동작:
-
입력 문장 src를 임베딩 레이어에 전달하여 입력 데이터를 밀집 벡터로 변환.밀집 벡터에 드롭아웃을 적용. 드롭아웃이 적용된 임베딩을 LSTM 레이어에 전달하여 숨겨진 상태(outputs), 마지막 숨겨진 상태(hidden), 그리고 마지막 셀 상태(cell)를 반환.
Decoder
- 2-layer (4 in the paper) LSTM
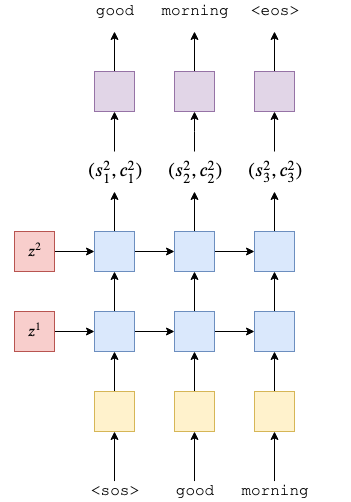
- Decoder 클래스는 PyTorch의 nn.Module 클래스를 상속
- 초기화 및 순방향(forward) 메서드로 구성됨
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, output_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout): # 초기화
super().__init__()
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.hid_dim = hid_dim
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_dim, emb_dim)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout = dropout)
self.fc_out = nn.Linear(hid_dim, output_dim)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, input, hidden, cell): # 디코더의 순방향 계산을 수행
#input = [batch size] # 현재 시간 단계의 입력
#hidden = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hid dim]
#cell = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hid dim]
# hidden&cell: 인코더에서 받아온 숨겨진 상태와 셀 상태
#n directions in the decoder will both always be 1, therefore:
#hidden = [n layers, batch size, hid dim]
#context = [n layers, batch size, hid dim]
input = input.unsqueeze(0) # 먼저 크기 조정함
#input = [1, batch size]
embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(input))
#embedded = [1, batch size, emb dim]
output, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedded, (hidden, cell))
#output = [seq len, batch size, hid dim * n directions]
#hidden = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hid dim]
#cell = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hid dim]
#seq len and n directions will always be 1 in the decoder, therefore:
#output = [1, batch size, hid dim]
#hidden = [n layers, batch size, hid dim]
#cell = [n layers, batch size, hid dim]
prediction = self.fc_out(output.squeeze(0))
#prediction = [batch size, output dim]
return prediction, hidden, cell
Seq2Seq
- 입력/소스 문장을 받음
- 인코더를 사용하여 컨텍스트 벡터를 생성
- 디코더를 사용하여 예측된 출력/대상 문장을 생성
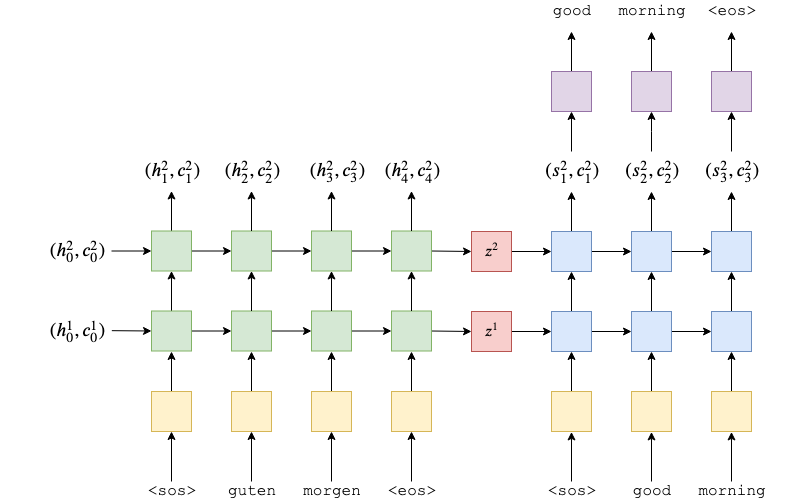
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, device): # 초기화
super().__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
self.device = device
assert encoder.hid_dim == decoder.hid_dim, \
"Hidden dimensions of encoder and decoder must be equal!"
# 인코더와 디코더의 숨겨진 차원 (hidden dimension)이 동일한지 확인하는 부분
assert encoder.n_layers == decoder.n_layers, \
"Encoder and decoder must have equal number of layers!"
# 인코더와 디코더의 RNN 레이어 수 (n_layers)가 동일한지 확인하는 부분
def forward(self, src, trg, teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5):
#src = [src len, batch size]
#trg = [trg len, batch size]
batch_size = trg.shape[1]
trg_len = trg.shape[0]
trg_vocab_size = self.decoder.output_dim
outputs = torch.zeros(trg_len, batch_size, trg_vocab_size).to(self.device)
# outputs 텐서는 디코더의 출력을 저장하기 위한 텐서로 초기화됨. 이 텐서는 device로 이동
hidden, cell = self.encoder(src)
input = trg[0,:] # 시작<SOS>
for t in range(1, trg_len):
output, hidden, cell = self.decoder(input, hidden, cell)
outputs[t] = output
teacher_force = random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio
top1 = output.argmax(1)
input = trg[t] if teacher_force else top1
return outputs- teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5: 이전 시간 단계의 예측 결과가 아닌 실제 대상 문장의 다음 토큰을 입력으로 사용
- outputs는 모든 시간 단계에서 디코더의 출력을 포함
- forward 함수에서는 Seq2Seq 모델의 순방향 계산을 정의함. 주어진 소스 문장과 대상 문장에 대한 예측값을 생성하는데, teaching_forcing_ratio를 사용하는 확률에 따라 입력을 선택함. 결과는 디코더의 출력값을 반환
Training the Seq2Seq Model
1. Initialize model
INPUT_DIM = len(SRC.vocab)
OUTPUT_DIM = len(TRG.vocab)
ENC_EMB_DIM = 256
DEC_EMB_DIM = 256
HID_DIM = 512
N_LAYERS = 2
ENC_DROPOUT = 0.5
DEC_DROPOUT = 0.5
enc = Encoder(INPUT_DIM, ENC_EMB_DIM, HID_DIM, N_LAYERS, ENC_DROPOUT)
dec = Decoder(OUTPUT_DIM, DEC_EMB_DIM, HID_DIM, N_LAYERS, DEC_DROPOUT)
model = Seq2Seq(enc, dec, device).to(device)- 하이퍼파라미터와 모델 자체를 초기화함. Seq2Seq 모델을 초기화하고 GPU 장치에 올림
2. Initializing the weights of model
def init_weights(m):
for name, param in m.named_parameters():
nn.init.uniform_(param.data, -0.08, 0.08)
model.apply(init_weights)- 논문에서 모든 가중치를 (-0.08, 0.08)의 균일 분포에서 초기화한다고 했기에 동일한 값 사이에서 가중치를 초기화함
3. Define a function
- 모델의 학습 가능한 매개변수 수를 계산하는 함수를 정의
def count_parameters(model):
return sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
print(f'The model has {count_parameters(model):,} trainable parameters')- model.parameters()로 모델의 모든 매개변수를 가져와서 requires_grad가 True인 매개변수들의 개수를 모두 합산하여 반환
4. Define optimizer
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters())- Adam optimizer 사용
5. Define loss function
- CrossEntropyLoss 함수는 로그 소프트맥스와 예측에 대한 음의 로그 가능도를 모두 계산함
TRG_PAD_IDX = TRG.vocab.stoi[TRG.pad_token]
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index = TRG_PAD_IDX)- 이 손실 함수는 각 토큰에 대한 평균 손실을 계산하지만 ignore_index인수로 pad 토큰의 인덱스를 전달하여 대상 토큰이 패딩 토큰일 때는 손실을 무시하여 모델이 패딩 토큰에 대한 예측을 수행하는 것을 피하도록 도움
6. Define training loop
def train(model, iterator, optimizer, criterion, clip): # 모델 학습
model.train() # 모델을 학습 모드로 설정
epoch_loss = 0 # 초기화하여 에포크 동안의 총 손실을 추적
for i, batch in enumerate(iterator): # iterator를 통해 미니배치를 순회
src = batch.src # 소스문장
trg = batch.trg # 대상문장
optimizer.zero_grad() # 이전 미니배치에서 계산된 그래디언트를 초기화
# 각 미니배치에서 새로운 그래디언트를 계산하고 파라미터를 업데이트할 수 있습니다.
output = model(src, trg) # 모델에 src와 trg를 전달하여 출력을 얻음
#trg = [trg len, batch size]
#output = [trg len, batch size, output dim]
output_dim = output.shape[-1] # 출력의 차원 정보를 가져와 output_dim에 저장
# output 텐서의 마지막 차원의 크기를 가져와서 output_dim 변수에 할당하면 모델의 출력 차원을 동적으로 처리
output = output[1:].view(-1, output_dim) # output 텐서를 [1:]로 슬라이싱하고 .view(-1, output_dim)을 통해 2차원 형태로 변환
trg = trg[1:].view(-1) # trg도 [1:]로 슬라이싱하고 .view(-1)을 통해 1차원 형태로 변환
#trg = [(trg len - 1) * batch size]
#output = [(trg len - 1) * batch size, output dim]
loss = criterion(output, trg) # loss 계산/이는 크로스 엔트로피 손실
loss.backward() # 역전파 수행하여 그래디언트 계산
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), clip) # 그래디언트 폭발을 방지하기 위해 그래디언트 클리핑을 수행
optimizer.step() # 옵티마이저를 사용하여 모델 파라미터를 업데이트
epoch_loss += loss.item() # 현재 미니배치에서 계산한 손실을 epoch_loss에 누적
return epoch_loss / len(iterator) # 학습이 끝나면, epoch_loss를 전체 미니배치 수로 나눈 평균 손실을 계산하고 반환- 모델을 학습 모드로 설정하고 에포크 동안의 총 손실을 추적
- 미니배치에서 소스와 대상 문장을 가져와 그래디언트 초기화 후 모델에 입력하여 출력을 얻음
- 출력과 대상을 손실 함수를 사용하여 비교하여 손실을 계산
- 역전파를 수행하여 그래디언트를 계산하고 그래디언트 클리핑을 수행
- 옵티마이저를 사용하여 모델 파라미터를 업데이트
- 각 미니배치에서 계산한 손실을 누적하고 에포크가 끝나면 평균 손실을 반환
7. Evaluation loop
- 훈련 루프와 유사하지만, 모델 파라미터를 업데이트하지 않으므로 옵티마이저나 클립 값은 전달하지 않아도 됨
def evaluate(model, iterator, criterion):
model.eval() # 모델을 평가 모드로 설정/ 드롭아웃과 배치 정규화 등의 regularization 기법이 비활성화됨
epoch_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad(): # 모든 작업을 no gradient 모드에서 수행하여 gradient 계산을 비활성화
# 이러면 메모리 사용 줄어들고 연산 빨라짐
for i, batch in enumerate(iterator):
src = batch.src
trg = batch.trg
output = model(src, trg, 0) # teacher forcing 끔
#trg = [trg len, batch size]
#output = [trg len, batch size, output dim]
output_dim = output.shape[-1]
output = output[1:].view(-1, output_dim)
trg = trg[1:].view(-1)
#trg = [(trg len - 1) * batch size]
#output = [(trg len - 1) * batch size, output dim]
loss = criterion(output, trg)
epoch_loss += loss.item()
return epoch_loss / len(iterator)8. Create a function epoch takes
- 훈련 진행 상황을 추적하고 훈련이 완료되기까지 얼마나 걸릴지 추정
def epoch_time(start_time, end_time):
elapsed_time = end_time - start_time
elapsed_mins = int(elapsed_time / 60)
elapsed_secs = int(elapsed_time - (elapsed_mins * 60))
return elapsed_mins, elapsed_secs- 두 시간을 입력으로 받아, 그 사이의 경과 시간을 분과 초로 계산하여 반환하여 각 epoch의 소요 시간을 측정
9. Training model
N_EPOCHS = 10
CLIP = 1
best_valid_loss = float('inf')
for epoch in range(N_EPOCHS):
start_time = time.time()
train_loss = train(model, train_iterator, optimizer, criterion, CLIP)
valid_loss = evaluate(model, valid_iterator, criterion)
end_time = time.time()
epoch_mins, epoch_secs = epoch_time(start_time, end_time)
if valid_loss < best_valid_loss:
best_valid_loss = valid_loss
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'tut1-model.pt')
print(f'Epoch: {epoch+1:02} | Time: {epoch_mins}m {epoch_secs}s')
print(f'\tTrain Loss: {train_loss:.3f} | Train PPL: {math.exp(train_loss):7.3f}')
print(f'\t Val. Loss: {valid_loss:.3f} | Val. PPL: {math.exp(valid_loss):7.3f}')- 주어진 epoch 수 동안 모델을 훈련. 매 epoch마다 훈련 및 검증 데이터에 대한 손실을 계산하고, 최상의 검증 손실을 기록한 경우 모델 상태를 저장함. epoch마다 현재 상태와 손실을 출력하여 훈련 진행을 모니터링
- 가장 좋은 검증 손실을 가진 상태에서의 모델 파라미터 (state_dict)를 불러와서 테스트 데이터셋에 모델을 실행
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('tut1-model.pt'))
test_loss = evaluate(model, test_iterator, criterion)
print(f'| Test Loss: {test_loss:.3f} | Test PPL: {math.exp(test_loss):7.3f} |')Result
| Test Loss: 3.951 | Test PPL: 52.001 |
- 낮은 손실 및 퍼플렉서티 값은 모델의 높은 품질을 나타냄
BLEU SCORE
- Bilingual Evaluation Understudy
from torchtext.data.metrics import bleu_score
# data :평가하려는 데이터셋
def calculate_bleu(data, src_field, trg_field, model, device, max_len = 50):
- src_field: 소스 언어 데이터 필드 (예: 영어)
- trg_field: 대상 언어 데이터 필드 (예: 프랑스어)
trgs = []
pred_trgs = []
for datum in data:
src = vars(datum)['src']
trg = vars(datum)['trg']
pred_trg, _ = translate_sentence(src, src_field, trg_field, model, device, max_len)
# model : 평가할 번역 모델
# max_len : 최대 번역 길이
#cut off <eos> token
pred_trg = pred_trg[:-1]
pred_trgs.append(pred_trg)
trgs.append([trg])
return bleu_score(pred_trgs, trgs)- 주어진 데이터셋에 대해 번역을 수행하고, 번역 결과와 원본 번역을 BLEU 메트릭을 사용하여 비교한다음 BLEU 점수를 계산하여 반환
bleu_score = calculate_bleu(test_data, SRC, TRG, model, device)
print(f'BLEU score = {bleu_score*100:.2f}')- calculate_bleu 함수를 사용하여 테스트 데이터에 대한 BLEU 점수를 계산하고, 그 값을 퍼센트로 출력함. 이를 통해 모델의 번역 품질을 수치화하여 확인할 수 있음.
