1. Numpy(넘파이)?
Numerical Python의 약자로 파이썬의 고성능 과학 계산용 패키지이다.
Matrix와 Vector와 같은 Array 연산의 사실상의 표준이다.
데이터 수식을 표현
- Numpy 특징
일반 List에 비해 빠르고 메모리 효율적
반복문 없이 데이터 배열에 대한 처리 지원
선형대수와 관련된 다양한 기능 제공
C, C++ 등의 언어와 통합 가능
2. ndarray
-
import
numpy의 호출 방법import numpy as np -
Array creation
데이터 타입을 알아보기 위한 type(), dtypetest_array = np.array([1,4,5,8],float) print(test_array) type(test_array[3]) # value: numpy.float64 test_array.dtype # value: dtype('float64') test_array.shape # value: (4,)shape : numpy array의 object의 dimennsion 구성을 반환
dtype : numpy array의 데이터 type 반환 -
Array shape
Array(vector, matrix, tensor)의 크기, 형태 등에 대한 정보
1) vectortest_array = np.array([1,4,5,"8"],float) print(test_array) # value: array([1., 4., 5., 8.])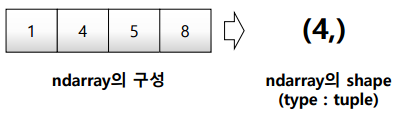 2) matrix
2) matrixmatrix = [[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]] np.array(matrix,int).shape # value: (3, 4)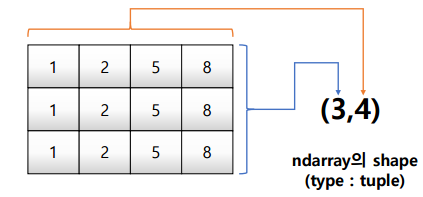 3) 3rd order tensor
3) 3rd order tensor
이미지 처리에 사용
젤 앞에 있는 것이 tensor의 깊이
row가 맨 뒤로 밀려진다.tensor = [[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]], [[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]], [[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]], [[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]]] np.array(tensor, int).shape # value: (4,3,4)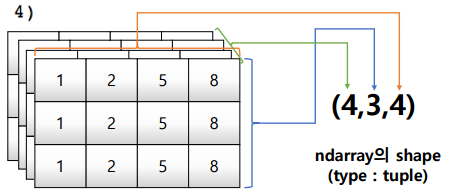 4) ndim & size
4) ndim & size
ndim : number of dimension = 텐서의 크기 = attribute와 유사
size : data의 개수tensor = [[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]], [[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]], [[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]], [[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]]] np.array(tensor, int).ndim # value: 3 np.array(tensor, int).size # value: 48
3. Handling shape
-
reshape
dimension이 다차원일 때 vector형태로 펴야 하는 경우 사용
number of data의 개수만 맞추면 된다.
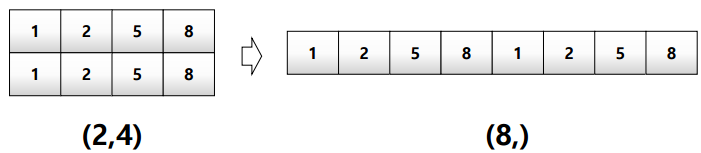
test_matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[1,2,5,8]] np.array(test_matrix).shape # value: (2, 4) np.array(test_matrix).reshape(8,) # value: ([1,,2,3,4,1,2,5,8])Array의 size만 같다면 다차원으로 자유로이 변형가능하다.
np.array(test_matrix).reshape(2,4).shape # value: (2, 4) np.array(test_matrix).reshape(-1,2).shape # value: (4, 2) # -1: size를 기반으로 row 개수 선정 -
flatten
다차원 array를 1차원 array로 변환test_matrix = [[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]]] np.array(test_matrix).flatten() # value: array([1,2,3,4,1,2,5,8,1,2,3,4,1,2,5,8])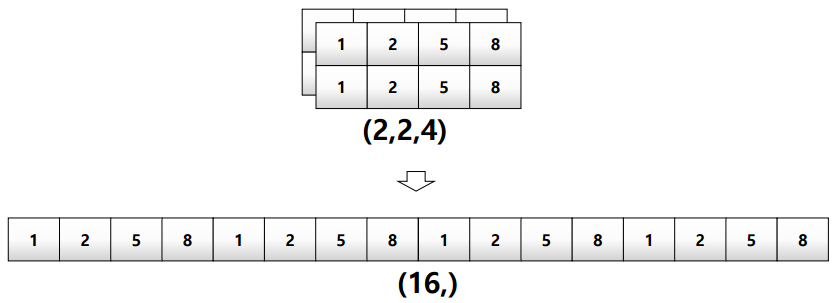
4. Indexing & slicing
-
indexing
print(a[0,0]) = print(a[0][0]) 같은 결과가 나온다. -
slicing
for문 사용하지 않고 원하는 부분을 추출 가능
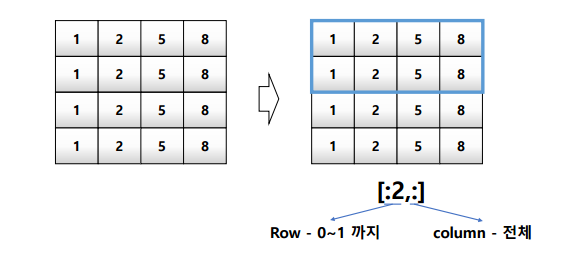
a[:, 2:] : row는 전체, column은 2열 이상
a[1,1:3] : row는 1행, column은 1~2열까지
5. Creation Function
-
arange
array의 범위를 지정하여 값의 list를 생성np.arrange(30) # value: array([0,1,2,3, ..., 27,28,29)] -
ones, zeros
1) zeros(0)으로 가득찬 ndarray 생성np.zeros(shape=10,), dtype=np.int8) # value: array([0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,], dtype=int8) # 10-zero vector 생성2) ones(1)로 가득찬 ndarray 생성
np.ones((2,5)) # value: array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.], # [1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,]]) -
identity
단위 행렬(i 행렬)을 생성함np.identity(n=3, dtype=np.int8) # value: array([[1,0,0], # [0,1,0], # [0,0,1]], dtype=int8)
6. operation fnctions
-
sum
ndarray의 element들 간의 합test_array = np.range(11) test_array.sum(dtype=np.float) # value: 55.0 -
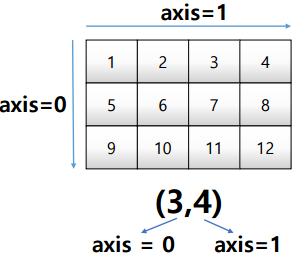
axis
모든 operation function을 실행할 때 기준이 되는 dimension 축
test_array = np.arrange(1,13).reshape(3,4) print(test_array) # value: ([[1,2,3,4], # [5,6,7,8], # [9,10,11,12]]) test_array.sum(axis=1), test_array.sum(axis=0) # value: (array([10,26,42]), array([15,18,21,24]))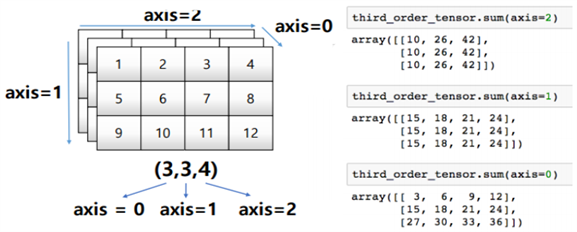
-
concatenate
Numpy array를 합치는 함수
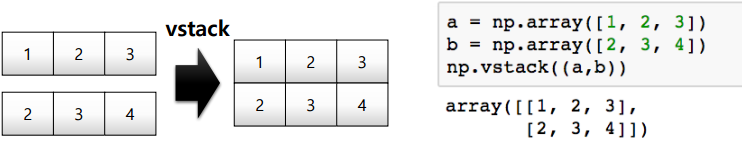
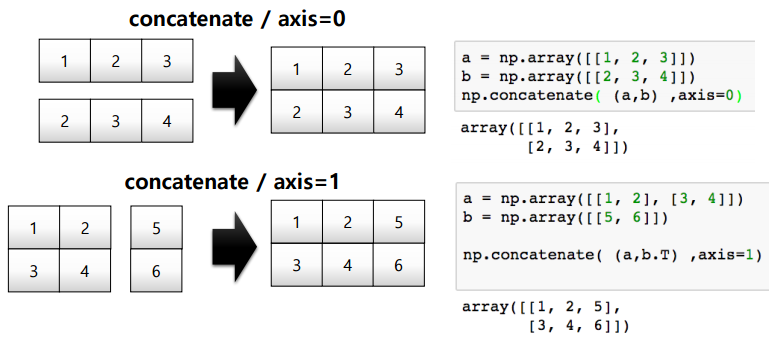
7. array operations
Numpy는 array간 기본적인 사칙 연산을 지원
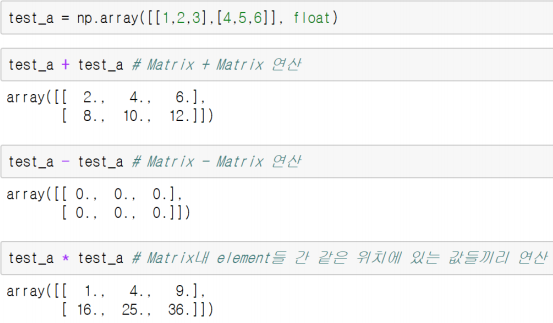 같은 위치에 있는 element끼리 연산.
같은 위치에 있는 element끼리 연산.
-
transpose
test_a = np.arange(1,7).reshape(2,3) print(test_a) # value: array([[1,2,3], # [4,5,6]]) -
broadcasting
shape이 다른 배열 간 연산을 지원하는 기능
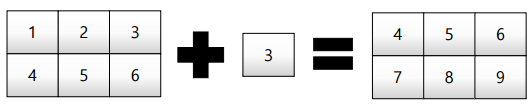
test_matrix = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],float) scalar = 3 test_matrix + scalar # Matrix - Scalar 덧셈 # vallue: array([[4., 5., 6., # 7., 8., 9]])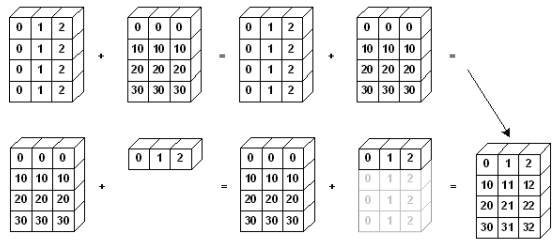 vector-matrix 간의 연산도 지원
vector-matrix 간의 연산도 지원
8. Comparison
-
All & Any
Array의 데이터 전부(and) 또는 일부(or)가 조건에 만족 여부를 반환a = np.arange(10) np.any(a>5), np.any(a<0) # value: (True, False) np.all(a>5), np.all(a<10) # value: (False, True) -
np.where
a = np.array([1,3,0], float) np.where(a>0, 3, 2) # value: array([3,3,2])✔ a>0이 true이면 앞에 3반환, false이면 뒤에 2반환
a=np.arange(10) np.where(a>5) # value: array([6,7,8,9]),) -
argmax& argmin
최대값 최소값 찾을때 많이 사용
최대값 최소값의 index가 반환된다.a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]) np.argmax(a), np.argmin(a) #value: (8, 0)
9. boolean & fancy index
-
boolean index
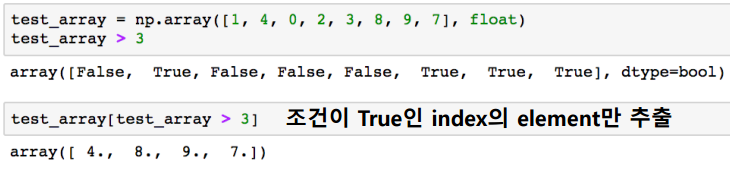
-
fancy index
numpy는 array를 index value로 사용해서 값을 추출a = np.array([2,4,6,8],float) b = np.array([0,0,1,3,2,1], int) print(a.take(b)) #value : array([2., 2., 4., 8., 6., 4.]) # a[b] = a.take(b)a : array의 element
b : array의 index
