Library Interpositioning
Interposition은 '중간에 끼워넣음'이라는 의미로, Intercept와 유사한 뉘앙스라고 생각하면 된다.
Library Interpositioning : 임의의 Function에 대한 호출을 프로그래머가 Intercept할 수 있는 Linking Technique
Compile / Link / Load / Run Time에 수행할 수 있다.
-
Compile Time : Source Code가 컴파일될 때 Interpositioning을 할 수 있다.
-
Link Time : Relocatable Object File이 Static하게 Link되어 Executable Object File이 될 때 Interpositioning을 할 수 있다.
-
Load / Run Time : Executable Object File이 Memory에 올라가고 Dynamic하게 Link되며 Execute될 때 Interpositioning을 할 수 있다.
-
Interpositioning의 용도 : 보안, 디버깅, 모니터링, 프로파일링 등을 위해 Interpositioning을 할 수 있다.
-
보안 : Sandboxing, 부호화(Encryption)에 사용할 수 있다.
-
디버깅 : 기존 라이브러리 함수에 특정 코드를 추가해 디버깅할 수 있다.
-
모니터링 & 프로파일링 : 함수가 몇 번 호출되었는지, 호출된 영역과 Argument들은 무엇인지 등을 확인할 때 사용할 수 있다.
- malloc Tracing이 대표적이다.
- malloc의 호출 상황을 Tracing하는 것이다. 메모리 누수를 감지하고, 할당 주소를 확인하는 용도로 말이다. ★
- malloc Tracing이 대표적이다.
-
Interpositioning의 용도 : 기존 Library Function의 Code에 간단한 추가 코드를 입혀 자신의 목적을 달성할 수 있다. ★
Simple Example
프로그램을 분해하거나 Source Code를 변화시키지 않는 선에서 Dynamic하게 Allocate되고 Free되는 Block들의 사이즈와 주소를 Tracing해보는 간단한 프로그램이다.
/* Main Program */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
int main(void) {
int *p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
free(p);
return(0);
}~> 위의 코드는 아주 간단한 동적할당 프로그램이다. 이 프로그램에 세 가지 방식으로 Interpositioning을 적용해보자.
Compile-Time
Compile Time에 malloc과 free 함수를 User-defined Functions로 대체해, malloc과 free의 동작 상태를 Tracing한다.
이때, malloc과 free 함수 자체의 Source Code에는 아무런 변화가 없다. ★
// 아래 코드를 mymalloc.c File 내부에 설치한다. ★★★
#ifdef COMPILETIME
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
/* malloc에 대한 Wrapper Function */
void *mymalloc(size_t size) { // 내가 짠 코드. 기존 malloc의 Wrapper로 사용!
void *ptr = malloc(size); // mymalloc 내부에서 '찐 malloc'을 호출한다.
printf("malloc(%d)=%p\n", (int)size, ptr); // 할당 Size를 Tracing한다.
return ptr;
}
/* free에 대한 Wrapper Function */
void myfree(void *ptr) {
free(ptr); // myfree 내부에서 '찐 free'를 호출한다.
printf("free(%p)\n", ptr); // 역시나 Tracing!
}
#endif
// 위 코드를 mymalloc.c File 내부에 설치한다. ★★★
// 아래 코드를 기존 malloc.h File 내부에 설치한다. ★★★
#define malloc(size) mymalloc(size)
#define free(ptr) myfree(ptr)
void *mymalloc(size_t size); // Prototyping
void myfree(void *ptr);
// 위 코드를 기존 malloc.h File 내부에 설치한다. ★★★위와 같이 새로운 소스 코드 파일 mymalloc.c와 기존 malloc.h 파일에 추가 코드를 설치한 후, Linux Shell에서 아래와 같이 명령을 입력해보자.
linux> make exp_c
gcc -Wall -DCOMPILETIME -c mymalloc.c
gcc -Wall -l. -o example example.c mymalloc.o
linux> make run_c
./example
malloc(32)=0x1edc010
free(0x12edc010)
linux>
~> malloc과 free의 진행 상황(할당 주소와 사이즈)을 Tracing할 수 있게 되었다.
- Compile Time Library Interpositioning의 특징
- malloc/free에 대한 호출을 mymalloc/myfree로 '사실상 Macro-Expansion'하는 것이다. 즉, 코드가 복붙되는 것이다. ★★
Link-Time
Link Time에 malloc과 free 함수를 User-defined Functions로 대체해, malloc과 free의 동작 상태를 Tracing한다.
이때, malloc과 free 함수 자체의 Source Code에는 아무런 변화가 없다. ★
// 아래 코드를 mymalloc.c File 내부에 설치한다. ★★★
#ifdef LINKTIME
#include <stdio.h>
void *__real_malloc(size_t size);
void __real_free(void *ptr);
/* malloc에 대한 Wrapper Function */
void *__wrap_malloc(size_t size) {
void *ptr = __real_malloc(size); // '찐 malloc'을 호출한다.
printf("malloc(%d) = %p\n", (int)size, ptr);
return ptr;
}
/* free에 대한 Wrapper Function */
void __wrap_free(void *ptr) {
__real_free(ptr); // '찐 free'를 호출한다.
printf("free(%p)\n", ptr);
}
#endif
// 위 코드를 mymalloc.c File 내부에 설치한다. ★★★
// Link Time의 경우, malloc.h는 수정할 필요가 없다. ★★★★★위와 같이 새로운 소스 코드 파일 mymalloc.c 파일에 위 코드를 설치한 후, Linux Shell에서 아래와 같이 명령을 입력해보자.
linux> make exp_l
gcc -Wall -DLINKTIME -c mymalloc.c
gcc -Wall -c example.c
gcc -Wall -Wl,--wrap,malloc -Wl,--wrap,free -o example example.o mymalloc.o
linux> make run_l
./example
malloc(32)=0x1edc010
free(0x12edc010)
linux>
-
'-Wl' Flag는 Linker에 Argument를 넘기는 역할을 수행한다. ★
- '-Wl' 뒤에 오는 ','를 공백으로 대체한다.
-
'--wrap,malloc' Argument는 Linker가 Reference를 특수하게 Resolve하도록 이끈다.
- 'malloc'에 대한 Reference를 '__wrap_malloc'으로 대체한다. ★
- '__real_malloc'에 대한 Reference는 'malloc'으로 대체한다. ★
Compile Time Interpositioning과 Link Time Interpositioning의 차이가 보이는가? Compile Time은 Intercept를 위한 .c를 만들고, Intercept 대상의 기존 .h 코드에 수정을 가해야하는 반면, Link Time은 Intercept를 위한 .c 코드만 만들면 된다. ★★★
- Link Time Library Interpositioning의 특징
- Linker를 사용해 malloc을 __wrap_malloc으로 대체
- Linker를 사용해 __real_malloc을 malloc으로 대체
Load / Run-Time
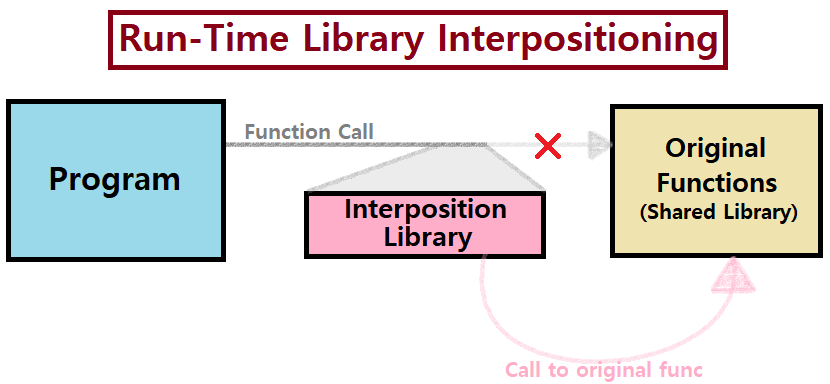
Load / Run Time에 malloc과 free 함수를 User-defined Functions로 대체해, malloc과 free의 동작 상태를 Tracing한다.
이때, malloc과 free 함수 자체의 Source Code에는 아무런 변화가 없다. ★
// 아래 코드를 mymalloc.c File 내부에 설치한다. ★★★
#ifdef RUNTIME
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
/* malloc에 대한 Wrapper Function */
void *malloc(size_t size) { // 기존 함수명과 동일명으로 작성(필수는x)
void *(*mallocp)(size_t size);
char *error;
// libc malloc 함수 코드에 대한 포인터를 dlsym을 통해 받아온다. ★★★
mallocp = dlsym(RTLD_NEXT, "malloc");
if ((error = dlerror()) != NULL)
unix_error(error);
char *ptr = mallocp(size); // '찐 malloc'을 호출한다.
printf("malloc(%d) = %p\n", (int)size, ptr); // Tracing
return ptr;
}
/* free에 대한 Wrapper Function */
void free(void *ptr) {
void (*freep)(void *) = NULL;
char *error;
if (!ptr) return;
freep = dlsym(RTLD_NEXT, "free"); // Get address of libc free ★
if ((error = dlerror()) != NULL)
unix_error(error);
freep(ptr); // '찐 free'를 호출한다.
printf("free(%p)\n", ptr);
}
#endif
// 아래 코드를 mymalloc.c File 내부에 설치한다. ★★★~> 위 코드는 동적으로 Interpositioning을 수행한다.
위와 같이 새로운 소스 코드 파일 mymalloc.c 파일에 위 코드를 설치한 후, Linux Shell에서 아래와 같이 명령을 입력해보자.
linux> make exp_r
gcc -Wall -DRUNTIME -shared -fpic -o mymalloc.so mymalloc.c -ldl
gcc -Wall -o example example.c
linux> make run_r
(LD_PRELOAD="./mymalloc.so" ./example)
malloc(32)=0x1edc010
free(0x12edc010)
linux>
- LD_PRELOAD Environment Variable : 환경 변수로, Dynamic Linker에게 Unresolved Reference를 mymalloc.so에서 먼저 찾아보라고 요청하는 기능을 수행한다. ★★
- '동적으로 Run하는 그 순간에!'
- Load/Run Time Library Interpositioning의 특징
- 따로 컴파일할 필요 없이, 동적으로 malloc을 '내 함수'로 Intercept한다. ★
※ 일반적으로 Compile Time과 Load/Run Time Library Interpositioning이 자주 사용된다. 그리고, 이러한 Interpositioning은 앞으로 어떤 프로젝트를 수행하던 간에 함수 추적에 아주 큰 도움이 될 것이다. 잘 기억하도록 하자.
Linking은 여기까지이다. 이제 남은 Chapter는 Virtual Memory에 대한 내용으로, 이번 System Programming 연재의 마지막 개념이 될 것이다. 정말 많은 길을 달려왔다. 조금 더 힘을 내보자!
