🔄 I/O-Bound vs CPU-Bound Processes
🧩 Process Types
- I/O-bound process: Spends more time performing I/O operations than computations(frequent I/O bursts)
- CPU-bound process: Spends more time performing computations with minimal I/O(frequent CPU busrts)
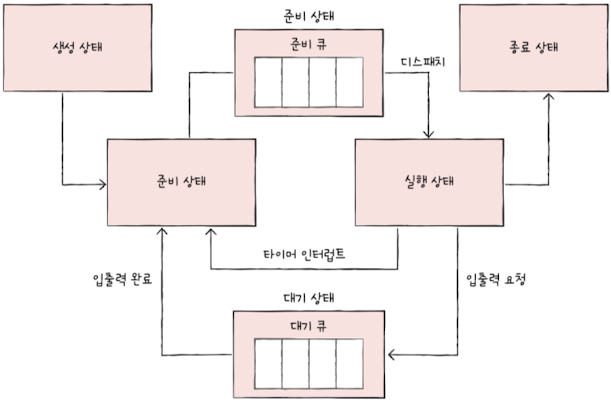
Most processes alternate between running and blocked states
🧠 Process Scheduling
OS determines the priority of each process and stores it in Process Control Block(PCB)
- I/O bound process is given higher priority to keep I/O devices busy and reduce system idle time.
- However, checking every PCB to find the highest-priority process can be inefficient.
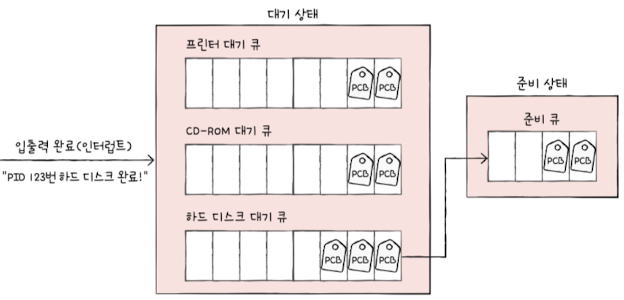
🧷 Scheduling Queues
To manage process flow, the OS maintains several queues:
- Ready queue: processes waiting to be assigned to the CPU
- Waiting queue: processes waiting for I/O operations to complete(blocked state)
⚖️ CPU Scheduling Types
🏃♂️ Preemptive Scheduling:
- OS can interrupt and reassign the CPU from a running process to another
- Increase responsiveness but introduces overhead due to frequent context switching
🧘 Non-Preemptive Scheduling: A running process keeps the CPU until it completes, becomes Blocked, or Ready
