🖥️ Operating System (OS)
: A program that runs in the kernel space of memory. Its primary role is to manage and allocate available system resources to user applications
🧩 Resources
: Resources are essential components required for running programs. They include:
- CPU
- Memory
- Secondary memory
- I/O devices
👤 User Interface
The OS provides user interfaces(not part of the kernel space) to interace with the system
- GUI(Graphic User Interface)
- CLI(Command Line Interface)
⚙️ Dual Mode: User Mode & Kernel Mode
To protect critical hardware access and system functions, modern computers operates in two modes:
- Kernel Mode
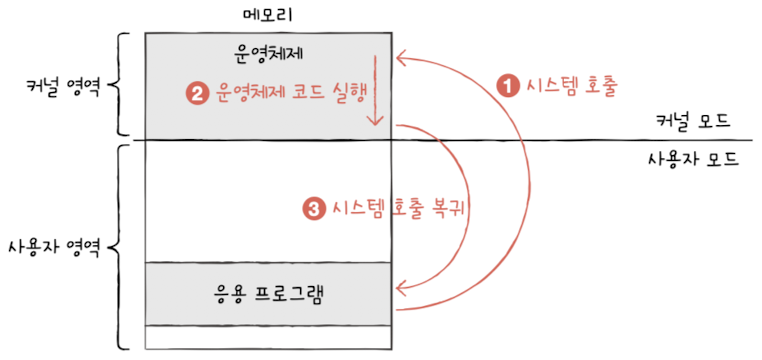
: The OS kernel runs here and has full access to the hardwareSystem call: software interrupt occured by applications to run interrupt code in kernel space
- User Mode: Applications run in this mode. They can't access directly hardware or priviledged instructions
💡 When a program needs system-level access(e.g. I/O, memory), it uses a system call, which triggers a software interrupt to transition into kernel mode.
📋 Main Roles of the Operating System
- Resource Management & Allocation
- CPU: Uses scheduling algorithms in the kernel to assign CPU time to processes
- Memory: Allocate sapce in RAM for running programs
- I/O devices: Handles requests via Interrupt service routine
- File system
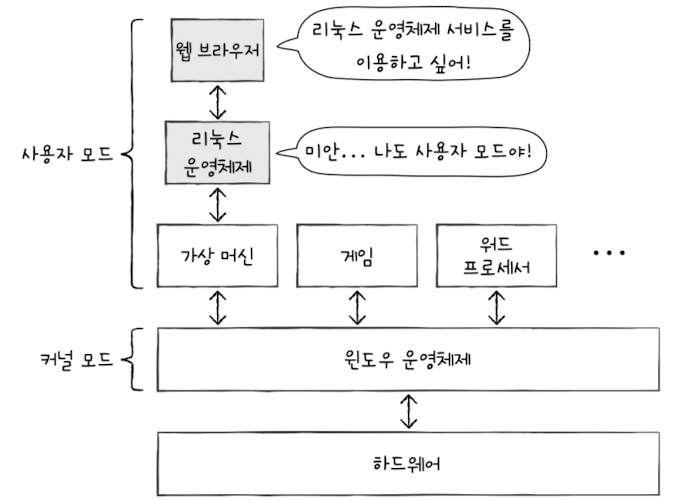
🖥️ Virtual Machine & Hypervisor Mode
- A Virtual machine(VM) is a program that runs in user mode, but it has its own operating system (guest OS)
- VMs run in user mode, so they can't access priviledged instructions directly
- To solve this, CPUs introduces a special mode called Hypervisor Mode
- Hosted Hypervisor: placed between the VM and the host OS
The hypervisor intercepts any system-level requests from the VM and either:
- Directly accesses hardware (in bare-metal hypervisors), or
- Requests the host OS to perform the priviledged operation