1. Image
- 특정 시간, 특정 방향의 빛의 Snapshot (시각적 자극을 비슷하게 나타냄)
- 사진이나 2차원 그림처럼 시각적 자극을 속이기 위해 만든 인공물
- Distributed amplitude of colors
- 2D function
- 시각적 자극의 강도(intensity / amplitude)를 나타내는 함수f(x, y)
- (x, y)는 2D 위치
2. Digital Image
- 이미지가 디지털 형태로 저장됨 (digital form / binary form)
- Digitization (이미지를 디지털로 바꾸는 방법)
1. Raster(Bitmapped) Image
- Finite set of digital values (Picture elements / pixels)
- JPEG, PNG, GIF …
2. Vector Image
- 2D 평면에 어떻게 그림을 그릴 것인지에 대한 방법이 저장 (lines, polygons, circles, curves…)
- Vecotor font, SVG, AI …
- 디지털 이미지의 장단점
- 장점
- Easy reproduction (그리기 쉬움)
- Fine detail (정보 디테일 많음)
- Easy to access a part
- Easy to modify globally (전체 수정 쉬움)
- 단점
- Large data
- Limited resolution (Bad for scaling)
- Hard to modify locally
3. Invisible Light Imaging
- Electromagnetic energy spectrum
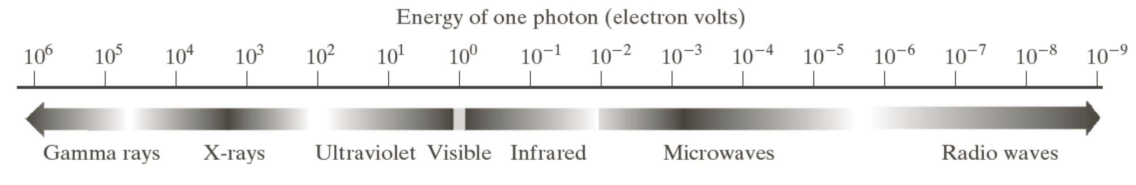
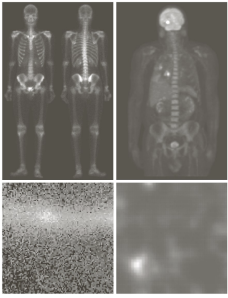
- Gamma-Ray
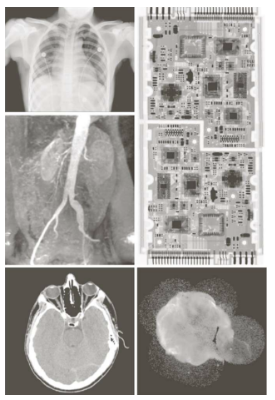
- X-Ray
- Ultra-violet band (자외선)
- Visible + Infrared band (가시광선 + 적외선)

- Microwave band

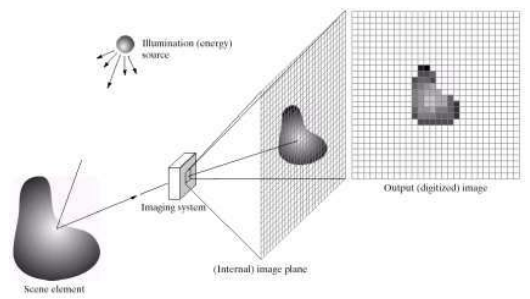
4. Digital Image Processing
- 사람이 해석할 수 있도록 이미지 정보를 개선
- 저장, 전송, 자율 시스템 인식을 위한 표현
- Fundamental Levels (Low level - 영처 / Mid, High level - 컴비)

- Key Stages in DIP
- Image Acputstion (이미지 입력)
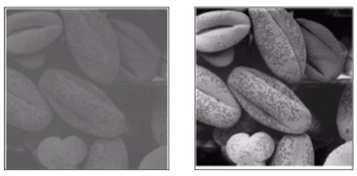
- Image Enhancement (이미지 향상) - 저화질을 고화질로
- Image Restoration (이미지 복원)

- Morphological Precessing

- Segmentation (영상 분할) - 이미지 내에 있는 객체들을 의미있는 단위로 분할
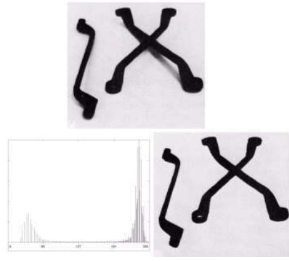
- Object Recognition (객체 인식)
- Representation & Description