Inference Optimization(DL) - Efficient Deep Learing: A survey on Making Deep Learning Models smaller, Faster, and Better
Inference Optimization은 Quantization과 같이 중요한 분야이다. 최근엔 AI Application이 주목을 받고 있고 이에 따라 Optimization이 각광을 받고 있는 현실이다.
On-Device 환경에서 Inference Optimization은 반드시 해야하는 과정이며, 이에 따라 survey를 읽으며 Insight를 얻고자 한다.
Survey : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.08962
해당 survey는 2021년도에 나온 survey이며, Knowledge Distillation, Purining 등 optimization 뿐만 아니라 Quntization도 다루고 있으며, On-Device에서의 Inference Optimization의 로드맵이 될 수 있다고 생각한다.
서베이나 논문의 경우에는 최대한 번역기를 사용하지 않으며, 읽고 해석한대로 내용을 작성했다. 그 이유는 영어 공부를 하기 위함이라, 틀린 내용도 많다.
However, with the progressive improvements in deep learning models, their number of parameters, latency, resources required to train, etc.
Optimization의 중요성을 한 문장으로 표현하면 위와 같다. DL이 발전할수록 model의 Depth는 깊어지고 이에 따라 Parameter도 기하급수적으로 증가한다. 수 많은 파라미터와 학습에 요구되는 하드웨어의 스펙, 모델의 크기에 따라 발생하는 지연 시간(latency)등에 의해 Optimization 분야가 중요해지기 시작한다.
We peresent and motivate the problem of efficieny in deep learning, followed by a thorough survey of the five core areas of model efficiency (spanning modeling techniques, infrastructure, and hardware) and the seminal work there.
저자는 DL의 효율성 문제에 대해 5가지의 핵심적인 방법론들과 관련 학술 정보를 해당 서베이에 담아냈다고 한다. 그러니 위와 같은 Optimization에 대해 처음 공부하는 사람들에겐 해당 서베이를 로드맵으로 잡고 각 task에 필요한 기법들을 적용하고 해당 분야들에 대해 깊게 공부해보는 것이 좋아보인다.
1. INTRODUCTION
첫 번째, 두번째, 세번 째 문단까지 대부분 DL의 history를 나열한다. 결국엔 저자가 하고 싶은 말은 다음과 같다.
While these models perform well on the tasks they are trained on, they might not necessarily be effcient enough for direct deployment in the real world.
수 많은 파라미터로 학습된 모델들은 학습 단에서는 매우 잘 수행하겠지만 즉시 배포(효율적으로)되어야 하는 환경에서는 불필요하다. (*실제로 최근 기업들은 큰 모델을 사용하지 않고 optimization을 통해 latency를 줄이는 작업을 하고 있다. 학습 단에서는 fine-tuning을 통해 많은 train 시간을 단축하고 이렇게 학습된 모델을 optimization을 통해 latency를 감소시킨다.)
Sustainable Server-Side Scaling
Training and deploying large deep learning models is costly.
매우 큰 모델 학습 및 배포는 매우 비싼 가격을 내야한다.
While training could be a one-time cost(or could be free if one is using a pre-trained models), deploying and letting inference run for over a long period of time could still turn out to be expensiver in terms of consumption of server-side RAM, CPU, etc..
모델 학습에는 한번의 비용을 지불하면 되지만 배포와 추론의 경우 서버 측면의 RAM, CPU 등등과 같은 자원의 가격이 매우 비싸진다는데에 있다.
그 뒤 문장은 그리 중요하진 않은데, 데이터 센터에 수십억 달러를 소비하는 Google, Faceook, Amazon등과 같은 기업들의 탄소배출량을 보면 매우 걱정된다는 내용이다.
https://www.hani.co.kr/arti/society/environment/1174232.html
관심있으면 한번 보면 좋을듯?
Enabling On-Device Deployment
Certain deep learning applications need to run realtime on IoT and smart devices (where the model inference happens directly on the device), for a multitude of reasons (privacy, connectivity, responsiveness).
앞서 말했던 내용인데, 최근 trend는 AI application이다. 특히, 보안, 연결성, 응답과 같은 여러 요인들로 인해 realtime을 요구하는 IoT와 smart기기들이 AI appliction을 활용되어진다.
It becomes imperative to optimize the models for the target devices.
On-Device와 같은 target device들로 인해 optimize(최적화)는 필수적이라는 것.
Privacy & Data Sensitivity
Being able to use as little data as possible for training is critical when the user-data might be sensitive.
시간이 흐를수록 개인정보에 민감해지는데, 이를 위해선 적은 양의 데이터로도 학습을 할 수 있도록 만드는 것이 겁나게 중요하다는 뜻. 따라서 효율적인 학습 모델은 적은 양의 데이터로 학습된 모델을 의미하는 것이기도 하다.
근데 이건 최적화 기법보단 학습단의 방법론으로 보는게 맞지 않나 생각함.
New Applications
Certain new applications offer new constraints (around model quality of footpring) that existing off-the-shelf models might not be able to address.
Explosion of Models
While a singular model might work well, training and/or deploying multiple models on the same infrastructure (colocation) for difference applications might end up exhausting the available resoucres.
같은 서버에서 단일 모델을 정상적으로 동작하지만, 여러 모델을 학습시키거나 배포해야하는 상황에 놓여진다면 이용가능한 자원이 부족한 상황에 쳐해질 수 있다는 것이다.
위와 같은 상황은 첫번 째에서 말한 내용과 동치로 볼 수 있다.
1.1 Efficient Deep Learning
효율적인 딥러닝이라 함은 추론의 효율성을 말하는 걸까? 학습의 효율성을 말하는걸까? 저자는 일단 2가지로 효율성을 정의한다.
- Inference Efficiency
- Training Efficiency
Inference Efficiency라 함은 모델이 작고 빠름을 의미한다. 구체적으론 얼마나 많은 파라미터를 갖는지? 저장공간의 크기는 어느정도인지? RAM 메모리 점유율을 어느정도 인지? 추론 지연시간은 어느정도인지? 로 평가할 수 있다.
Training Efficeincy라 함은 학습하는데 얼마나 많은 시간이 걸리는지? 몇개의 GPU를 사용했는지, 메모리 사용량은 어느정도인지? 인데, 이는 결국 한가지의 질문으로 통합된다.
"해당 task를 성공적으로 수행하는데, 얼마나 많은 자원(resource)이 필요한가?"

As an example in Figure 2, the green dots represent pareto-optimal models, there none of the othrer models (red dots) get better accuracy with the same iference latency, or the other way around.
Optimization을 판단하는 것은 그리 어렵지 않다. 위의 Figure2를 보면 Pareto-Optimal Model이 Non Pareto-Optimal Model보다 Inference latency는 같지만 accuracy는 대폭 향상된 것을 볼 수 있으니깐 말이다.
따라서, 효율성이라는 것은 Pareto-frontier와 같은 모델을 발견하고 향상시키는 것으로 정의할 수 있다.
To achieve this goal, we propose turning towards a collection of algoithms, techniques, tools, and infrastructure that work together to allow users to train and deploy pareto-optimal models with respect to model quality and its footprint.
위의 목표를 달성하기 위해서는 다음과 같은 방법이 필요하다. pareto-optimal model(성능 좋은)과 같은 사용자에게 제공하기 위한 학습과 배포를 같이 동작시키는 알고리즘, 기술, 도구, 서버와 같은 각종 techniqual 이론들을 수집하였고 이를 제안하고자 한다.
2. A MENTAL MODEL
해당 section에서 저자는 1.1 section에서 설명한 내용을 보강하려 한다. Pareto-frontier과 같은 optimal한 model을 위해서는 MENTAL MODEL에 대한 정의와 내용을 정확히 아는 것이 중요하다고 말하는 section이다. (* MENTAL MODEL은 저자가 만든 optimal model을 위한 techiqual한 단어.)
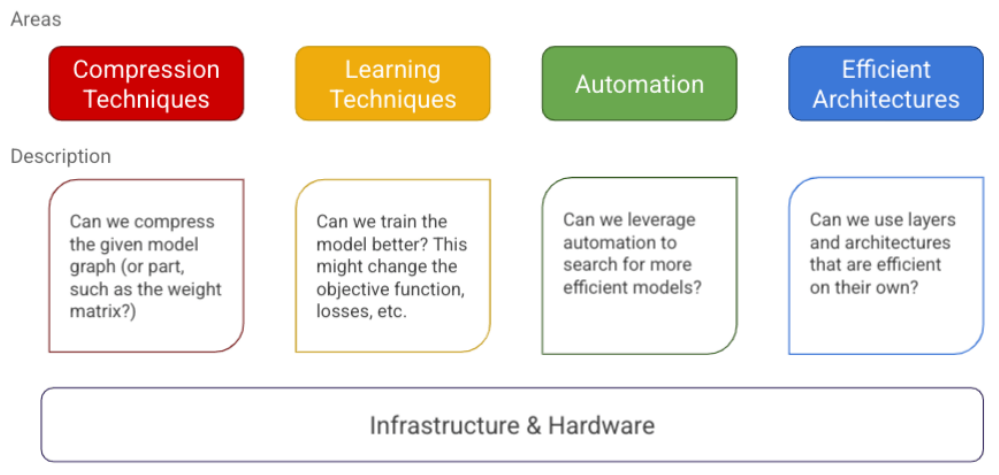
we present the mental model to think about the collection of algorithms, techniques, and tools related to efficient deep learning.
효율적인 DL과 관련된 알고리즘, 기술, 도구 모음에 대한 MENTAL MODEL을 제시한다.
We propse to structure them in five major areas, with the first four focused on modeling, and the final one around infrastructure and tools.
우리는 모델링(techiques)에 초점을 맞춘 4가지와 infrastructure과 tools을 위한 한가지를 종합한 5가지의 구조를 제안한다.
- Compression Techniques
These are general techniques and algorithms that look at optimizing the model's architecture, typically by compressing its layers.
- Compression Techniques
일반적인 방법으론 layer를 compression(압축)을 의미하는데, 저자는 Quantization을 대표적인 방법으로 꼽았다. 32bit floating-point로 학습하는 것을 8 bit INT로 학습하는 것을 의미한다.NPU환경에서는 부동소수점을 지원하지 않는 경우가 많다. 추론 환경에서 사용되는 환경이고 단순한 계산만 가능하다. (*d-dimension의 곱셈, 덧셈)
- Learning Techniques
These are algorithms which focus on training the model differently(to make fewer prediction errors, require less data, converage faster, etc..)
- Learning Techniques
Learning Techniques는 model을 다른 방식으로 학습하는데 초점을 맞춘 방식이다. 쉽게 말하자면 작은 것부터 조금씩 변경하는 것을 의미하는데, 이는 파라미터의 조정을 의미한다.
An example of a learning technique is distillation, which allows improving the accuracy of a smaller model by learning to mimic a larger model.
Learning technique의 한가지 예시에는 Distillation(증류)가 있는데, 이는 Knowledge Distillation으로 알려져 있는 유명한 Optimization 기법 중 하나이다. 짧게 설명하자면 큰 모델의 Weight의 Knowledge를 작은 모델에게 전이하는 방법인데, KD 방법도 여러가지가 있으므로 이는 추후에 KD를 다룰 때, 깊게 설명하고자 한다.
- Automation
These are tools for improving the core metrics of the given model using automation.
- Automation
모델에는 주요 지표들이 있다. classification에서는 Accuracy, Detection에서는 mAP등과 같은 metrics가 있는데, 이런 core metrics(핵심 지표)들을 향상시키는 자동화 기법이 필요하다는 것을 말한다.
이는 실제로 많은 모델들에게 적용되어 있는 기법이므로 AI application 적용만 하는 것이라면 크게 신경쓸 필요는 없다. (이미 Implementation이 되어 있으므로)
- Efficienct Architectures
These are fundamental blocks that were designed from scratch(convolutional layers, attention, etc.), that are a significant leap over the baseline methods used before them(fully connected layers, and RNNs respectively)
- Efficienct Architectures
처음부터 model을 설계할때, 어떤 관점으로 모델을 설계하는지도 중요하다. CNN의 경우에는 분리된 weight들을 공유하여 이미지 분류를 효과적으로 수행할 수 있도록 설계되었다. Seq2Seq 모델에서는 Inforamtion Bottleneck 문제를 해결하는 attention layers를 설계한 것처럼.
따라서, 효율성(optimization을 위한)을 얻기 위해서는 model architecutre도 세밀한 구현이 필요하다는 것을 의미한다.
- Infrastructure
We alse need a foundation of infrastructure and tools that help us build and leverage efficient models.
- Infrastructure
별거 없는 내용이긴 한데, efficient model을 설계하기 위해선 framework를 잘 사용해라? 라는 의미이다. (framework에는 Pytorch, Tensorflow 등등이 있다.)
3 LANDSCAPE OF EFFICIENT DEEP LEARNING
3.1 Compression Techniques
Compression techniques as mentioned earlier, are usually generic techniques for achieving a more efficient representation of one or more layers in a neural network, with a possible quality trade off.
앞서 언급했던 것처럼 Compression techniques(압축 기법)은 신경망에서 하나 혹은 그 이상의 layer를 효율적으로 표현하기 위한 일반적인 방법으로 품질이 저하될 수 있다.
The efficiency goal could be to optimize the model for one or more of the footprint mertrics, such as model size, inference latency, training time required for convergence, etc. in exchange for as little quality loss as possible.
효율성의 목표는 가능한 적은 품질 손실을 대가로 모델의 크기, 추론 지연 시간, 수렴에 요구되는 학습 시간 등등과 같은 footprint 지표들에 대해 모델을 최적화하는 것일 수 있다.
In some cases if the model is over-parameterized, these techniques can improve model generalization.
모델이 과하게 파라미터화되어 있다면, 이러한 기법들이 모델 일반화에 도움이 될 수 있다.
여기서 말하는 과-파라미터화라함은 문제 해결에 필요한 파라미터보다 더 많은 파라미터가 모델에 존재함을 의미한다.
예를 들어, A라는 데이터를 학습하는데, 1 billion의 parameter만 있으면 되는데, 학습 모델 크기가 큰 10 billion의 parameter로 학습하게 된다면 해당 모델은 train data에 fit이 되어버려 overfitting이 발생할 수 있다는 것이다. 이런 상황에 pruning 기법을 사용하면 좋다는 것을 의미한다.
3.1.1
Pruning. Given a neural network f(X, W), where X is the input and W is the set of parameters(or weights), pruning is a technique for coming up with a minimal subset W' such that the rest of the parameters of W are pruned(or set to 0), while unsuring that the quality of the model remains above the desired threshold.
프루닝에 대한 기본적인 개념에 대한 설명.
input은 X이고 파라미터(가중치) W로 구성된 신경망 F(X,W)가 주어졌을때, 모델의 품질을 요구하는 임계값 이상을 유지하면서 W에 속한 나머지 파라미터(가중치)를 제거(가지치기)또는 0으로 만들면서 W`이라는 최소 부분집합을 찾는 기법.
After pruning, we can say the network has been made sparse, where the sparsity can be quntified as the ratio of the number of parameters that were pruned to the number of parameters in the original network.
프루닝 이후에, 네트워크는 sparse(희소) 상태라고 부르는데, 이 희소성은 원본 신경망의 파라미
터의 수에서 pruning된 파라미터의 수로 나눈 비율로 정량화할 수 있다.
The higher the sparsity, the lesser the number of non-zero parameters in the pruned networks.
희소성이 높을수록, 프루닝된 네트워크에서 non-zero parameters의 수가 적다는 것을 의미한다.
이는 실제로 중요한 기법이다.
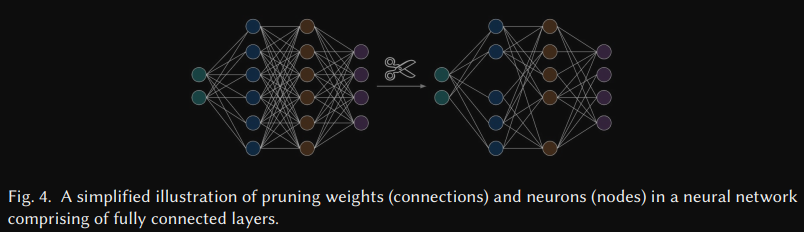
어찌보면 pruning과 dropout이 같은 역할을 하는 것처럼 보이지만 작동 방식과 적용 시점이 다르다.
Dropout은 학습 중에 일부 뉴런을 비활성화하는 방식이고 학습이 완료되면 모든 뉴런이 활성화된다. 이는 일반화 능력을 향상시키기 위한 기법 중 하나이다.
pruning은 학습이 완료된 후에 모델의 성능에 큰 영향을 주지 않는 파라미터들을 영구적으로 제거한다. 이렇게 제거된 파라미터들은 0이 되거나 완전히 삭제되어, 모델의 구조가 단순해지고 계산량이 줄어든다.
즉, Dropout은 정규화 기법이고 Pruning은 경량화 기법이다.
These methods usually take a network that has been pre-trained to a reasonable quality and then iteratively prune the parameters which have the lowest 'saliency' score, such that the impact on the validation loss is minimized.
이런 방법들은 어느정도 성능이 나오는 사전 학습된 네트워크에 사용되고 validation loss에 미치는 영향을 최소화하기 위해 매우 작은 saliency 점수를 갖는 파라미터들을 반복적으로 제거한다.
Once pruning concludes, the network is fine-tuned with the remaining parameters.
pruning이 끝난 뒤에는, 남은 파라미터를 사용하여 네트워크를 fine-tuned한다.

원본 파라미터 중 원하는 수가 제거될 때까지 Algorithm 1을 반복한다.
OBD approximates the saliency score by using a second-derivative of the parameters, where L is the loss function, and wi is the candidate parameter for removal.
OBD는 L은 loss function이고 wi는 제거될 파라미터들의 후보로 구성된 parameter들을 이차미분을 사용하여 saliency 점수를 근사한다.
The intuition is that the higher this value for a given parameter, the larger the change in the loss function's gradient if it wre to be pruned.
직관적으로 해당 파라미터의 값이 높을수록, pruned했을 때 loss function의 gradient가 크게 변한다는 의미를 갖는다.
***계속 추가할 예정.
