🧠 What computer understand?
Computer only understand binary information -> 0s and 1s
Binary information is divided by two types
- Data
- Instructions
Data vs. Instructions
Data: 'content' that computer can process
ex) images, photos, number, text, etc
Instructions: tell computers what to do
💻 4 main parts of the computer
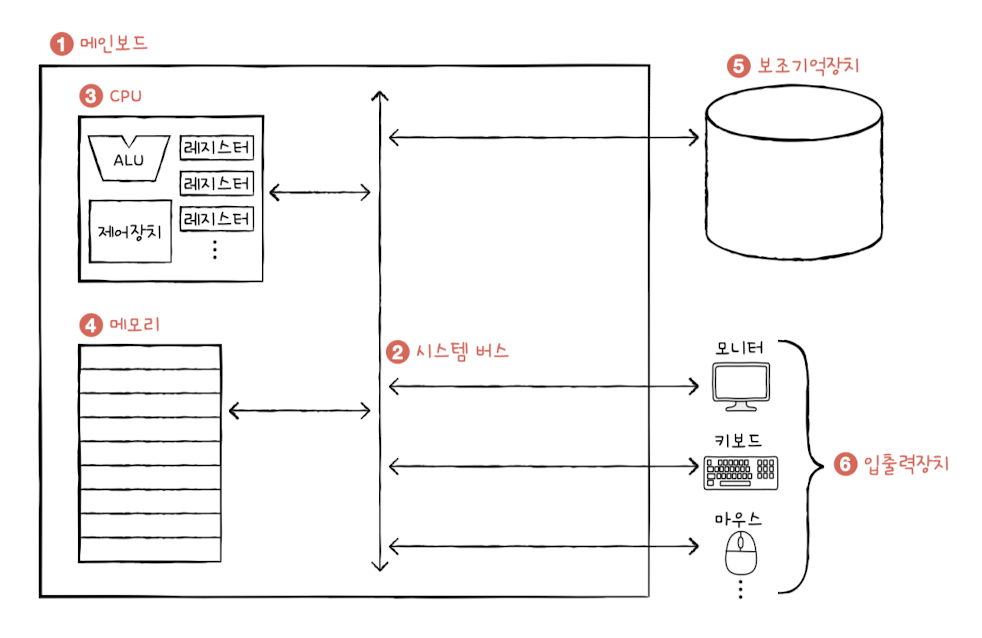
1) Memory: Storage space for both data and instructions
- To run a program, data and instructions must be stored in a memory
- Address is unique identifier for a memory location
2) CPU: Read, Interperate, and execute instructions
- ALU(Arithmetic Logic): Calculator
- Register: stores data temporarily to run the process
- CU(Control Unit): tells all parts of the computer what to do and when to do it based on the instruction it interprets
CU controls how the rest of the computer works
ex) telling the memory to read or write data
ex) telling ALU to perform a calcuation
ex) CU interprets instructions and sends signals
ex) CU send a read signal to memory to fetch data from memory
ex) CU send a write signal to store data in memory
3) Secondary Memory: Stores data even after the computer is turned off
- Main memory(RAM) loses its data after the computer shuts down, so we need secondary memory to preserve the work that users have done
- ex) Hard Disk, SSD, USB, CD-ROM
4) I/O devices: Devices that are located outside the computer but are connected to it and exchange data with computer
ex) keyboard, mouse, printer, etc.
Mother board: All components are installed in the motherboard and exchange data and instructions through the system bus
Four types: address bus, control bus, and data bus(data and instructions)
EX) CPU fetches an instruction from memory
1) CPU uses address bus to point to the instruction address
2) CU in CPU uses control bus to send 'read' signal
3) the instruction is transferred via the data bus
