💥 Deadlock
A deadlock occurs when two or more processes are waiting for each other's resources indefinitely, causing a system halt
How does resource-allocation graph look like if it has a deadlock
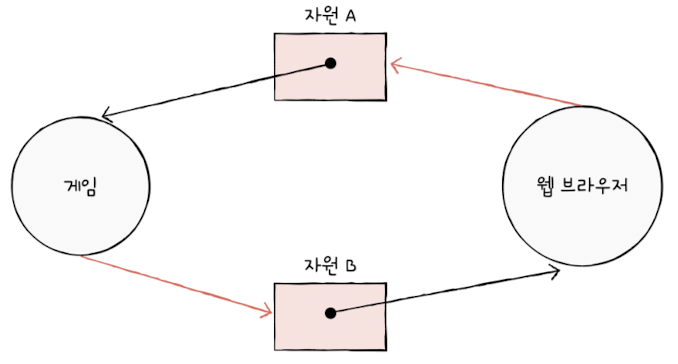
Circle = Process
Square = Resource
Arrow from process to resource = process is requesting the resource
Arrow from resource to process = resource is allocated to the process
🧠 Key Insight:
If the graph contains a cycle, deadlock may occur.
Conditions that cause Deadlock
Deadlock can happen only if all four of the following conditions hold simultaneously:
1. Mutual Exclusion: Resources cannot be shared — only one process can use at a time.
2. Hold and Wait: A process is holding at least one resource and waiting to acquire more.
3. Non-preemptive: A resource can’t be forcibly taken from a process holding it.
4. Circular Wait: A set of processes are waiting for each other in a circular chain
If even one of these is broken, deadlock can be prevented
🛠 How Does the OS Handle Deadlocks?
- 🔒 Prevention: Break one of the 4 necessary conditions
- Mutual exclusion: hard to eliminate it in real life
- Hold and Wait: Distribute all or none resources to a process
=> This can cause low resource utilization and risk of starvation - Preemptive: CPU can be preemptive, but some resources such as printers can't be
- Circular wait: Impose strict resource ordering to prevent cycles
- ⚠️ Avoidance: Ensure the system stays in a safe state
- Distribute resources considering the number of resources
- OS distribute resouces to stay safe status
- 🧹 Detection & Recovery
- Preemptive: take resources from other process and give to one process until deadlock solves
