JDBC API.
Java DataBase Connectivity의 약자로 JDBC는 자바 언어로 데이터베이스 프로그래밍을 하기 위한 라이브러리이다. JDBC는 다양한 클래스와 인터페이스로 구성된 패키지 java.sql와 javax.sql로 구성되어있음.
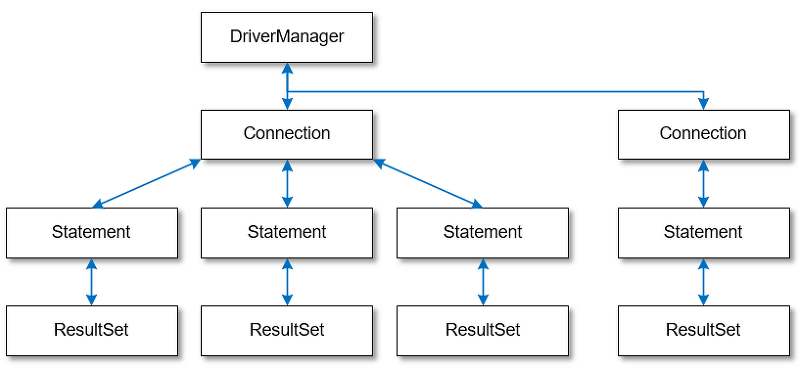
JDBC API는 DB에 종속적이진 않으나 JDBC DRIVER Manager는 각 DBMS 회사에서 제공하는 라이브러리 압축파일이다. MySQL 데이터베이스관리시스템을 사용하지만 오라클을 사용한다면 오라클용 JDBC 드라이버가 필요.
MYSQL용 Driver
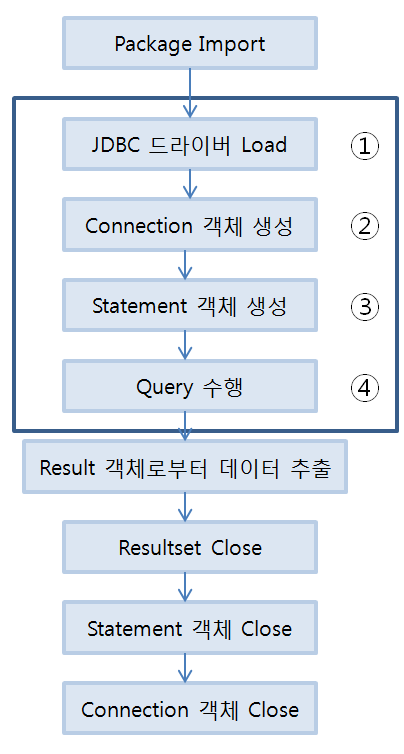
전체적인 구조
데이터베이스를 연결 -> SQL 문을 질의-> SQL 문의 결과를 처리
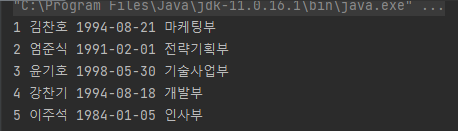
간단한 코드 실행 예시
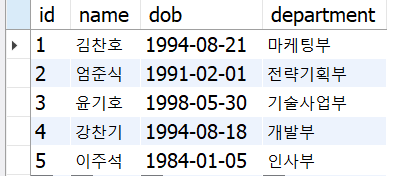
EMP 테이블
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/webshop?useSSL=false";
String user = "root";
String password = "test1234";
// DB 연결 객체..
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null; // select 문 사용시 결과 주입.
try {
// URL , USER, PW순..
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
url,user,password);
String sql = "SELECT * FROM emp";
// 2. 쿼리 수행을 위한 PreparedStatement 객체 생성
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3. executeQuery: 쿼리 실행 후
// ResultSet: DB 레코드 ResultSet에 객체에 담김
rs = pstmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){ // 결과 다음줄이 있으면 계속반복
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String dob = rs.getString("dob");
String dep = rs.getString("department");
System.out.println(id+ " " + name +" " + dob +" " + dep);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
try {
conn.close();
pstmt.close();
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}JAVA 클래스와 SQL 연동
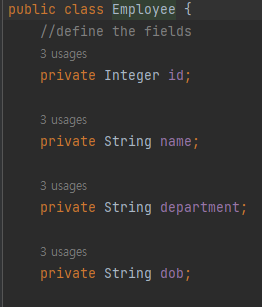
Employee Entity
public class Employee {
//define the fields
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String department;
private String dob;
}EmployeeDAO Interface
public interface EmployeeDAO {
// 직원 전체목록
List<Employee> getAll();
// 직원한명 가져오기(id필요)
Employee get(int id);
// 직원저장
boolean save(Employee employee);
//직원삭제
boolean delete(int id);
//직원 업데이트
boolean update(Employee employee);
}EmployeeDAOImpl
전체조회, 조회, 저장, 갱신, 삭제
public class EmployeeDATOImpl implements EmployeeDAO {
Connection connection = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null; // SELECT문 결과...
Statement statement = null; // SQL문 객체 .
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; // SQL문 객체(?를 변수처럼 넣을수 있따.)
@Override
public List<Employee> getAll() {
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>();
Employee employee = null;
try {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM emp";
connection = DBConnectionUtil.openConnection(); // DB연결객체
statement = connection.createStatement(); // SQL문 실행객체
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); // SQL실행 결과를 rs에 저장.
while (resultSet.next()) {
employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
employee.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
employee.setDob(resultSet.getString("dob"));
employee.setDepartment(resultSet.getString("department"));
list.add(employee);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
@Override
public Employee get(int id) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
try {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM emp WHERE id=" + id;
connection = DBConnectionUtil.openConnection(); // DB연결객체
statement = connection.createStatement(); // SQL문 실행객체
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); // SQL실행 결과를 rs에 저장.
if (resultSet.next()) {
employee.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
employee.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
employee.setDob(resultSet.getString("dob"));
employee.setDepartment(resultSet.getString("department"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return employee;
}
@Override
public boolean save(Employee e) {
boolean flag = false;
try {
// String sql = "INSERT INTO emp VALUES("
// +e.getName()+","+e.getDob()+","+e.getDepartment()+")";
String sql = "INSERT INTO emp(name,dob,department) VALUES (?,?,?)";
connection = DBConnectionUtil.openConnection(); // DB연결객체
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, e.getName());
preparedStatement.setString(2, e.getDob());
preparedStatement.setString(3, e.getDepartment());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 저장 수정 삭제!!
flag = true;
} catch (SQLException sqlException) {
sqlException.printStackTrace();
}
return flag;
}
@Override
public boolean delete(int id) {
boolean flag = false;
try {
// String sql = "DELETE FROM EMP WHERE ID=?"+id;
String sql = "DELETE FROM emp WHERE ID=?";
connection = DBConnectionUtil.openConnection(); // DB연결객체
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, id);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 저장 수정 삭제!!
flag = true;
} catch (SQLException sqlException) {
sqlException.printStackTrace();
}
return flag;
}
@Override
public boolean update(Employee employee) {
boolean flag = false;
try {
String sql = "UPDATE emp SET name =?, department=?, dob=? WHERE id=?";
connection = DBConnectionUtil.openConnection(); // DB연결객체
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, employee.getName());
preparedStatement.setString(2, employee.getDepartment());
preparedStatement.setString(3, employee.getDob());
preparedStatement.setInt(4, employee.getId());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 저장 수정 삭제!!
flag = true;
} catch (SQLException sqlException) {
sqlException.printStackTrace();
}
return flag;
}
}
- 전체 조회는 정적 SQL이여서 Statement 객체 사용.
- 저장, 수정, 삭제와 같이 (id, 객체정보) 동적 sql일 경우 PreparedStatement사용
-> why? 정적 사용시... 작성시 실수 및 코드 가독성이 저하됨.
String sql = "INSERT INTO emp VALUES(" +e.getName()+","+e.getDob()+","+e.getDepartment()+")";
다만 순서는 0번부터가 아니라 1번째부터 넣어야 된다.
String sql = "INSERT INTO emp(name,dob,department) VALUES (?,?,?)";
connection = DBConnectionUtil.openConnection(); // DB연결객체
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, e.getName());
preparedStatement.setString(2, e.getDob());
preparedStatement.setString(3, e.getDepartment());
🎇 TIP
- 쿼리를 수행할 때 동적으로 할당해야 하는 값이 있으면 PreparedStatement 객체를 사용하고, 동적으로 할당할 필요가 없으면 Statement 객체를 사용한다.
- 쿼리의 결과가 있으면 executeQuery() 메서드를 호출하여 ResultSet 객체에 담고, 쿼리의 결과가 없으면 executeUpdate() 메서드를 호출하여 int형 변수에 결과 값을 할당한다.
| execute 종류 | 반환타입 | 사용용도 |
|---|---|---|
| executeQuery() | 수행결과로 ResultSet 객체의 값을 반환 | SELECT 구문을 수행할 때 사용되는 함수 |
| executeUpdate() | 수행결과로 Int 타입의 값을 반환 (INSERT / DELETE / UPDATE 관련 구문에서는 반영된 레코드의 건수를 반환, CREATE / DROP 관련 구문에서는 -1 을 반환 | SELECT 구문을 제외한 다른 구문을 수행할 때 사용되는 함수 |
-> CREATE / DROP 관련 구문에서는 -1 을 반환)
중간 중간 하다가 String SQL ='', 들어가는 SQL 문법을 틀렸지만 이에 대한 오류를 발견하기가 어려웠음. 또한 SQL 연결하기 위해 CONNECTION 설정 및 STATE설정이 꽤나 반복적이고 실수하기가 쉽다고 생각함.. 그래서 SQL Mapper를 사용하는 MyBatis, ORM을 사용하는 JPA에 대한 사용을 충분히 고려할 만하다고 생각한다.