1. Polynomial.h 코드
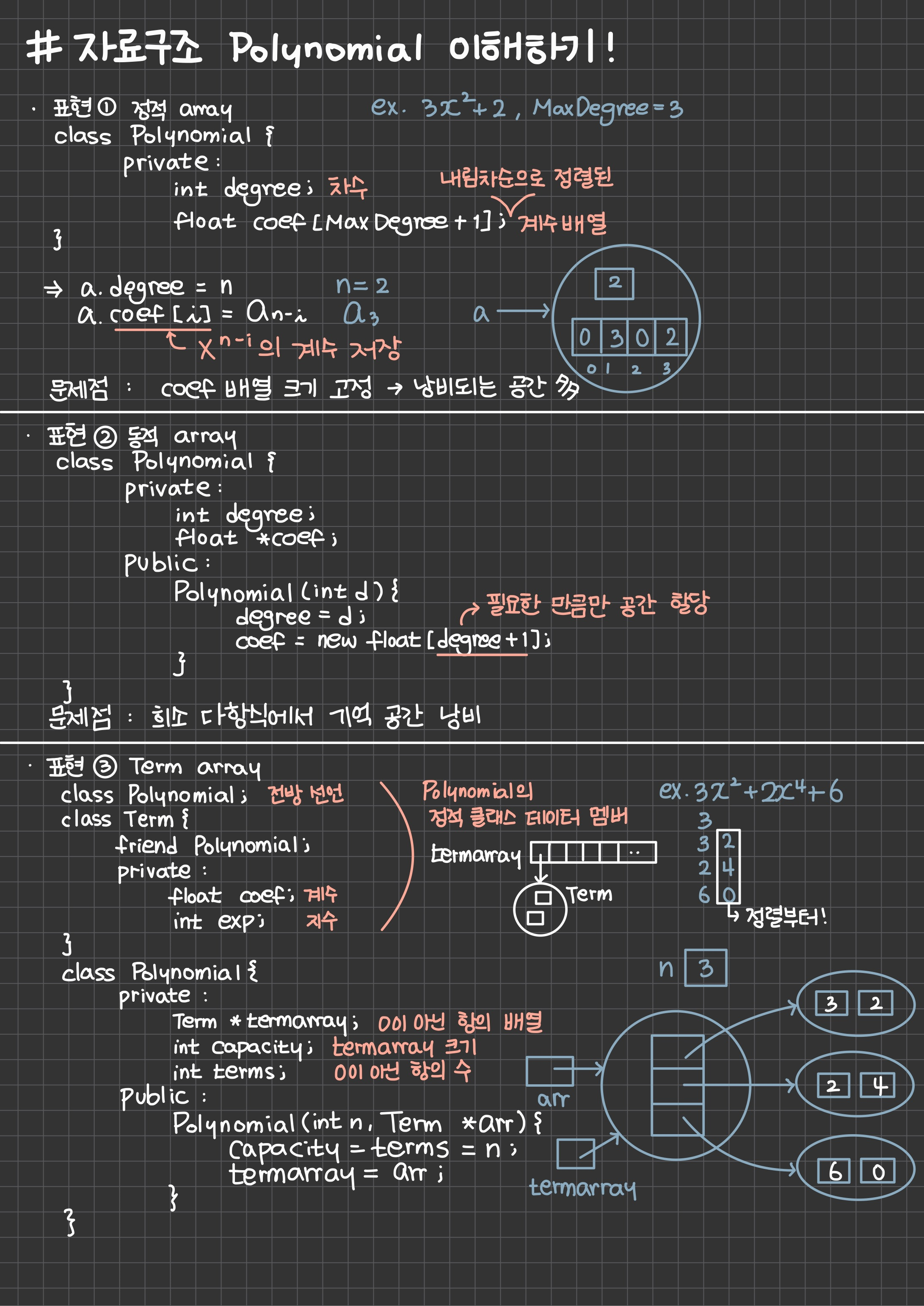
class Polynomial;
class Term {
friend Polynomial;
private:
int coef; //계수
int exp; //차수
};
class Polynomial {
private:
Term *termArray; //0이 아닌 항의 배열
int capacity; //termArray의 크기
int terms; //0이 아닌 항의 수
public:
Polynomial () {
terms = 0;
capacity = 0;
}
void LoadPolynomial(std::string& filename);
//인자로 받은 파일명으로 파일에 있는 다항식을 읽어서 멤버 변수에 저장
void NewTerm(const int theCoef, const int theExp);
//공간최적화를 위해 배열의 크기를 늘릴 때 사용
void SortPolynomial();
//다항식 내림차순 정렬
void PrintPolynomial();
//다항식을 지수의 내림차순으로 출력
void add(Polynomial a, Polynomial b);
//계수가 같은 항들의 차수를 더함.
};2. Polynomial.cpp 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include "polynomial.h"
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void Polynomial::SortPolynomial() {
int tmp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < capacity-1; i++)
for (int j = capacity-1; j > i; j--) {
if (termArray[j-1].exp < termArray[j].exp){
swap(termArray[j-1], termArray[j]);
}
}
return;
}
void Polynomial::LoadPolynomial(std::string& filename) {
ifstream in;
in.open(filename);
if (!in.is_open()) {
cerr << "해당 파일이 없습니다." << endl;
return;
}
in >> capacity;;
termArray = new Term[capacity];
int i = 0;
while (!in.eof()) {
in >> termArray[i].coef;
in >> termArray[i].exp;
i++;
}
in.close();
SortPolynomial();
return;
}
void Polynomial::NewTerm(const int theCoef, const int theExp){
termArray[terms].coef = theCoef;
termArray[terms++].exp = theExp;
}
void Polynomial::add(Polynomial a, Polynomial b) {
capacity = a.capacity + b.capacity;
termArray = new Term[capacity];
int aPos = 0, bPos = 0;
while ((aPos < a.capacity) && (bPos < b.capacity)) {
if (a.termArray[aPos].exp == b.termArray[bPos].exp) {
int t = a.termArray[aPos].coef + b.termArray[bPos].coef;
if(t) NewTerm(t, a.termArray[aPos].exp);
aPos++;
bPos++;
}
else if (a.termArray[aPos].exp < b.termArray[bPos].exp) {
NewTerm(b.termArray[bPos].coef, b.termArray[bPos].exp);
bPos++;
}
else {
NewTerm(a.termArray[aPos].coef, a.termArray[aPos].exp);
aPos++;
}
}
for (; aPos < a.capacity; aPos++)
NewTerm(a.termArray[aPos].coef, a.termArray[aPos].exp);
for (; bPos < b.capacity; bPos++)
NewTerm(b.termArray[bPos].coef, b.termArray[bPos].exp);
return;
}
void Polynomial::PrintPolynomial() {
for(int i = 0; i < terms; i++) {
cout << termArray[i].coef << " " << termArray[i].exp;
if (i == (terms-1))
return;
else
cout << ""<< endl;
}
return;
}
int main(void) {
Polynomial p1, p2, p3;
string file1, file2;
getline(cin, file1);
p1.LoadPolynomial(file1);
getline(cin, file2);
p2.LoadPolynomial(file2);
p3.add(p1, p2);
p3.PrintPolynomial();
return 0;
}3. Polynomial 코드를 이해하기 위한 끄적